Science - First Year Christmas Test
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The title says it-
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Corrosive
Can burn through material or skin
Flammable
May easily catch fire
Harmful
Could cause sickness or a rash
Toxic
Acts as a poison
Oxidising
Gives out a lot of heat in a reaction
Soluble
Can dissolve
Insoluble
Cannot dissolve
Solute
The substance being dissolved eg. suger or salt
solvent
The liquid used to dissolve something eg. water
Solution
A solute and a solvent mixed together
Saturated solution
When no more solute can be dissolved into the solvent
Dilute
When there is more solvent than solute
Concentrated
When there is more solute than solvent
Element
A substance made up of one type of atom
Mixture
A substance made up of 2 or more types of atoms not chemically combined (easily separated)
Compound
Made up of 2 or more types of atoms, chemically combined (not easily separated)
Cells
The basic building block of living things
Nutrition
The way in which living things get their food
Excretion
The way in which living things get rid of wastes that they produce
Response
The way in which living things react to change in their surroundings
Reproduction
The way in which living things produce new living things
Biodiversity
The range of living things
What does an animal cell contain?
Cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm
Cell membrane
Holds contents of cell in place and controls what passes in and out of cell.
Nucleus
A round structure that controls the cell, contains chromosomes.
Cytoplasm
A liquid that surrounds the nucleus, carries out cell reactions, contains small structures like mitochondria
What is in a plant cell?
Vacuole, nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, cell wall.
Vacuole
A small liquid filled bay in cytoplasm, gives strength to plant cells (stores cell sap)
Cell wall
Gives strength and structure to the plant cell
Mitochondria
Supplies energy to the cell (by respiration)
Chloroplast
Makes food (by photosynthesis)
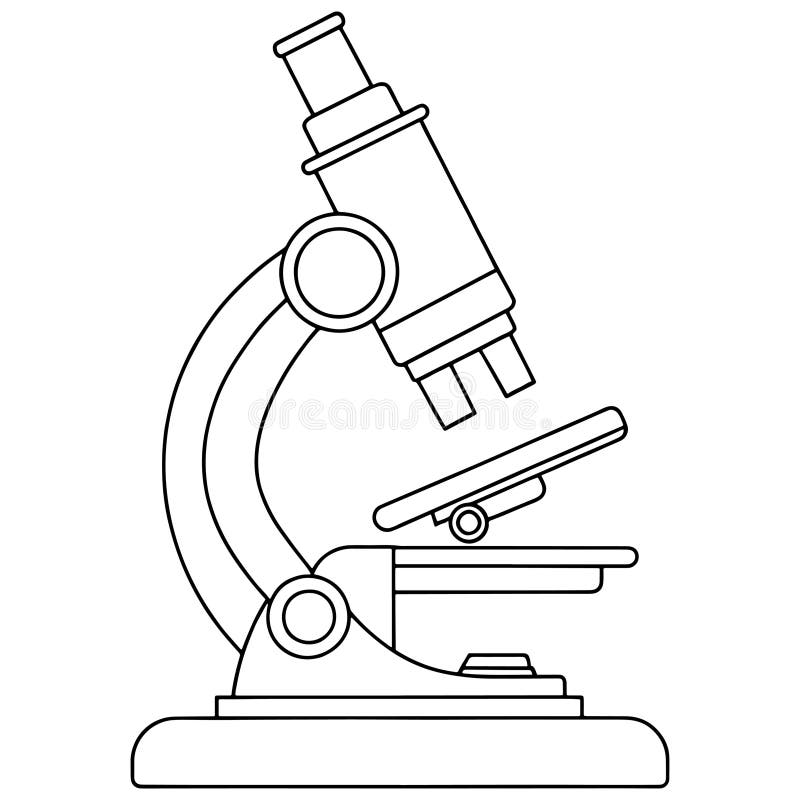
What parts are on a microscope?
Eyepiece lens, course focus knob, fine focus knob, nosepiece, stage, clip objective lens, mirror.
Ingestion
Taking in food
Digestion
breaking down food
Absorption
Taking digested food from our intestines into our blood
Assimilation
Using the food in the cells of the body
Egestion
Getting rid of undigested waste
What are in the digestive system?
Mouth, oesophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
Mouth
Takes in and digests food with teeth and salivary glands (physical and chemical digestion)
Physical Digestion
Breaking down food using mechanical or physical methods.
Chemical Digestion
breaking down food using enzymes (or hydrochloric acid in the stomach)
What teeth are in the mouth?
Incisors, canines, pre-molars, molars
Amylase
Breaks down starch into maltose
Oesophagus
Forces food down from the mouth to the stomach with the muscle called peristalsis
Stomach
A muscular bay that holds food for a few hours, digesting it with hydrochloric acid and churning it (physical and chemical)
Small Intestine
A long but thin tube that digests and absorbs nutrients from the food
Liver
Produces a liquid called bile
Bile
Helps digest fat in small intestine
pancreas
Produces many different enzymes, to help digest food
Large intestine
It reabsorbs water, if too much is taken back, there’s too little left, causing constipation. If too little is taken back, the waste becomes liquid, causing diarrhoea.
Matter
Anything that occupies space
What are three forms of matter?
Solid, liquid, gas
Solid
A definite shape, definite volume, can’t move and can’t be compressed.
Liquid
Can move freely, definite volume but not shape and can’t be compressed.
gas
Freely moves, no definite volume or shape, can be compressed.
Melting
When a solid is heated (gains energy) it changes to liquid
Boiling
When a liquid is heated and it turns to gas
Condensation
When cooling a gas (removing energy) causes it to change to liquid
Freezing
When a liquid is cooled and change to a solid
Diffusion
The movement of particle from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. (mainly in liquids and gases)
Filtration
Separation of an insoluble solid from a liquid
What is in a filtration set?
A beaker, sand+water mixture, filter paper, funnel
Residue
Sand left in filter paper
Filtrate
The clean filtered water after filtration
Chromatography
Seperation of mixture from liquid
what is in the chromatography experiment?
Chromatography paper, beaker, ink(marker), pencil line, water
Evaporation
Separation of a soluble solid from a liquid (eg salt+water)
What is in the evaporation experiment?
mixture(salt+water), wire gauze, tripod, Bunsen burner, evaporating dish
Distillation
Separation of two liquids with different boiling points (eg water at 100, alcohol at 78)
What is in the distillation experiment?
Thermometer, round bottom flash, mixture (alcohol + water), wire gauze, tripod, bunsen burner, liebig condenser, beaker