Revision SCT
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What enhances the activity of Na+/K+ pump
Insulin
Aldosterone
thyroxine
Aldosterone
Catecholamines (e.g. dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine).
What blocks Na+/K+ pump
Ouabain
Digitoxin
Digoxin
What are the effects of the Na+/K+ blockers?
Depolarisation
Swelling of the cell
Cardiac glycosides effect: POSTIVE INOTROPIC ACTION
Note: ouabain, digitoxin and digoxin are cardiac glycosides
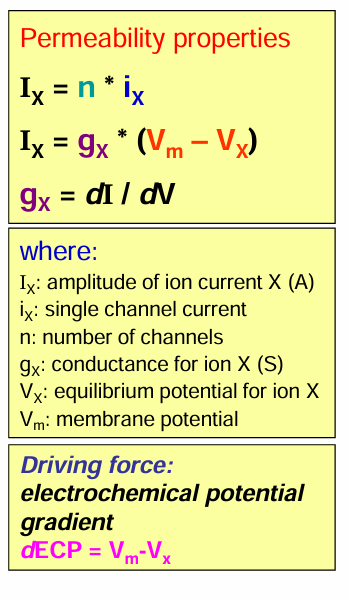
what is the equation for showing permeability properties
SEE IN THE PICTURE ATTACHED
Note: Driving force = Vm - Vx
What are the properties of ion channels:
Cannot be saturated thus has large Vmax
Gating: Voltage, ligand, mechanical
Selectivity: selectivity filter + ionic radius. Cation; non-selective cation channel; anion channel
Inhibition: specific and non-specific blockers.
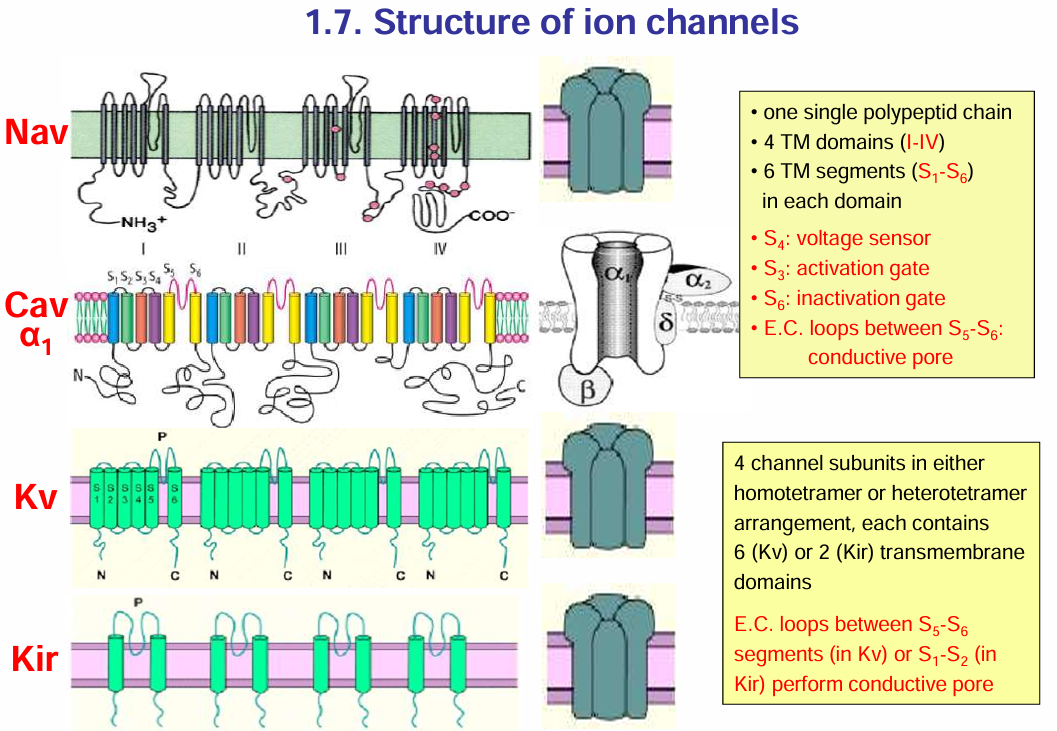
Structure of ion channels
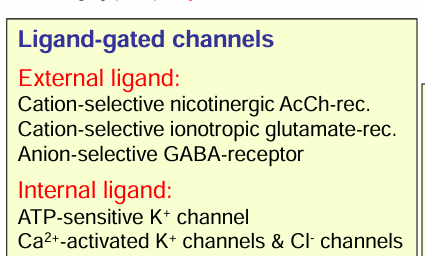
Ligand gated channels:
What voltage gated channels are activated by depolarisation?
