Structure and Topology of DNA
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 1 of Molecular Biology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Central Dogma
The flow of genetic information: DNA → RNA → Protein
(info storage → info conveyance → function)
Where is DNA found?
In nearly ever cell except for red blood cells.
Percent of genome coding for protein.
~1-2%
What evidence supported the DNA model?
X-ray diffraction data from Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
Photo 51
X-shaped X-ray diffraction pattern indicating a helical structure.
Nucleotide components
Nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group.
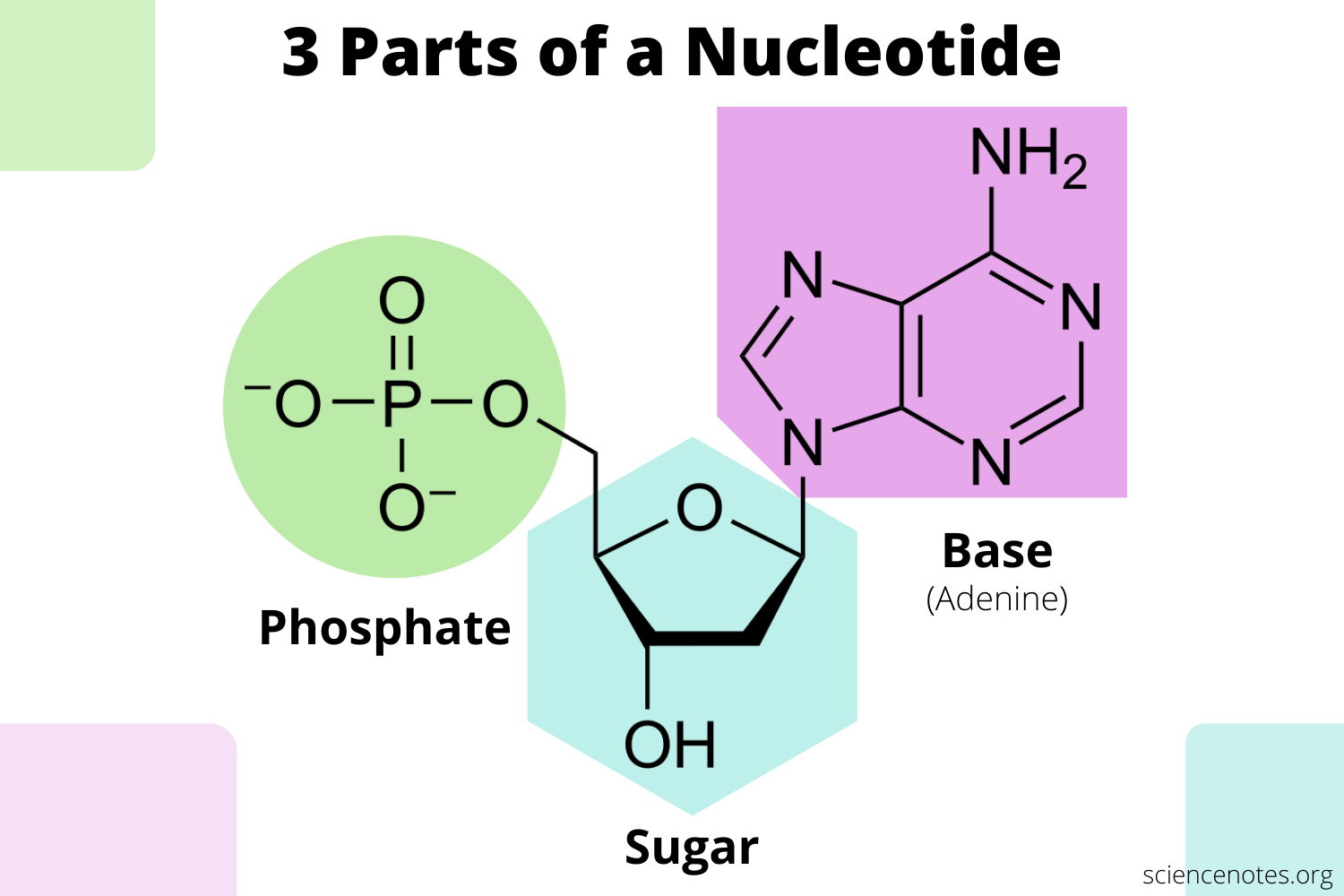
Nucleoside vs Nucleotide
→ Nucleotide = Base + Sugar
→ Nucleotide = nucleoside + phosphate
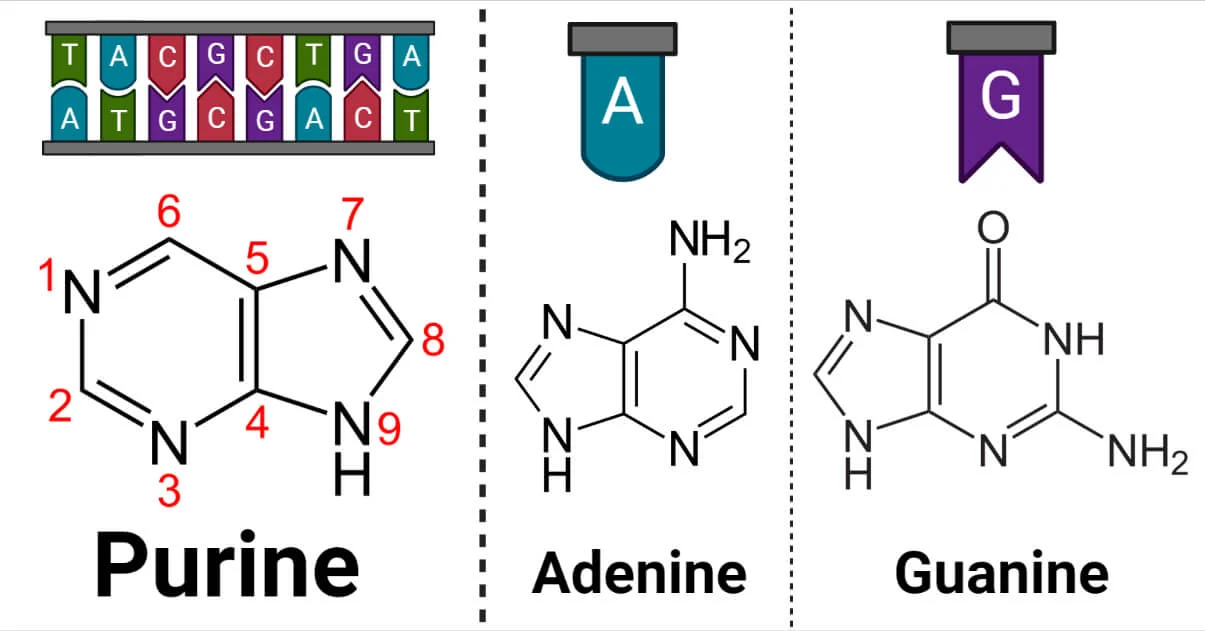
Purines
Adenine (A), Guanine (G).
