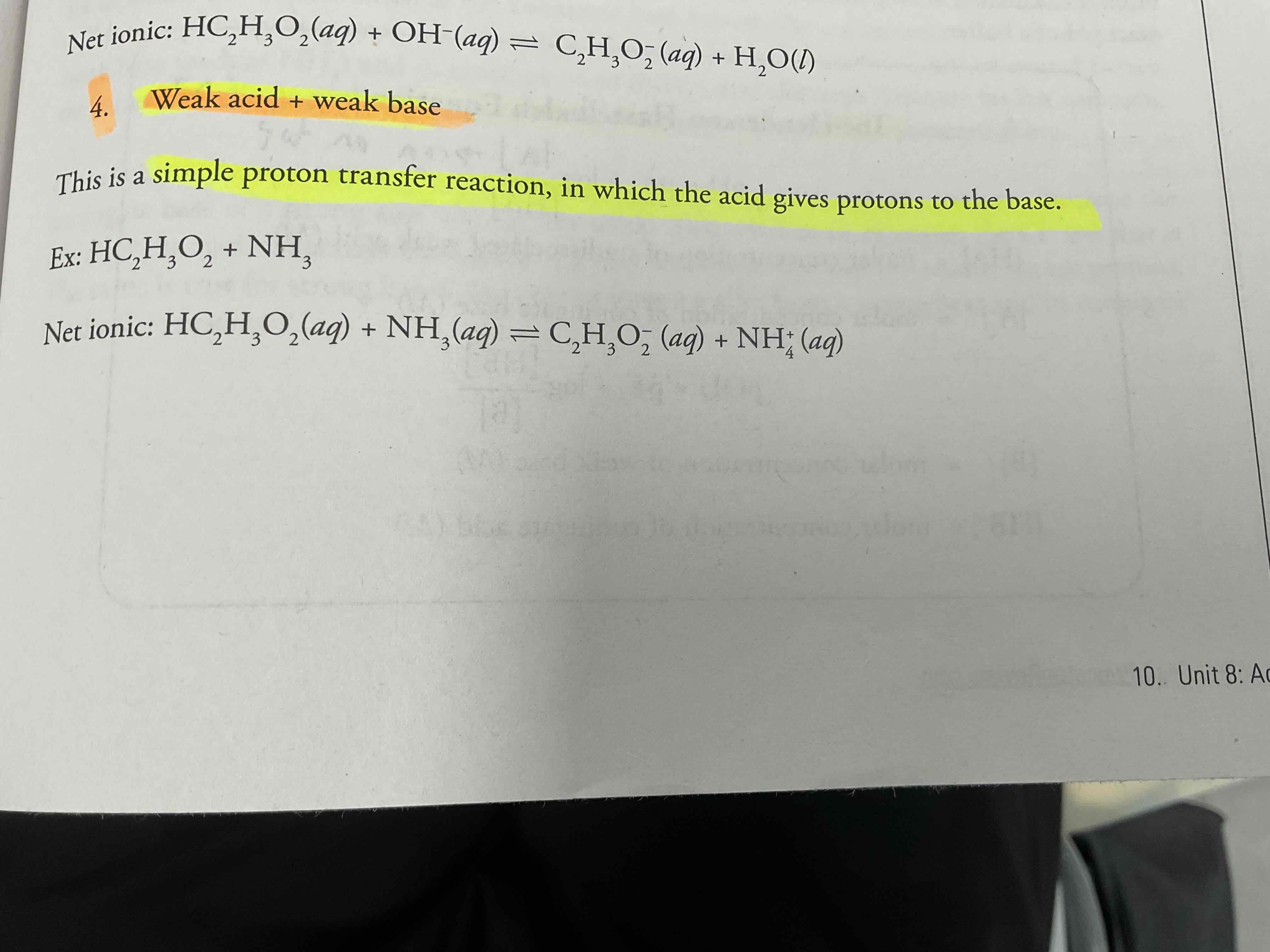AP Chem unit 8
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Acid
A compound that donates a proton (H+ ) in a reaction (according to bronsted-Lowry
Base
A compound that accepts a proton (H+) according to bronsted-Lowry
Strong Acid, Strong base
Strong acid dissociates completely.
Strong bases ionizes completely
Weak acid, Weak base
These will establish equilibrium (do not react completely)
Water is _________. Meaning it can act as a acid or a base
Amphoteric
Common strong acids
HCl, HBr, HI, HNo3, HClo4, H2SO4
Common strong bases.
.Any Group 1 or 2 hydroxides:
LiOH NaOH KOH BaOH2 SrOH2
PH,
p anything equals?
