Apologia Chemistry Module 2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What does the Continuous Theory of Matter believe about substances?
substances are composed of long, unbroken blobs of matter
What does the Discontinuous Theory of Matter state about matter?
matter is composed of tiny individual particles
The law of Mass Conservation states that _____
matter cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change forms;
Total Mass before reaction = Total Mass after reaction
Discontinuous Theory of Matter
The idea that substances are composed of tiny, individual particles like grains of sand
How is data collected for qualitative measurements?
data is collected by using your senses such as sights, sounds, smells, textures
How is data collected for quantitative measurements?
data is collected using numbers such as time, mass, distance, volume, temperature
What is a Decomposition Reaction?
a chemical reaction that breaks down compounds into simpler products

What are elements?
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom. (identical atoms)
Cannot be broken down (decomposed) into simpler components.
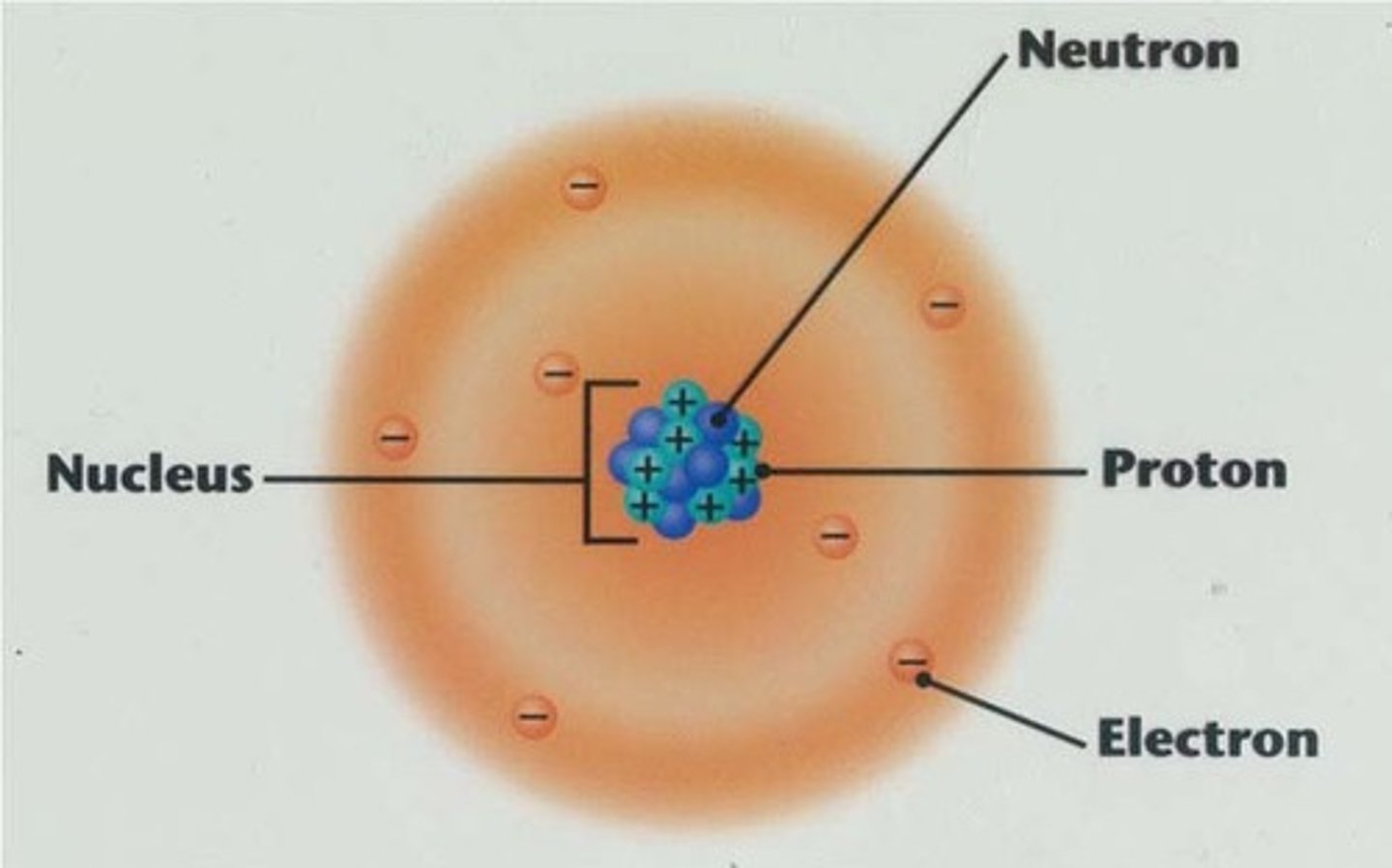
What are Atoms?
the basic unit of a chemical element.
All matter is made up this.
Made up of electrons, protons and neutrons.
