Ch.4 The Molecule of Life
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Amino acids not included
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Macromolecules
large and usually polymers
All but lipids are polymers
Dehydration
removes a water molecule forming a new bond
Hydrolysis
adds a water molecule breaking a bond
Carbohydrates
serves as fuel and building material
monosaccharides (single sugar)
disaccharides (two)
polysaccharides (long chain)
Glucose (C6H12O6)
most common monosaccharide
monosaccharide
classified by location of carbonyl group + # of C in carbon skeleton
Trioses
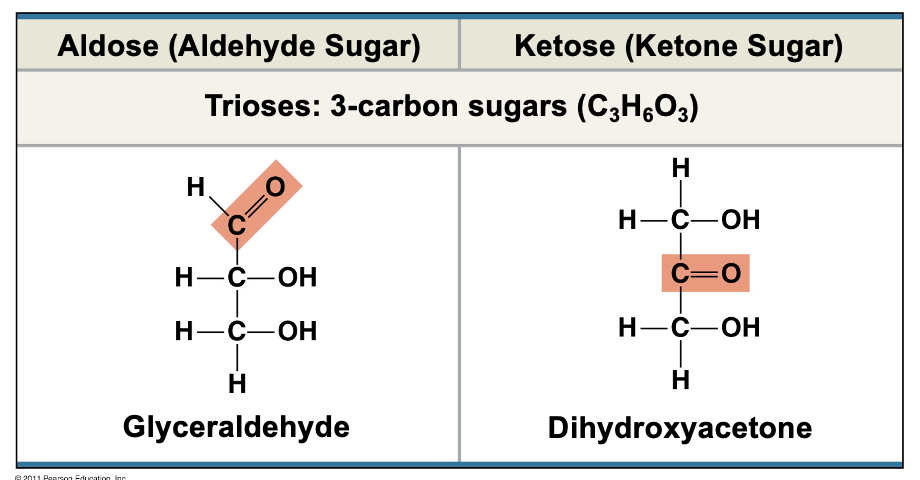
3 carbon sugars (C3H6O3)
Pentoses
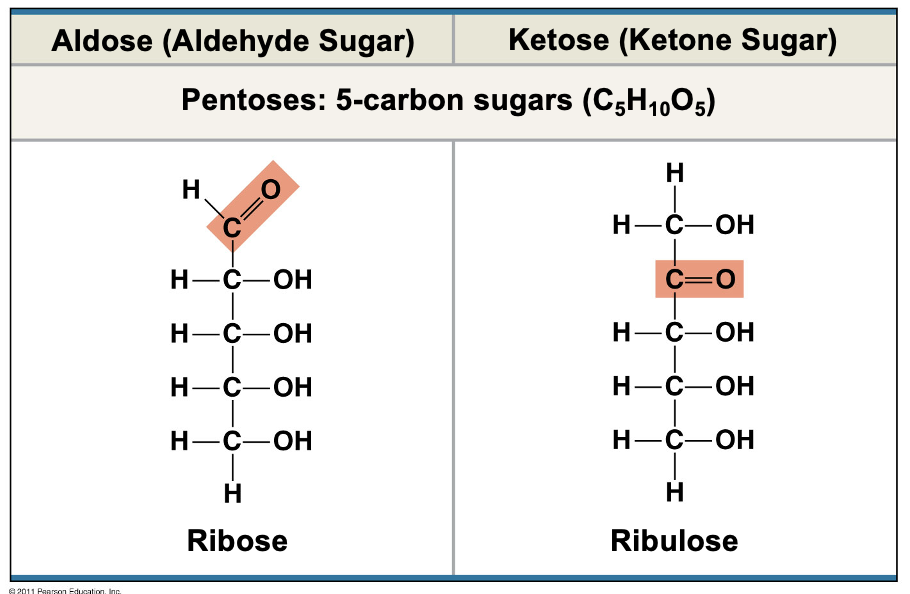
5 carbon sugars (C5H10O5)
Ribose
Hexoses
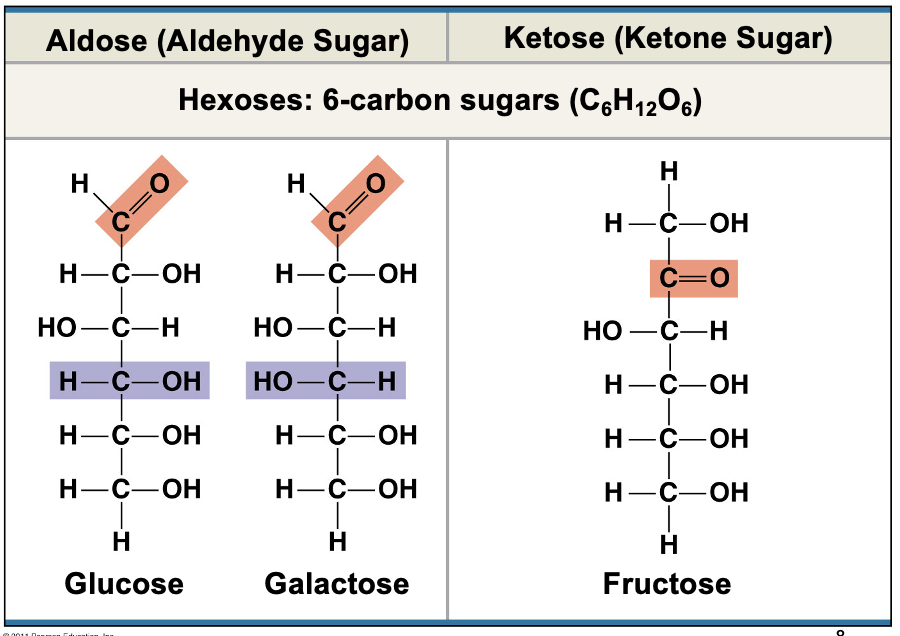
6 carbon sugars (C6H12O6)
Glucose + Fructose
Disaccharide
formed when a dehydration reaction joins 2 monosaccharides
Covalent bond called glycosidic bond
Starch
“storage polysacharide”
plants, consists entirely of glucose membrane
amylose
Glycogen
“storage polysacharide”
animals, humans + other vertebrates store mainly in liver and muscle cells
Cellulose
“structural polysacharide”
major component of the tough wall of plant cells
differ in glycosidic linkages
Alpha (α) vs Beta (β) rings
Alpha- below
Beta- above
Enzymes that digest starch by hydrolyzing α linkages cant hydrolyze β linkages in cellulose
Chitin
“structural polysacharide”
found in exoskeleton of arthropods and the cell walls of many fungi
Polymer of N-acetylglucosamine
Lipids
DO NOT FORM POLYMERS
Little or no affinity for water (hydrophobic)
fats, phospholipids, steroids
Fats
