BIOL 300 Exam 1 - George Mason University (You got this!!)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Root
The base of the phylogenetic tree, is the most recent common ancestor of ALL taxa
Node
In phylogenetic trees, the point where a branch splits, representing the common ancestor from which the descendant species diverged
Taxon (Plural: Taxa)
A biological group given a name (Ex: family, species, class, etc...)
Clade
A group of organisms evolved from a common ancestor
Sister species
Two species that are each other's closest relatives
Sister clades
Two clades that are each other's closest relatives
Lineage
A series of populations, species, or genes descended from a single ancestor over evolutionary time
Common ancestor
Ancestral organism shared by two or more lineages
Homology
A similarity between two or more features that is due to inheritance from a common ancestor
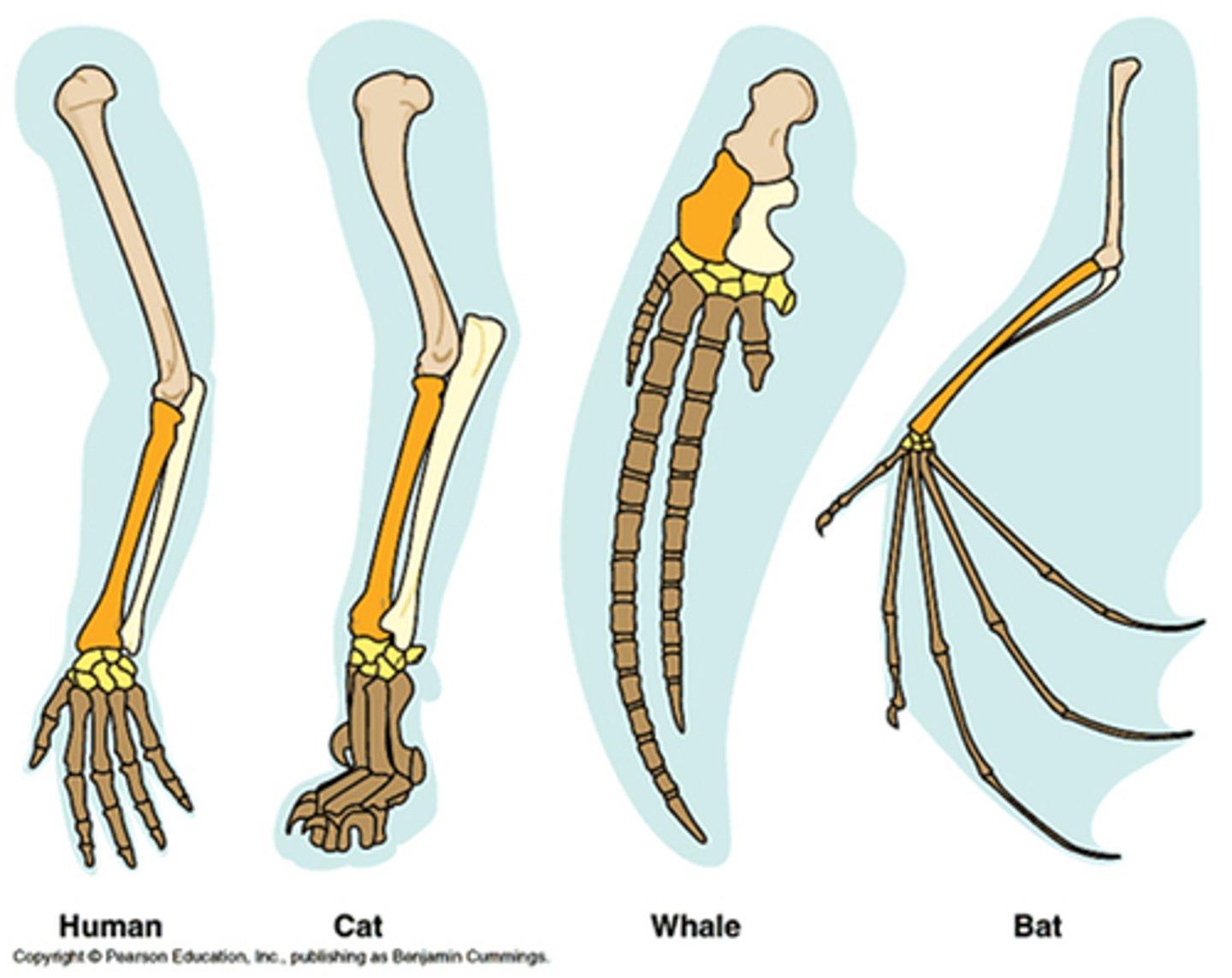
Synapomorphy
