Chapter 15: Musculoskeletal system
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Human Musculoskeletal System (Locomotor System)
The organ system that gives humans the ability to move
Skeleton (bones)
Muscles (skeletal muscles)
Joints (connect individual bones to form a functioning unit)
Ligaments (fibrous tissues that connect bones to other bones)
Tendons (fibrous tissues that connect bones to muscles)
Common Musculoskeletal Conditions: Joints
Osteoarthritis (wearing down of cartilage between bones)
Rheumatoid arthritis (autoimmune inflammatory disorder of the joints)
Psoriatic arthritis (inflammatory arthritis in people with psoriasis)
Gout (inflammatory arthritis due to crystallization of uric acid)
Common Musculoskeletal Conditions: Bone
Osteoporosis (density and quality of bone is reduced, [porous bone])
Osteopenia (bone mineral density is lower than normal)
Fractures
Common Musculoskeletal Conditions: Muscles
Sarcopenia (loss of muscle with aging and immobility)
Myopathies
Arthroscopy
Endoscopic procedure that allows examination of a joint interior with a specially designed endoscope
Highly accurate as it allows direct visualization of the anatomic site
Test results and clinical significance
Torn cartilage
Torn ligament
Degenerative arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Synovitis (inflammation of the lining of the joint)
Cyst
Arthrocentesis with synovial fluid analysis
Used to establish the diagnosis of
Joint infection
Arthritis
Gout
Synovitis
Neoplasms
Also done to identify the cause of joint inflammation
Sterile needle is inserted into the joint space and synovial fluid is aspirated
Synovial fluid is then examined microscopically and chemically
Synovial Fluid Analysis
Bone (Long) X-Rays
This x-ray study is performed to evaluate any bone for
fracture
infection
arthritis
tendonitis
bone spurs
Bone age can be determined in children to evaluate growth by comparing appearance and growth plates against standard bone atlases
Serial x-rays of wrists and arms, pelvis and skull
Healing of a fracture can be monitored
Vertebral Radiography (Spinal X-ray)
Spinal radiography is used to evaluate back or neck pain
Evaluation of any area of the spine
The type and the extent depends on the patient’s clinical
condition
Test results and clinical significance
Degenerative arthritis changes
Disk disorders
Traumatic or pathologic fractures
Scoliosis
Spondylosis (arthritis due to wear and tear to the spine)
Suspected spinal osteomyelitis (infection of the bone)
Myelography: Provides radiographic visualization of
The spinal canal
Nerve roots
Surrounding meninges
Myelography: Procedure
Radio-opaque dye is injected into the subarachnoid space of the spinal canal and the contents of the canal can be fluoroscopically outlined.
Take X-rays of the spine
CT scan or MRI scans can be performed for more detailed images
Myelography: Test results and clinical significance
Spinal cord tumors
Herniated disk
Arthritic bone spurs
Lumbar stenosis
Osteoporosis Diagnosis
A bone mineral density (BMD) test, also called DEXA (Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scan:
Uses low-dose X-rays to measure bone mineral density (how much calcium and other minerals are)
in a specific area of your bone. This test helps:Diagnose osteoporosis/Osteopenia
Predict fracture risk.
Monitor patients who are receiving treatment for osteoporosis
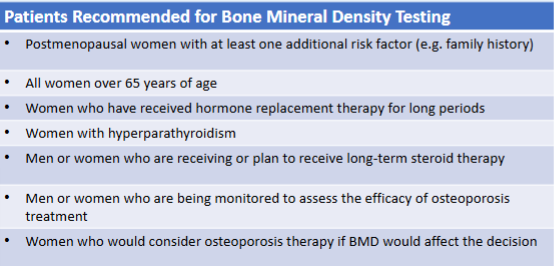
Diagnosis of osteoporosis... cont.
The spinal bone is the best representative of cancellous (spongy) bone
The radius (forearm) is the best representative of cortical (dense bone)
The hip is suitable for analysis of mixed bone.
Diagnosis of osteoporosis: Results expressed as a T score and a Z score
T-score: The difference between your bone mineral density and 0, which is the bone mineral density of a
healthy young adult.
Z-score: The difference between your bone mineral density and the average bone mineral density for healthy
people of your age, ethnicity, and sex.
T/Z-score of -2.5 or lower indicates osteoporosis.
T/Z-score between -1 and -2.5 indicates osteopenia.
T/Z-score between 0 and -1 indicates normal bone density.
The T-score is typically used for individuals under the age of 50 while, a Z-score is used for older people.