3 fatty acids joined to glycerol by an ester linkage, creating a triacylglyercol
main function energy storage
very in length + location of double bonds
Saturated fatty acids
max # of H atoms + no double bonds
Unsaturated fatty acids
one or more double bonds
Hydrogenation
process of adding H
creates unsat. fats with trans double bonds = cardiovascular disease
Phospholipids
2 fatty acids (hydrophobic) + a phosphate group (hydrophilic head) are attached to glycerol
Steroids
lipids characterized by a C-skeleton consisting of 4 fused rings
Cholesterol
Proteins (8)
“account for more than 50% of dry mass of cells”
Enzymes
Defense (immune)
Storage (egg albumin)
Transport (hemoglobin)
Structural (collagen)
Motor (myosin)
Receptor (serration)
Hormonal (insulin)
Amino Acids
have carboxyl + amino groups
“R groups” distinguish them
linked by peptide bonds
Polypeptide
polymer of amino acids
2 to 1000 amino acids with unique sequence
Shapes of protein (3)
Ribbon
Space-filling
Wire-frame
lvls or proteins (4)
Primary- sequence of amino acids
Secondary- stabilize by H-bonds between (α helix + β pleated sheet)
Tertiary- how α helix + β pleated sheet come together (disulfide bridge)
Quarternary- polypetide subunit form 1 macromolecule
Denaturation vs Renaturation
unfolding vs folding of protein
Deoxyribonucleic (DNA)
“nucleic acid”
info containing molecule, form double helix
makes RNA
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
“nucleic acid”
transfer molecule
makes protein
Nucleic Acids
made of monomers called nucleotides
N base, pentose sugar, phosphate group (no nucleoside)
DNA base pairings
Adenine (A) with Thymine (T)
T replaced with uracil (U) in RNA
Guanine (G) with Cytosine (C)