UNIX terminal
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
zip files
bunch of files zipped and stored in another file
what does this code do:
unzip “file.zip”
unzips said file
unique features of autocomplete on unix systems
after the file name, if:
there is a space and the reader does not blink, it suggests completed file name
if there is no space and the reader blinks, it suggests incomplete file name
describe the unix directory system
Files and directories (folders) organized hierarchically
Root directory: "/" (base of the entire filesystem)
Single unified hierarchy for the whole system
what do these directories mean on unix?
Working directory
Parent directory
Subdirectories
Working directory: Your current location
Parent directory: Contains the current directory (..)
Subdirectories: Contained within the current directory
what are the 3 path (location of directory/file) types on unix?
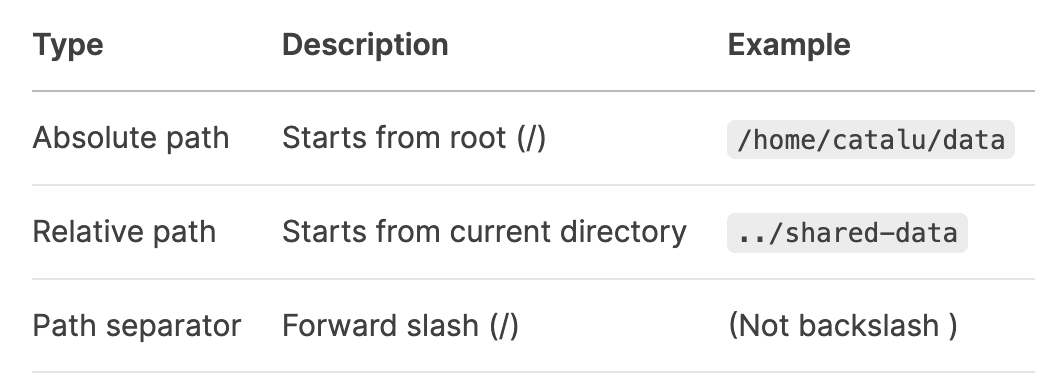
what are the meanings of each of these symbols?

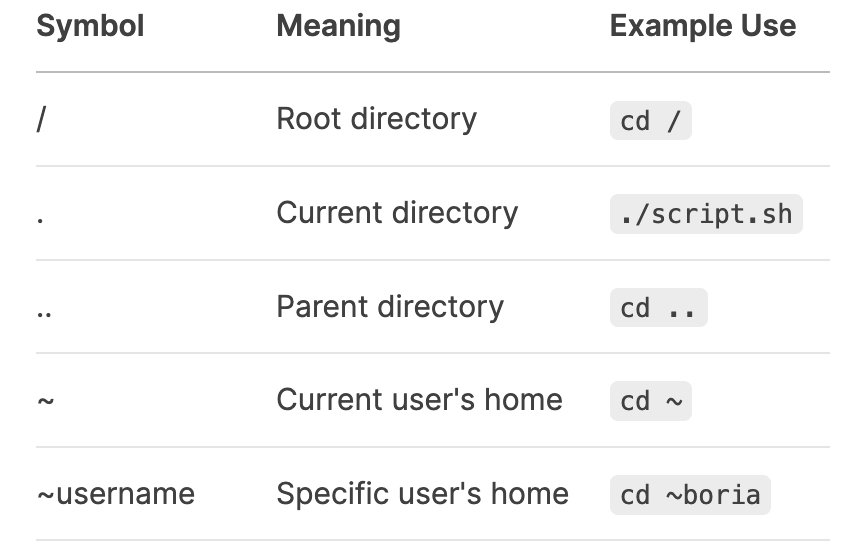
what is the use of these core system directories?
/boot
/bin, /sbin
/lib
/etc
/dev
/proc, /sys
/boot: Boot loader files
/bin, /sbin: Essential system binaries (user/admin commands)
/lib: Shared system libraries
/etc: Configuration files
/dev: Device files
/proc, /sys: Virtual filesystems for system/process info
what is the use of these user & program directories
/usr
/usr/bin
/usr/local
/usr/lib
/opt
/home
/root
/usr: Installed software (secondary hierarchy)
/usr/bin: User executables
/usr/local: Locally installed programs
/usr/lib: Libraries for /usr programs
/opt: Optional/add-on software
/home: User home directories (except root)
/root: Root user's home
what is the use of these variable & temporary data; and some special/mount points
/var
/var/log
/var/cache
/tmp
/rmt
/mnt
/var: Dynamic files (logs, caches, etc.)
/var/log: System logs
/var/cache: Application cache
/tmp: Temporary files (auto-cleaned)
/rmt: Removable media mount point
/mnt: Temporary mount points (common alternative to /rmt)
wget command
downloads a file from the internet
types the address (URI) into the terminal
ls command
list
show the contents of a directory
mkdir command
mkdir = make directory
makes a subdirectory
cd command
cd = change directory
allows users to navigate between directories in the UNIX file system
pwd command
print working directory
displays the current directory path
what does this do:
mv ../file_name .
mv ../file.txt ../file2.txt .
mv = move
. “dot” = current directory
.. “2 dots” = parent direcotry
so this moves the file_name from the parent directory to the current directory
second one moves both files to current directory from parent directory
mv old-name new name
renames files and directories
cp command
cp = copy
copy files rather than move
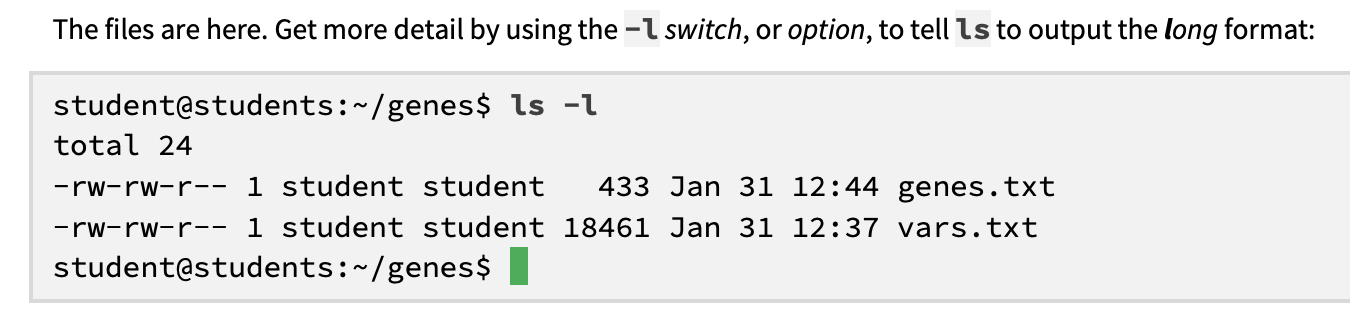
ls -l (LS -L for clearer)
the -l switch tells ls to output the long format
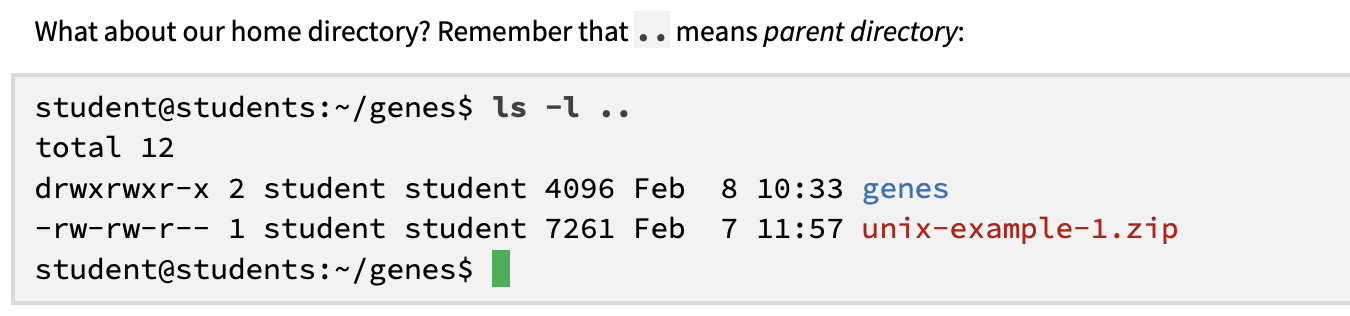
ls -l ..
.. “dot dot” = parent directory
the attributes of in ls:
d =
a leading dash (-) =
l on first position =
permission types (3)
permission groups (4)
d = directories
a leading dash (-) = regular files
l on first position = soft link