A trait that arose in the ancestor of a phylogenetic group and is present in all of its members, thus helping delimit and identify that group. Also known as a shared derived trait. (Ex: Mammals produce milk)
Ancestral trait
The trait originally present in the ancestor of a given group; may be retained or changed in the descendants of that ancestor
Derived trait
A trait that differs from from the ancestral trait (Ex: how marsupials are mammals but have pouches unlike most mammals)
Autapomorphy
Found in one taxon but not in the outgroup or any other taxons
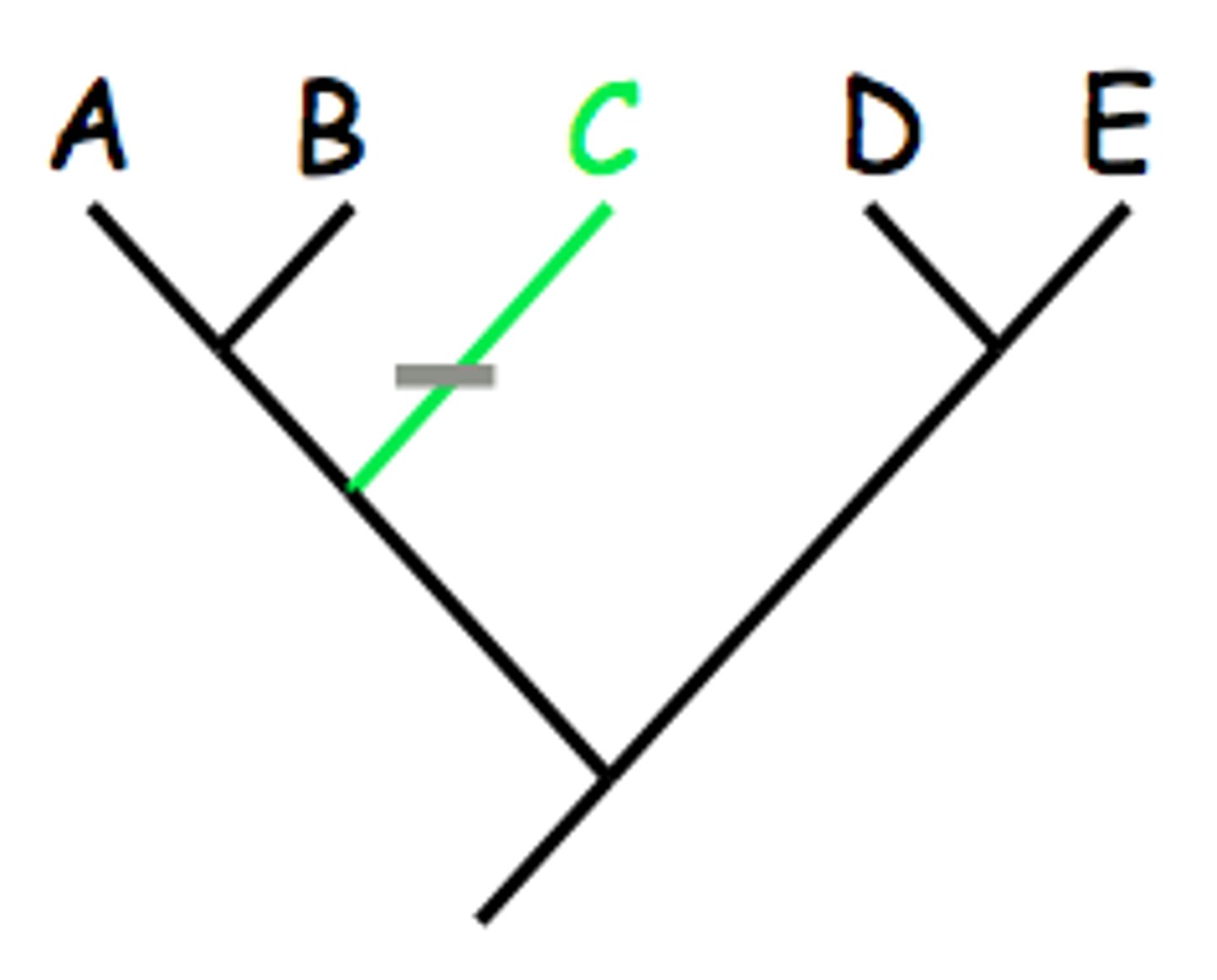
Evolutionary reversal
The reappearance of an ancestral trait in a group that had previously acquired a derived trait (ex: how penguins lost the ability to fly)
Homoplasy
The presence in multiple groups of a trait that is not inherited from the common ancestor of those groups. Can result from convergent evolution, evolutionary reversal, or parallel evolution
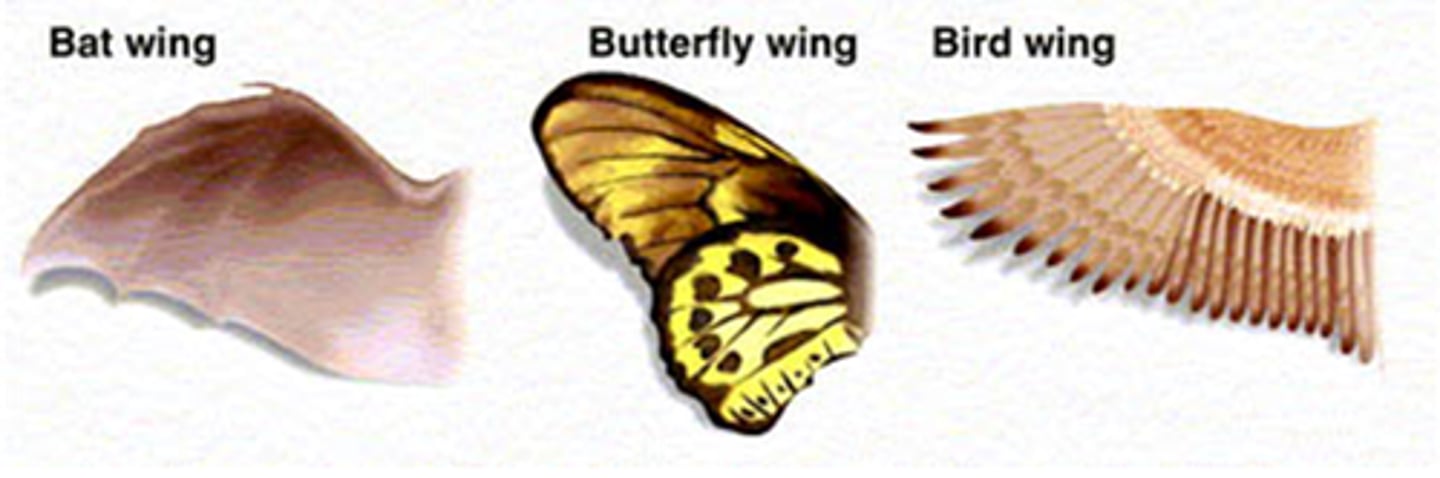
Analogous trait
