Sexual Reproduction & Meiosis
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Last updated 5:56 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
1
New cards
sexual reproduction
is a type of reproduction in which the genetic materials from two different cells combine, producing an offspring
2
New cards
Where do Sex cells form?
reproductive organs
3
New cards
How many types of sex cells?
Two
4
New cards
What are the types of sex cells?
egg and sperm
5
New cards
What is the female sex cell?
Eggs
6
New cards
What is the male sex cell?
sperm
7
New cards
Fertilization
Fusion of an egg and sperm cell
8
New cards
After fertilization, what is the new cell that's formed is called?...
Zygote
9
New cards
What happens after fertilization?
A zygote goes through mitosis and cell division.
10
New cards
Mitosis and cell division produce nearly all of the cells in a __________?
Multicellular Organism
11
New cards
In the body cells of most organisms, chromosomes occur
in pairs
12
New cards
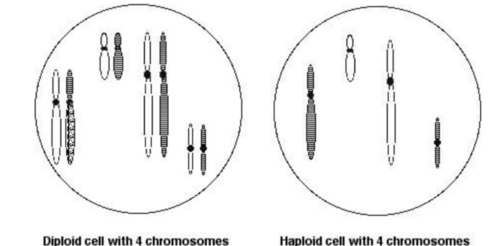
Cells that have pairs of chromosomes are called_____?
Diploid Cells
13
New cards
Organisms that reproduce sexually form two kinds of cells, what are they?
Body Cells & Sex Cells
14
New cards
In the body cells of most organisms, chromosomes occur in pairs. Cells that have pairs of chromosomes are called
diploid cells
15
New cards
Pairs of chromosomes that have genes for the same traits arranged in the same order are called
homologous chromosomes
16
New cards
Are chromosomes always identical?
No, because one chromosome is inherited from each parent
17
New cards
Different organisms have different numbers of
chromosomes
18
New cards
Human diploid cells have ____ of chromosomes
23 single
19
New cards
Human diploid cells have a total of (how many) chromosomes.
46
20
New cards
What happens is a zygote has too many or too few chromosomes?
It will not develop properly
21
New cards
What does the process of meiosis help do?
Maintain the correct number of chromosomes
22
New cards
What happens if a mistake occurs in animal cells?
Sometimes the zygote dies. But if it lives, every cell in that organism will have the wrong amount of chromosomes and may not grow normally.
23
New cards
What does a person with down syndrome have?
An extra chromosome.
24
New cards
Organisms that reproduce sexually also form ...
egg and sperm cells, or sex cells
25
New cards
Sex cells have (how many chromosomes) from each pair of chromosomes.
1
26
New cards
Haploid cells
cells that have only one
chromosome from each pair.
chromosome from each pair.
27
New cards
Meiosis
Organisms produce sex cells using a special type of cell division
28
New cards
What happens in meiosis?
one diploid cell divides and makes four
haploid sex cells.
haploid sex cells.
29
New cards
Meiosis occurs only during the formation of?
sex cells
30
New cards
Mitosis and cytokinesis involve ____
division of the _____ & _____
division of the _____ & _____
one; nucleus and cytoplasm
31
New cards
Meiosis involves ___divisions of the ___ & ___
Two; nucleus and the cytoplasm.
32
New cards
The two divisions in meiosis are phases called...
Meiosis I & Meiosis II
33
New cards
Meiosis results in how many haploid cells
four
34
New cards
Meiosis results in (#) haploid cells, each with (?)
the number of chromosomes as the original cell.
the number of chromosomes as the original cell.
4; half
35
New cards
A reproductive cell goes through interphase before beginning which phase?
Meiosis I
36
New cards
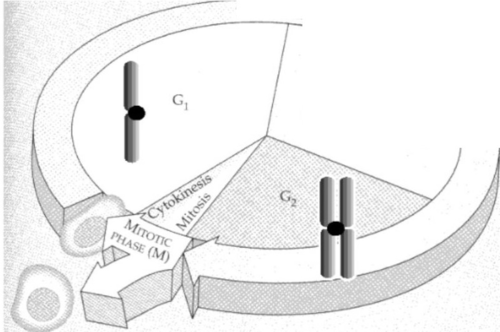
What happens during interphase?
the reproductive cell grows and copies, or duplicates, its chromosomes.
37
New cards
Each duplicated chromosome consists of (#?) sister ___ joined by a ___
2 - chromatids - centromere
38
New cards
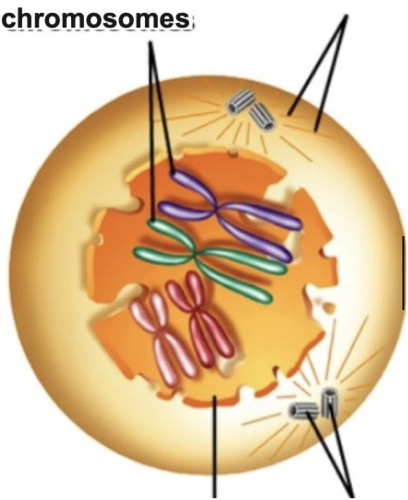
What happens during prophase I
duplicated chromosomes condense, or shorten, and thicken.
39
New cards
Homologous chromosomes
come together and form pairs
40
New cards
During the meiosis I prophase, the membrane around the nucleus does what?
Breaks apart and the nucleolus disappears
41
New cards
What does a cell go through before beginning meiosis I
Interphase
42
New cards
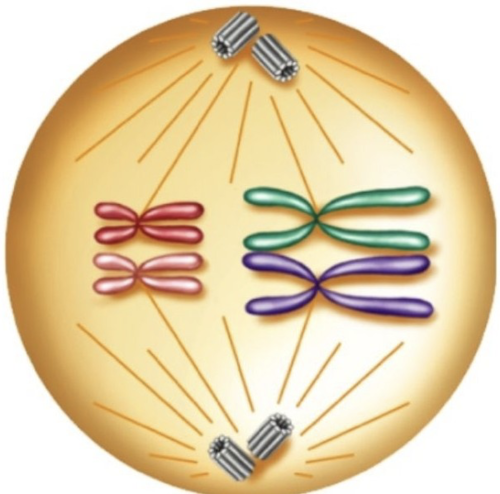
What happens in metaphase I ?
homologous chromosome pairs line up along the middle of the cell.
43
New cards
What happens during anaphase I
Chromosome pairs separate and are pulled toward opposite ends of the cell. The sister chromatids stay together.
44
New cards
What happens During telophase I
-A membrane forms around each group of duplicated chromosomes.
-The cytoplasm divides through cytokinesis, and two daughter cells form.
-Sister chromatids remain together.
-The cytoplasm divides through cytokinesis, and two daughter cells form.
-Sister chromatids remain together.
45
New cards
During which phase does sister chromatids remain together?
Telophase I
46
New cards
What happens to chromosomes before prophase II ?
chromosomes are not copied again before prophase 11. They remain short and thick sister chromatids.
47
New cards
What happens during prophase II?
the membrane around the nucleus breaks apart, and the nucleolus disappears in each cell.
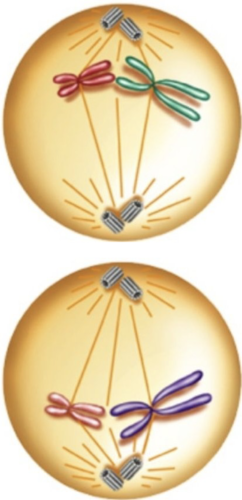
48
New cards
What happens during metaphase II?
The chromosomes (sister chromatids) line up along the middle of the cell in single file
49
New cards
What happens during anaphase II?
The sister chromatids of each duplicated chromosome are pulled apart then they move toward opposite ends of the cells
50
New cards
What is the final phase of meiosis?
Telophase
51
New cards
what happens during telophase II?
-a nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromatids.
-The chromatids are again called chromosomes.
-The cytoplasm divides through cytokinesis, and four haploid cells form.
-The chromatids are again called chromosomes.
-The cytoplasm divides through cytokinesis, and four haploid cells form.
52
New cards
What phase is this?
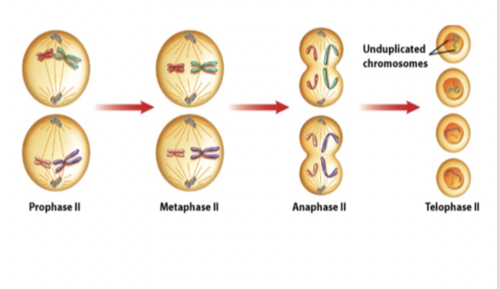
53
New cards
Review: Meiosis Phase II
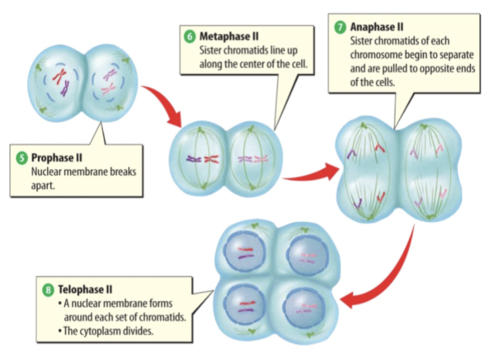
54
New cards
List 3 reasons why meiosis is important
1. Meiosis is important to sexual reproduction.
2. It forms the correct haploid number of chromosomes.
3. This maintains the correct diploid number of chromosomes in organisms when sex cells join.
4. Leads to genetic variation
2. It forms the correct haploid number of chromosomes.
3. This maintains the correct diploid number of chromosomes in organisms when sex cells join.
4. Leads to genetic variation

