MARKETING - Chapter I
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
1900 - 1910 Period of Discovery
Marketing theory was borrowed from economics, which thus resulted to distribution, worldwide trade, and commodity markets. The concept of marketing came into being and the business activity was thus named.
1910 - 1920 Period of Conceptualization
Many marketing concepts were being developed. These concepts were classified and terms were defined.
1920 - 1930 Period of Integration
Principles of marketing were postulated. The general body of thought was integrated for the first time.
Paul W. Ivey
First to use “Principles of Marketing” as a book to title
1930 - 1940 Period of Specialization
Specialized areas of marketing continued to be developed, hypothetical assumptions were verified and quantified, and some new approaches were developed to explain marketing knowledge. The scientific aspects of the subject were considered.
1940 - 1950 Period if Reappraisal
The concept and traditional explanation of marketing was reappraised in terms of current needs for marketing knowledge.
1950 - 1960 Period of Reconception
Traditional approaches to the study of marketing were supplemented by increasing emphasis on managerial decision making, the societal aspects of marketing, and quantitative marketing analysis. Many new concepts, some borrowed from the field of management and from other social sciences, were introduced into marketing.
1960 - 1970 Period of Differentiaton
As marketing expanded, new concepts took on substantial identity as significant components of the total structure of thought. Among them were such elements as managerialism, holism, environmentalism, systems, and internationalism.
1970 Period of Socialization
Social issues and marketing became much more important. It is the influence not of society upon marketing, but of marketing upon society that became a focus of interest.
“Marketing is managing profitable customer relationships. It is the process by which companies create value for customers and build strong relationships[s in order to capture value from customers in return.”
Marketing defined by Kotler and Armstrong
“Marketing is the process of continuous and profitably satisfying the target customer’s needs, wants, and expectations superior to competition.”
Marketing defined by Ac-Ac
attract new customers by promising superior value and keep and grow current customers by delivering satisfaction
goal of marketing
unnecessary
Peter Drucker said that the aim of marketing is to make selling __________
A. Create Value for Customers and Build Customer Relationships
UNDERSTAND the marketplace and customer needs and wants.
DESIGN a customer - driven marketing strategy.
CONSTRUCT an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value.
BUILD profitable relations and create customer delight.
B. Capture Value from Customers in Return
CAPTURE value from customers to create profit and customer equity.
the marketing process
Marketing & Production
Products manufactured or suppled to customers must be consistent with customer specifications. This means that production should only produce products that will satisfy customer’s needs and wants.
Marketing & Human Resources
The marketing strategy by itself cannot produce good results, say, meeting target sales, profit, and market share. A company needs good people to implement these strategies. A marketing plan is useless if the people who execute the plan are not committed to the idea. Organization is a source of competitive advantage.
Marketing & Finance
One of the common conflicts in a company involves sales and finance. Marketers and finance people should coordinate their functions to successfully achieve company objectives. Go (2001) mentioned that the wealth conversion principle results to irreconcilable differences between marketing and finance.
Wealth Conversion Principle
Business firms need cash to operate. For a company to create wealth or profit , it must have a good and cheap source of funds. These funds must be used to buy inventories at a lower price. The inventories are often then sold at a higher price and cash is collected from each sales transaction. Buying creates inventory while selling most often creates receivables since not all sales can be transacted on a pure cash money basis.
needs
wants (a. expectations)
demands
exchange
market
five core customer and marketplace concepts
needs
states of felt deprivation, basic reason or the minimum requirements consumers look for in a product or services
wants
the form of human needs take as they are shaped by culture and individual personality; the determining dimensions among many choices
expectations
values/intangibles associated with a product or service
a part of wants but become extremely important when products or services are not differentiated
demands
human wants that are backed by buying power
exchange
act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return
market
the set of all actual and potential buyers of a product or service
market offering
consumers needs and wants are fulfilled through
not limited to physical products, also include services
combination of products, services, information, or experiences offered to a market to satisfy a need or want
include persons, places, organizations, and ideas
product
goods-and-services combination the company offers to the target market
services
the activities or benefits offered for sale that are essentially intangible and do not result in the ownership of anything
marketing myopia
the mistake of paying more attention to the specific products a company offers to the benefits and experiences produces by these products.