A trait that is morphologically and functionally similar to that of a different species but that arose from a distinct, ancestral condition
Ingroup
In a phylogenetic study, the group of organisms of primary interest
Outgroup
In phylogenetics, a group of organisms used as a point of reference for comparison with the groups of primary interest
Monophyletic
Pertaining to a group that consists of an ancestor and all of its descendants
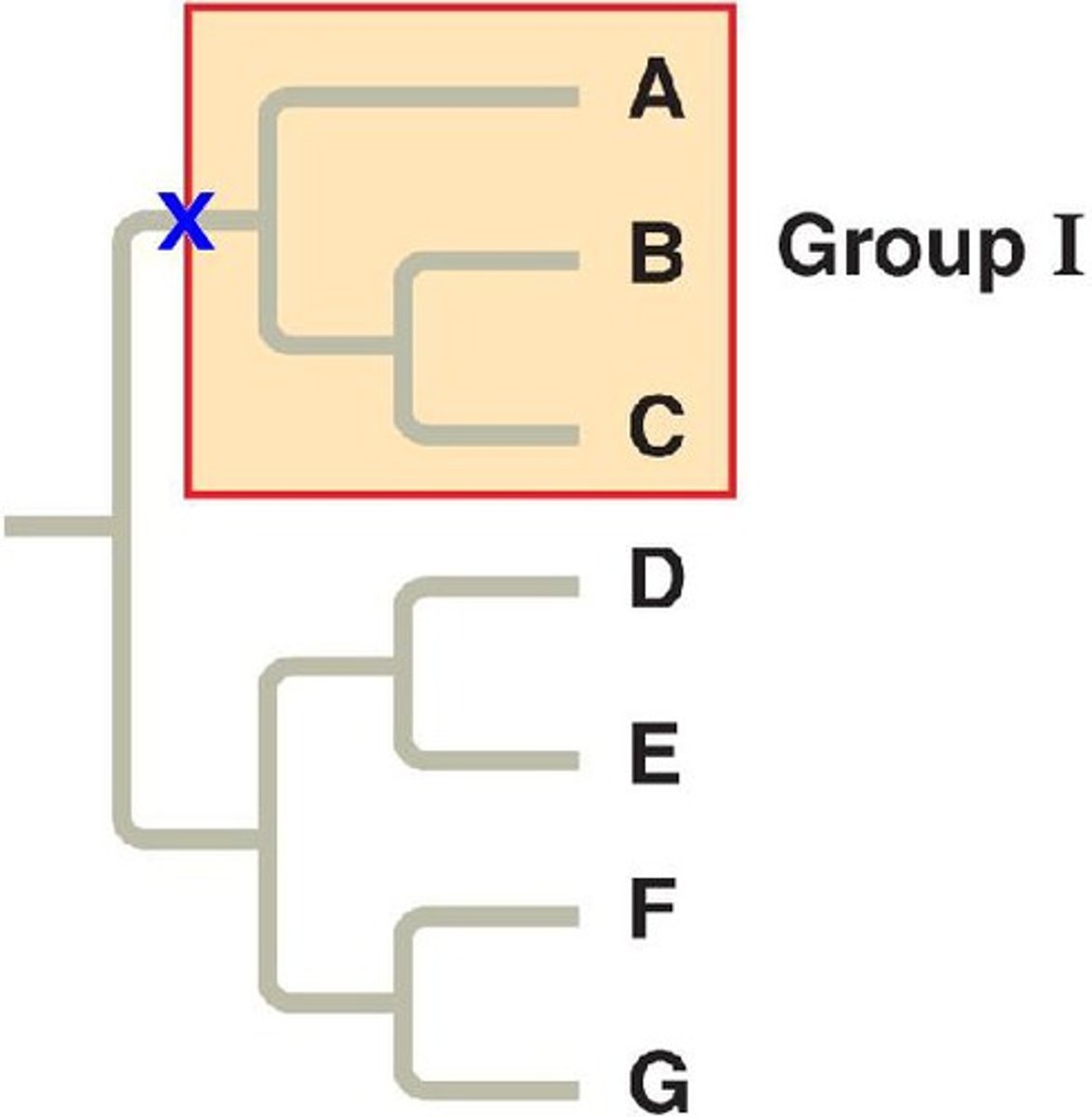
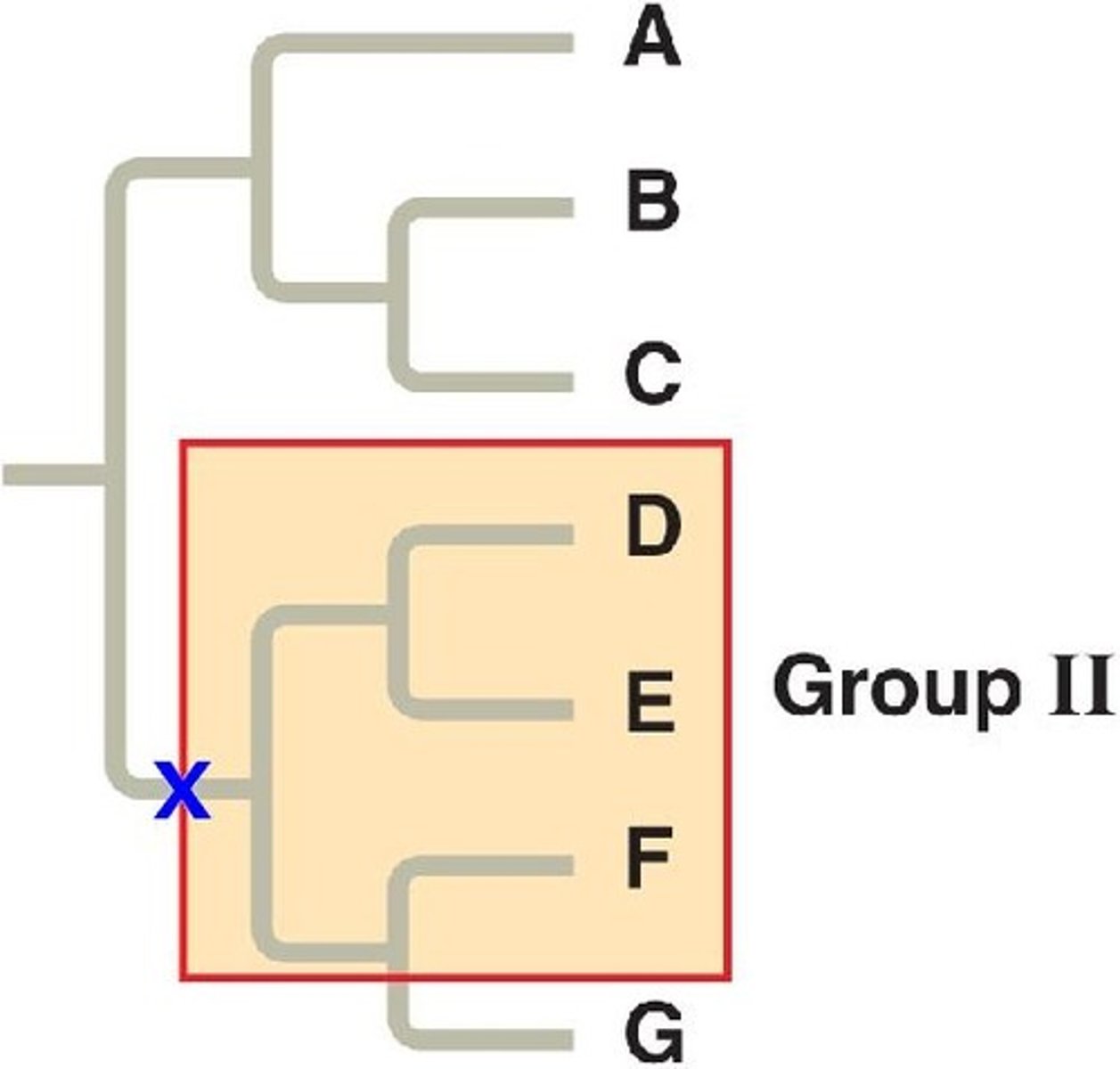
Paraphyletic
Pertaining to a group that consists of an ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants
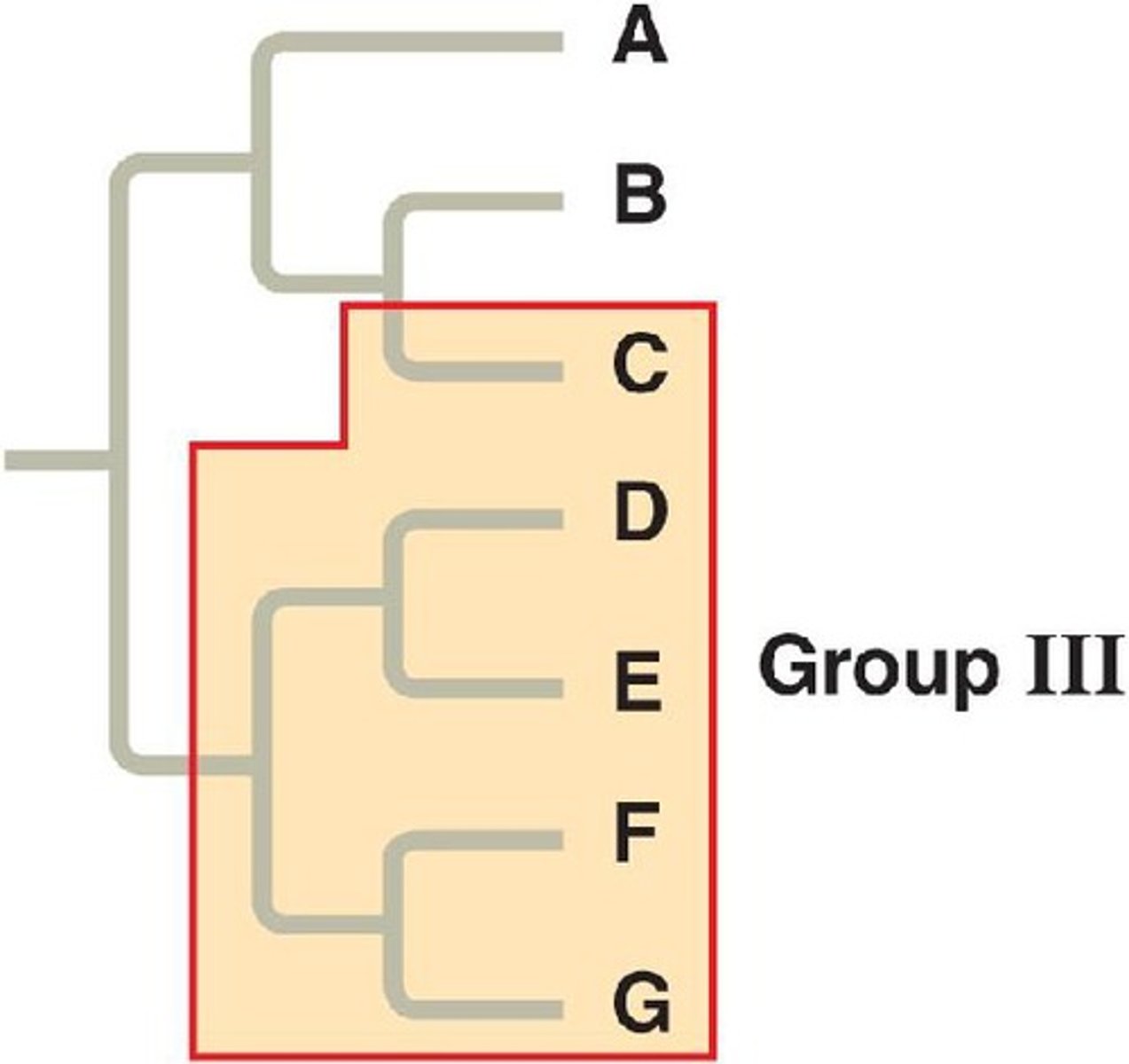
Polyphyletic
Pertaining to a group consists of multiple distantly related organisms, and does not include the common ancestor of the group
Stratum (Plural: strata)
A layer of rock laid down at a particular time in the past
Sedimentary rock
Rock formed by the accumulation of sediment grains on the bottom of a body of water. Often contains stratified fossils that allow geologists and biologists to date evolutionary events relative to each other