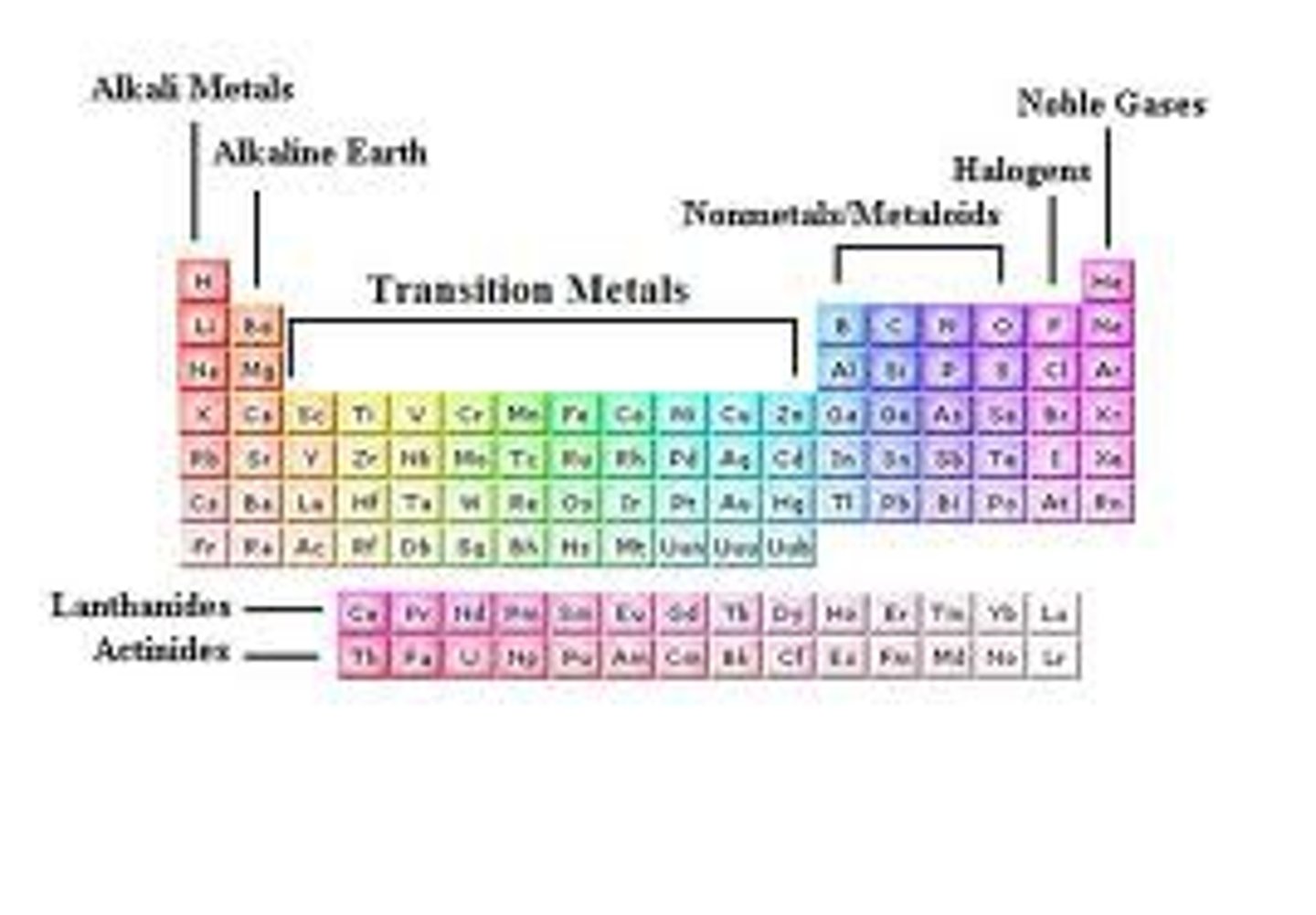
What is the Periodic Table of Elements?
A table that classifies elements by their physical and chemical properties; rows are called periods; columns are called groups;
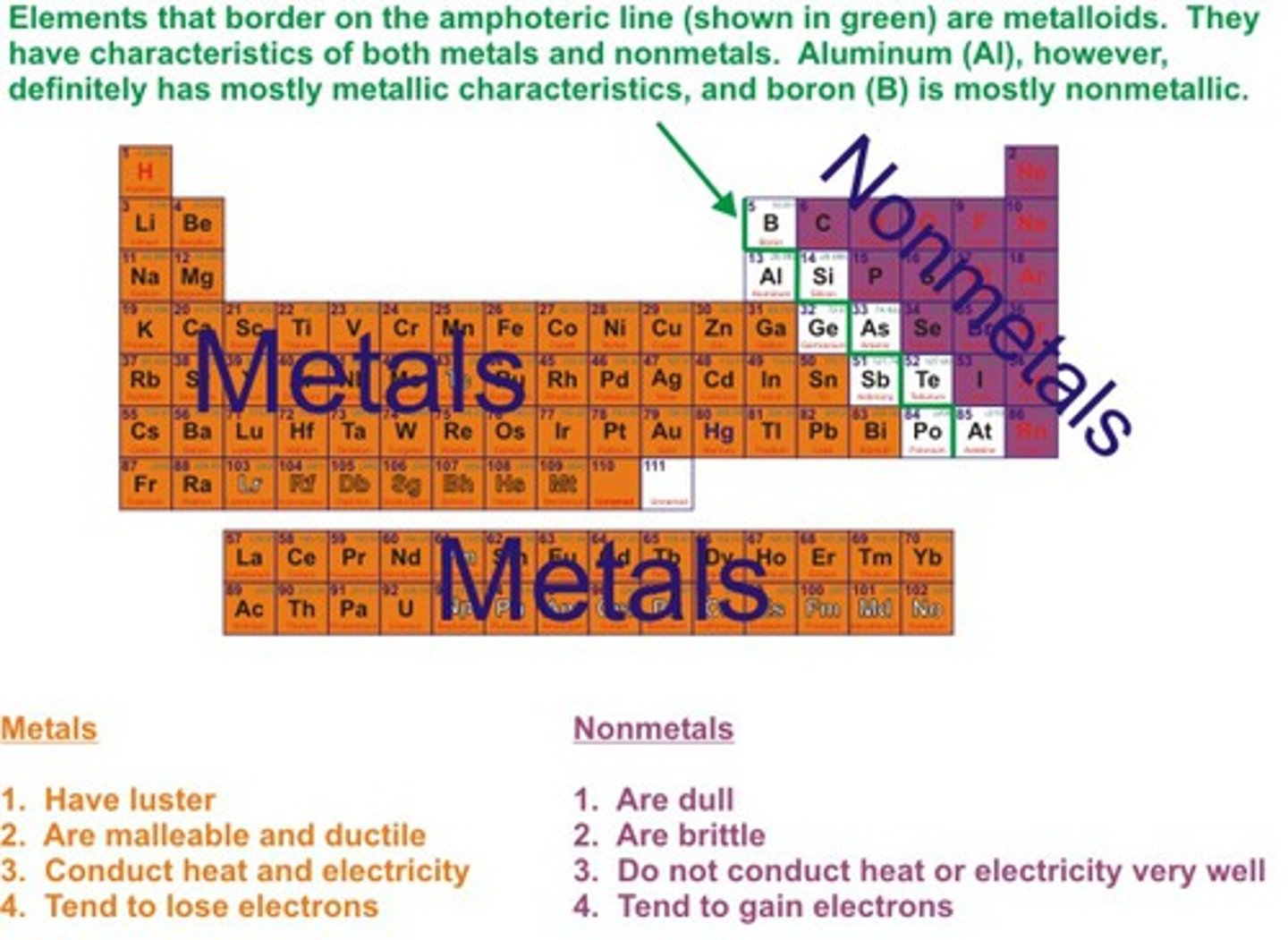
What are metals?