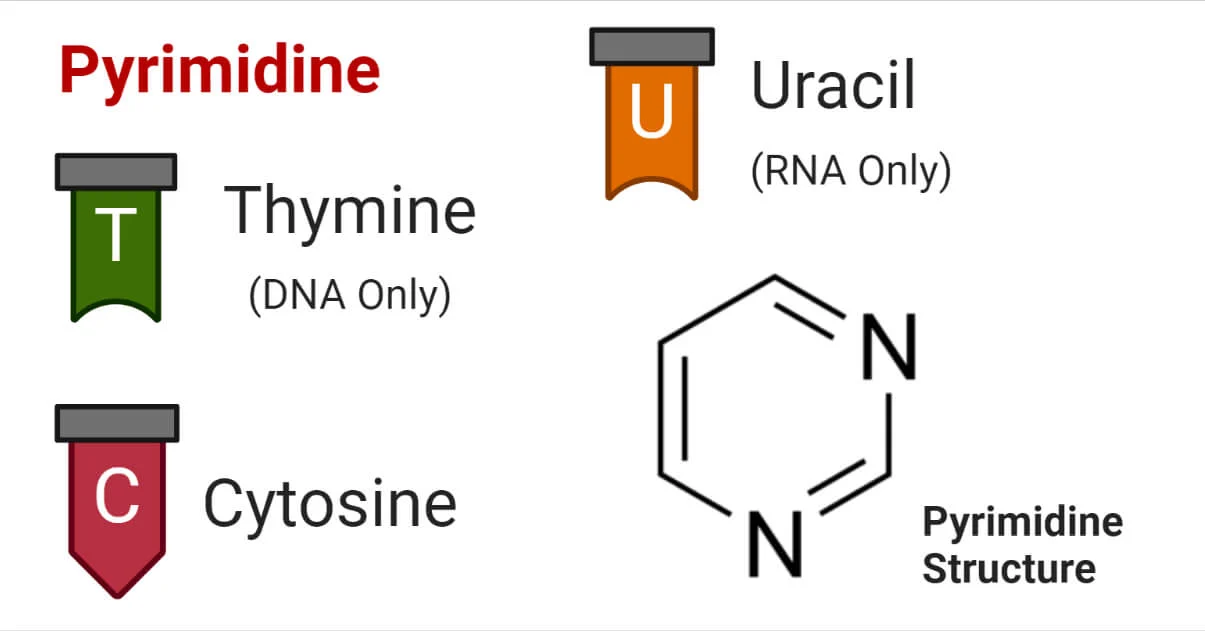
Pyrimidines
Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U).
DNA bases
A,T,G,C
RNA bases
A,U,G,C
DNA vs RNA
DNA:
Double Stranded
Deoxyribose
H at 2’ carbon
has thymine
more stable
RNA:
Single Stranded
Ribose
OH at 2’ carbon
has Uracil
Less stable
Cytosine deamination
C → U
Why is uracil in DNA a problem?
Uracil in DNA can damage the genetic code if not corrected.
Why DNA uses thymine instead of uracil?
Allows detection of cytosine deamination.
Pentose Sugars
Ribose (RNA)
Deoxyribose (DNA)
Sugar pucker
DNA: C-2’ endo pucker