Voltage gated sodium channels
Voltage gated K+ channels
Voltage gated calcium channels
What voltage gated channels are activated by Hyperpolarisation?
Kir, If
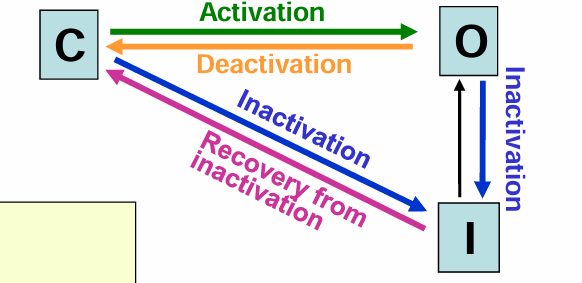
States of an ion channel
Equation for osmotic pressure

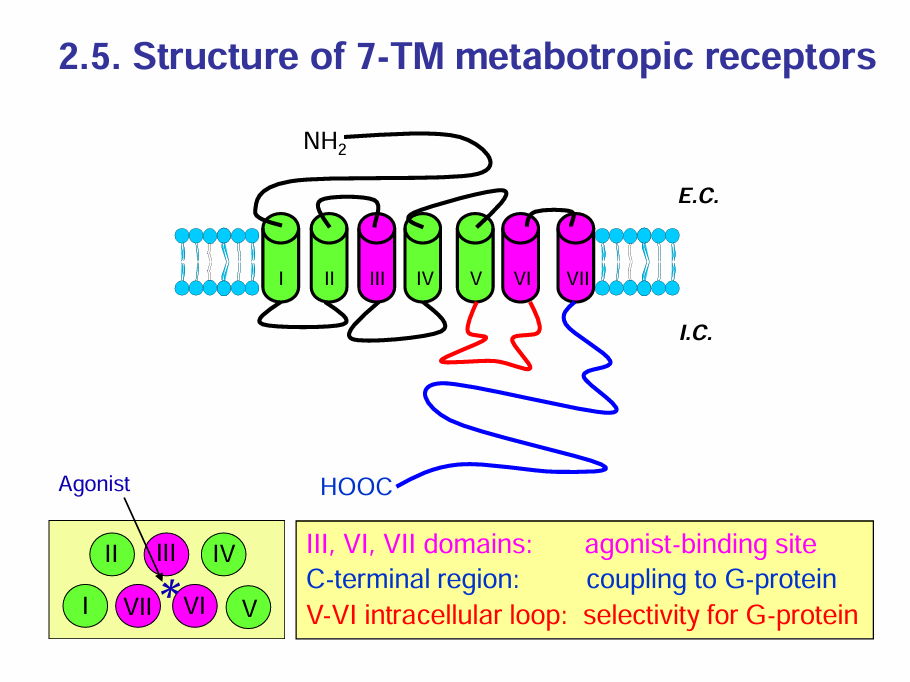
Structure of the 7TM Metabotropic receptors
What are the functions of the various G proteins
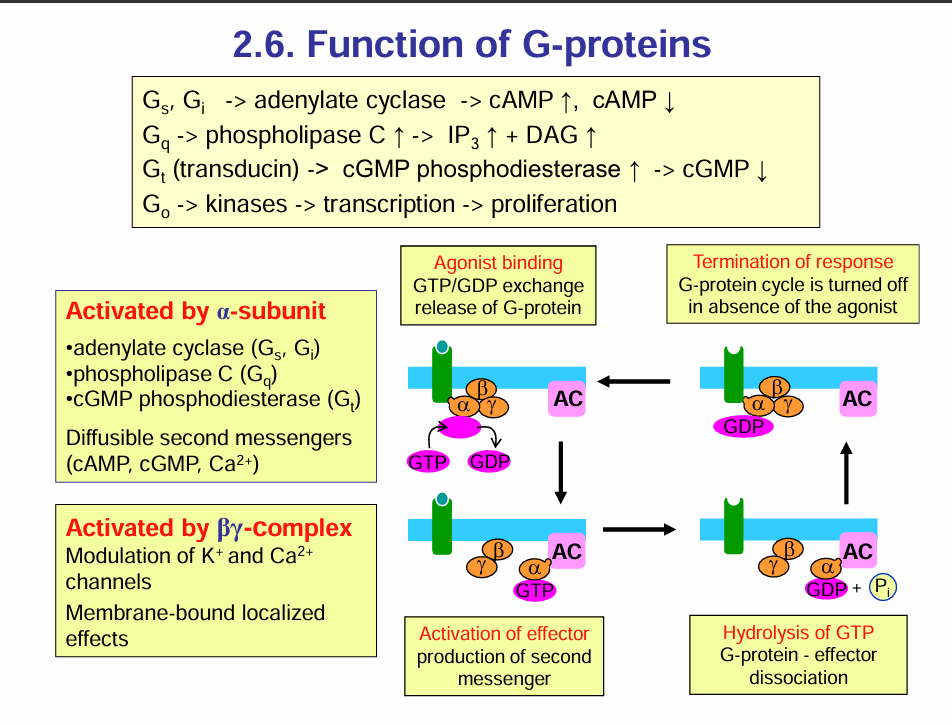