explain what these codes are doing
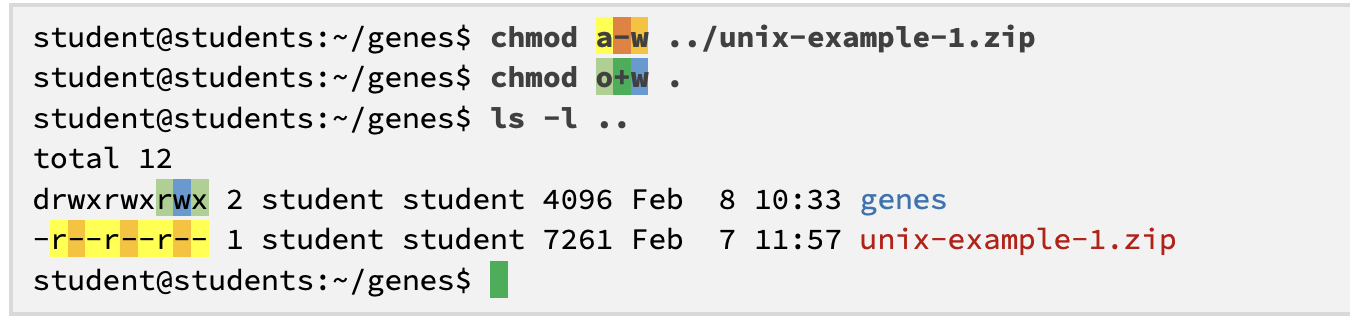
chmod = change permission of files and directories, controlling who can read, write and execute them