55
New cards
Review: Differences between mitosis and meiosis
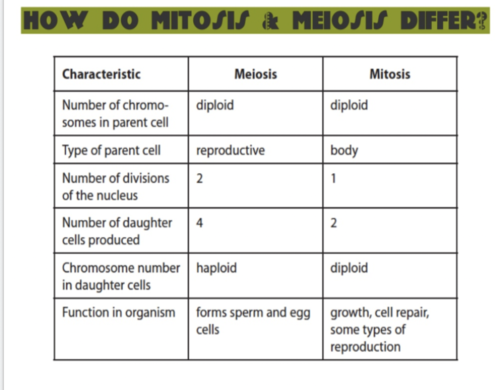
56
New cards
Review: Creating Haploid Cells
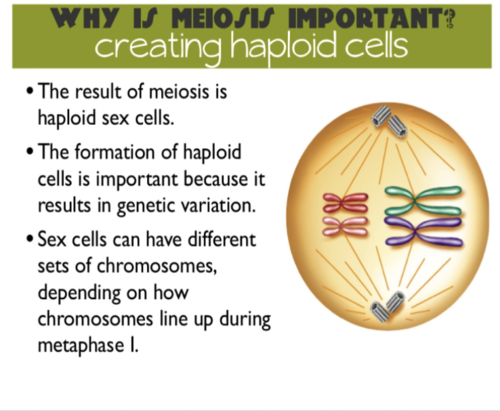
57
New cards
Review: Advantages of sexual reproduction

58
New cards
Review: Genetic Variation II

59
New cards
Review: Genetic Variation

60
New cards
Review: Disadvantages of sexual reproduction
