Ch 4 DNA Technology
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
The order of nucleotides in a DNA strand or fragment is called
DNA sequence
DNA sequencing can be used for several purposes, including the determination of ________ and for the construction of _______
gene or genomic sequences; nucleic acid sequences for experimental purposes
The first widely used sequencing approach and employs dideoxy nucleotides (ddNTPs)
Sanger dideoxy method
ddNTPS can be incorporated into growing DNA strands via _______ involving the ddNTP _________
phosphodiester bonds; 5' phosphate groups
Incorporation of ddNTpS in this way results in the _______ of DNA strand elongation due to the lack of ________ to which new nucleotides can bind
termination; 3' hydroxyl groups
A technique for generating multiple copies of a DNA sequence
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
The reagents required for PCR include the following:
- source DNA template
- primer pairs
- thermostable DNA polymerase
- deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs)
PCR occurs in a repeating cycle of three steps
Denaturation, Annealing, and Elongation
PCR in which product amplification is quantified in real time as the reaction progresses, typically by using fluorescent DNA markers
Real-time or quantitative PCR (qPCR)
Endonucleases that typically originate in bacteria and cut double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) at nonterminal sites (ie, at places other than dsDNA ends)
Restriction enzymes
In nature, restriction enzymes protect bacteria from _________ by cutting viral DNA into _______, thereby _______ transfer of foreign DNA into bacterial cells
bacterial viruses (ie, bacteriophages); small pieces; restricting
