1. Cell Ultrastructure and Microscopes
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What is a cell?
The basic units of all life
→ All things are made of cells
What is a tissue?
A group of different specialist tissues, which work together to carry out multiple functions
What is an organ?
A group of specialist organs, which work together to carry out multiple functions
What is organ system?
Group of similar cells that work together for a particular function
What do eukaryotic cells have that prokaryotic cells don’t have?
nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
What is the function of a plasmid? (prokaryotic)
Double stranded circular ring of DNA that contains additional genes (e.g. for antibiotic resistance)
What is the function of circular DNA? (prokaryotic)
Coiled single strand of genetic material (DNA)
What is the function of a ribosome? (prokaryotic)
Small organelles found in the cytoplasm where proteins are synthesised (site of translation).
What is the function of a lipid granule? (prokaryotic)
stores of food
What is the function of mesosome? (prokaryotic)
Infolding of the cell membrane where respiration takes place.
Highly folded to increase the surface area to maximise the rate of respiration.
What is the function of flagellum? (prokaryotic)
Whip/tail like structure used to propel the bacterium through liquid.
What is the function of the cell wall? (prokaryotic)
Used to support the prokaryotic cell and prevent it bursting.
What is the function of the cell surface membrane? (prokaryotic)
Holds the cell together and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell
What is the function of the cytoplasm? (prokaryotic)
Watery fluid substance where chemical reactions take place
What is the function of the pili? (prokaryotic)
Used for the transfer of genetic material during sexual reproduction
What is the function of the capsule? (prokaryotic)
Protective outer covering from environmental dangers e.g. antibiotics, lysozyme
Deduce how genetic material is stored as?
stored in the form of free circular DNA
How is genetic material stored in eukaryotes?
Store genetic information as DNA found within the nucleus
How do prokaryotes respire if they don’t have mitochondria?
Mesosome
→ enzymes for respiration
Label structure of prokaryotic cell:
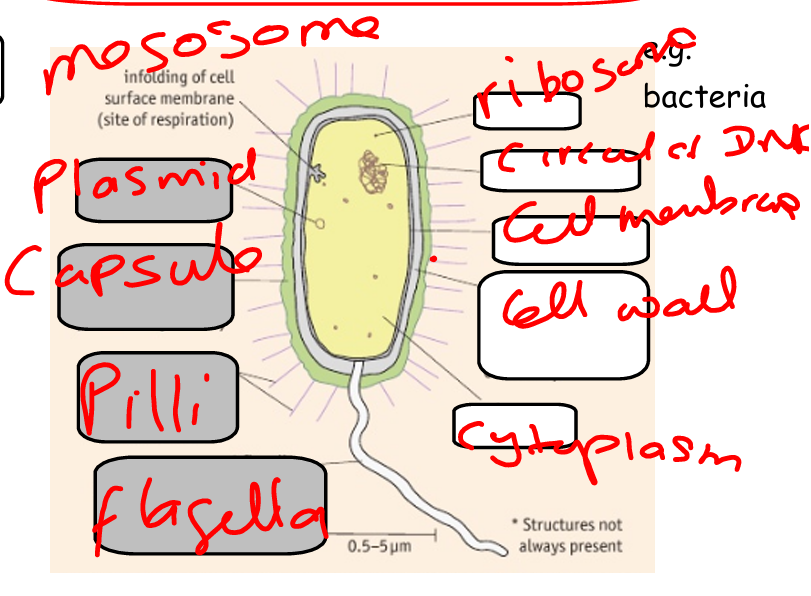
Suggest why the mesosome is highly infolded:
Increases the surface area
to maximise the rate of respiration
to provide energy for the movement of the flagella
Labelled structure of animal cells (eukaryotic):
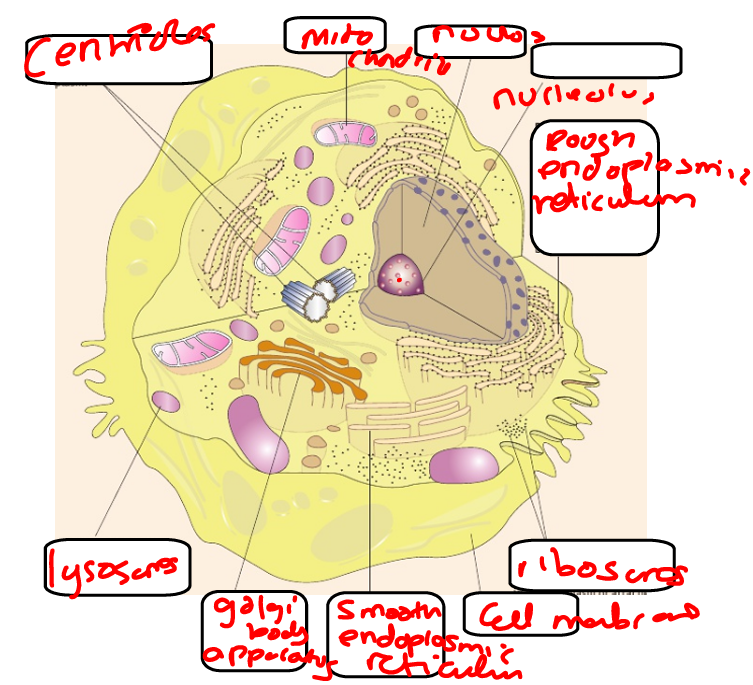
What is the function of the nucleus? animal cell
Membrane bound organelle that contains the genetic material of the cell
What is the function of the ribosome? animal cell
Site of translation.
