Derm E2: skin cancer
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
what is the most common form of skin cancer?
basal cell carcinoma
What are clinical features of basal cell carcinoma (BCC)?
rare to metastasize- grows slowly
nodular: firm, translucent or pearly skin colored smooth nodule w/ telangectasias; well defined, rolled border
superficial: thin scaly plaques, pink/red w/ fine threadlike border and telangiectasias; periphery may be rimmed w/ fine translucent papules
morpheaform: smooth, flesh colored papules, may be atrophic, lesions can bleed w/ minimal trauma, majority on head or neck
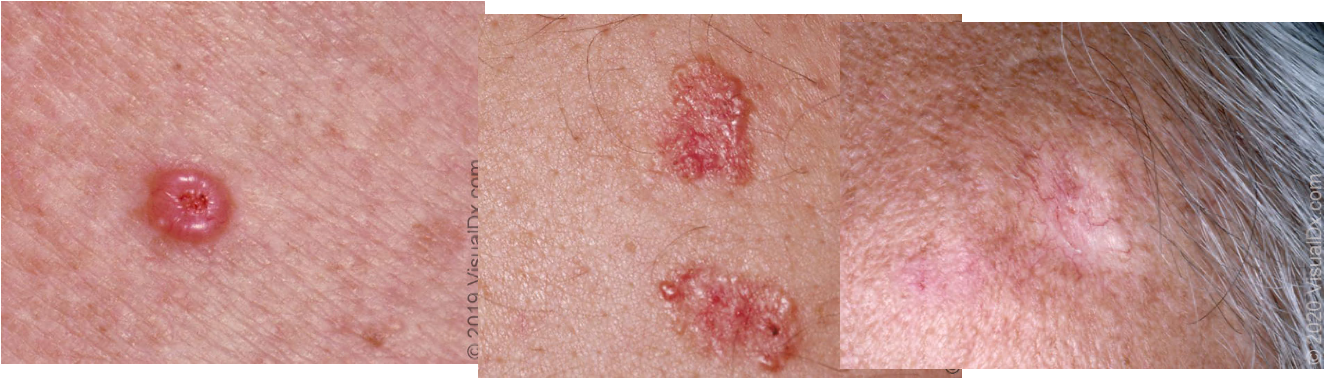
what are risk factors for BCC?
genetics, sun exposure, Fitzpatrick I-II, hx radiation or phototherapy exposure
How do you dx BCC?
skin bx; histopathology shows islands of basaloid cells
what is 1st line tx for BCC?
excision→ preferred is Mohs surgery (nasolabial area, around eyes, ear canal, posterior auricular sulcus, scalp)
electrodessication and curettage
What is 2nd line tx for BCC?
topical imiquimod or 5-FU
What is squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)?
malignant cutaneous tumor arising from epidermal keratinocytes
caused by DNA mutations from UV exposure, smoking, aging, and immune suppression
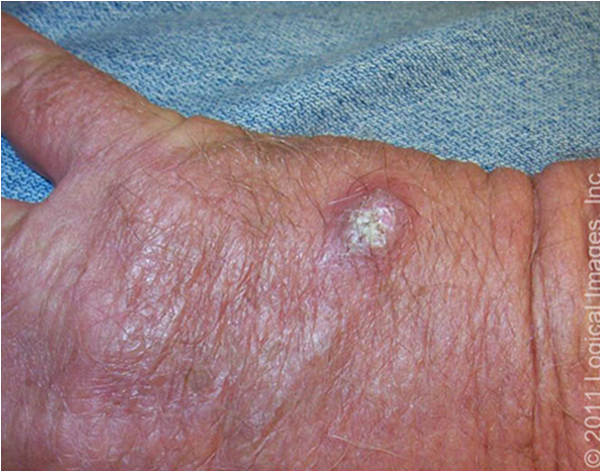
what are risk factors for SCC?
sun exposure, immunosuppression
what are clinical features of SCC?