Which enzymes are activated by the alpha subunits of the G proteins
Adenylate cyclase
Phospholipase C
cGMP phosphodiesterase
Activated by the beta-gamma subunit
Modulation of K+ and Ca2+ channels
Membrane bound localised effects
NO …..
is responsible for cardio protection. It prevents/ opposes excessive ca2+ entry.
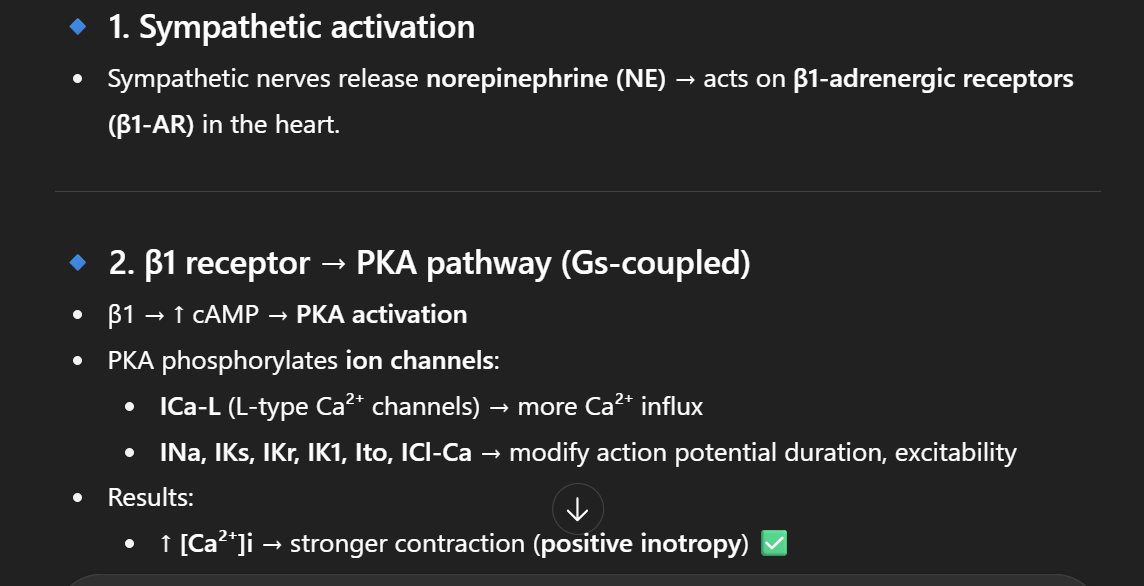
Beta 1 receptor
stimulates the PKA pathway
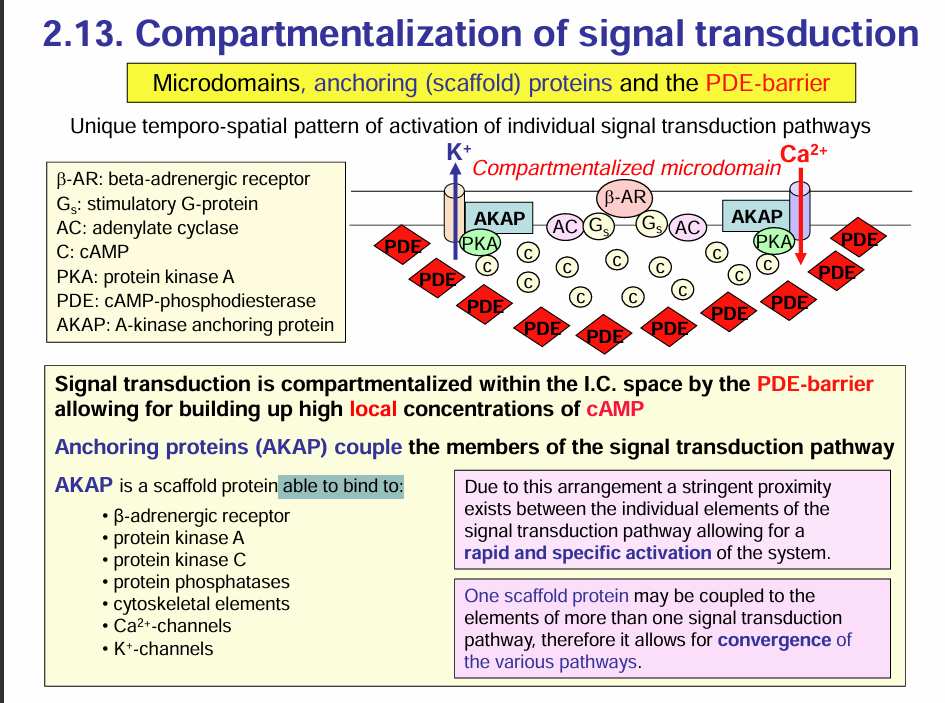