- May be free or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the function of mitochondria? animal cell
Site of respiration (energy release)
What is the function of centrioles? animal cell
Control the spindle fibres which are required in cell division
What is the function of rough endoplasmic reticulum? animal cell
Involved in the production and transport of proteins through the cell
What is the function of golgi apparatus? animal cell
Involved in the transport and modification of proteins through the cell
What is the function of lysosome? animal cell
Contains digestive enzymes that breakdown defunct organelles, food particles or pathogens
What is the function of cell surface membrane? animal cell
Controls what enters and leaves the cell.
What is the function of nucleolus? animal cell
Darkly stained region of the nucleus
- Where ribosomes are synthesised
What is the function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum? animal cell
Involved in the production and transport of lipids throughout the cell
What is the function of the cytoplasm? animal cell
Site of translation and other chemical reactions of metabolism
Label the structure of plant cells (eukaryotic):
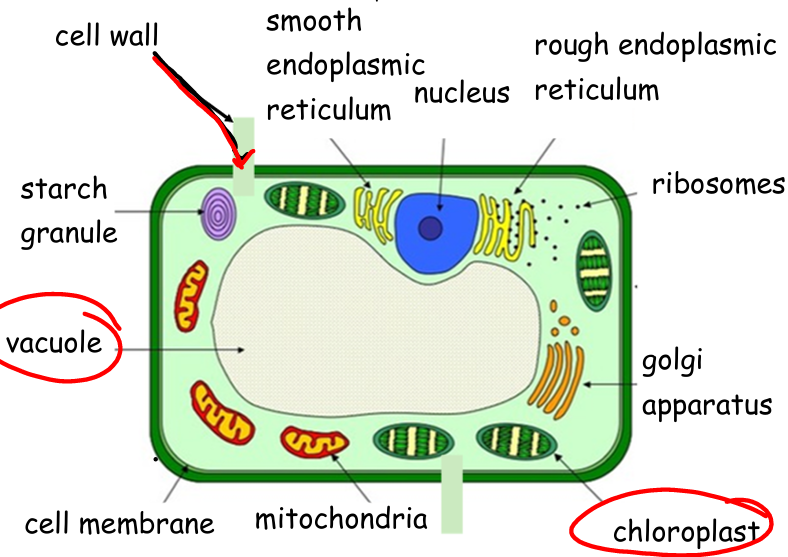
What is the function of the chloroplast?
Site of photosynthesis the reaction that creates glucose for the plant cell
What is the function of the cell wall?
Contains cellulose to provides structural support for the plant cell
What is the function of the vacuole?
Stores cell sap (water and sugars) to keep the cell turgid
What is the function of the starch granule?
Where starch is stored
COMPARING PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC SUMMARY TABLE:
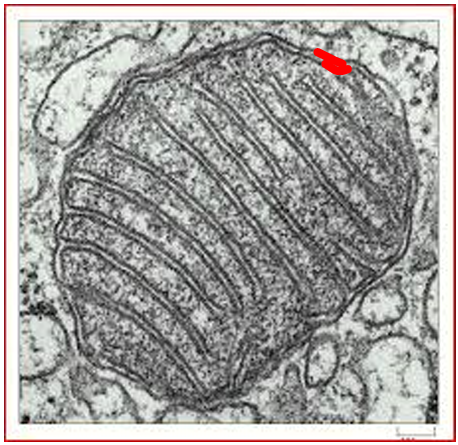
What organelle is this?
Mitochondria
double outer membrane
folded inner membrane
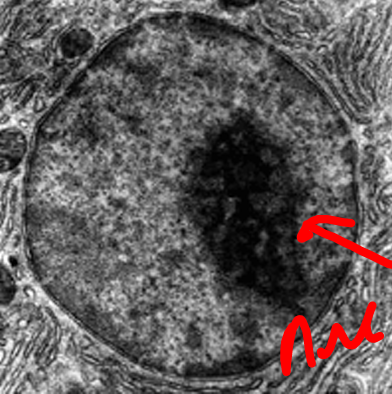
What organelle is this?
