z. lab 1: intubation & vaccines
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
intubation: placement of a _____, _____ tube into the _____ to maintain an _____ _____ or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain _____
flexible
plastic
trachea
open airway
drugs
what are the benefits to intubating a patient?
maintaining an open airway
prevention of aspirating saliva
prevention of gastric regurgitation
seals the respiratory system & breathing circuit
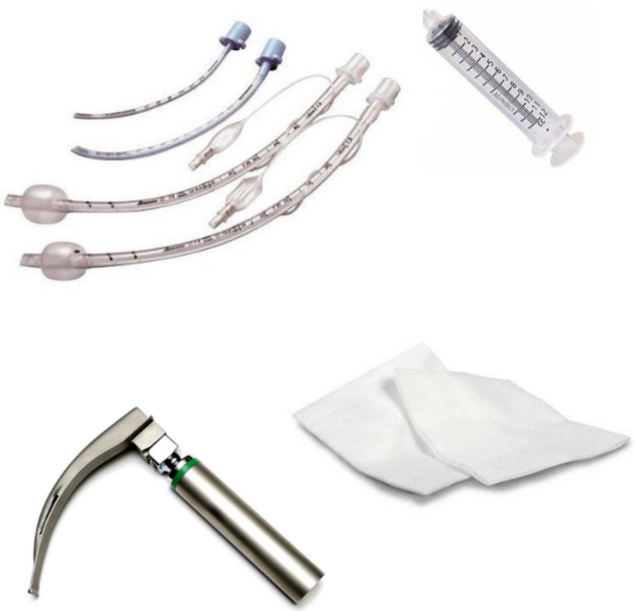
what equipment is used for intubation?
3-12 mL syringe
inflate the cuff
endotracheal tubes
varying sizes
gauze squares
to hold tongue
laryngoscope
to move epiglottis & expose tracheal opening
oxygen
sterile lubricant
supplies to secure endotracheal tube
what types of material are used for endotracheal tubes?
silicone
red rubber
polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
what types of endotracheal tubes are there?
plain/uncuffed
cuffed
plain: cole tube
best for _____ species, _____ animals, or _____ pets
excellent _____-_____; provides less resistance
avian
pediatric
exotic
pressure-flow
what should plain tubes be used for avian species & NOT cuffed?
birds have a complete trachea (rings are closed) & using a cuffed tube will cause pressure necrosis if inflated too much since the trachea has no elastic ligament to accommodate the expansion
what feature of the avian species allow for an airtight seal at the entrance of the larynx?
shoulders
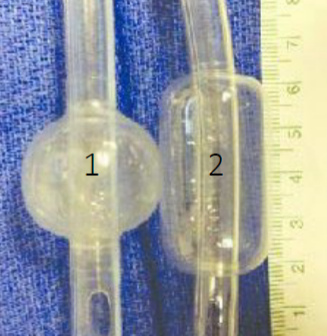
cuffed tube
used in _____ _____
serves two purposes
prevent _____ _____ around the tube
reduces risk of _____ of _____ or _____ secretions
there are two types:
_____ pressure, _____ volume (1)
_____ pressure, _____ volume (2) - less _____ to the tracheal _____
all species
gas leaks
aspiration
gastric
oral
high
low
low
high
damage
mucosa
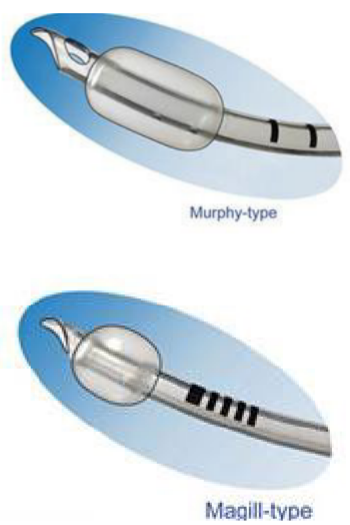
what is the different between a murphy cuffed tube & a magill cuffed tube?
murphy - most common & has a murphy eye
an emergency opening if the distal end of the lumen of the tube becomes clogged
magill - does not have the murphy eye, otherwise very similar
what things should be kept in mind when selecting an endotracheal tube?
rapid intubation
minimize trauma
ensure proper airway protection
too large - trauma
too small - leaks; protection compromised
always choose 3 tubes
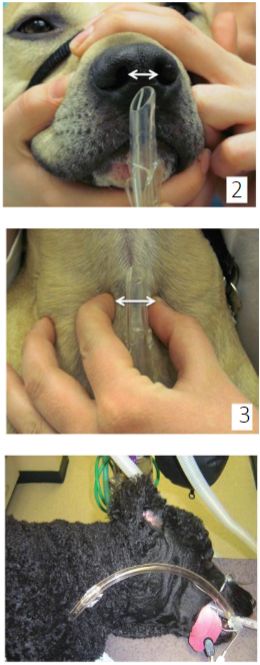
what are the 4 ways to measuring the correct endotracheal tube size?
correlating BW to tube size in brachycephalic breeds
evaluating the width of the nasal septum
palpation of the width of the thoracic trachea just above the thoracic inlet
proximal end should not pass incisor teeth & distal end should not pass shoulders
what are stylets used for?
for small or very flexible tubes, they provide extra support for intubation
for cats with laryngospasm
** ensure tip does not protrude beyond tip of endotracheal tube
what are the two types of laryngoscopes?
macintosh - curves
miller - straight
sternal recumbency
on stomach
access to face & back
lateral recumbency
on side
access to teeth
dorsal recumbency
on back
access to abdomen
intubation procedure for dogs
sedate/anesthetize
pull out tongue
examine epiglottis & soft palate
apply lubricant
locate tracheal opening with a laryngoscope
intubate
inflate cuff with syringe
intubation procedure for cats
same as dogs
laryngospasm: arytenoids remain closed
can use one drop of lidocaine to prevent
can be toxic if more than 0.5 mL used
ways to confirm proper intubation
visual - tube passes through arytenoids
cough - tube has advanced into trachea
condensation - tube clear on inhalation, cloudy on exhalation
palpation - ventral cervical regional should reveal one rigid structure
ways to monitor anesthesia
circulation
electrocardiography (ECG)
oscillometric blood pressure measurement - low BP = low blood flow = low O2 to organs
ventilation
capnography: measurement of CO2 in exhaled breath
oxygenation
pulse oximetry
body temperature
thermometer - lower BT when anesthetized
depth of anesthesia
gas analyzer
when should extubation occur?
after confirmation that the pharyngeal reflex is reestablished (swallowing)
what should occur before extubation?
check for excessive secretions (saliva)
fully deflate cuff
what should occur after extubation?
monitored
head is kept elevated to avoid aspiration
flow-by O2 administered
respiration & oxygenation monitored until animal is fully awake
administration by injection is referred to as the _____ route
parenteral
injection: the act of putting a _____, especially a _____, into a muscle or other organs using a _____ & _____
liquid
drug
needle
syringe
what are the different types of injections?
intramuscular - muscle
subcutaneous - tissue under skin
intravenous - veins
intradermal - skin
intraperitoneal - abdominal cavity
intrapleural - thoracic cavity
intraosseous - bone
what are the 3 most commonly used injections?
subcutaneous
intramuscular
intravenous