-R switch
applies changes (change permission of files and directories) recursively, to a directory and all its subdirectories and enclosed files
commands that change ownership of files and directories
chown command
chgrp command
chown
changes the user who owns them
not useful for non-privileged users
chgrp
changes only the group
makes files available to a specific group
groups command
whoami command
groups
see which groups you’re in
if your sysadmins (system administrator) creates a group for each project
whoami
shows the username of the current logged-in user
cat command
cat = concatenate
shows the contents of a file
if given more than one file, outputs contents of all of them one after another
tab-separated text file
one data record per line
each line containing the same number of fields in the same order, fields separated by a tab character
sometimes there’s a header
first line of the file that describes the fields of the records
often begins with hash (#) or semicolon (;)
tabs
tab = tabulate
standare tab stops at every eighth column
column position that is a multiple of eight
if fields are longer than 8 columns, the tab will go to the next ab stop
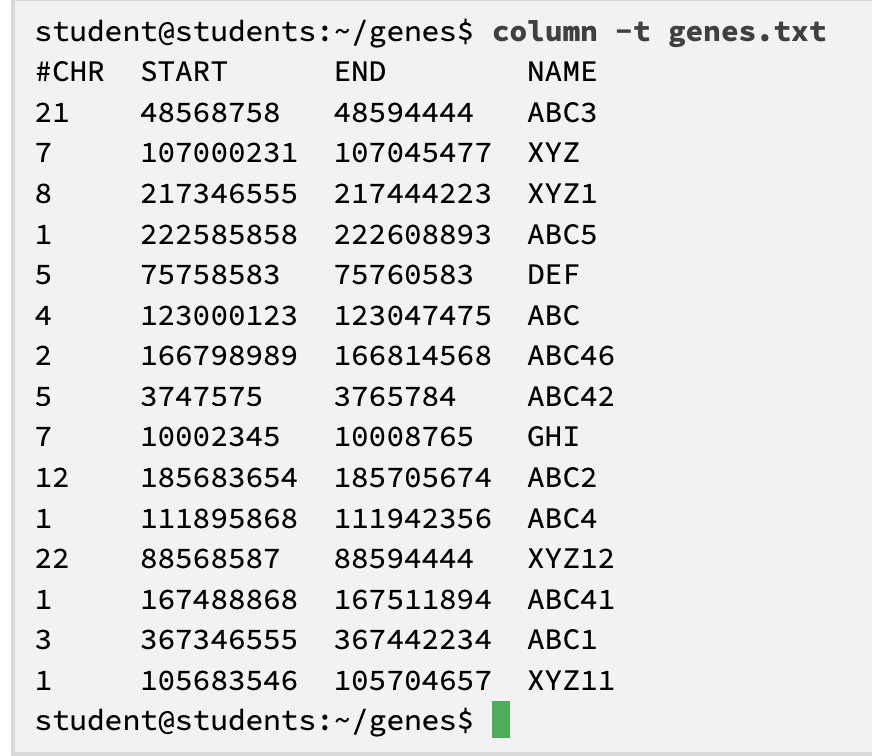
column -t command
a tool for humans
replaces tabs with spaces so that the table is readable
displays multiple columns in a formatted table
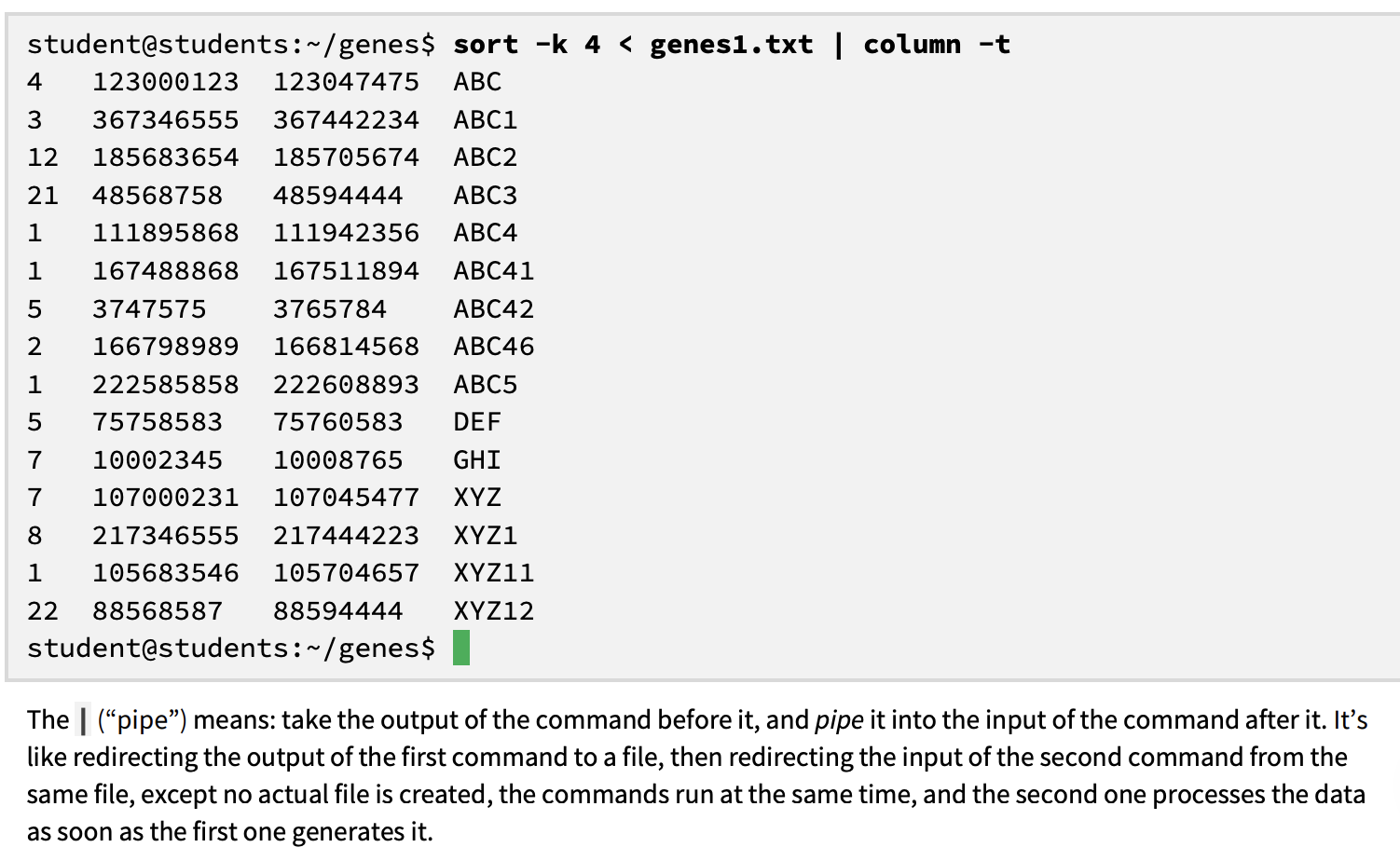
sort command
sorts text lines
by default sorts lexicographically (as in a dictionary: by the first character; if that’s the same, then by the second character, and so on)
ignores non-printable characters (including tabs) → does not work well for numbers
what does this code do

grep
global regular expression print
finds lines that contain specific text
-v = reverse
““ for texts
^ = at the beginning of a line
finds lines that DO NOT contain the # character at the beginning of the line
basically removes the header
what does this code do