may present in multiple ways- papules, scaly or crusted plaques, nodules, hyperkeratotic
grows over wks-mos
may ulcerate
lesions may be tender/painful
can present as in situ vs invasive
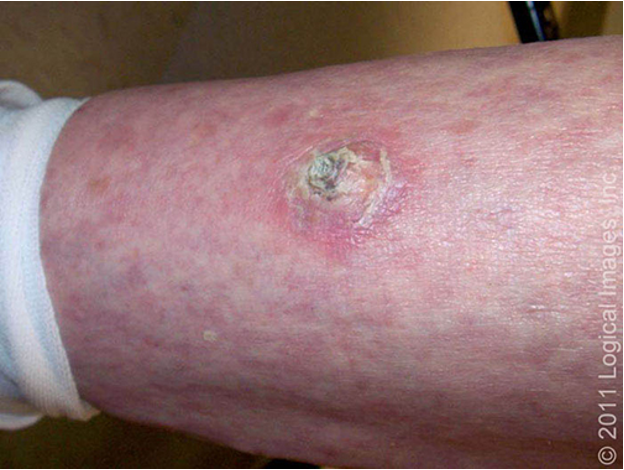
what are clinical features of SCC in situ / Bowen’s dz?
slow growing, erythematous, well demarcated scaly patch/plaque
typically asx- pain/tenderness suggest invasive
Erythroplasia of Queyrat- red plaque on on glans penis or labia minora; may be assoc. w/ bleeding, pruritus, pain
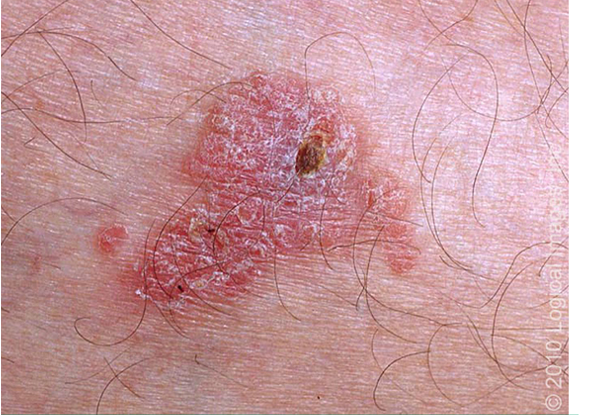
What is the histopathology of SCCIS?
keratinocytes dysplasia of full thickness of epidermis w/o infiltration of atypical cells to dermis; thickening of epidermis (acanthosis); hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis of stratum corneum
what are clinical features of invasive cutaneous SCC?
well differentiated lesions → indurated, firm, hyperkeratotic papules, plaques, nodules
poorly differentiated → fleshy, granulomatous papules, nodules; w/ ulceration, hemorrhage, necrosis
slowly evolving → tissue destruction; can metastasize 1-3 yrs after initial dx; can cause burning/paresthesias/visual changes if neural invasion
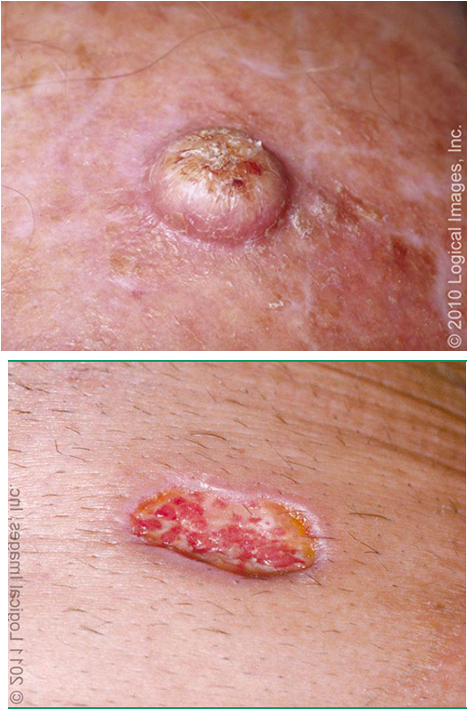
what is histopathology of invasive cutaneous SCC?
dysplastic keratinocytes involving full thickness of epidermis that penetrates epidermal basement membrane to involve dermis or deeper tissue
what are high risk features of recurrence/metasstasis of invasive SCC?
located on lips, ears, forehead, cheeks
> 2cm
recurrent or multiple tumors
wounds, scars, or sites of previous radiation
neuro sx
clark level IV or higher (invades reticular dermis or SC fat)
Where is SCC located?
sun exposed: face, ears, hands, forearms, legs
atypical: anogenital region or areas w/ chronic inflammation
how do you dx SCC?
skin bx- confirm dx, stage, and aid w/ management
histology: keratinocytic dysplasia
dermoscopy: differentiate b/t in situ vs invasive
what is 1st line tx for SCC?
surgical excision
alt: Mohs surgery
what is 2nd line tx for SCC?
nonsurgical options- electrodessication and curettage, cryotherapy (only for low risk, well defined lesions)
what is Merkel cell carcinoma?
rare, aggressive cutaneous malignancy that typically appears in older individuals
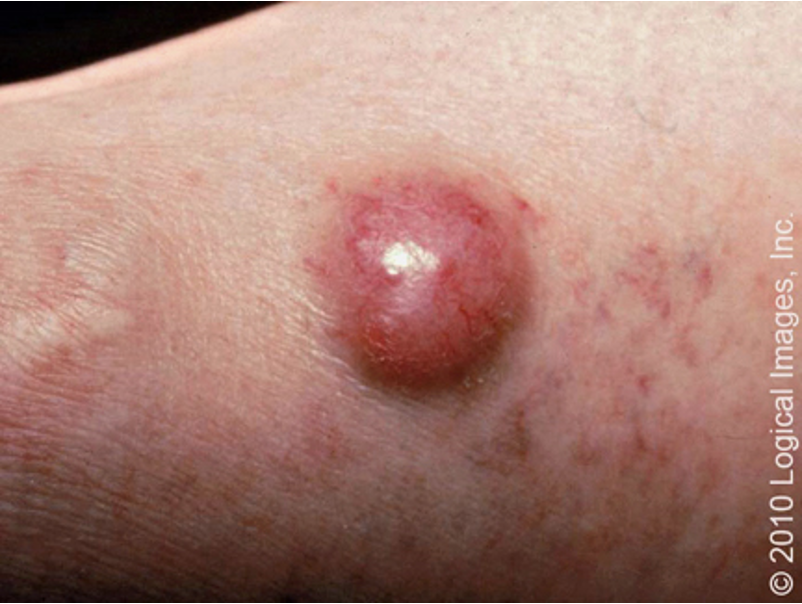
what are clinical features of Merkel cell carcinoma?
rapidly growing, firm, contender intracutaneous nodule
skin colored or bluish-red
1cm - 2cm+
high risk of metastasis
located in sun exposed areas
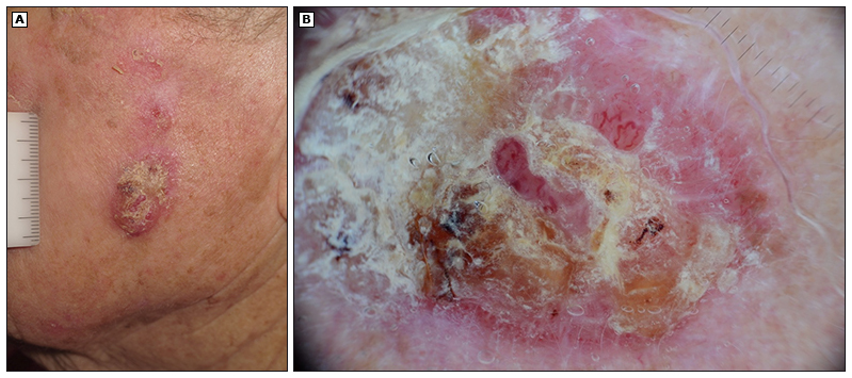
How do you dx Merkel cell carcinoma?
skin bx; AEIOU mnemonic:
Asx or non tender
Expanding rapidly
Immune suppressed
Older than 50
UV exposed skin
What is the management for Merkel cell?
requires imaging for metastasis, staging, and sentinel node bx
What is melanoma?
potentially deadly form of skin cancer → uncontrolled growth of melanocytes occurring in 2 growth phases
radial/horizontal- arises from superficial tumor confined to epidermis
vertical- invade basement membrane and deeper tissues
Where can melanoma be located?
anywhere on body including oral cavity, genitalia, glans or prepuce, labia minora, mucus membranes (lining of resp, GI, GU, rare)
what are risk factors for melanoma?
MMRISK
Moles: atypical/dysplastic nevus >5
Moles: common moles > 50
Red or blonde hair and freckling: these ppl often have few or no moles
Inability to tan: Fitzpatrick I and II
SunburnL severe sunburn < 14 y/o
Kindred: FHx melanoma
What would dermoscopy show for melanoma?
atypical pigment: brown-black dots/globules; 5-6 colors asymmetrically distributed; blue-white-veil depigmentation; irregular vascular pattern
what is dx workup for melanoma?
history
PE- ABCDE
dermoscopy- atypical pigment
Skin bx/pathology: excisional bx should include 2mm margins; breslow thickness (strongest predictor of outcome) and clark levels
staging- if regional LN involved
what is tx for melanoma?
surgical excision- only curative if early
for stage III-IV distant metastases- surgery ± chemo, radiation, palliative care
How often should follow ups be for melanoma?
skin check every 3-6 mos for 3 years
PE and labs yearly
ophthalmology exam yearly
(late recurrence can occur >10 yrs after dx)
what are clinical features of superficial spreading melanoma?
MC histological subtype of melanoma
variably pigmented macule or thin plaque w/ irregular border ranging few-several cm
multiple shades of red, blue. black, gray, white
traditionally stays in horizontal growth phase
dermoscopy inc dx accuracy >50%
located anywhere on body
histology- asymmetric, poorly circumscribed, lack cellular maturation
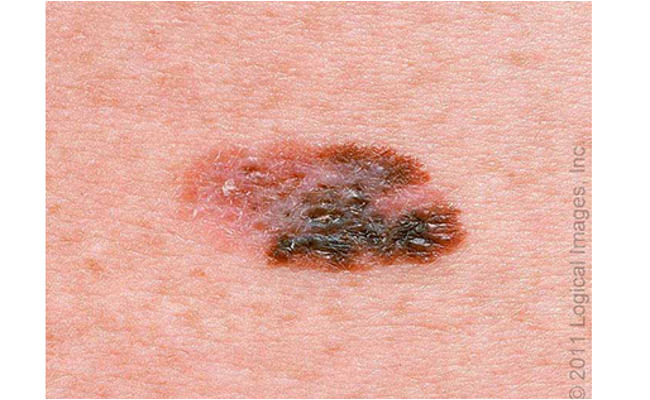
what are clinical features of nodular melanoma?
enters vertical growth phase from inception
darkly pigmented, pedunculate or polypoid papules/nodules
uniform color or melanotic, symmetric orders, small diameter → early detection difficult
>2mm thick upon dx
rapidly enlarges over wks to mos
may ulcerate or bleed
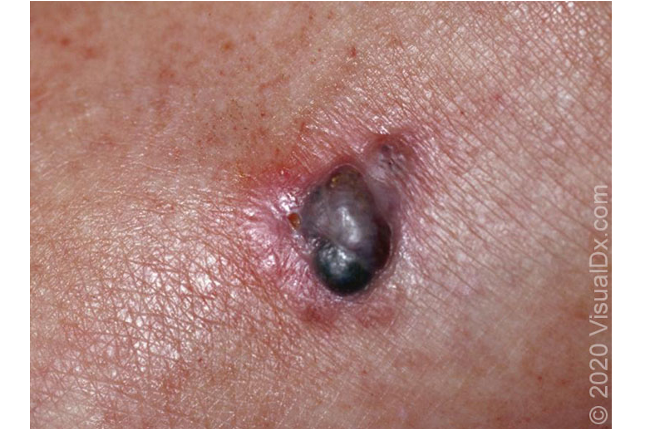
what are clinical features of lentigo malignant melanoma?
commonly arises on sun damaged areas of skin in older pts
begins as freckle like, tan or brown macule
gradually enlarges and darkens w/ asymmetric foci or pigmentation, color variegation
raised areas signify vertical growth into dermis
blurred borders w/ notch “geographic” shapes
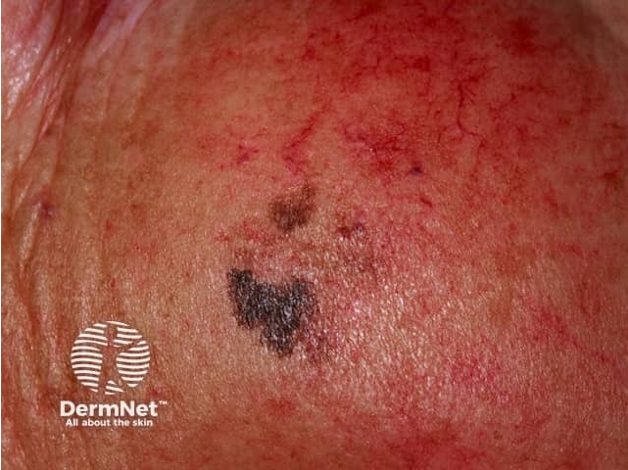
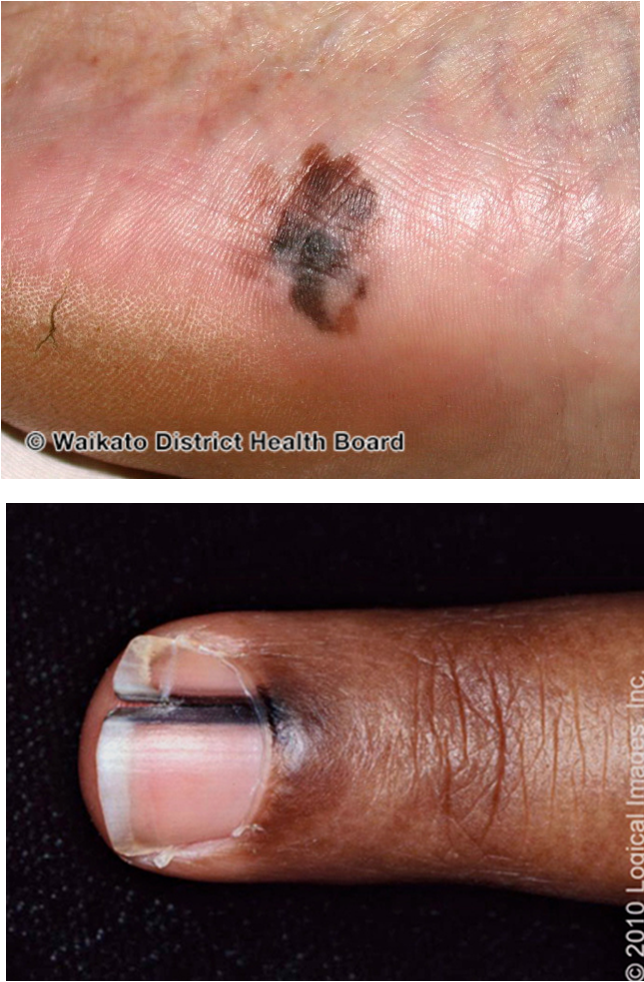
what are clinical features of acral lentiginous melanoma?
MC type of melanoma seen in Fitzpatrick III and above
arises most commonly on palmar, plantar, subungual, and mucosal surfaces
dark brown/black, irregularly pigmented macules or patches w/ raised areas, ulceration, bleeding
occasionally can present as amelanotic/hypomelanotic lesions
slow growing- can take mos-yrs
hutchinson’s sign- involvement of proximal nail fold
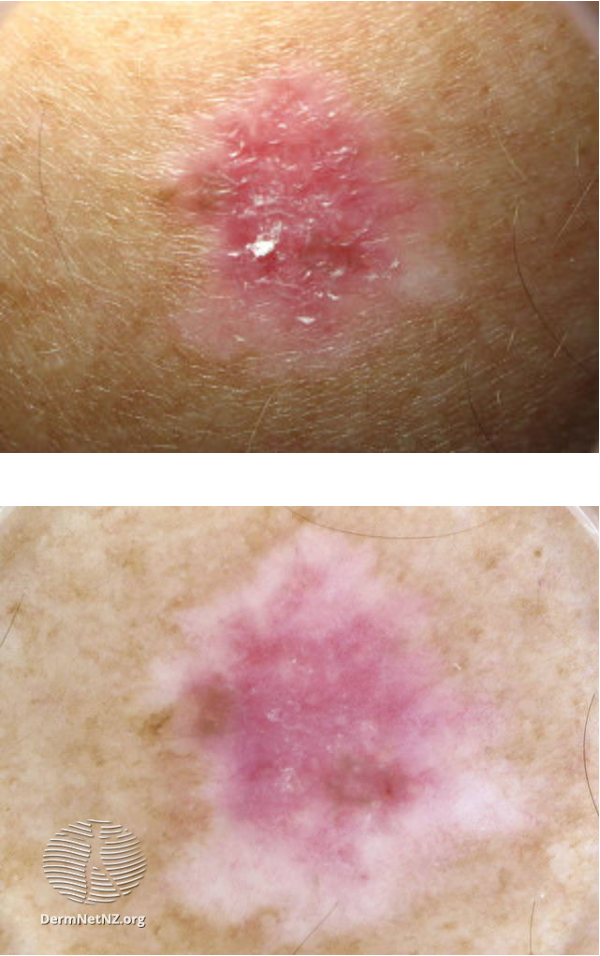
what are clinical features of amelanotic melanoma?