AKAP is a scaffold protein able to bind to:
•β-adrenergic receptor
•protein kinase A
•protein kinase C
•protein phosphatases
•cytoskeletal elements
•Ca2+-channels
•K+-channels
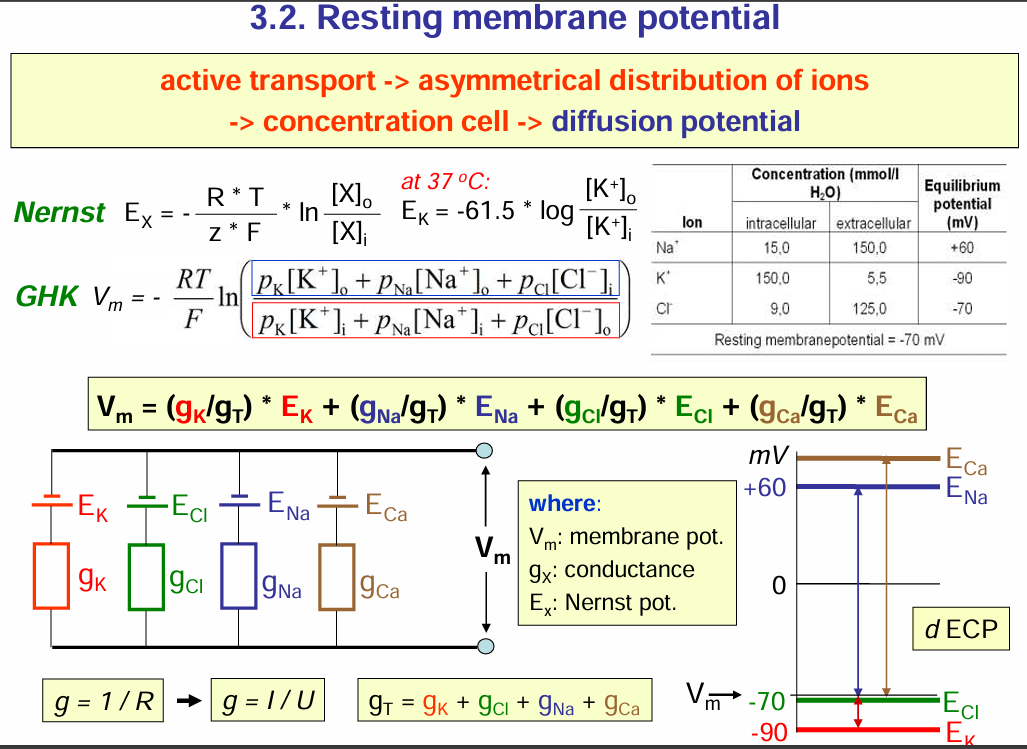
What is the magnitude of the donnan potential
-10mv. Thus this is too small and this cannot explain the highly negative resting potential of excitable cell.