elements that have luster, can be bent (malleable), and conduct electricity ("below" the "stairs")
Become Cations because they lose electrons
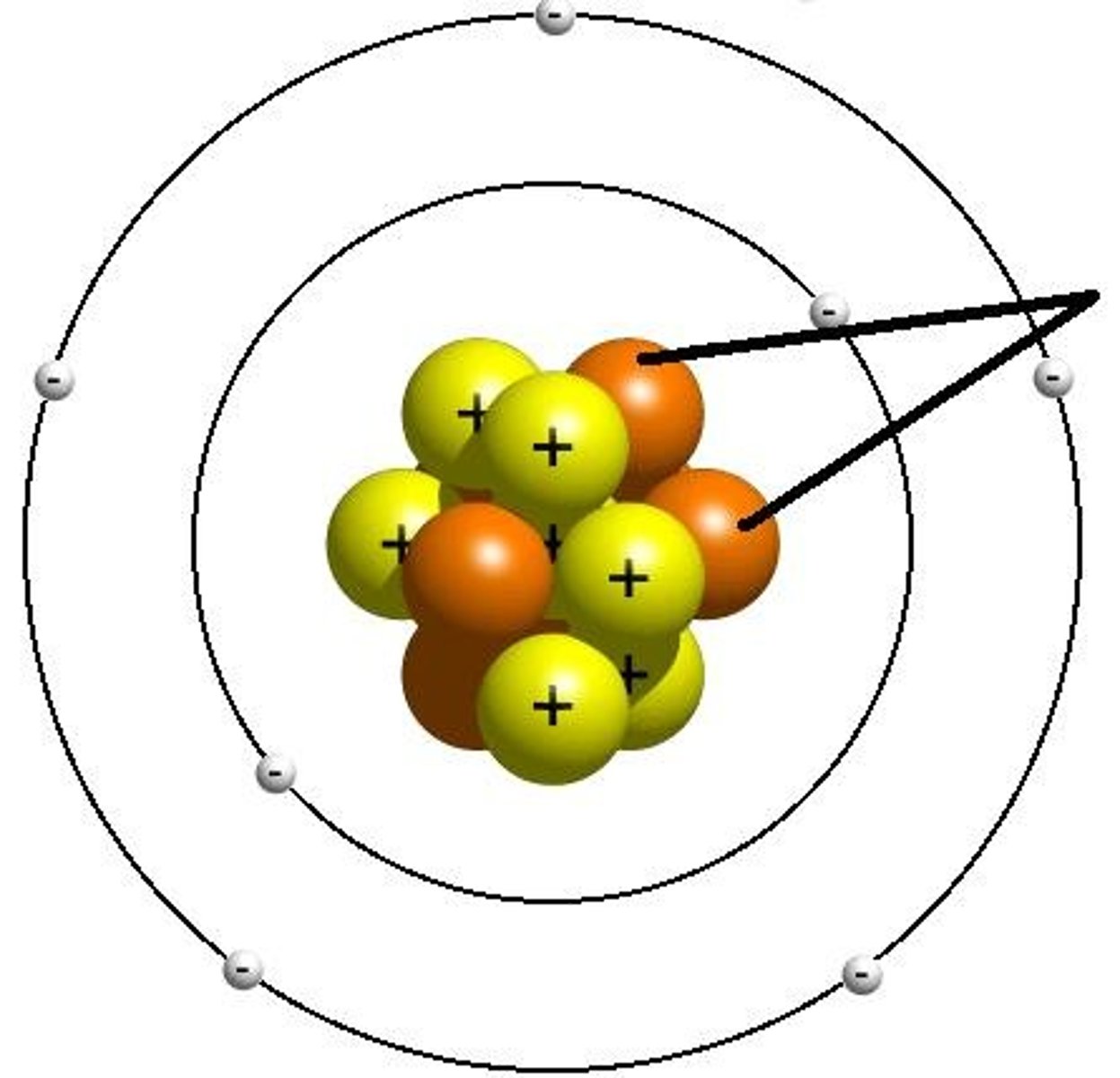