smart marketers
they look beyond the attributes of the products and services they sell, by orchestrating several services and products, they create brand experiences for consumers1
company —→ 1) Customer —→ 2) Competitors
strategic 3CS of marketing
to satisfy needs wants & expectations of targeted customers
objective with customers
to outperform them
objective with competition
to ensure corporate health and profit
objective with company
strategic marketing management
marketing strategy
marketing tactics
three levels of marketing activities
strategic marketing management
focus is vision & mission, industry & competition analysis, key factors for success, strengths & weaknesses analysis, opportunity & threats analysis
marketing strategy
market segmentation, target market positioning
marketing tactics
product, placement, promotions, pricing
1) Customers
2) Company 3) Competitors
marketing triangle
market - emerging opportunities
industry - impending threats
factors to consider in formulating marketing strategies and tactics with customers:
competitor’s strategies and tactics
competitor’s strength and weaknesses
competitor’s strategic focus
factors to consider in formulating marketing strategies and tactics with competitors
company’s strengths and weaknesses
industry structure and the firm’s competitive position
personal values and preferences of key owners and excecutives
societal expectations
factors to consider in formulating marketing strategies and tactics with company
marketing mix
conceptual approach
systems/holistic approach
marketing management
macro - marketing
social marketing
comparative marketing
enumerate the contemporary marketing approaches
E. Jerome McCarthy
who developed the marketing mix
marketing mix
consists of four Ps — product, price, placed and promotion — all of which influence buyer’s decision and resources
marketing success
desirable product + effective promotion or demand stimulation + acceptable price + availability in right places = _________ _______
product
anything marketed to satisfy a want or a need, may be a person, a place, an organizational, an idea or a good offered to a target market
target market
consist of buyers who share common needs or characteristics that the company decides to serve
place
considers all the functions, problems, and institutions involved in getting the right product to the market, also refers to the channel of distribution that marketers work in and through to move goods from manufacturers to the consumers.
promotion
includes advertising, sales promotions, public relations, personal selling, and direct marketing.
concerned with any communication tool used to persuade and influence the target market
setting the PRICE
wherein factors like competition, existing practices on mark ups, discounts and terms of sale, product appeal, and legal restrictions must be considered,
independent
elements of the marketing mix are ___________
conceptual approach
an approach that studies the ideas of marketing rather than the activities of marketing
as a marketing concept
as a concept in marketing
the conceptual approach is viewed in two ways
“Consumer is King” approach
counterpart of the conceptual approach
system/holistic approach
an approach that is based on the understanding that activities or processes are interdependent to other activities or processes. it is a holistic/unified view of marketing
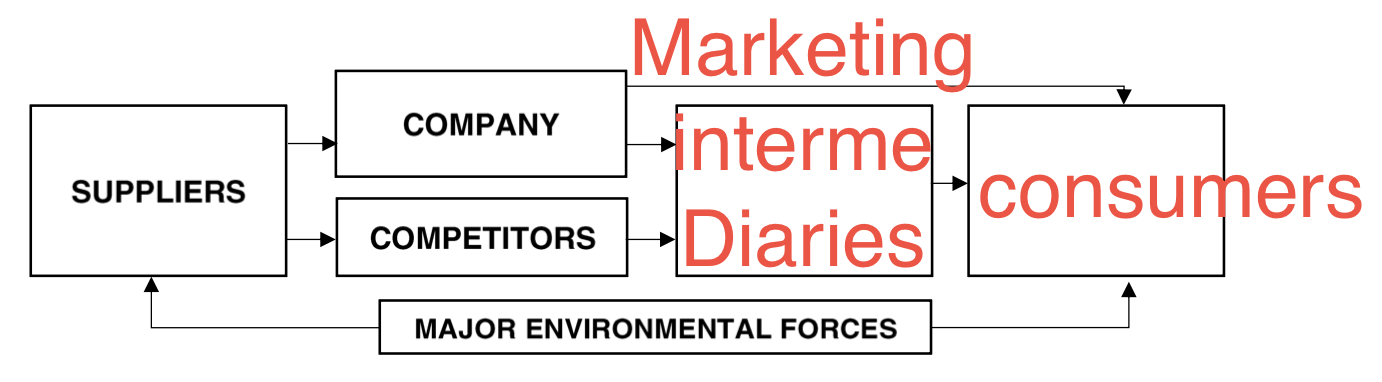
modern marketing system
marketing management
emphasizes marketing management as a decision-making process and how decision makers, specifically rhetorical marketing managers, handle specific marketing problems and situations