RNA: C-3’ endo pucker
Why is the sugar pucker important?
It influences the A or B form helices. RNA generally adopts the compact geometry of A-form helices because of its C-3’ endo sugar pucker.
Phosphodiester bond
Covalent bond linking nucleotides.
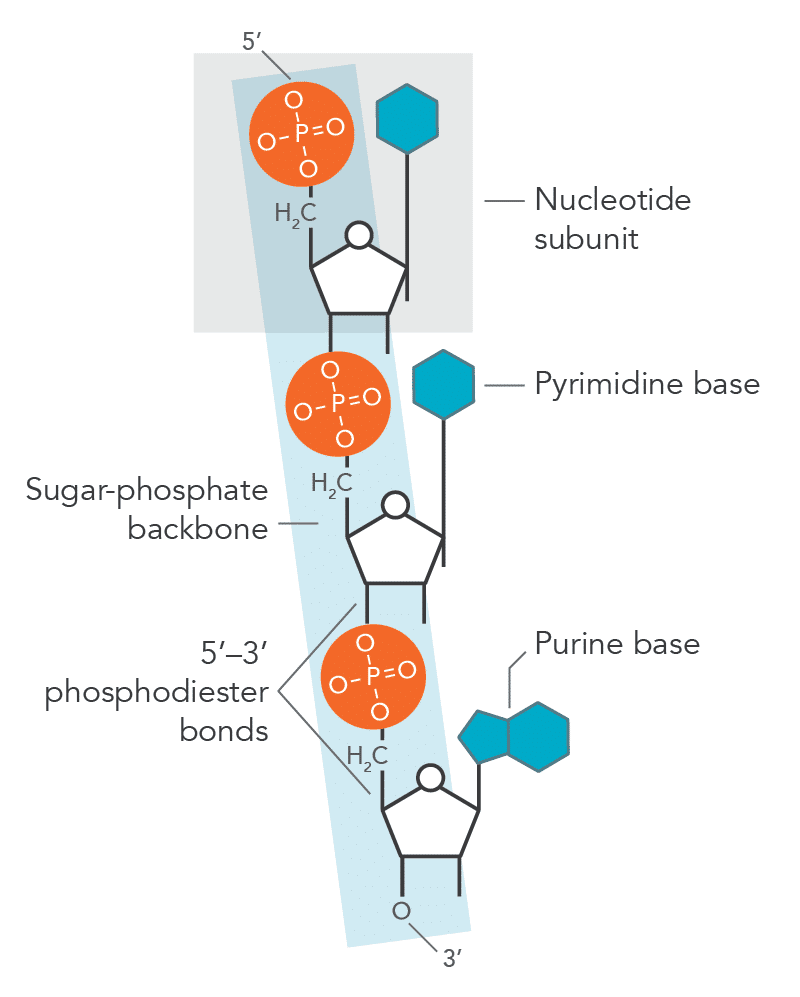
Bonds formed between
3’-OH of one nucleotide
5’-phosphate of the next
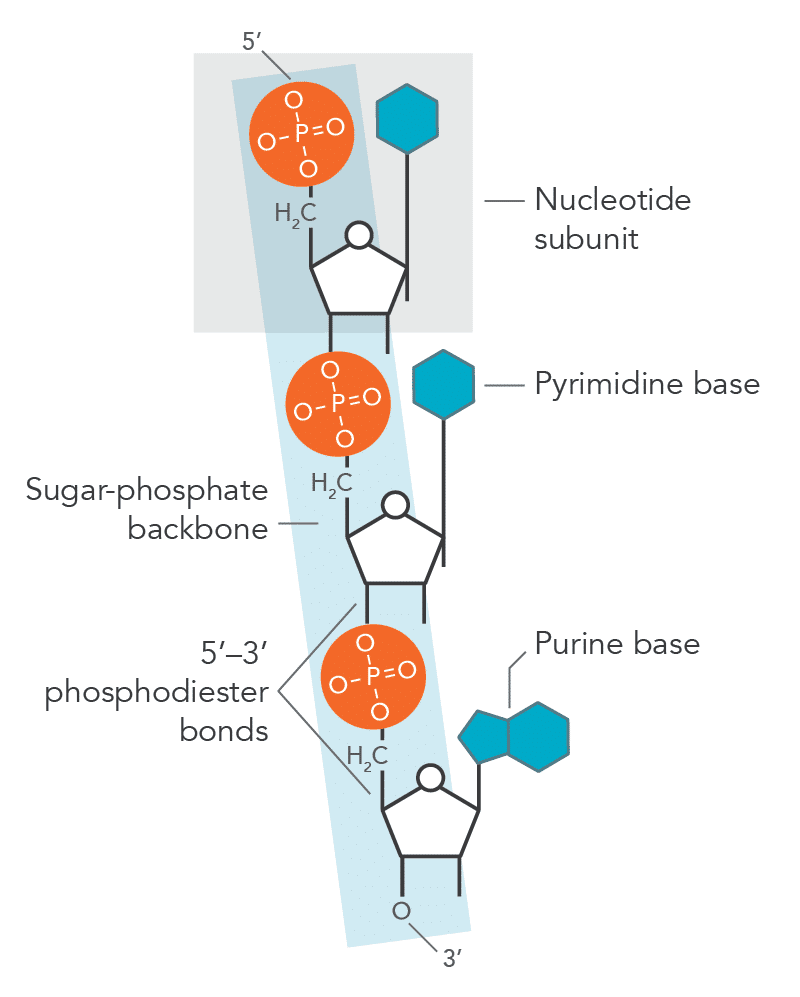
Directionality of DNA/RNA
5’ → 3’, if direction is not given on the exam assume this.
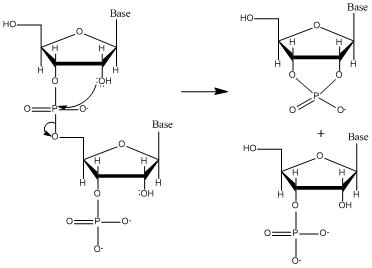
Why RNA is less stable than DNA.