What are Electrons?
negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus
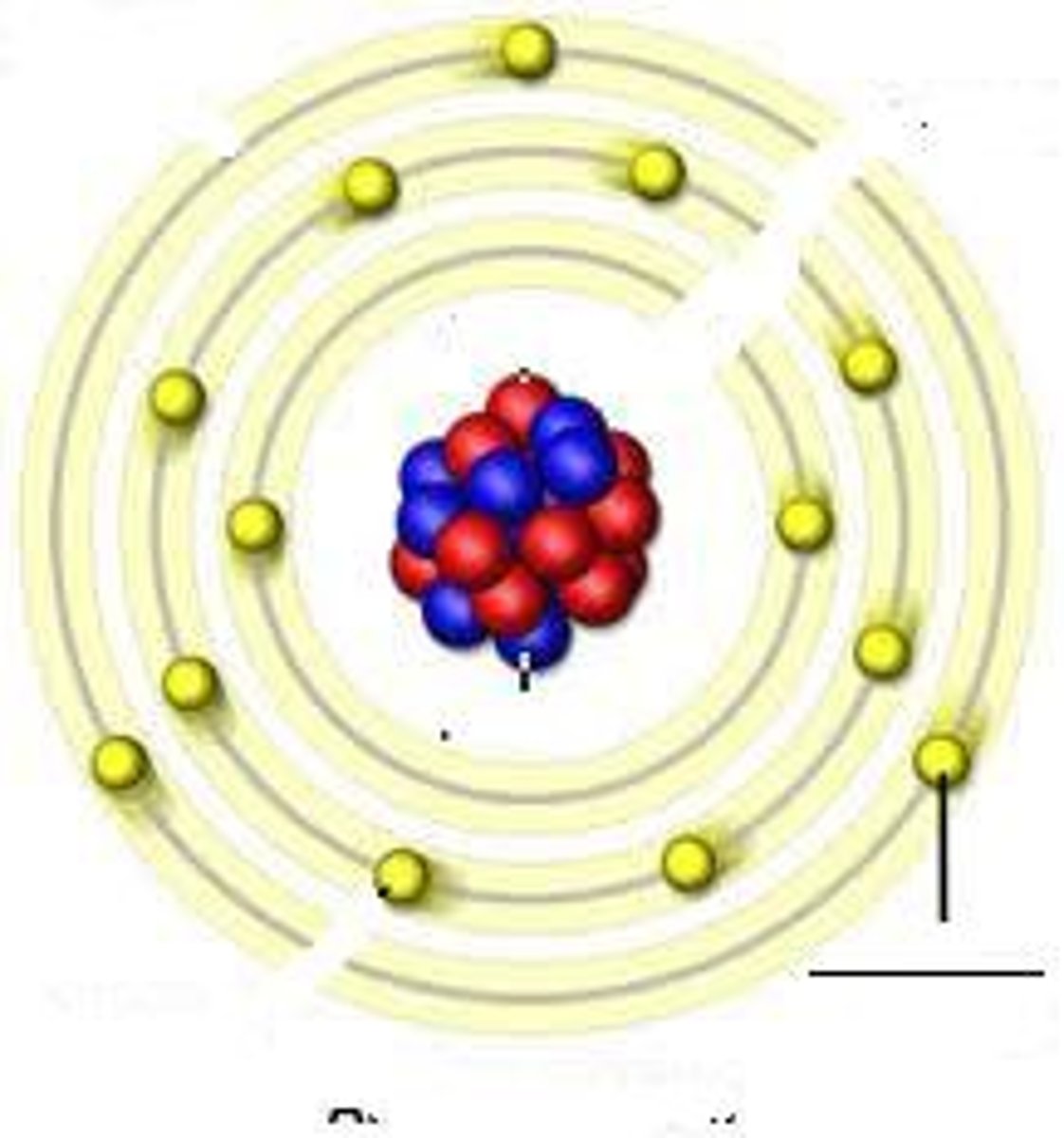
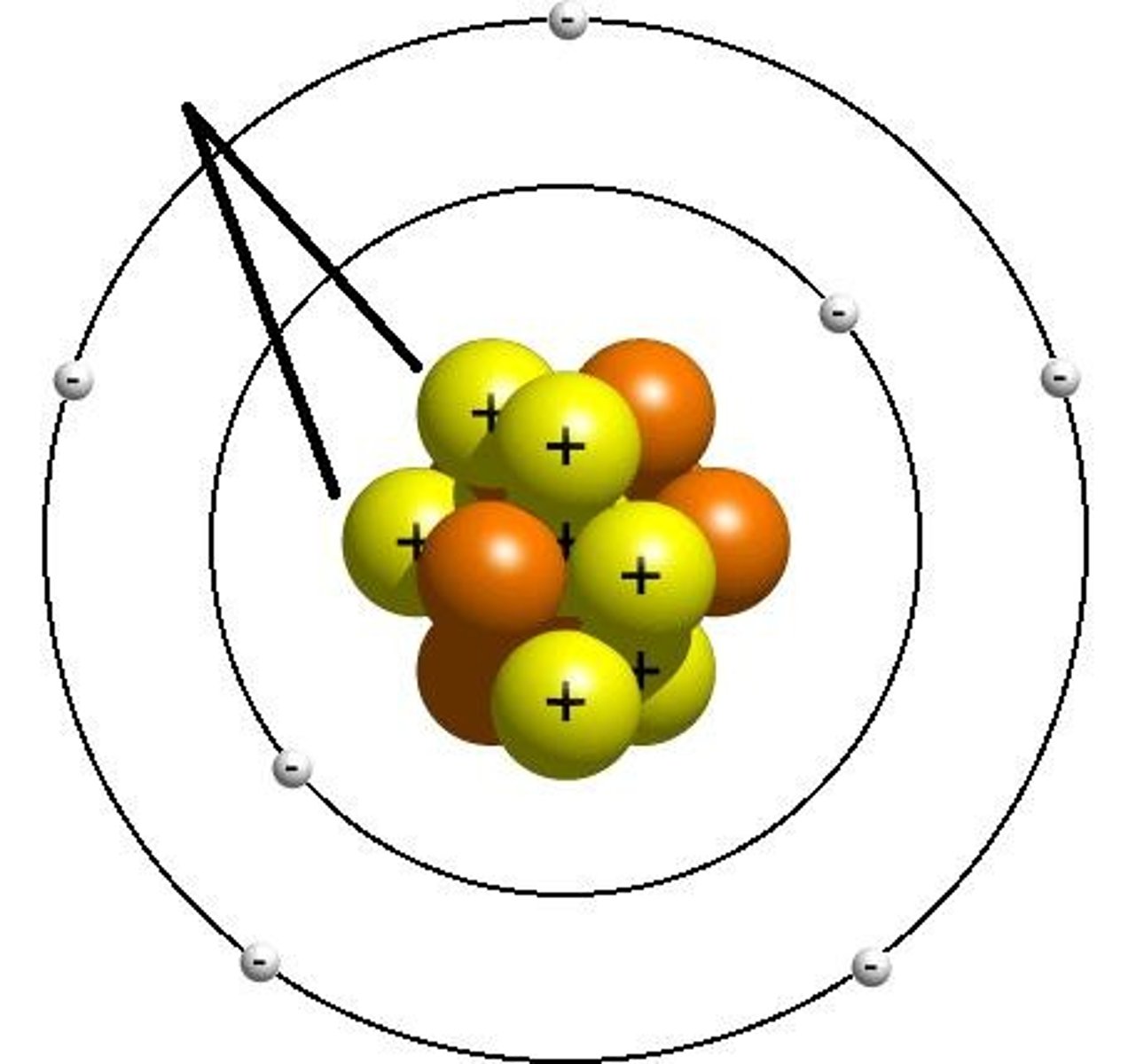
What are Protons?