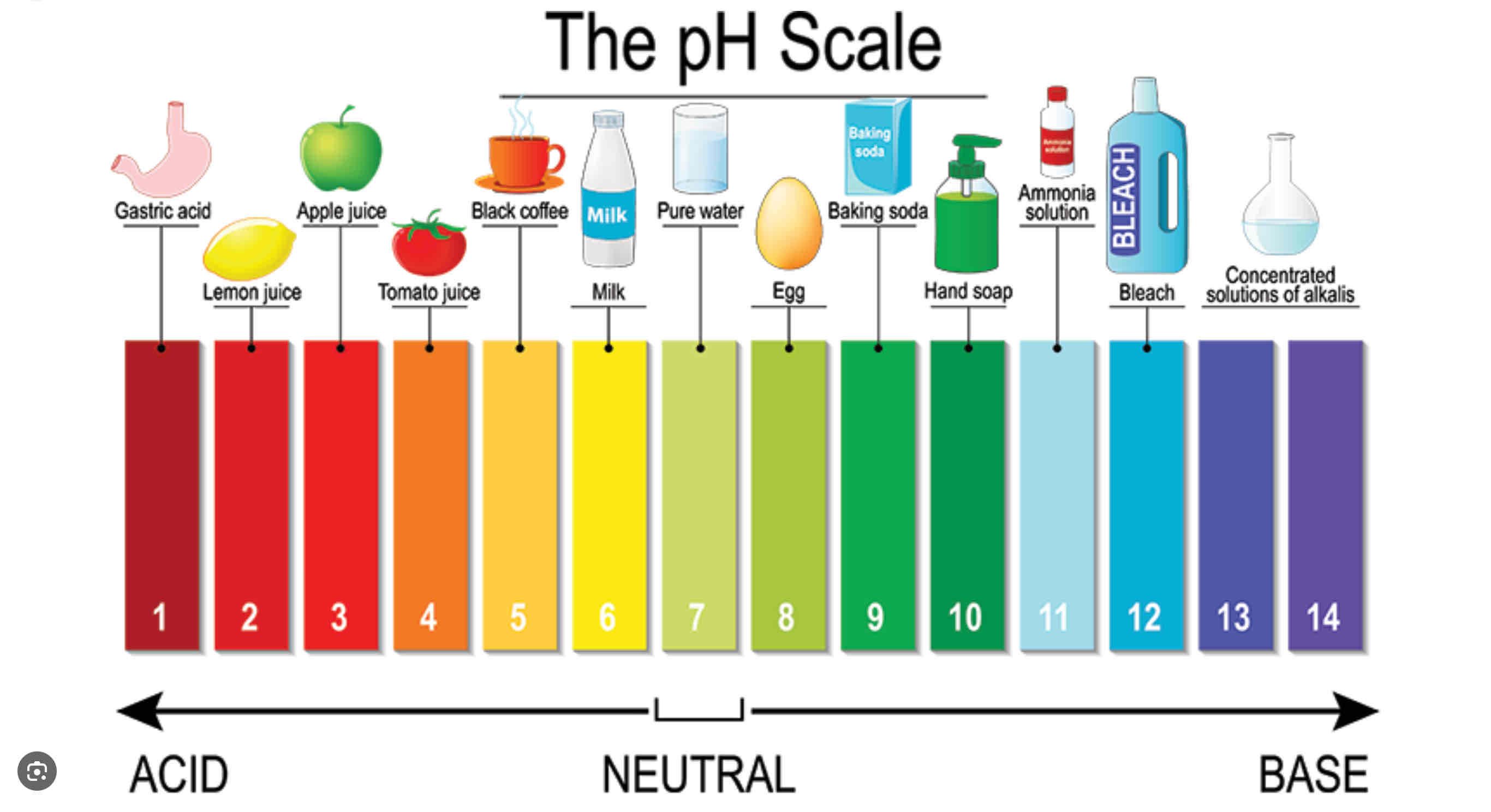
Ph scale?
Value that can tell us concentration of Acid or base.
P (anything) = - log (anything)
pH = ?
Anything in [] = concentration = moles/ L
-log [H+]
pOH=
-log [OH-]
Increasing Ph means ______ [H+]
Decreasing ph means______[H+]
Decreasing ;
Increasing
When there is High Ph, it is ________ for additional base to dissolve
Harder,
Because at high Ph there isn’t a high abundance in H+ ions make the solubility lower, because base need to react with acid to form water or else doesn’t dissolve.
Due to common ion
When there is abundance in H+ ions (low ph), the solubility of addition base would ______
Increase,
The H+ ions will react with the OH, decreasing concentration shift equilibrium to the right.
For strong acids / bases, you can ______ find ____ from concentration.
strong acids goes to ________. No tendency for_______
Always; Ph
Completion; reverse
Weak acids / bases
Unlike strong, they do not dissociate all the way through, and most acid molecules remain as undissociated aqueous particles.
To solve for pH of these, sometimes Ice box is needed
X is always insignificant in weak acids
For weak acids / bases , x in ice box is?
Almost always insignificant compared to the initial concentration of the acid, so we just use the initial concentration in calculation
Concentration’s relation with percent dissociation?
The lower the concentration is for an acid the higher the percent dissociation.
Because over abundance of water molecules makes it easier for acid to find water to donate to, and it hinders the reverse reaction, because H3O+ and conjugate base are more spread out in a dilute solution (low concentration).
Greater concentration lead to greater conjugate base
Are all hydrogen in acid dissociable?