2’-OH participates in hydrolysis.
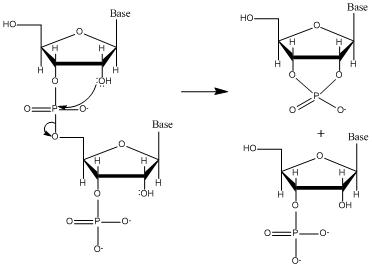
RNA hydrolysis
Occurs rapidly under alkaline conditions (high ph).
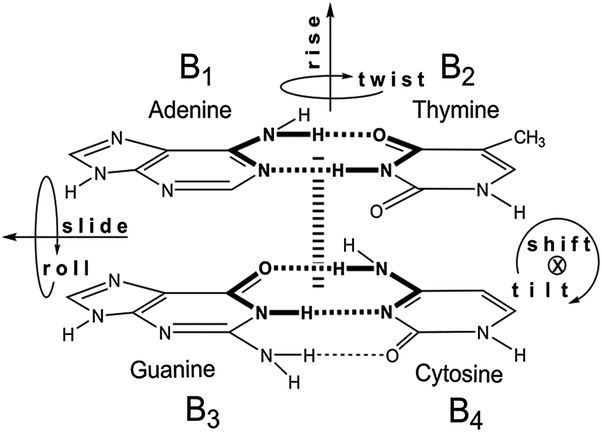
Watson-Crick base pairing.
A = T (or U)
G ≡ C
Hydrogen bonds of base pairs.
A-T: 2 H bonds
G-C: 3 H bonds
Base stacking
Hydrophobic interactions between planar bases.
Importance:
Major stabilizing force of DNA
Minimizes water interaction
Stabilizes 3D structure
UV absorbance
The bases absorb the light (delocalized pi electrons in bases).
Nucleic acids absorb UV light at 260 nm
Proteins: 280 nm
Chargaff Rules
DNA base composition differs among species
Same species = same base composition
Composition does not change with age or environment
number of A=T and number of G=C
DNA helix characteristics
Right handed
Antiparallel strands
bases inside
sugar-phosphate backbone outside
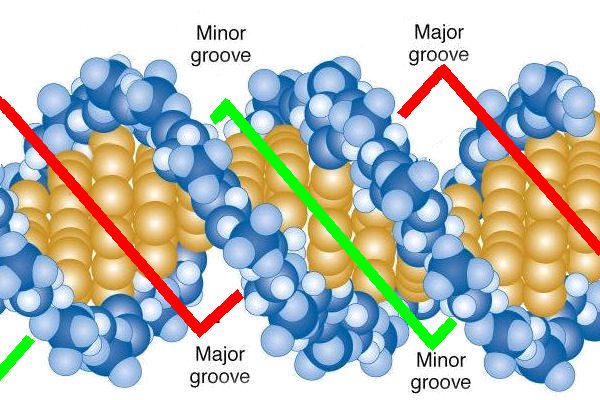
Major groove and minor groove
major groove is wide while the minor groove is narrow.