Positively charged particles
found in the nucleus
What are Neutrons?
the particles of the nucleus that have no charge
What are Ions?
positively and negatively charged atoms
What are nonmetals?
elements that are brittle, lack luster, and do not conduct electricity (above the "stairs")
Become anions because they gain electrons
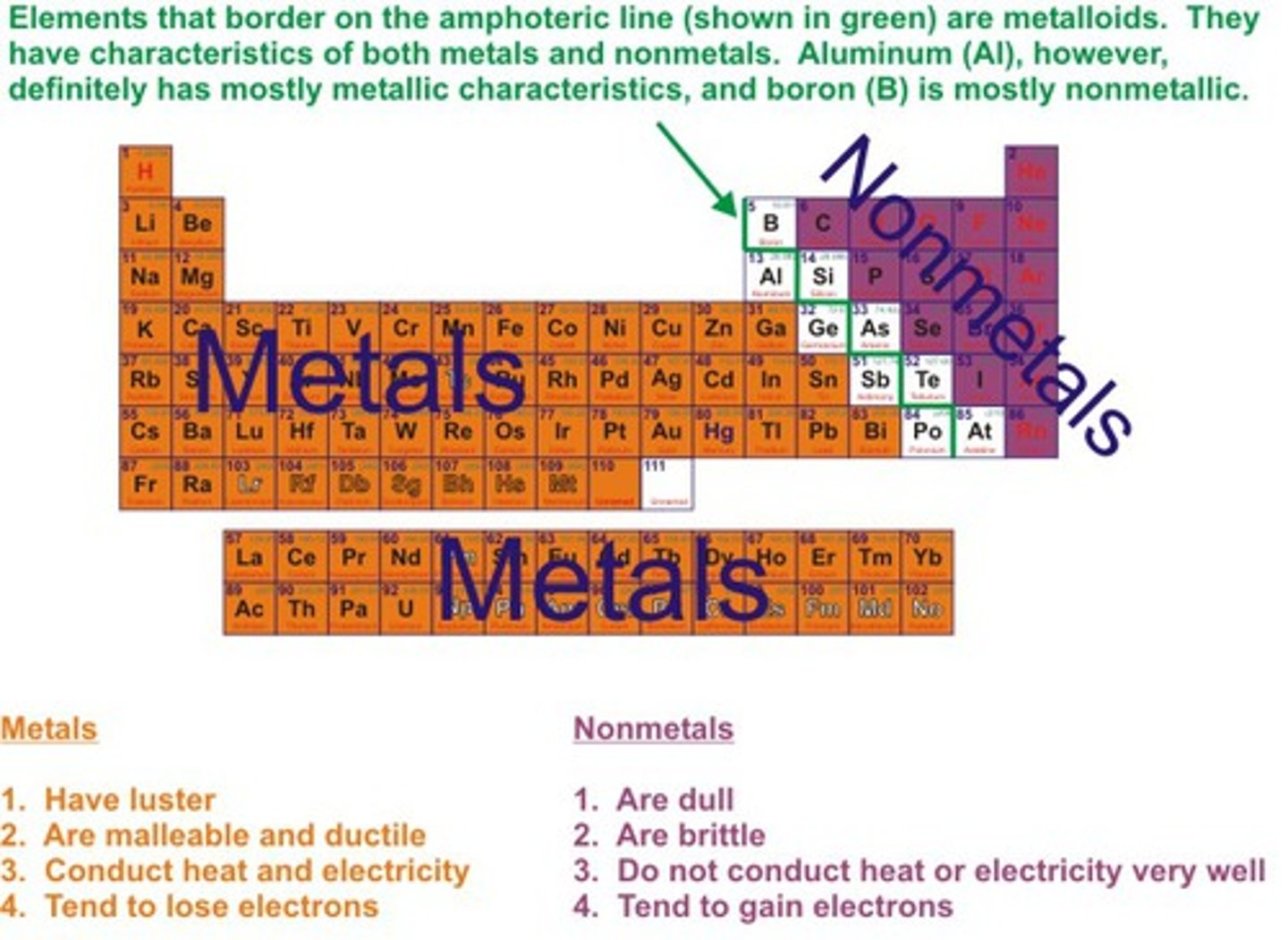
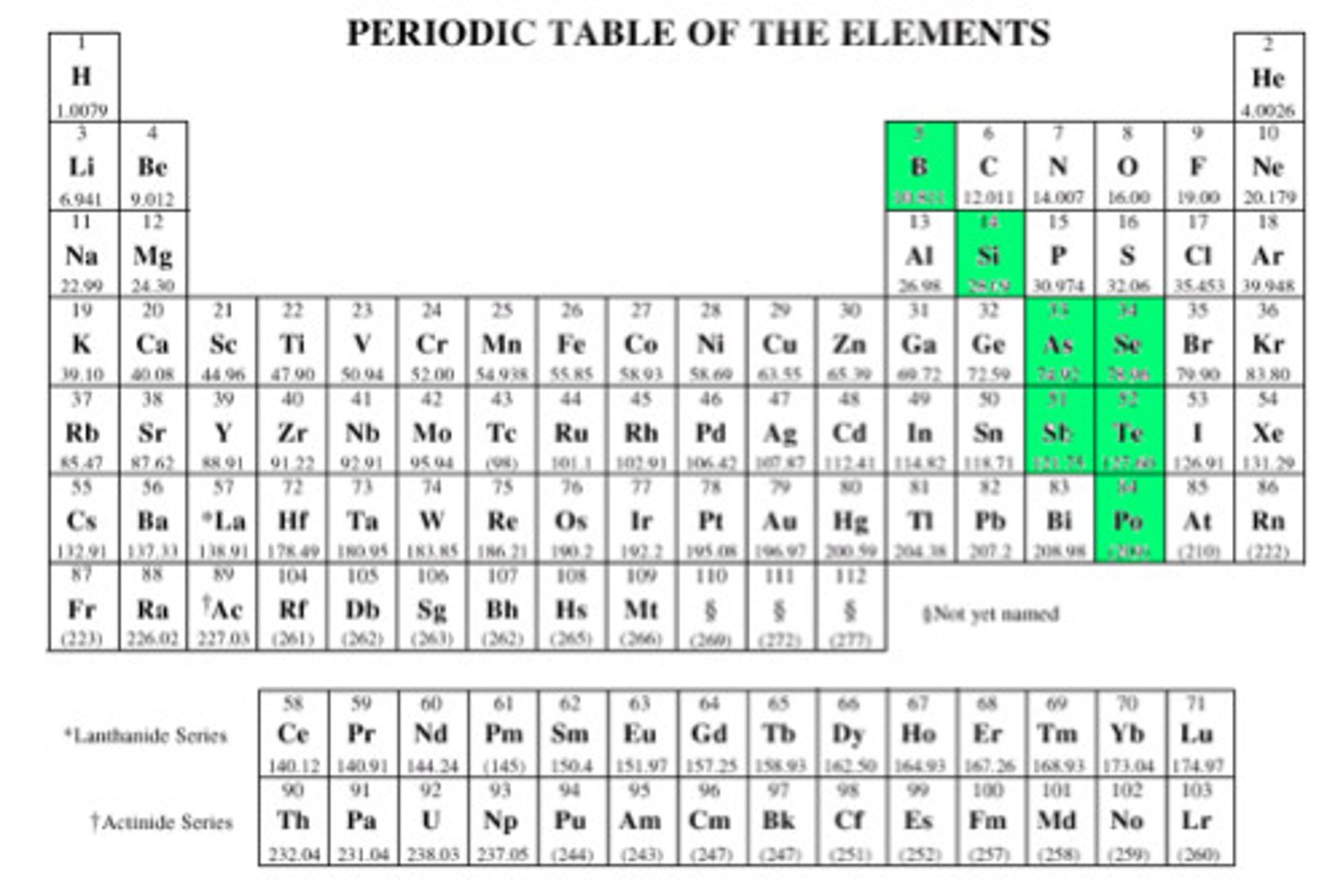
What are Metalloids?
Elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals. Live on the "stairs"
What is a compound?
substances that can be decomposed into elements by chemical means
What is the Law of Definite Proportions?
the proportion of elements in any compound is always the same

What are Dimensionless Quantities?
a quantity with NO UNITS of measure (units have cancelled out).
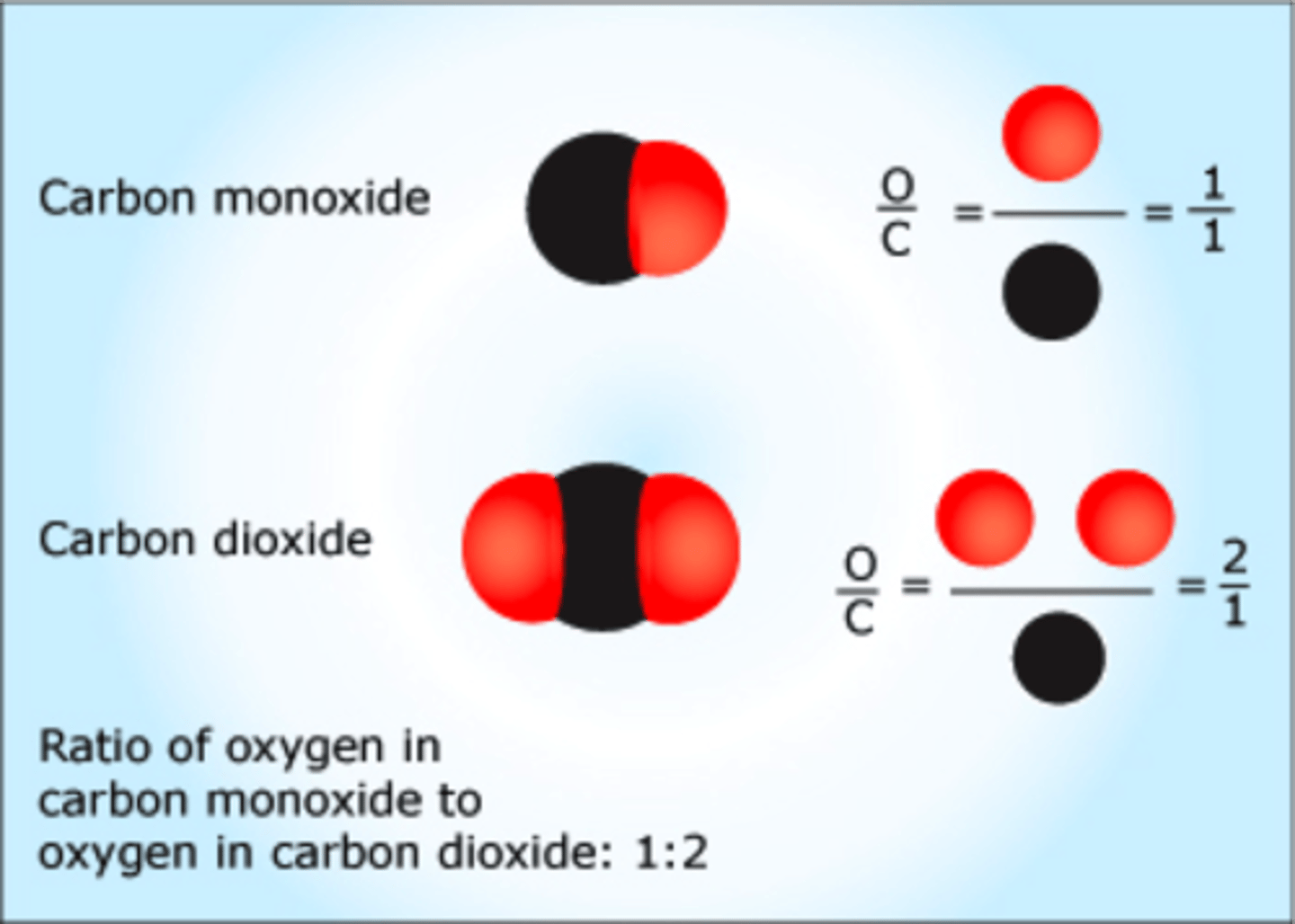
What is the Law of Multiple Proportions?
if two elements combine to form different compounds, the ratio of masses of the second element that react with a fixed mass of the first element will be a simple, whole-number ratio
Atoms of different elements have _______________
different properties
Atoms of different elements can only join together in what kind of ratios?
in simple, whole-number ratios
What are Molecules?
groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Can be same atoms (O2) or different atoms (CO2, H2O)
What are Compounds?