-k option
the sort key
tells sort that a key needs to be sorted in numeric order
can sort by more than one key as well
here it sorts first by the first field, numerically; then by the second field, also numerically
the | “pipe” command
takes the output of the command before it, and pipe it into the input of the command after it
redirects the output of the first command on a file, and redirect the input of a second command from the same file
no new file is created
rm command
eg
rm genes?.txt
rm genes[12].txt
rm genes{1,2}.txt
rm genes*.txt
rm = remove
deletes files
the question mark matches any one character (any files with the same name with anything for ? will be deleted)
[12] = the brackets match any one character in that set
{1,2} = the braces match any one of the comma-separated alternatives within
* = matches any sequence of characters, including none at all (so even genes.txt would be deleted)
head command
-n switch
tail command
what do these output:
head -n 15
head -n -2
tail -n 5
tail -n +3
head: outputs first 10 lines of the files
-n: changes the number of lines
tail: outputs last 10 lines of the file
output:
-n 15 = first 15 lines
-n -2 = all but last 2 lines of the file
tail -n 5 = last five lines
tail -n +3 = all lines from the third line (skips the first 2 lines)
less command
q command
h key
-S command
wc command
less = inspects the entire file
q = quite the entire file view
h = shows a list of commands
-S = turns off line wrapping and enables lateral scrolling
wc command
wc -l
wc = word count, outputs the number of words in input
wc -l = counts the number of lines
ctrl-D
ctrl-C
ctrl-V
ctrl-D
D = end
signals end of input, causing programs to terminate or complete input.
ctrl-C
C = cancel
interrupts a running process or command
ctrl-V
V = verbatim
so that you can search for texts following a tab character
its all ABC instead of ABC1 ABC3, etc
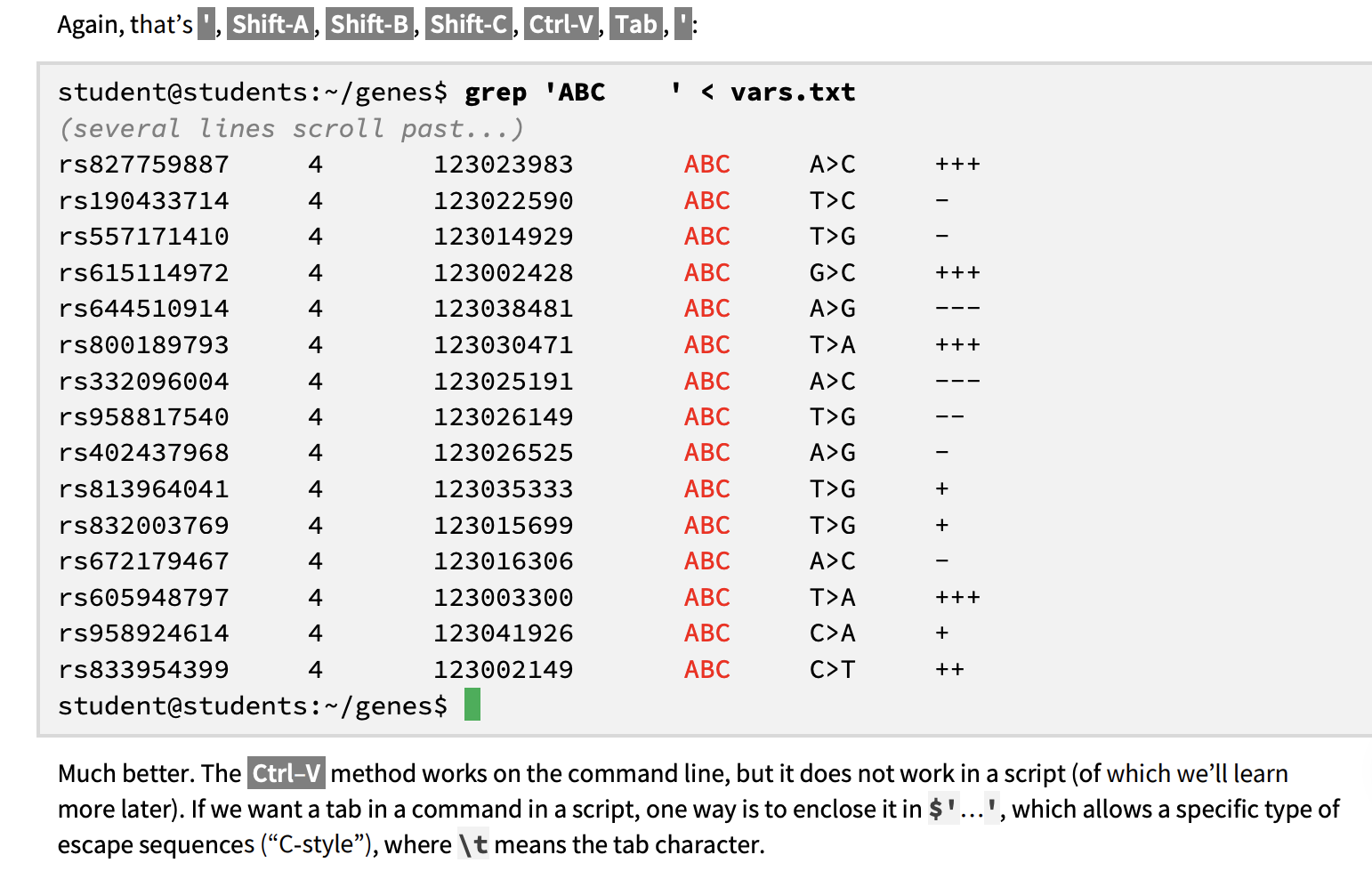
$’…’ command
\t