B-DNA
The most common DNA form in cells
right-handed
10.5 bp per turn
bases perpendicular to helix axis
3.4 Angstroms between bp
A-DNA
right-handed
more compact
11 bp per turn
favored in low water conditions
Z-DNA
left-handed
12 bp per turn
GC-rich sequences
occurs in short stretches in cells
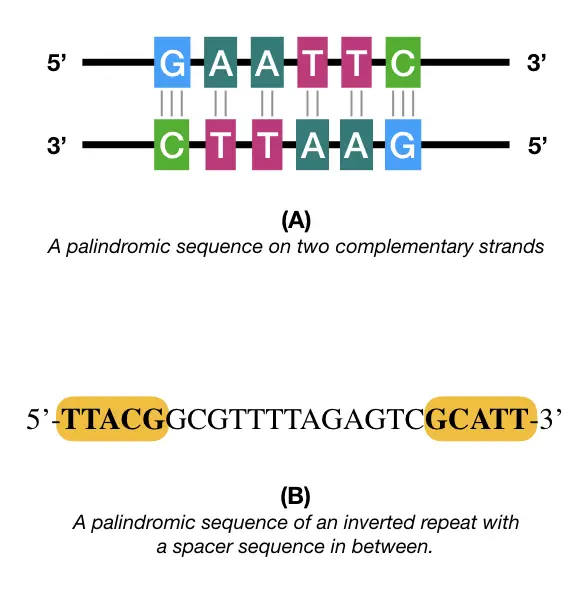
Palindromic sequences
Same sequence forward and backward
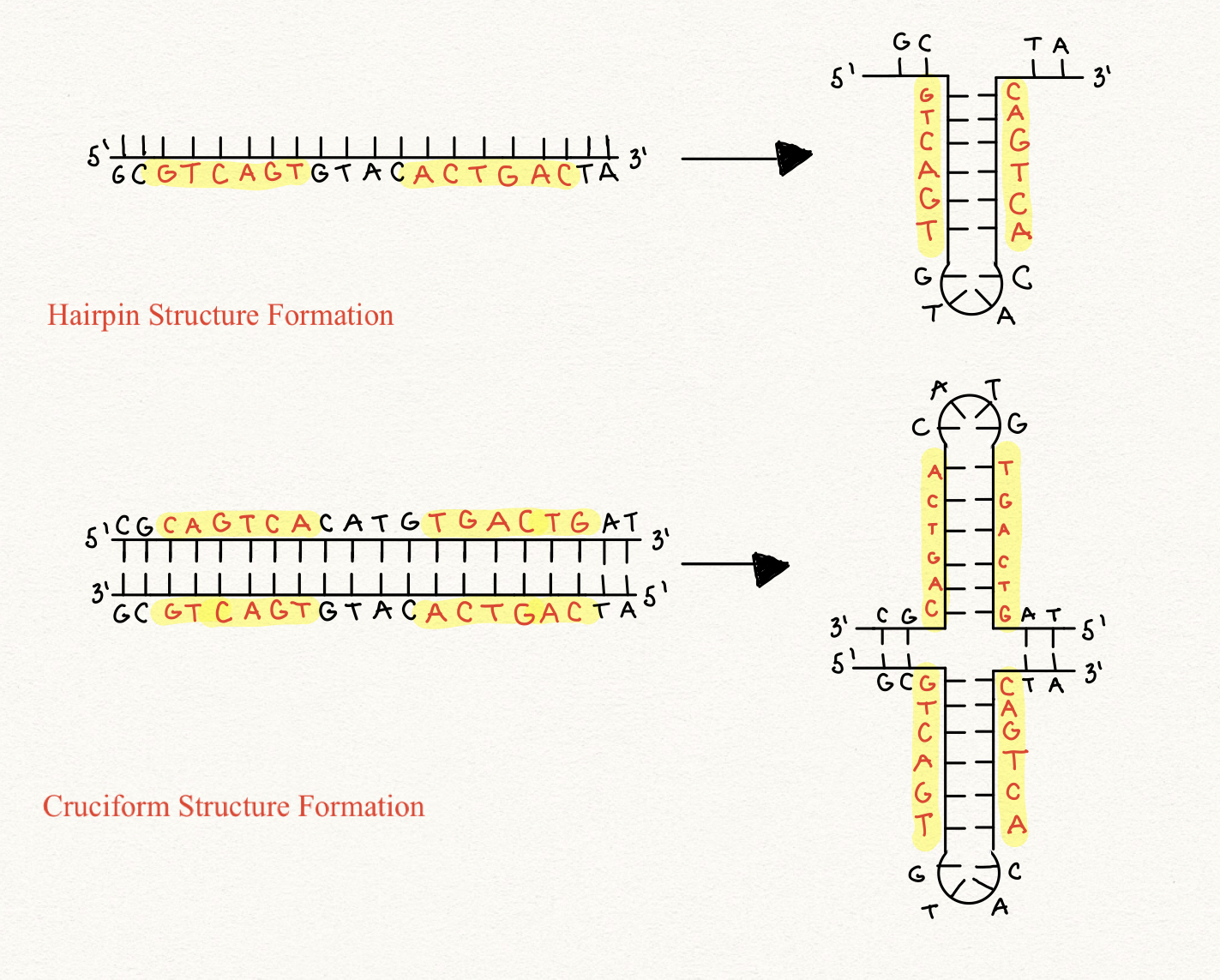
hairpins and cruciforms
form from inverted repeats. DNA folds back on itself.