Some enzymes, like _____, cut evenly across dsDNA to create blunt ends or cuts in dsDNA that do not create single-stranded regions.
Alul
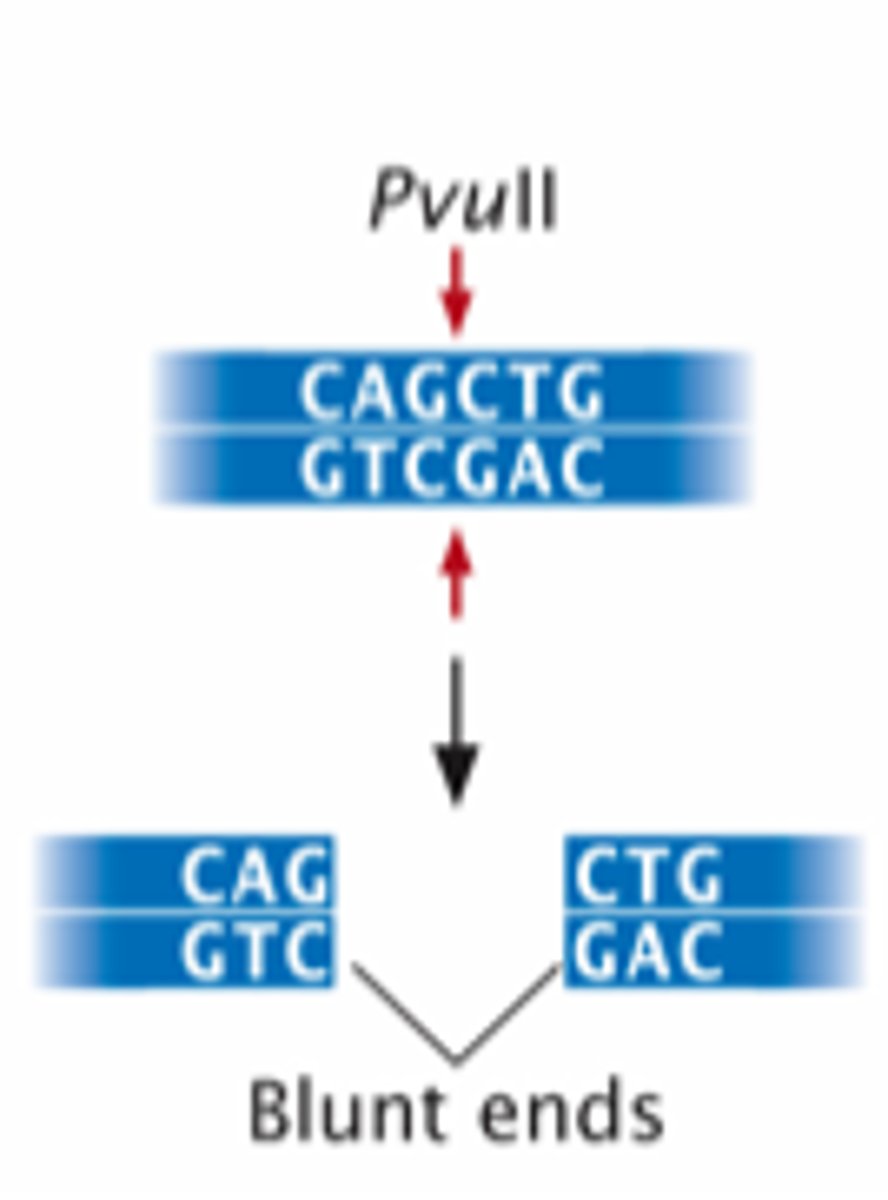
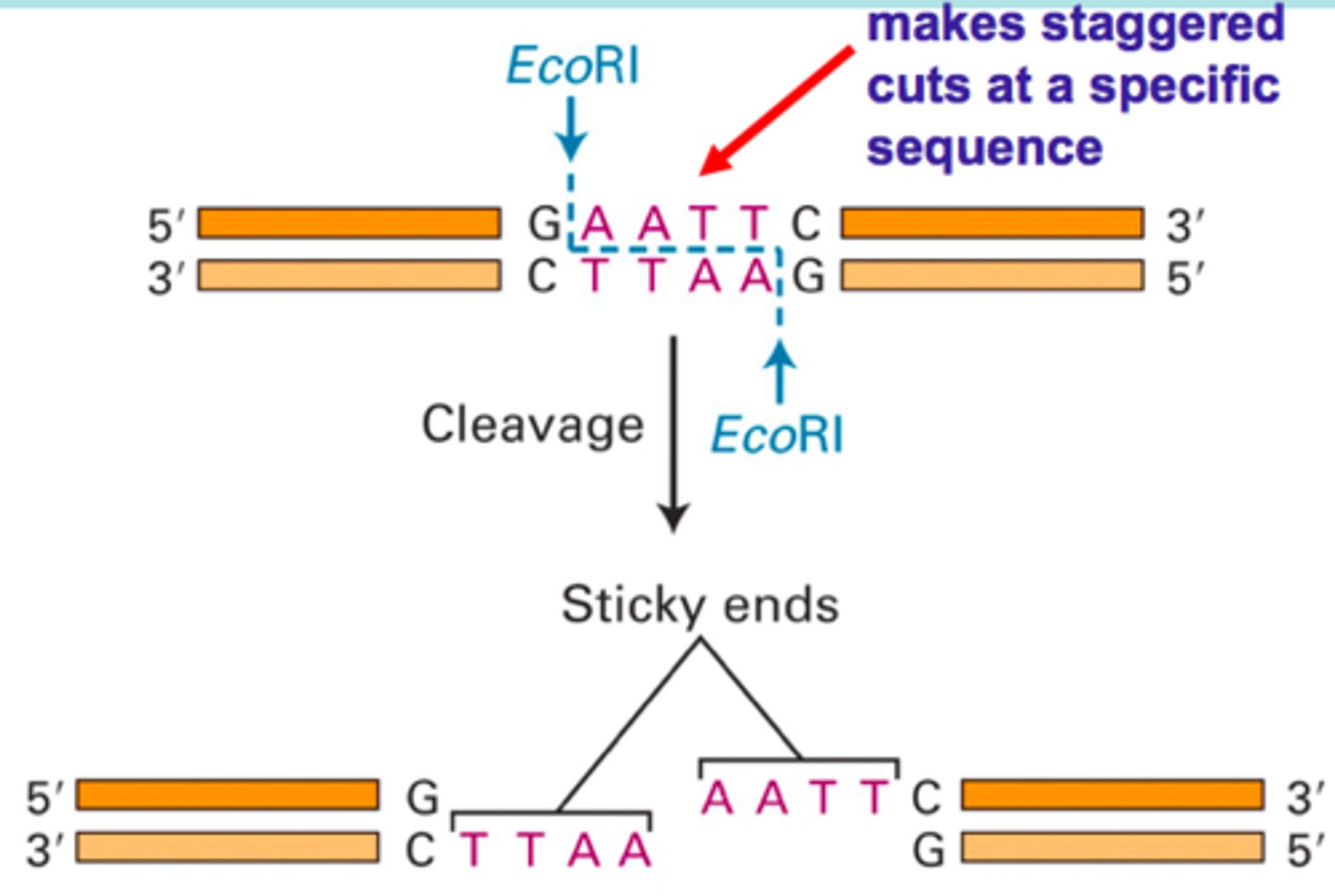
Other enzymes, like ______ cut unevenly across dsDNA, thereby creating short single-stranded segments known as sticky ends on each of the cut strands
EcoRI
The insertion of a previously isolated gene into a DNA sequence, typically to make multiple copies of the gene
Gene cloning
Gene cloning is often carried out for the ultimate purpose of creating a _____ amount of a specific gene's transcribed or translated products (______)
large; RNA or protein
The gene or gene products formed during cloning are called _____, meaning that they are from more than one source
recombinant
One approach to gene cloning consists of cutting ______ with a restriction enzyme and adding the _______ to be cloned along with a ______
plasmid DNA; DNA fragment; DNA ligase
Small, circular, nonchromosomal DNA, typically found in bacteria (may have a single origin of replication)
Plasmid DNA
The ends of the DNA fragment and the plasmid must ____ for it to be a successful incorporation of the fragment into the plasmid
match
A way to accomplish that is to match the ends of the DNA fragment and the plasmid is by
- using the same restriction enzyme in both the isolation of the DNA fragment and the cutting of the plasmid
- using PCR to add restriction sites at each end of the sequence to the cloned
When the use of different restriction enzymes produces a combination of noncomplementary blunt and sticky ends on the DNA fragments and the plasmid, _______ and _______ can be added to fill in the staggered ends. The resulting fragment and plasmid, both blunt-ended, are then joined by ______.