Radioisotopes
A radioactive isotope of an element (Ex: C-14)
Background extinction rate
At any given time a certain number of species are going extinct (5-11%), but is balanced out by new species generated
Biogeography
The scientific study of the distribution and diversity of organisms across earth
Hadean Eon
4.6-4.5 bya
This eon represents the formation of Earth. Life wasn't present yet, but the Earth was cooling. Atmosphere has no free oxygen, but the oceans are forming. A ton of meteorites were hitting Earth constantly.
Archaean Eon
3.8 bya
Life originated in this eon. Prokaryotes specifically are thriving. Earth accumulates atmosphere but still barely any oxygen. Meteor impacts decrease dramatically.
Proterozoic Eon
2.5 bya
Atmospheric oxygen levels emerge, and photosynthesis, multicellular organisms and eukaryotes emerge. This extremely long eon contains the "snowball Earth" hypothesis, which hypothesized that the Earth was completely covered in ice for millions of years.
Cambrian Period (Paleozoic Era)
542 mya
Atmospheric oxygen levels approach levels found today and rapid diversification of multicellular organisms and diverse photosynthetic protists
Ordovician Period (Paleozoic Era)
488 mya
Massive glaciation where sea levels drop by 50 meters, this caused a mass extinction
Silurian Period (Paleozoic Era)
444 mya
Sea levels rise and two large land masses emerge. The climate is hot and humid. Jawless fish diversify and first ray-finned fishes; plants and animals colonize land
Devonian Period (Paleozoic Era
416 mya
Continents collide at the end of this period, jawed fishes diversify, first insects and amphibians, mass extinction probably at least partially caused by a meteor
Carboniferous Period (Paleozoic Era)
359 mya
Climate cools down, extensive fern/horsetail/giant club moss forests; first reptiles in this period, insects also diversify
Permian Period (Paleozoic Era)
299 mya
Extensive lowland swamps, oxygen levels are 50% higher than today, by the end Pangea is formed. Reptiles diversify, giant amphibians and insects are present, and the largest mass extinction takes place as oxygen levels drop rapidly
Triassic Period (Mesozoic Era)
251 mya
Pangea begins to drift apart; the climate is hot and humid. Early dinosaurs, first mammals, marine invertebrates diversify, mass extinction at the end of this period
Jurassic Period (Mesozoic Era)
201.6 mya
Two massive continents form, Laurasia in the north and Gondwana in the south. Warm climate, diverse dinosaurs and radiation of ray-finned fish. First fossils of flowering plants
Cretaceous Period (Mesozoic Era)
145.5 mya
Laurasian continents attached to one another; Gondwana begins to drift apart. Meteorites strikes near current Yucatan peninsula. Dinosaurs continue to diversify, with a mass extinction wiping them out at the end of this period
Still learning (15)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!