CH. 3 ~ By the People ~ Debating American Government Third Edition Chapter 3
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Diffusion
The spreading of policy ideas from one city or state to others.

Granted Powers
National government powers listed explicitly in the constitution.

Commerce Clause
Empowers congress to regulate commerce with foreign nations, between states, and with Indian tribes. (Article 1, Section 8)

Necessary and Proper Clause
The constitutional declaration that defines Congress's constitutional authority to exercise "necessary and proper" powers to carry out its designated functions. (Article 1, Section 8)

Inherent powers
National government powers implied by, but not specifically named in the constitution.

Supremacy Clause
The congressional declaration that the national government's authority prevails over any conflicting state or local government's claims. (Article 6, Section 2)

reserved powers
The constitutional guarantee that the states retain government authority not explicitly granted to the national government. (10th Amendment)

Concurrent powers
Government authority shared by state and national governments.
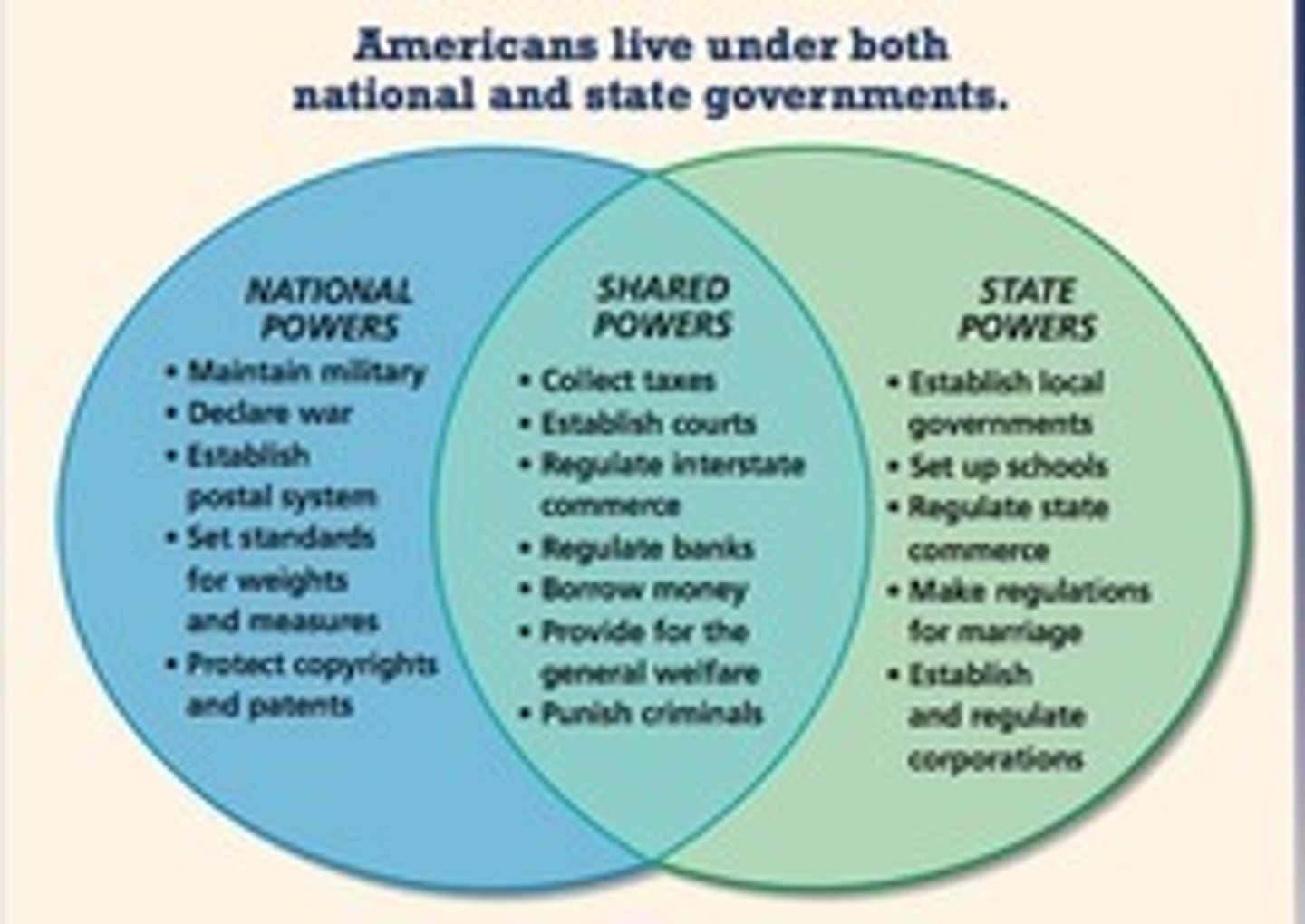
Full Faith and Credit Clause
The constitutional requirement that each state recognize and upholds laws passed by another state. (Article 4, Section 1)

Dual Federalism
Layer cake federalism, the clear division of governing authority between national and state governments.
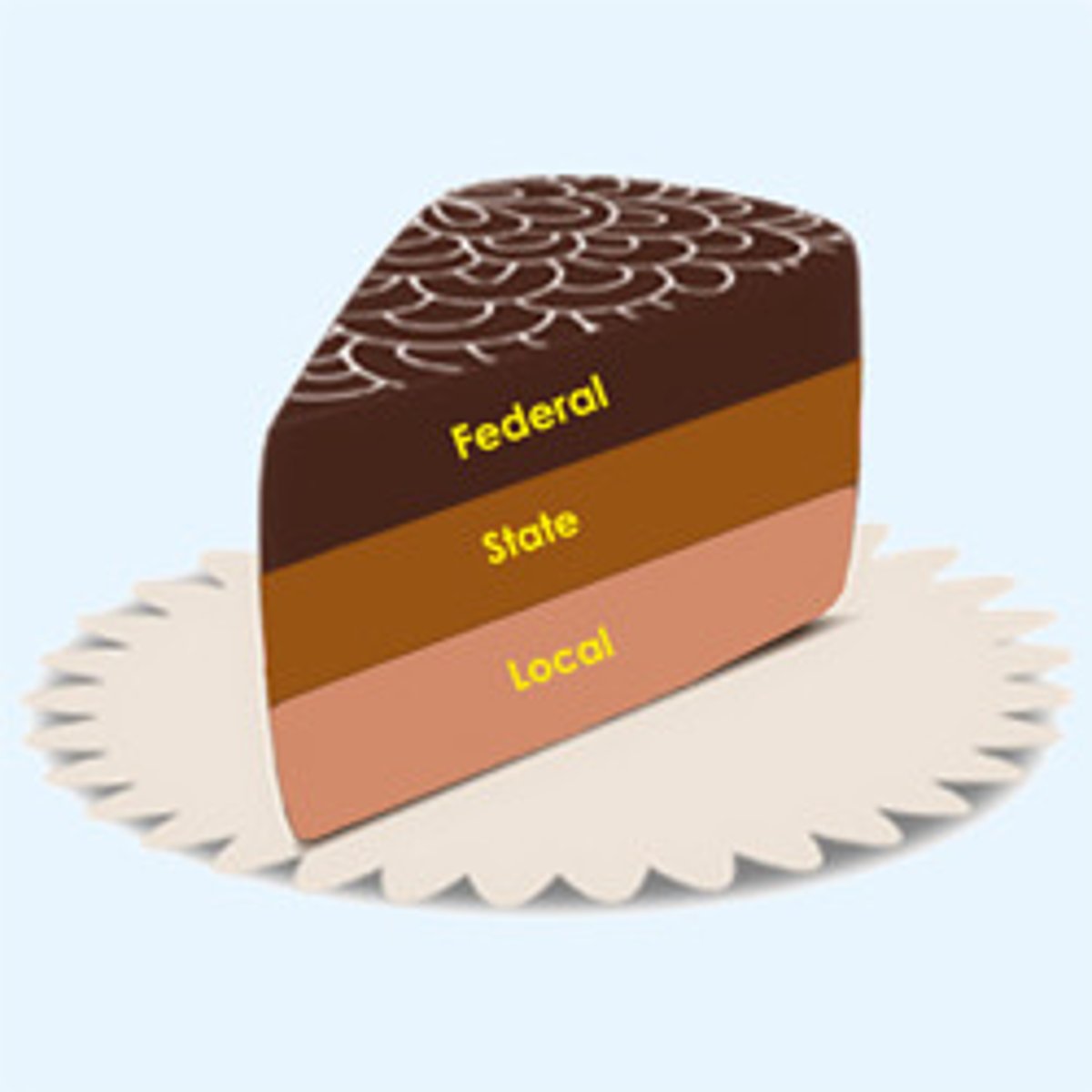
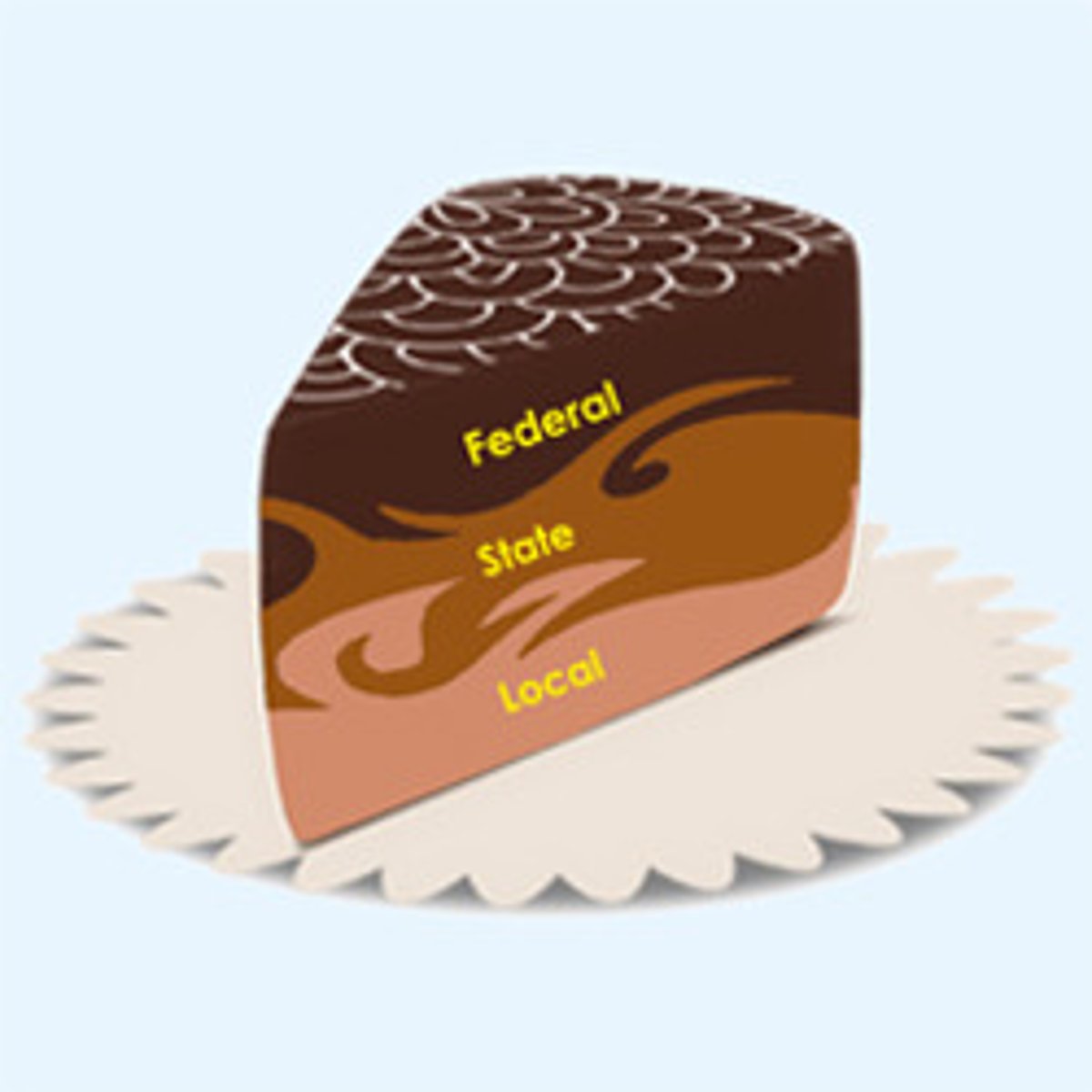
Cooperative Federalism
Marble cake federalism; a system of mingled governing authority, with functions overlapping across national and state governments.

grants-in-aid
National government funding provided to state and local governments, along with specific instructions about how the funds may be used.

New Federalism
A version of cooperative federalism, but with stronger emphasis on state and local government activity vs national government.
block grants
Federal money given to the states with few restrictions about how it should be spent.

Progressive Federalism
Approach that gives state officials considerable leeway in achieving national programs/goals.
Unfunded Mandate
An obligation imposed on state/local governments by federal legislation without federal funding.

Devolution
The transfer of powers and responsibilities from the federal government to the states.
Preemption
The invalidation of a U.S. State law that conflicts with federal law.

Civic Volunteerism
Citizen participation in public life without government incentives or coercion.
Executive Branch
The part of government that carries out, or executes, the laws; the president.

Legislative Branch
The branch of government having the power to make laws; congress.
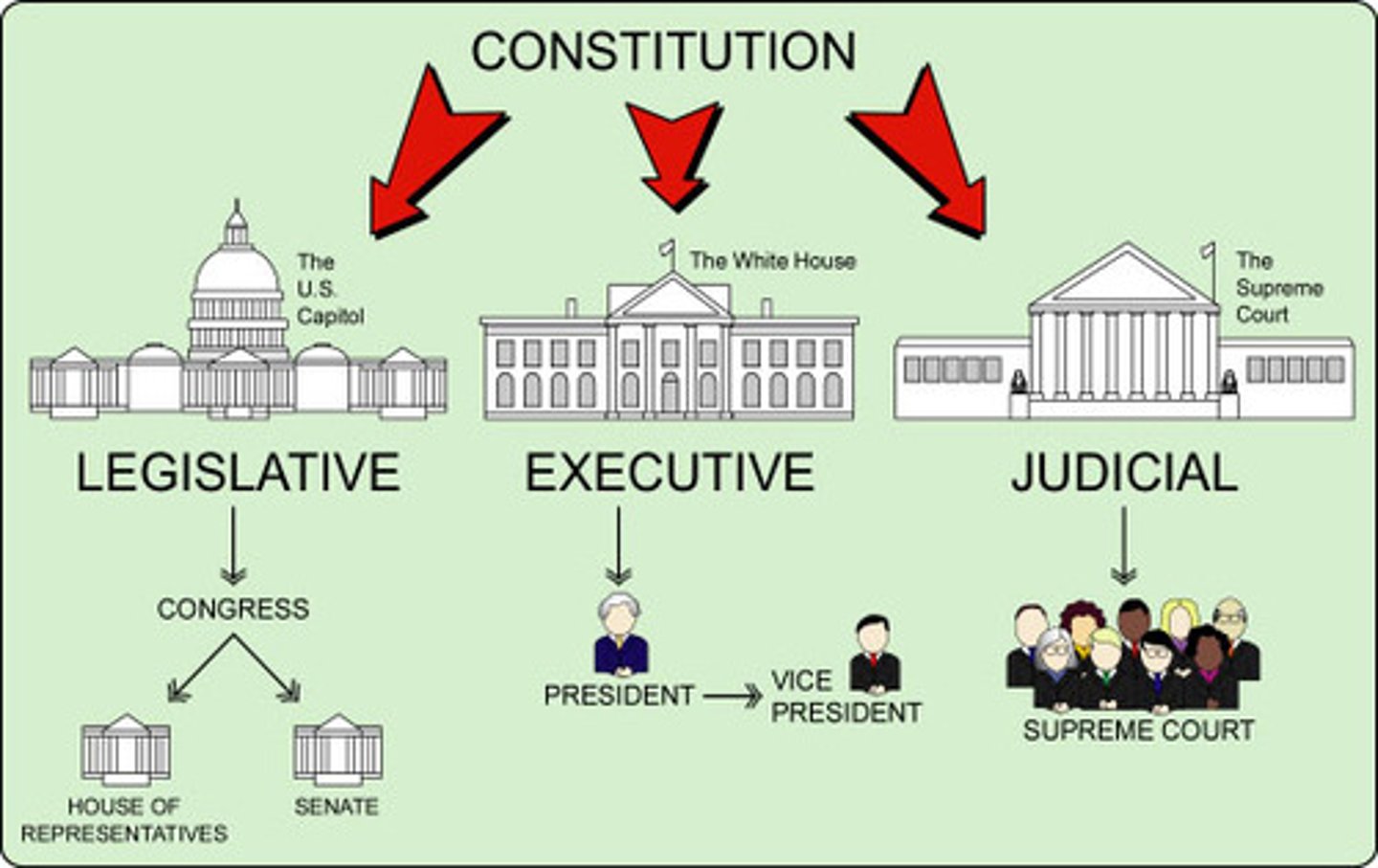
Judicial Branch
Branch of government that decides if laws are carried out fairly; the courts.