Diagnostic Laboratory Tests of the Musculoskeletal System
Rheumatoid Factor (for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis)
Bone Turnover Markers (to monitor treatment for osteoporosis)
Uric acid (in blood and urine)
Used for the diagnosis of gout and the identification of persons at risk of stone formation
Vitamin D (to evaluate ability for calcium absorption)
Alkaline phosphatase (useful for the detection of bone disorders)
Aldolase (used to aid in the diagnosis and surveillance of skeletal muscle diseases)
Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
Rheumatoid factor test is the most useful immunologic test for confirming rheumatoid arthritis
~80% of patients with RA show positive result for RF test
RFs are IgG antibodies produced by lymphocytes in the synovial membranes in the joints which react with other IgG or IgM antibodies to form immune complexes, complement activation and tissue destruction
The RF test is directed towards identification of the IgM antibodies that react with RF
RF test method: latex agglutination test
Diagnostic Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
American College of Rheumatology Criteria for RA
Morning stiffness for at least 6 weeks
Pain in at least one joint for the preceding 6 weeks
Swelling in at least one joint for the preceding 6 weeks
Symmetric bilateral joint swelling
Presence of subcutaneous nodules
Radiographic changes compatible with RA
Bone Turnover Markers (BTM)
Bone is continuously being turned over
Bone resorption (breakdown by osteoclasts)
Bone formation (by osteoblasts)
Osteoporosis is associated with increased bone resorption
Common disease in postmenopausal women
BTMs
“N” and “C-” telopeptides: Short, non-helical amino acid sequences at the ends of collagen molecules (released into blood and excreted in the urine following bone breakdown).
Good indicator of bone breakdown
Osteocalcin: Non-collagenous protein that is primarily found in bone
Good indicator of bone metabolism.
Bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (found in osteoblasts)
Good indicator of bone formation
Bone Turnover Markers (BTM): Increased levels
Osteoporosis
Osteodystrophy
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Rapid Bone Growth
Bone tumors
Paget’s disease
Bone Turnover Markers (BTM): Decreased levels
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Effective antiresorptive therapy
Vit D Deficiency
Uric Acid Testing
Levels can be measured in both blood and urine
Helpful in evaluating uric acid metabolism in gout
Uric acid crystal formation in the synovial fluid is the gold standard test for the diagnosis of gout
Uric acid is a nitrogenous breakdown product of purines like
adenine and guanine. (a DNA building block)
Produced in the liver
Excreted by the kidney (75%) and the intestines (25%)
Elevated levels in the blood (hyperuricemia) may indicate Gout
A form of arthritis caused by deposition of uric acid crystals in weight bearing joints.
Uric acid can become supersaturated in the urine and form kidney stones
Uric Acid: Test results and clinical significance - Increased Levels (hyperuricemia)
Gout
Multiple myeloma
Cancer chemotherapy
High purine diet
Chronic alcohol ingestion
Decreases kidney tubular secretion of uric acid
Uric Acid: Test results and clinical significance - Decreased Levels (hypouricemia)
Renal disorders
e.g., renal hypouricemia
Excessive fluid intake
Fanconi syndrome
kidney is unable to reabsorb filtrate
Uricosuric drugs
Drugs that increase uric acid excretion in the urine (e.g., steroids)
Vitamin D Test (Blood)
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin
Vitamin D2 is provided by dietary sources
Vitamin D3 is produced by the skin exposed to sunlight (UVB radiation)
Vitamin D is converted into its physiologically active form in the liver and the kidneys (becomes a hormonally active form)
Binds to vitamin D receptors in target organs
Vitamin D encourages calcium absorption by the intestine
Also acts on bone, kidney and parathyroid gland cells leading to the maintenance and regulation of calcium levels in the blood
Clinical Features and Associated Vitamin D Levels
Vitamin D Tests
25(OH)D Test:
Measures the level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in the blood, which is the main form of vitamin D that circulates in the body. It reflects both:
Vitamin D prostatus bute skin from sunlight exposure.
Vitamin D obtained from food or supplements.
1,25(OH)2D Test (Calcitriol):
Measures the active form of vitamin D, which is produced in the kidneys.
It's not usually used to check for overall vitamin D status but may be used to monitor kidney problems or to help find the cause of abnormal calcium levels in the blood.
Vit D test: Test results and clinical significance: Increased Levels
Increased dietary intake
Increased Calcium intake
Hyperparathyroidism
Vit D test: Test results and clinical significance: Decreased Levels
Rickets
Osteomalacia (softening of bones)
Osteoporosis
Gastrointestinal malabsorption syndrome
Renal & Liver disease
Inadequate dietary intake
Inadequate exposure to sunlight