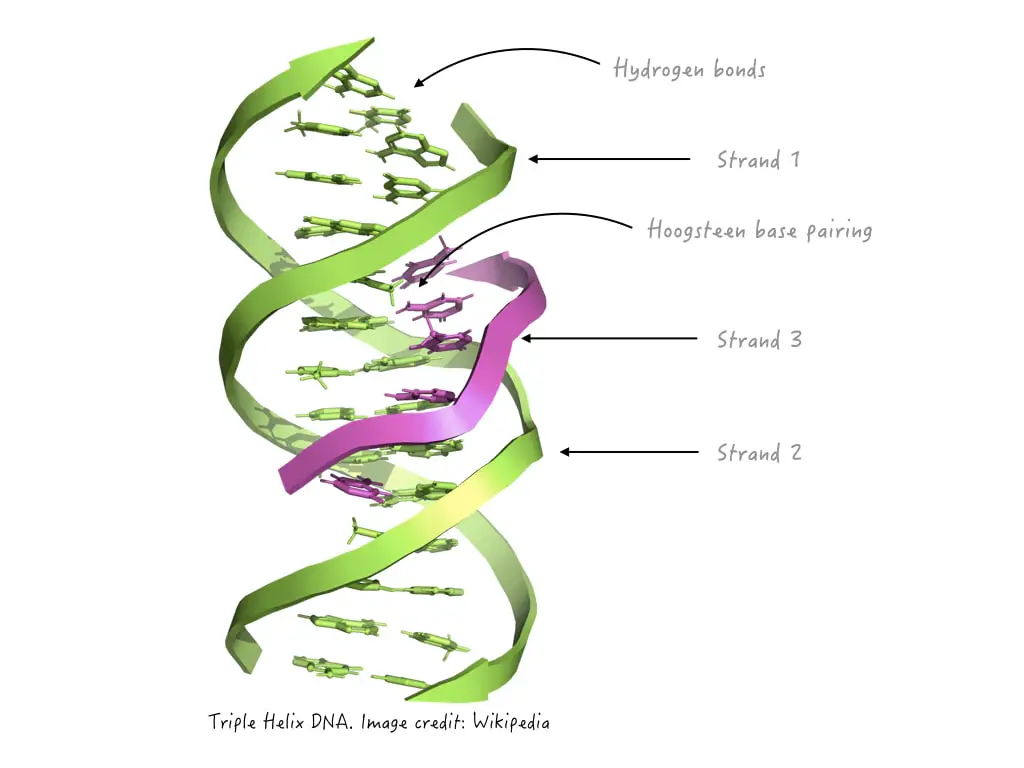
Triplex DNA
three strands
linked to huntington disease
Tetraplex DNA
Four strands
important for telomere stability
RNA structure characteristics
Mostly single-stranded
Forms internal base pairing
hairpins, loops, stems
RNA helices geometry
A-form geometry
Non-watson-crick base pairs for RNA
G-U, A-A are common
Why RNA forms stable folds
2’-OH enables hydrogen bonding
Metal ions stabilizing RNA
Mg+, K+, Na+
DNA denaturation
Separation of strands
Melting temperature (Tm)
Temperature where 50% is denatured
the Tm is higher when there is a higher GC content since they have more hydrogen bonds (more stable) than AT.
Hybridization
base pairing between strands from different sources

Blotting techniques
Southern blot: DNA
Northern blot: RNA
Western blot: Protein
Chemical Modifications
Most common DNA modification: base methylation
CpG islands:
Regions rich in CG
Often regulate gene expression
Effects of DNA methylation
typically inhibits transcription.