the large negative potential comes mainly from the Na+/K+ pump not just the donnan potential
EQUATIONS TO REMEMBER
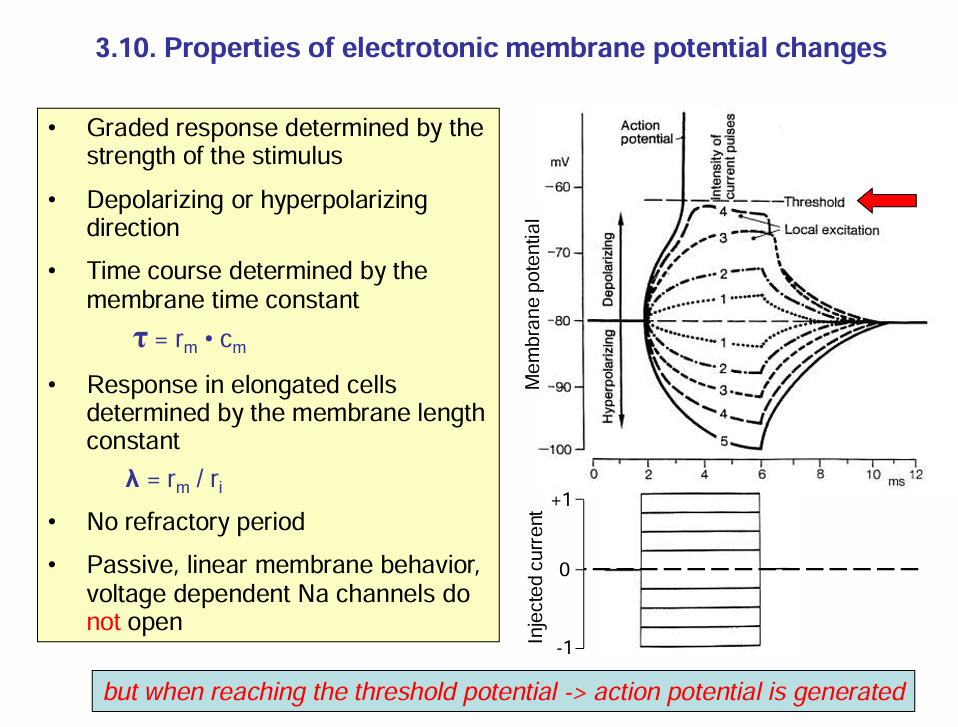
Characteristics of electrotonic potential
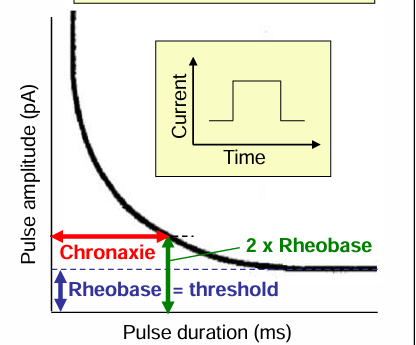
Rheobase and chronaxie
Rheobase: the minimum current needed to rogger an action potential if applied for a very long duration. UNIT OF RHEOBASE = PICOAMPERES
Chronaxie: the time required to reach the threshold if the current is twice the rheobase. UNIT OF CHRONXIE = Milliseconds