2 or more different elements chemically combined (H2O, CO2)
Identify as molecule or compound or both: C6H12O6 (glucose)
molecule AND Compound
Identify as molecule or compound or both: H2SO4 (sulfuric acid)
both: molecule and compound
Identify as molecule or compound or both: O3 (ozone)
molecule only
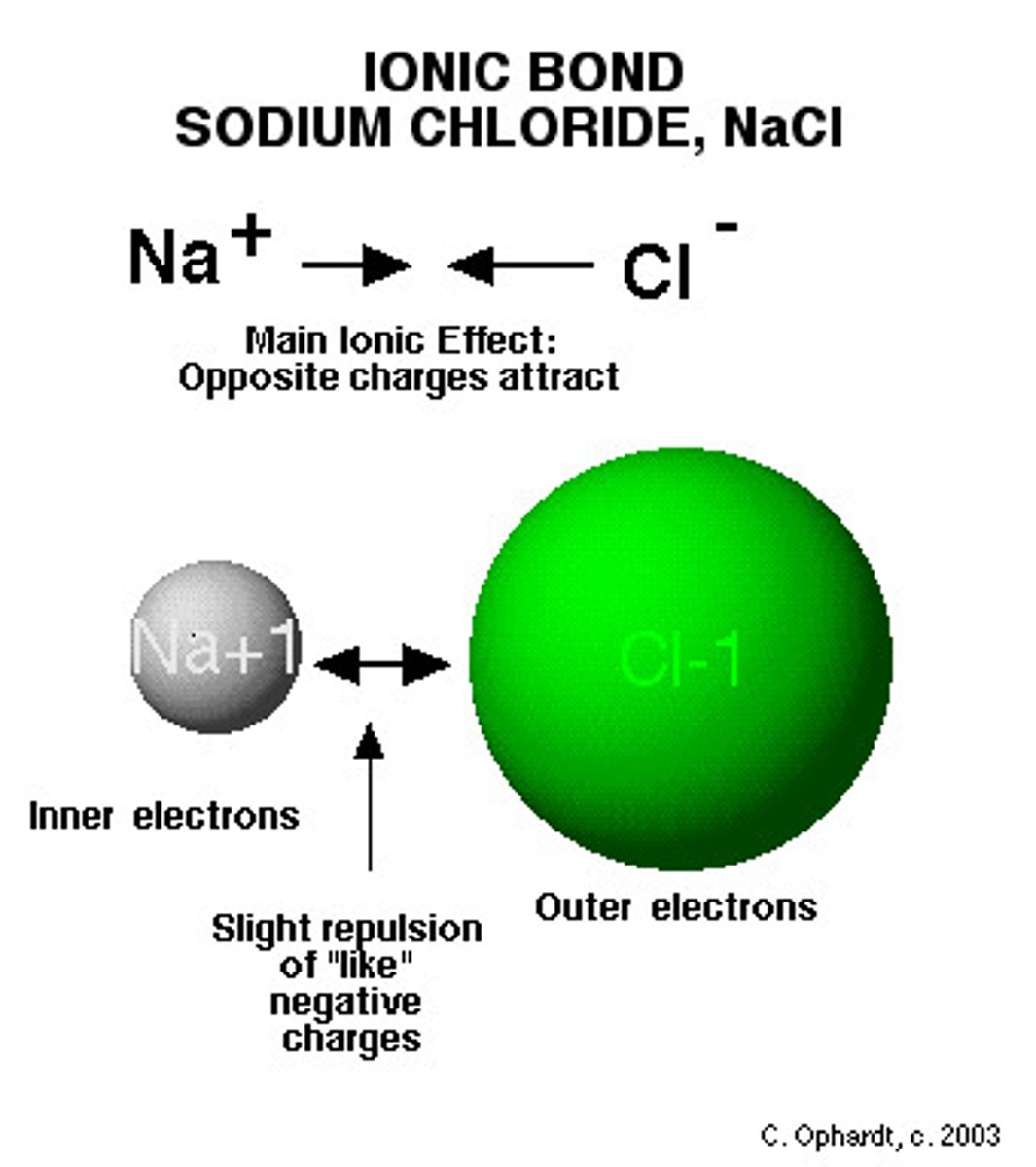
What is an Ionic Compound?
a substance that consists of at least 1 metal atom and at least 1 nonmetal atom; conducts electricity when dissolved in water. (opposites attract)
Electrons are TRANSFERRED so there is a charge.
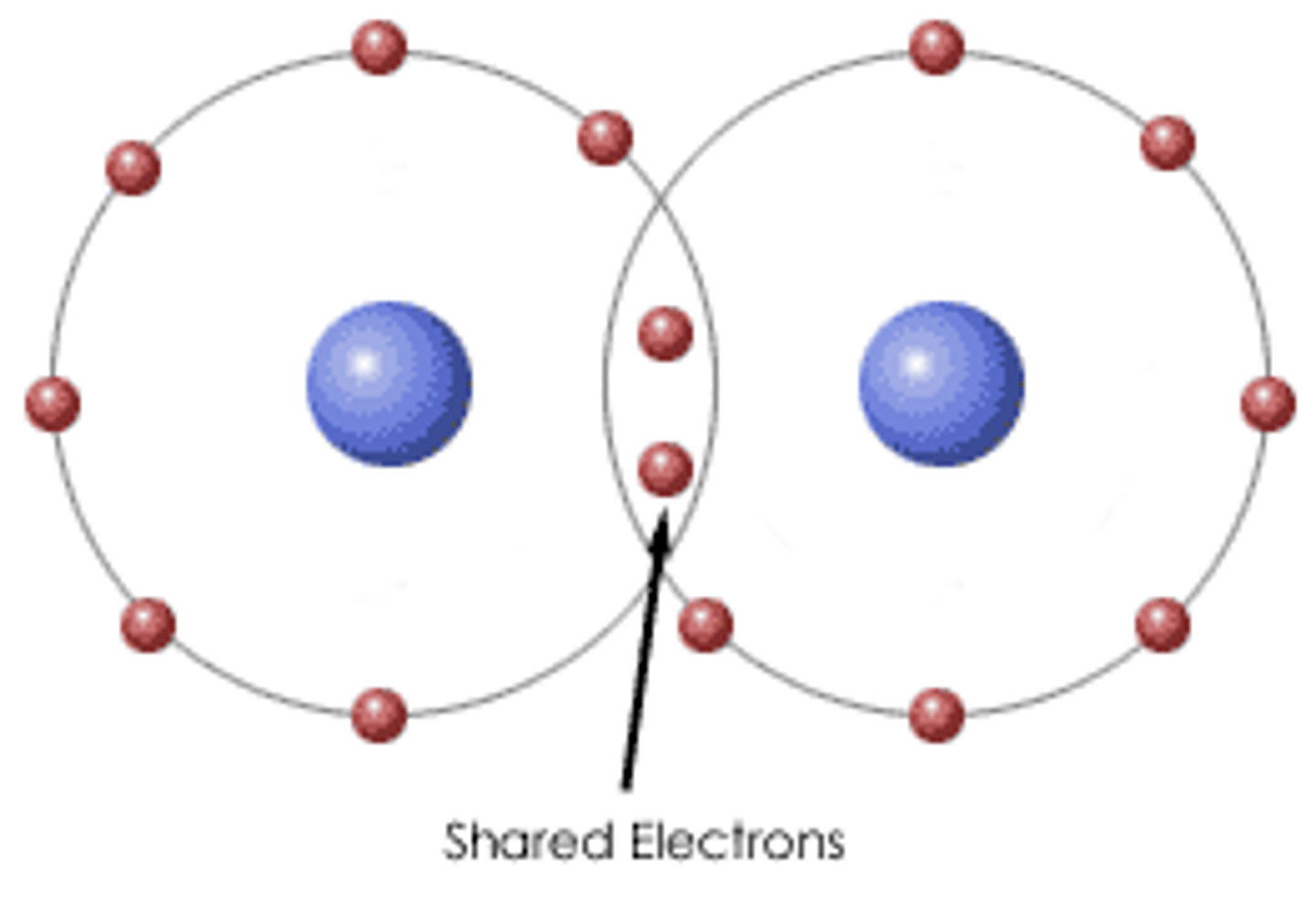
What is a Covalent Compound?