$’…’ encloses a command that has a tab
\t means the tab character
what does this code do

asks for ABC followed by a character that’s not (^) a letter (A-Z) nor a number (0-9)
what does this code do

\b = word boundary
also searches for ABC with nothing following
but this means something BEFORE might appear in the output
so use ‘\bABC\b’ instead
USE SINGLE QUOTES
what is the problem with this code

a new file would be made called G
it is the same as:

what does this code do

the \ tells shell not to interpret > as a special character
what does this code do:

awk
splits input lines into fileds (columns?)
$1 first field
$2 second field etc
executes the print command for each line of input
{} braces are a required part of the syntax
each print generates one line of output
what does this code do:

here, awk separates the fields with tabs instead of spaces (default)
-v = assign variable
OFS = output field separator
‘\t’ = literal tab character
what does this code mean:

why not use awk?
cut -f 5 = keep the fifth field
eg cut -f 1-3,5 keeps fields 1,2,3,5 (NO SPACE BEFORE AFTER COMMA)
if we do not need to change the order of fields, it is easier to use cut
tab can use tabs or spaces as field separators
cut assumes tabs
what does the -d command do when used with cut
cut strictly only uses tabs as separators
to split on spaces, the -d option helps specify the delimiter explicitly

what does this code do
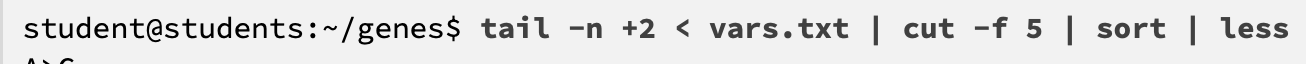
removes the header (displays from 2nd row)
only shows 5th field
sorted
less means more (shows everything)
uniq command
uniq and sort combined
-c switch
uniq = unique
removes consecutive duplicated lines in its input
uniq and sort combined
shows a list of all distinct (unique) lines in the input, with all duplicates removed
-c
tells uniq to count the occurrences of each distinct line
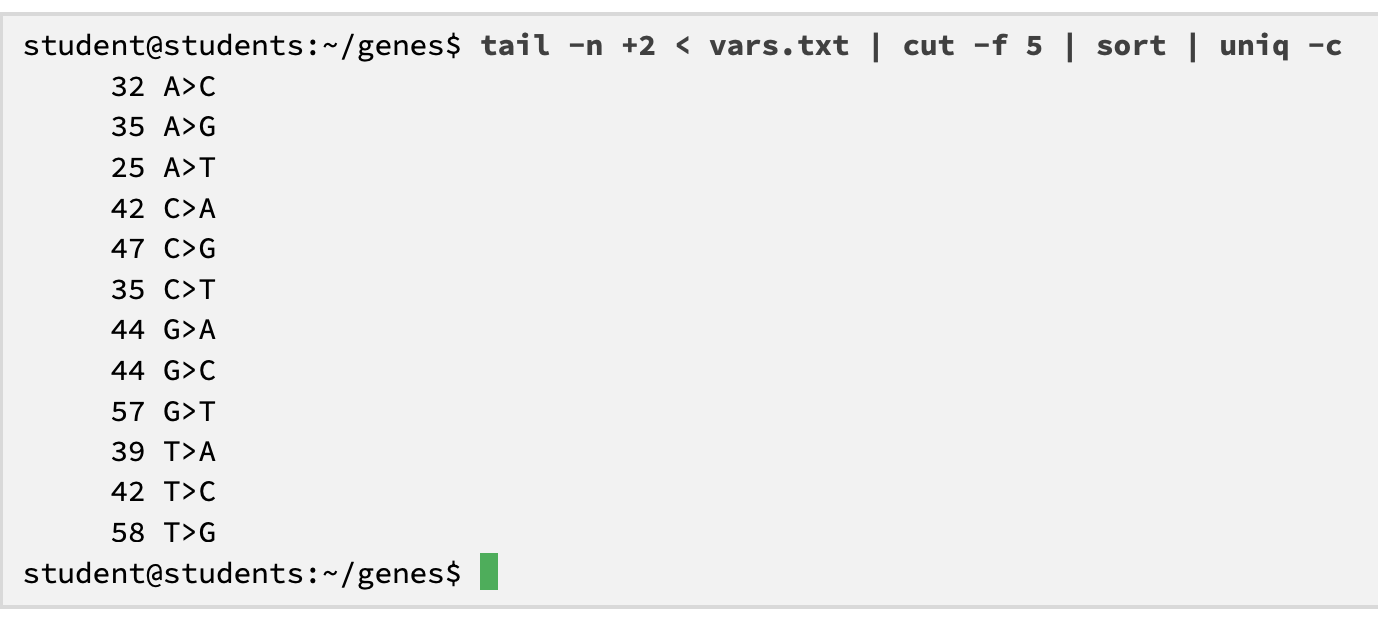
what does this code do:

removes header
filters for the lines that include +
only display 4th column
sorted
counts the number for each unique (removes duplicated)

what does it mean when the last character of a line is \ (backslash)
the command continues as if the line hadn’t ended
continuation prompt

what does this code do

removes header
sort by 4th column
into new file genes2.txt
organise by column -t: replaces tabs with space
what is the sed program
explain the substitute command
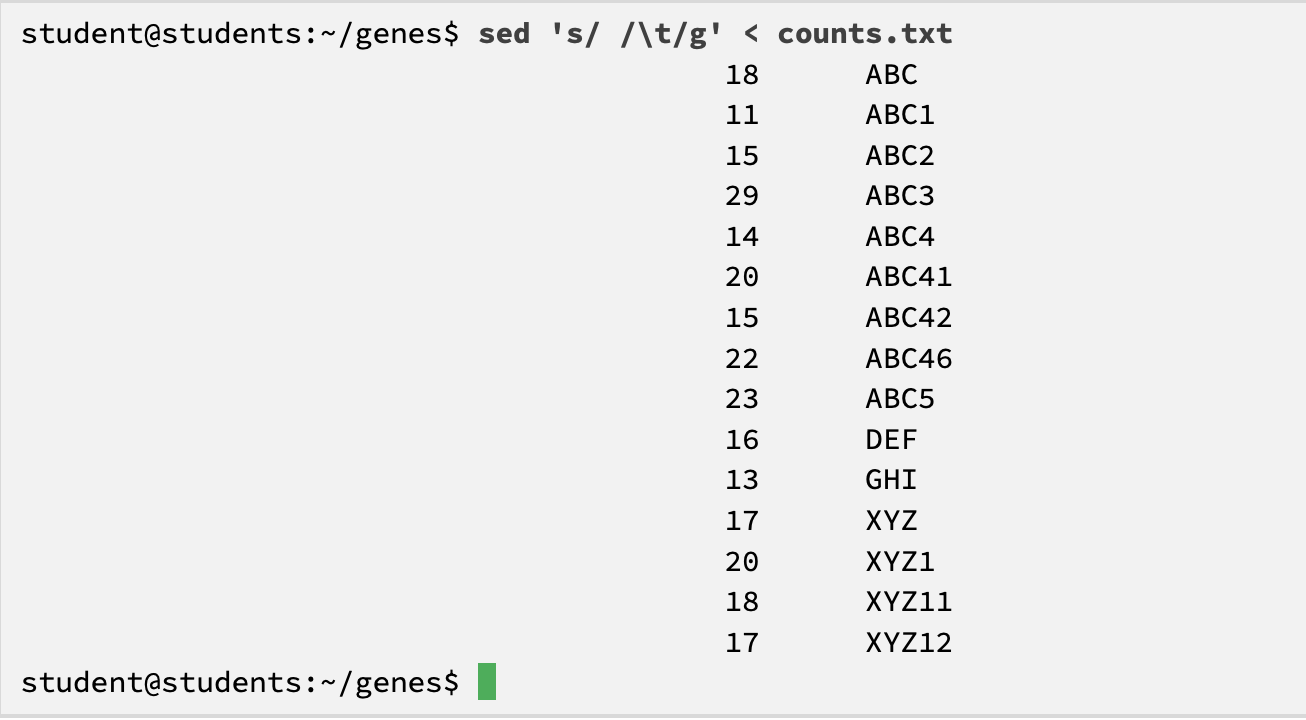
sed = stream editor
substitute command
s/old/new
finds first occurrence of old (the space) in each line and replaces it with new (the tab)
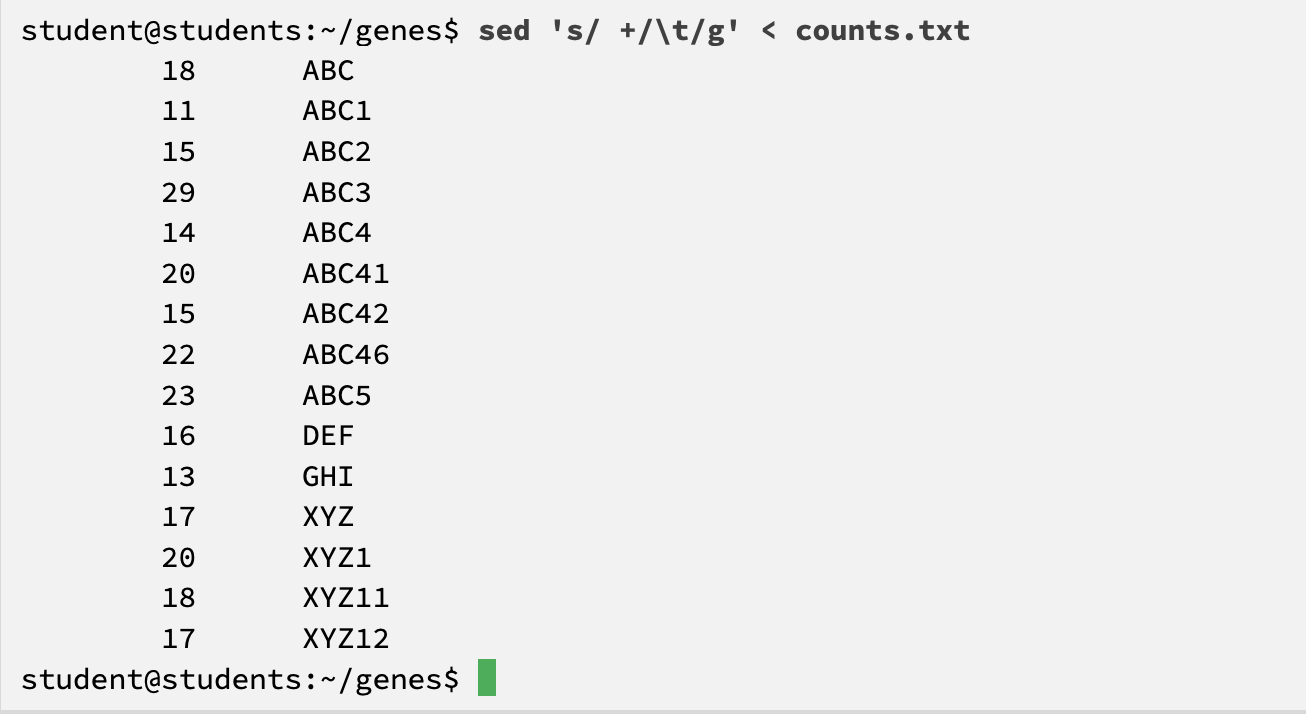
g option (global)
find adn replace all occurrences in each line
the + means what’s immediately before it (here it is a space)
what does this code do