Equation for calculating the speed of conduction
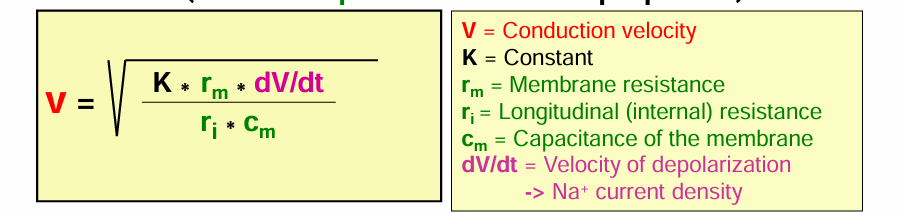
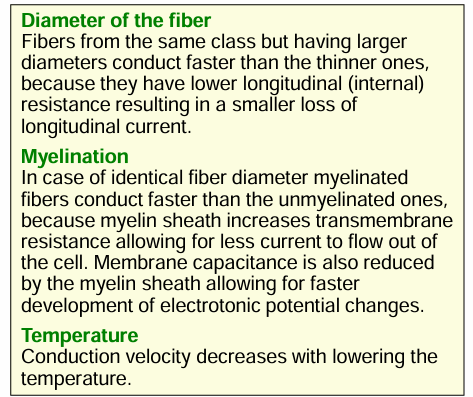
Factors that affect the speed of conduction
TAKE NOTE: Myelination increases the membrane resistance but decreases the capacitance.
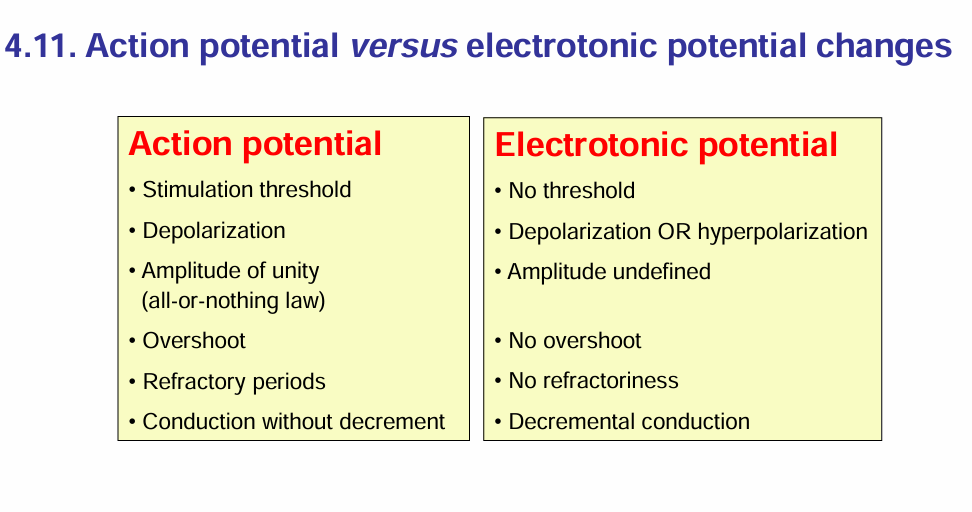
Differences between action potential and electrotonic potential