Nucleus and nucleolus
Large organelle
Double membrane/envelope with pores
Nucleolus stains darker
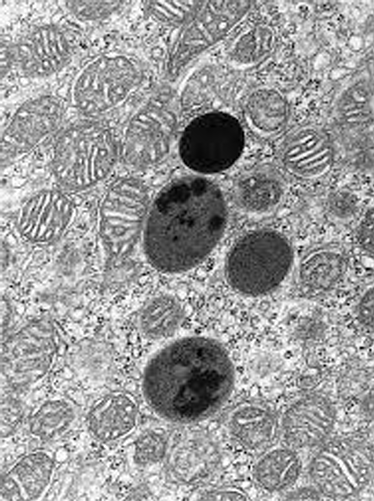
What organelle is this?
Lysosome
single smooth membrane
Dark stain
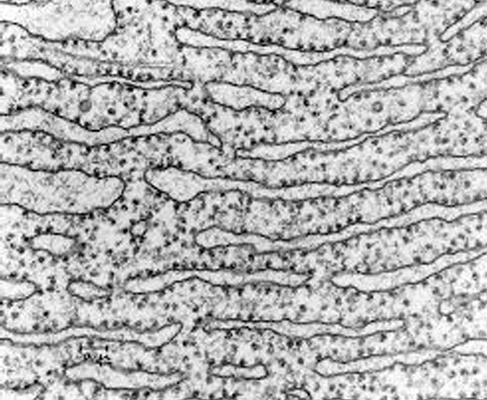
What organelle is this?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
many parallel sacs with ribosomes
→ (smooth would have no ribosomes)
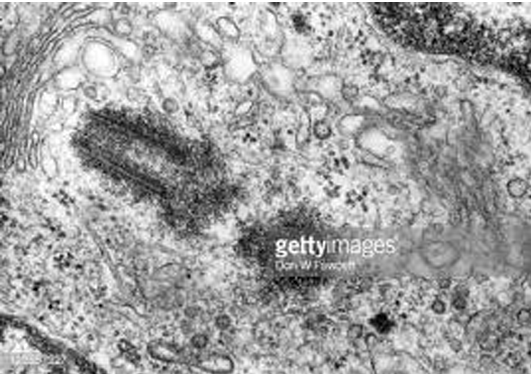
What organelle is this?
Centrioles
Always in pairs with one at right angles to the other
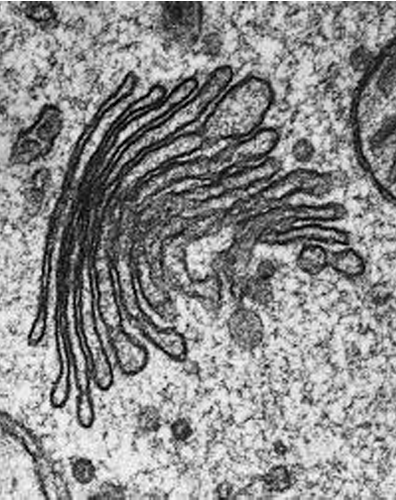
What organelle is this?
Golgi body apparatus
banana shaped sacs stacked parallel to each other
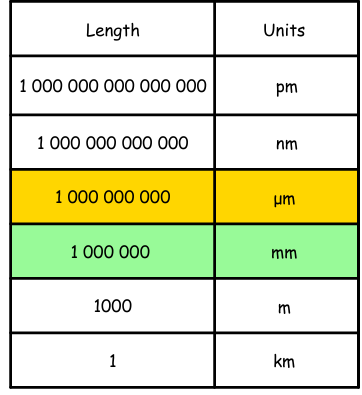
SI UNITS:
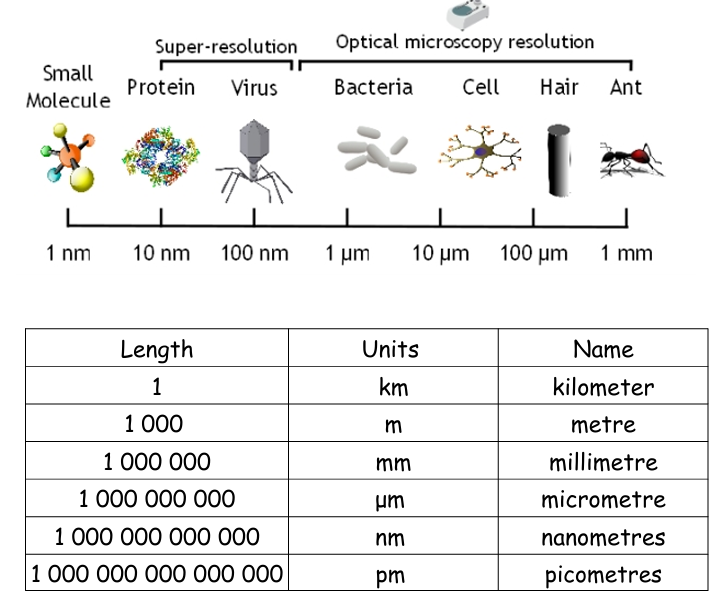
UNITS OF MEASUREMENT: