Lymphocytes and Lymphatic Organs and Tissues
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are the circulating lymphocytes?
T cells (thymus-dependent)
B cells (bone marrow-derived)
NK cells (natural killer cells, also bone marrow-derived)
What does the production and distribution of lymphocytes involve?
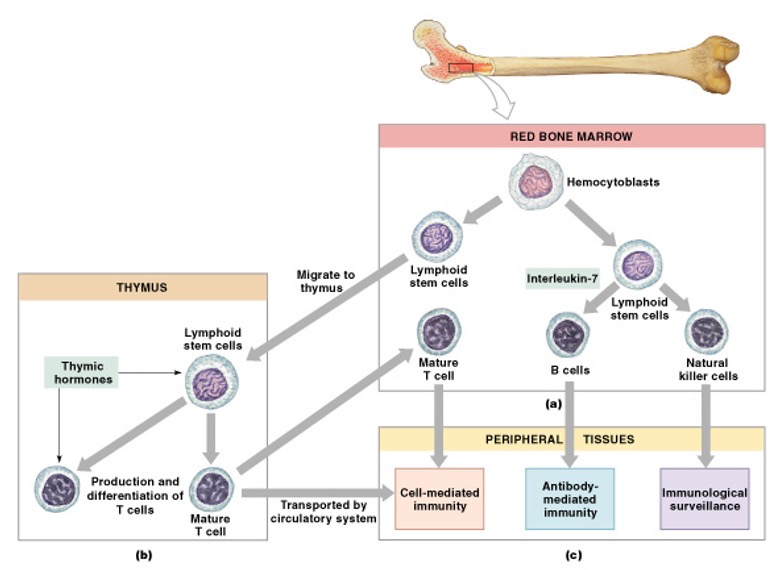
What happens in the primary lymphatic organs?
Where immune cells become immunocompetent
What are the primary lymphatic organs?
Red bone marrow
Thymus (which grows until 2, then shrinks to half the size by the time you’re 17, before shrinking slows but still takes place)
What do the secondary lymphatic organs and tissues include?
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Lymphoid nodules
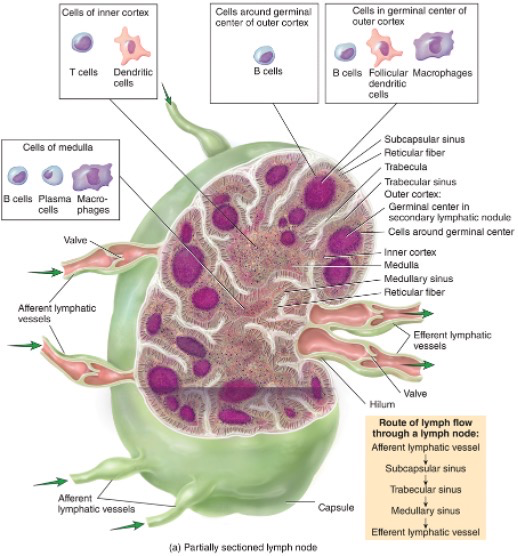
What does a partially sectioned lymph node look like?
What does the anterior view of an inguinal lymph node look like?