dNTPS and DNA polymerase; DNA ligase
After the addition of the DNA fragment, the _______ are added to bacterial cells, and the cells are ________ to take up the plasmids
plasmids; stimulated
To stimulate the cells, you would
heating up the cells
The process of taking up plasmids
transformation
An ______ gene is typically inserted into the plasmid with the DNA sequence containing the gene to be _______, and the bacterial colonies are then grown in media containing the antibiotic.
antibiotic resistance; cloned
DNA generated from an RNA template, typically mRNA
complementary DNA (cDNA)
Because _______ lacks introns, cDNA represents the _______ amount of genetic information necessary for gene expression: a contiguous sequence of nucleotides coding for a protein.
mature mRNA; minimum
To generate cDNA, _____ is first used as a template for the synthesis of a single cDNA strand
mRNA
The single ______ strand is then used as a template to synthesize a complementary second cDNA strand, thereby completing the synthesis of ______
cDNA; double-stranded cDNA
To initiate synthesis of the first cDNA strand, isolated mRNA is typically mixed with _______ composed of ______
primers ; thymine nucleotides
These primers, known as ______, are complementary to the ______of eukaryotic mRNA molecules
poly-T or oligo(dT) primers; 3' poly-A tails
The enzyme ______ uses the primer-bound mRNA as a template for the synthesis of DNA, adding ______ to generate single-stranded cDNA
reverse transcriptase; dNTPs
The mRNA strand is then partially ________ by the reverse transcriptase, leaving the first cDNA strand bound to the original RNA in some regions
degraded
The second (complementary) cDNA strand is then synthesized by ______, using the first cDNA strand as a template
DNA polymerase
The RNA fragments that remain bound to the first cDNA strand serve as _______ to which DNA polymerase successively adds _______
primers; dNTPs
Remaining RNA fragments are _______ during the synthesis of the second cDNA, as the _______ of DNA polymerase displaces NTPs as its adds dNTPs
removed; 5' --> 3' exonuclease activity
_______ is then added to seal any nicks in the DNA, completing the synthesis of the ______ cDNA
DNA ligase; double-stranded
Collections of cloned DNA fragments and can be generated in several ways
DNA libraries
The first approach to DNA library construction is to _______ (using restriction enzymes) or _______ (using sudden, forceful movements) break chromosomal DNA into smaller pieces of _______
enzymatically; mechananically; double-stranded DNA
A second approach for constructing a DNA library begins with mRNA, which is _______ into ______ before being inserted into ______ and transferred to recipient cells for amplification
reverse transcribed; double-stranded cDNA; plasmids
A third approach uses ______ to amplify cDNA of ______ or ______
PCR; individual genes; genomic fragments
Separating DNA molecules of different sizes by using an electric current to induce the molecules to migrate through a special gel
DNA electrophoresis
The bands produced during electrophoresis can be visualized using stains such as _____, which inserts between the nucleic acid bases and fluoresces under ultraviolet light
ethidium bromide
DNA bands can also be detected using a technique called
Southern blotting
Southern blotting uses a nucleic acid probe to detect only bands that contain a
specific DNA sequence
The base pairing of complementary strands of nucleic acids via hydrogen bonding
Hybridization
Are used to determine which part or parts of a sample contain the complementary nucleic acid sequence
Hybridization probes
The use of ionizing electromagnetic radiation for imaging or imaging-related measurements
Radiography
The type of radiography in which internally released ionizing radiation is used for imaging or measurement purposes
Autoradiography
RNA detection methods include hybridization to an ______, _____, and _____
RNA or DNA probe; autoradiography; UV absorption
The electrophoretic separation of RNA molecules followed by detection using a single-stranded nucleic acid (typically DNA) probe that hybridizes with a specific RNA sequence
Northern blotting
Consists of probes for many distinct sequences rather than a single sequence, also another method of detecting RNA
microarray
A complementary hybridization probe hybridizes with RNA molecules in a tissue sample, allows gene expression to be localized within a tissue or cell
In situ RNA hybridization
If the hybridization probe is labeled with a fluorescent tag, then fluorescence within the sample reveals the location(s) of complementary RNA molecules, and the method is called
fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
Used to produce complementary DNA molecules from the RNA in a sample, and then PCR is used to amplify the cDNA
RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase
When the mathematical relationship between amplification cycle number and the amount of cDNA synthesized is used to quantify the amount of RNA in a sample, the process is referred to
RT-qPCR
A technique for measuring the amount of a specific protein in a sample using an immune-based detection mechanism
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Proteins can also be studied using
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE)
Proteins separated on ______ retain their native structure and charge, both of which affect electrophoretic migration
nondenaturing (native) gels
Denaturing gels employ ______ such as _____ to impart a uniform charge to proteins
denaturants; sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
This negative charge is _______ to size, minimizing charge differences between proteins, so separation of proteins by denaturing gel electrophoresis (eg, SDS-PAGE) occurs primarily on the basis of ______
proportional; size
Proteins in a sample can be electrophoretically separated, transferred to a membrane, and visualized in a process known as
western blotting
The protein bands are detected via binding to a primary antibody, to which a secondary antibody binds for visualization (eg, via chemiluminescence, fluorescence, or autoradiography
true
Prior to adding antibodies, membranes are typically exposed to _____ or another substance to block _____ binding sites, a step that reduces background binding
milk; nonspecific
Antibody-based detection of specific proteins can also be used for the visualization of proteins in histological sections
Immunohistochemistry
A means of studying protein-protein interactions using the affinity of a protein for a binding partner
Pulldown assays
Organisms or cells in which one or more genes have been removed or made nonfunctional
Knockout models
One approach for developing knockouts is derived from a bacterial defense system that collects ______ DNA segments from _____, enabling each bacterium to accumulate previously encountered viral DNA sequences
short; infecting viruses
The viral sequences are inserted at regular intervals between clusters of palindromic sequences of bacterial DNA, forming
clustered, regularly, interspaced, short, palindromic repeats (CRISPR)
In _______ gene editing, a synthetic sgRNA is employed to target a sequence of interest.
CRISPR-Cas 9
Another approach for generating knockouts, called the ______ strategy, employs a recombinase enzyme called Cre, which recognizes special DNA sequences called loxP sites
Cre-loxP
Cre cuts out the portion of the DNA between two ______ sites as well as ______ of the two loxP sites, then it ______ the two cut ends to leave a single loxP site
loxP; one; joins
A means of assessing the location of the gene(s) responsible for a recessively inherited phenotype
Complementation assay
Designed to post-transcriptionally modulate gene expression by manipulating mRNA function using short (-20-25 nucleotides), synthetic oligonucleotides that undergo Watson-Crick base pairing
Antisense strategies
Some of these oligonucleotides have counterparts in nature
RNA interference (RNAi)
Examples of RNAi
Short interfering RNA (siRNA) and mircoRNA (miRNA)
siRNA pairing is usually ______. This specificity makes the guide strand-target strand pair a target for ______ by a specific endonuclease, ultimately resulting in the enzymatic destruction of the target ______.
complete and specific; destruction; mRNA
miRNA undergoes ______ mRNA pairing, allowing miRNA to interact with ______ mRNA sequences rather than ______ specific mRNA sequence
partial; multiple; a single
miRNA typically either ______ translation of the bound mRNA or _____ of a pre-mRNA, although with extensive pairing mRNA ______ can be triggered
represses; alters splicing; destruction
Single-stranded synthetic antisense RNA molecules that hybridize with target mRNA and sterically block translation or alter splicing, similar to miRNA's role in RNAi.
Morpholinos
Morpholinos are ______ and possess a six-membered morpholine ring, which makes morpholinos ______ susceptible to degradation and is thought to ______ the likelihood of off-target effects
uncharged; less; reduce
An attempt to treat a condition or augment health by altering the complement of genes possessed or expressed
Gene therapy
The application of biotechnological methods or knowledge to questions about evidence in legal proceedings
forensics
A type of DNA analysis that focuses on differences in DNA fragments' lengths generated by the polymerase chain reaction or by treatment of DNA samples with an endonuclease
DNA fingerprinting
Well-adapted for survival in a specific type of harsh environment
extremophiles