anything that starts (^) with a space, ends with anything (*), replace it with nothing
replace the remaining space with a tab
what does this code do:
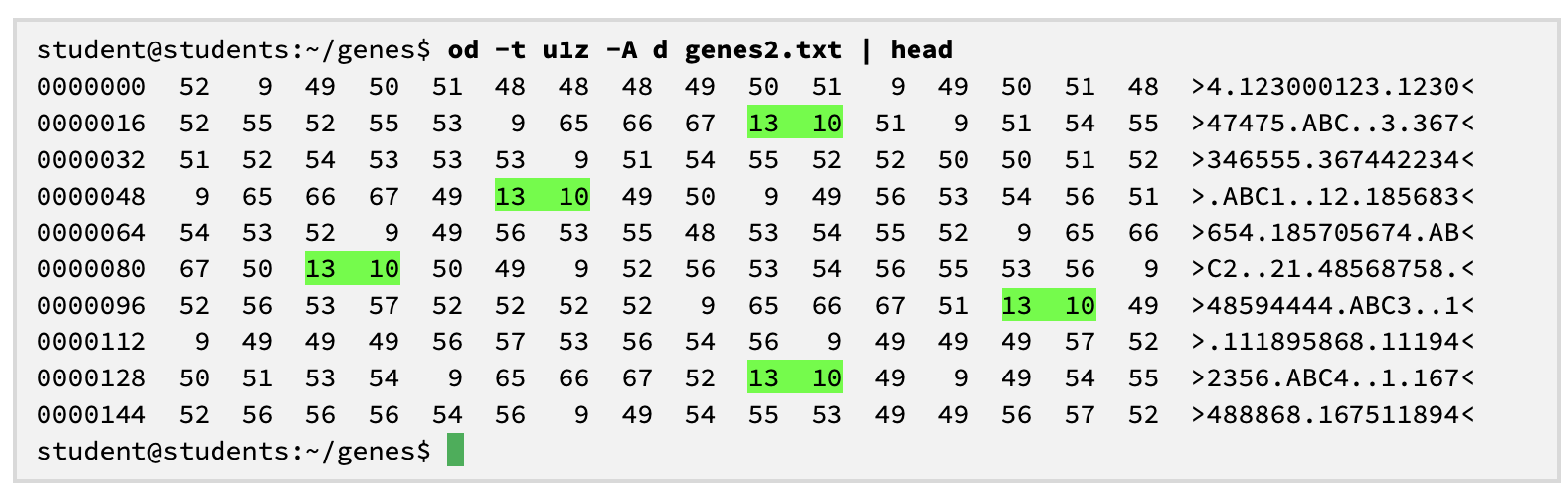
od = octal dump
octal = 8
dump = show content raw without any processing
-t u1z
use a different format
print the unsigned decimal values (u) of every byte (1)in separate column (z)
-A d
tells it to display the position within the file (the address) as a decimal number
basically, it shows that the file contains a character code 13 followed by a 10 after each line (Windows-stye newlines), we would need to remove the carriage returns using sed
what does this code do

join command = merges 2 files, where a given field has the same value in the 2 files
lines from one file where the respective field does not have a match in the other file are normally discarded
-1 option: selects field from the first file
-2 option: selects field from the second file
so the output should be that the lines are merged where both files share the same values in the specified fields
what does this code do:

echo = outputs what it’s told
-e switch tells it to interpret escape sequences
example of escape sequences:
what is the difference between > and »
>
redirects the output of a command to a file
overwrites the file if it already exists
>>
appends to an existing file, preserves its contents
if the file does not exist, both operations create it
what does this code do
history
displays recently used commands
the output of history can be redirected into a file, creating a shell script (a list of commands in a text file)
what does the this code do:
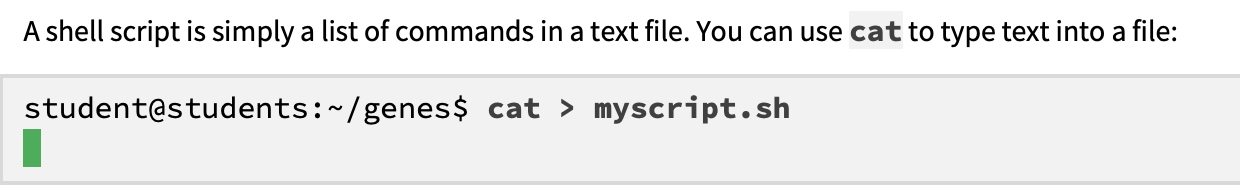
Cat = copies standard input (keyboard) to standard output (redirected to
myscript.sh).press
Ctrl-Dto end inputlimits:
no editing after typing; requires perfect input.
for modifications, use a text editor (e.g.,
vi,nano,tile).
name the 4 unix text editors, how to exit them, and their characteristics