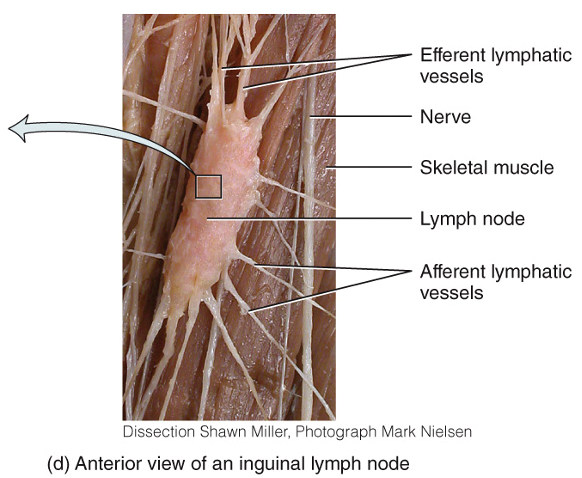
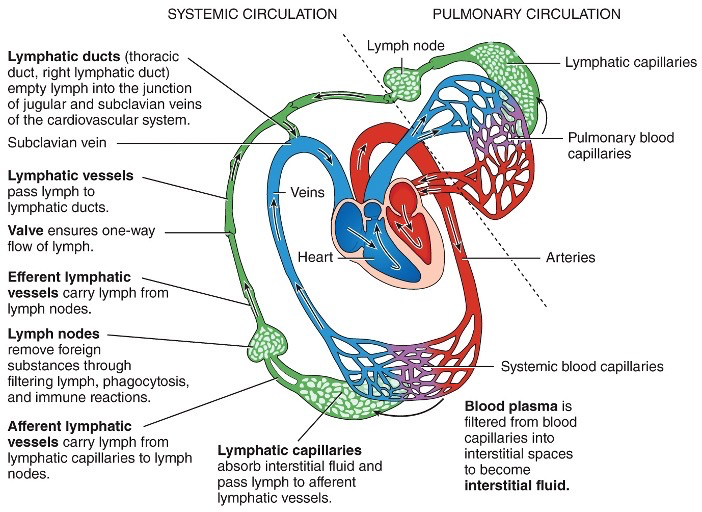
What are afferent lymphatic vessels?
Where lymph comes in
What are efferent lymphatic vessels?
Where clean lymph exits
What is involved in the formation and flow of lymph?
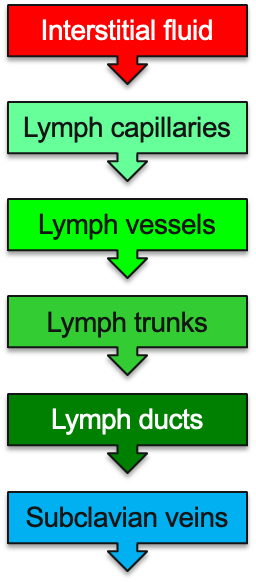
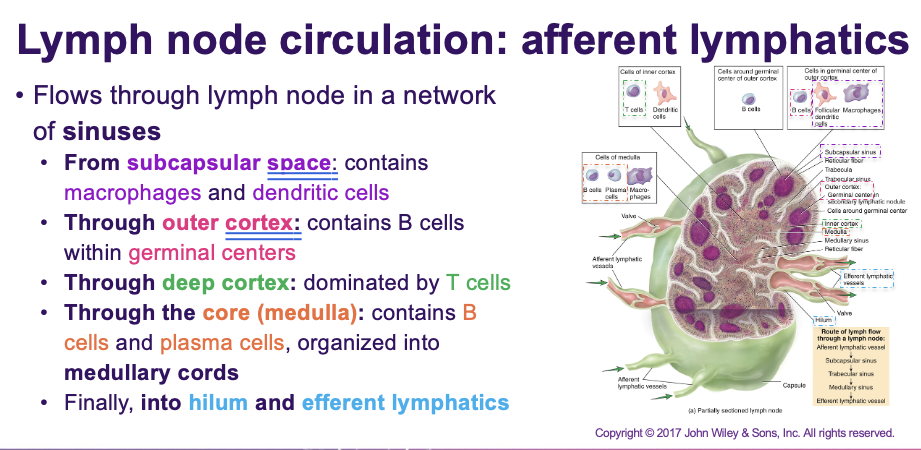
What happens in lymph node circulation in afferent lymphatics?
What are the functions of lymph nodes?
A filter: purifies lymph before return to venous circulation
Removes: debris, pathogens, 99% of antigens
What do lymph nodes in the gut, trachea, lungs, and thoracic duct do?
Protect against pathogens in digestive and respiratory systems
Where are glandular lymph nodes found and what do they do?
There are large lymph nodes at the groin and base of the neck which swell in response to inflammation
What is lymphadenopathy?
Chronic or excessive enlargement of the lymph nodes, which may indicate infections, endocrine disorders, or cancer
What are lymphoid nodules?
Dense masses of lymphocytes and macrophages, which are separated by spaces called lymph sinuses
What’s the difference between lymph organs and lymphoid nodules?
Lymph organs (lymph nodes, thymus, spleen) are separated from surrounding tissues by a fibrous capsule (protective coat)
Lymphoid nodules are a bundle of lymphoid tissue without a fibrous capsule