No, because only the hydrogens that are attached to elements with very big electronegativity differences can dissociate., Ex: oxygen. not like carbon with similar diff
Can Ph effect solubility?
Yes, due to common ion effect, high ph substance have hard time dissolving in high pH, low ph substance have hard time dissolving in low ph
pH + pOH=
14
Neutralization reactions:
Strong Acid + Strong base =?
Dissociated completely
Always RESULTS in creation of water H2O and salt

Strong Acid + weak base
Conjugate acid of the weak base will be produced
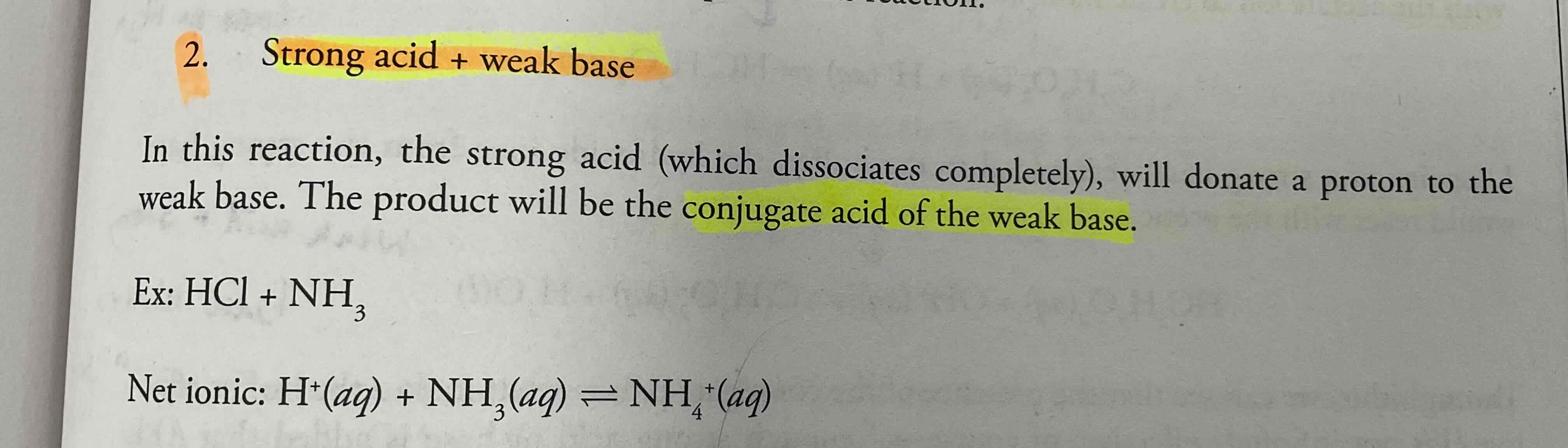
Weak acid + strong base = ?
Conjugate base of the weak acid and water
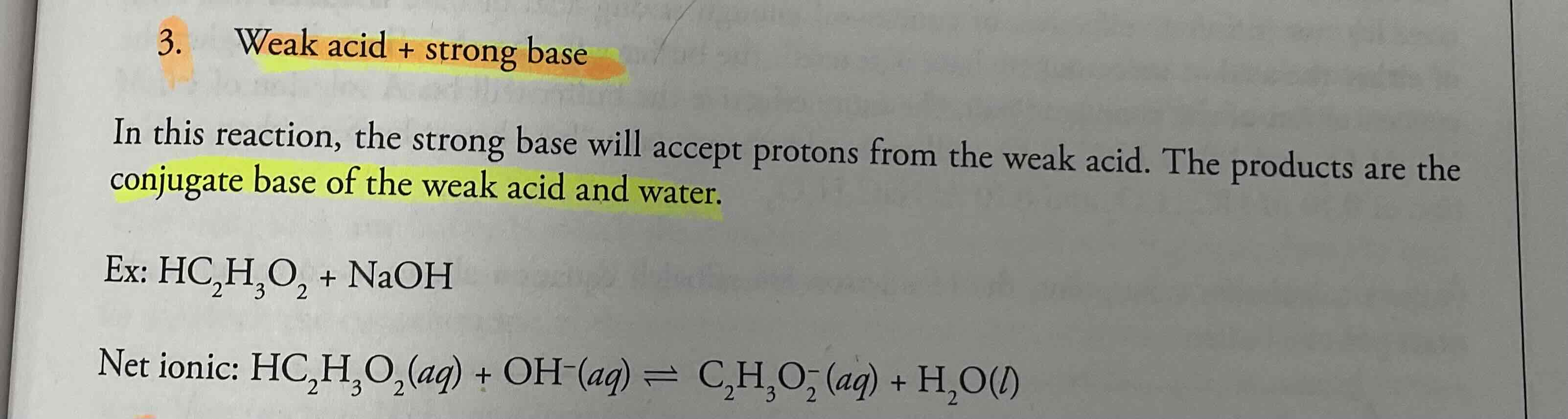
Weak acid + weak base = ?
Simple proton transfer reaction, in which the acid gives protons to the base.