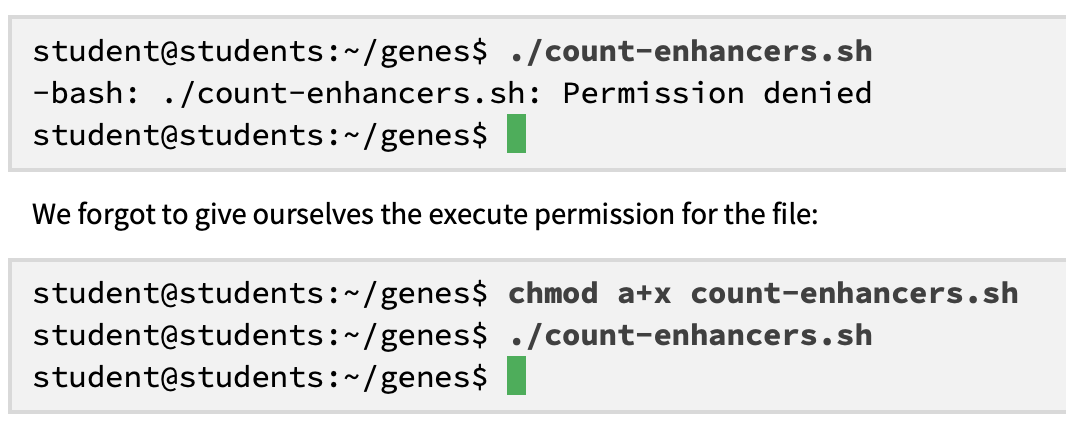
why may unix dispaly “command not found”
cause:
Unix systems search for commands only in directories listed in the
PATHvariable.The current directory (
.) is not included by default.
solution;
explicitly specify the script’s path
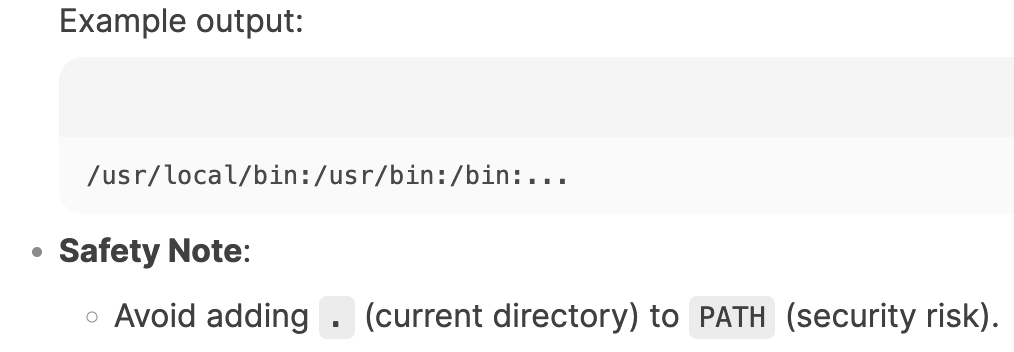
what does the PATH environment variable do?

list directories where the system looks for executable commands
what does this code do:

what does this code do:

creates/assigns a variable name
what does this code do
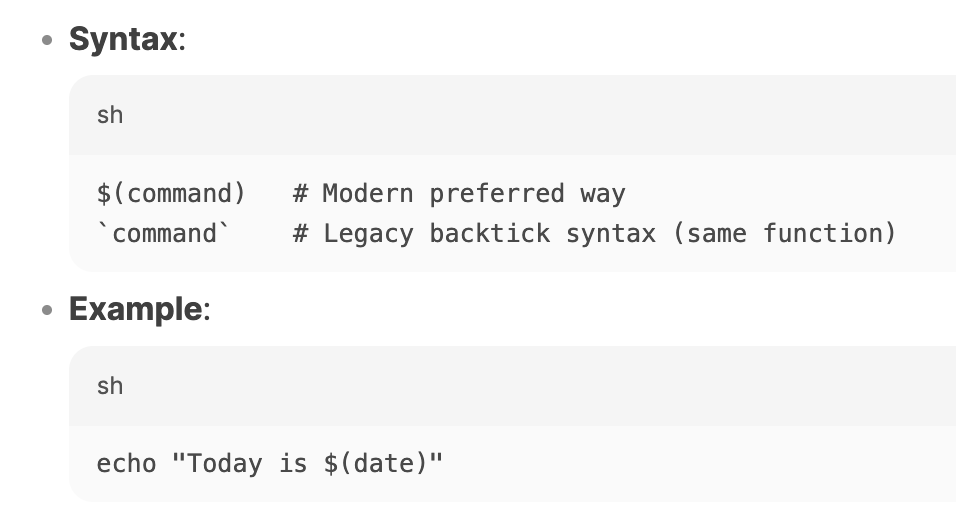
command substitution
executes the command and is replaced with the output of the command
what does this code do

arithmetic expansion
tells the shell to do arithmetic
replaced by the value of the expression
what are the quoting rules in echo

what does this code do
shebang (hashbang) #!
specifies the interpreter for a script


use the #!/bin/bash shebang for consistent arithmetic handling
what are the different shell types in echo

grep -c command
counts matching lines (instead of displaying them

what’s the difference between hyphen and en dash