a substance that consists of solely nonmetal atoms; does not conduct electricity when dissolved in water
Electrons are SHARED, so there is hypothetically no charge.
How to name ionic compounds?
The name of the metal comes first, followed by the name of the nonmetal, changing the nonmetal's ending to "ide".

How to name covalent compounds?
add prefixes to elements and add -ide to the end of the anion
ionic compounds can have ____type(s) of possible molecules
one
What would be the -ide name of this non-metal? HYDROGEN?
hydride
What would be the -ide name of this non-metal? CARBON
carbide
What would be the -ide name of this non-metal? NITROGEN
nitride
What would be the -ide name of this non-metal? OXYGEN
oxide
What would be the -ide name of this non-metal? flourine
flouride
What would be the -ide name of this non-metal? phosphorus
phosphide
What would be the -ide name of this non-metal? sulfur
sulfide
What would be the -ide name of this non-metal?chlorine
chloride
What would be the -ide name of this non-metal? bromine
bromide
What would be the -ide name of this non-metal? iodine
iodide
How do we fix the fact that covalent molecules/compounds can come together in many different ways?
Add prefixes
What do we add when naming covalent compounds?
numerical prefixes
What number does the prefix mono indicate?
1
What number does the prefix di indicate?
2
What number does the prefix tri indicate?
3
What number does the prefix tetra indicate?
4
What number does the prefix penta indicate?
5
What number does the prefix hexa indicate?
6
What number does the prefix hepta indicate?
7
What number does the prefix octa indicate?
8
What number does the prefix nona indicate?
9
What number does the prefix deca indicate?
10
Name the 3 Steps to naming ionic compounds.
1) Start with the name of the first atom in the molecule
2) Replace the name of the next atom in the molecule with its -ide name.
3) Put the 2 names together
Identify as ionic or covalent and then Name this compound: NaCl
ionic, sodium chloride
Identify as ionic or covalent and then Name this compound:N2O3
covalent. dinitrogen trioxide
Identify as ionic or covalent and then Name this compound: SiF4
Covalent, silicon tetrafluoride
Identify as ionic or covalent and then Name this compound: CaCl2
ionic, calcium chloride
What is true of a homogeneous mixture?
it is always the same no matter what part of the sample is observed
What is true of a Pure substance?
a substance that contains only one element or compound
What is true of a heterogeneous mixture/?
the composition is different depending on what part of the sample is observed
Define: Mixture
a substance composed of at least 2 different compounds and/or elements
What is the difference between the continuous theory of matter and the discontinuous theory of matter?
The continuous theory of matter states that matter comes and long, continuous sheets. The discontinuous theory, however, assumes that matter comes in little packets and the only reason matter looks continuous is that we cannot magnifier enough to see the little packets of matter.
What two laws were instrumental in the development of Dalton's atomic theory? What law did Dalton predict using his theory?
The law of mass conservation and the law of definite proportions were instrumental in the development of Dalton's atomic theory. Dalton predicted the law of multiple proportions.
List the four assumption of Dalton's atomic theory. Which of the assumptions are wrong? Why?
Dalton's atomic theory assumed four things:
A. All elements are composed of small, invisible particles called Adams.
B. All Atoms of the same element have exactly the same properties.
C. Atoms of different elements have different properties.
D. Compounds are formed when Atoms are joined together. Since Atoms are invisible, they can join together only in simple, whole number ratios.
The assumptions that are wrong are a and B Adams are not truly invisible, and the mass of atoms can change within the element.
What are the physical characteristics that distinguish metals from nonmetals?
Metals are malleable, have a Lester, and conduct electricity. Nonmetals are bridle, lack luster, and do not conduct electricity.
How can you determine whether an atom is a metal or a nonmetal from the periodic table? Are there any exceptions?
A heavy, jagged line runs down the right side of the chart. If an atom (excluding hydrogen) lies to the left of that line, it is a metal. If it lives to the right of that line, or if it is hydrogen, it is a nonmetal. Hydrogen is the exception.
How can you determine whether a compound is ionic or covalent ?
If a compound has a metal in it, it must be ionic. It has no metals, it is covalent
Why do chemists use two different naming systems for compounds?
The way Atoms can join together is different between ionic and covalent compounds. And ionic compounds there is only one possible combination of atoms. In covalent compounds, many combinations are possible therefore we need to naming systems.
If a substance can be physically separated into its components, is it a pure substance or a mixture?
Anything that can be separated into its components must be a mixture. Compounds must first be decomposed before they can be separated into their component elements.
What element makes up the majority of the air we inhale?
Nitrogen makes up 78% of the air we breathe.
Why doesn't distilled water conduct electricity?
Distilled water does not conduct electricity because there are no charged particles in the water that can carry the electricity.
Classify the following as either a mixture or a pure substance:
A. Soil B. Silver C. Nitric acid, HNO3
D. Lemonade
Soil is a mixture. Silver is a pure substance. Nitric acid is a pure substance. Lemonade is a mixture.
What is the Hydrogen Problem?
Even though hydrogen is left of the jagged line, it is always considered a nonmetal.
Chemical Symbol
a one-, two-, or three-letter abbreviation of the name of an element