melanoma lesion w/ NO pigment
may present as pink or red ,accuses/papules/nodules
well defined borders
often clinically confused w/ benign lesions (hemangioma, pyogenic granuloma, SKs)
what is mycosis fungoides?
cutaneous T cell lymphoma, form of non-hodgkin lymphoma that presents as patches, plaques, tumors, or erythroderma
unknown cause
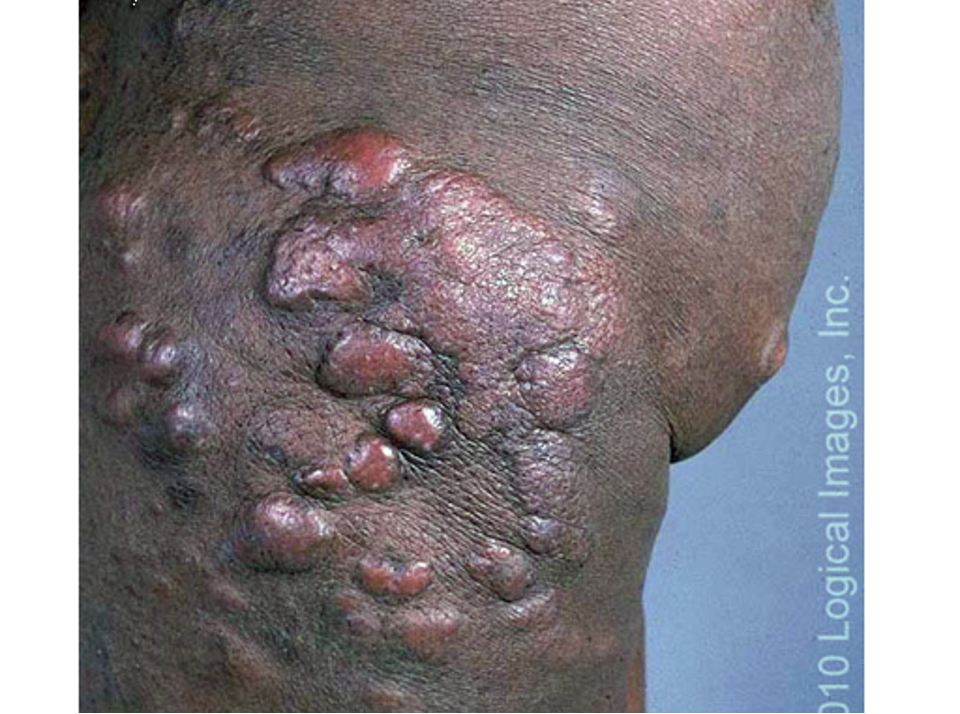
what are clinical features of mycosis fungoides?
presents as chronic itch (even before clinical signs)
patch stage: poorly defined, irregular scaling red patches
hypopigmented variant- pale, finely scaly patches
plaques stage: well demarcated, annular itchy thickened lesions w/ red, violet, or brown color
tumor stage: large irregular lumps (>1cm) developing from plaques
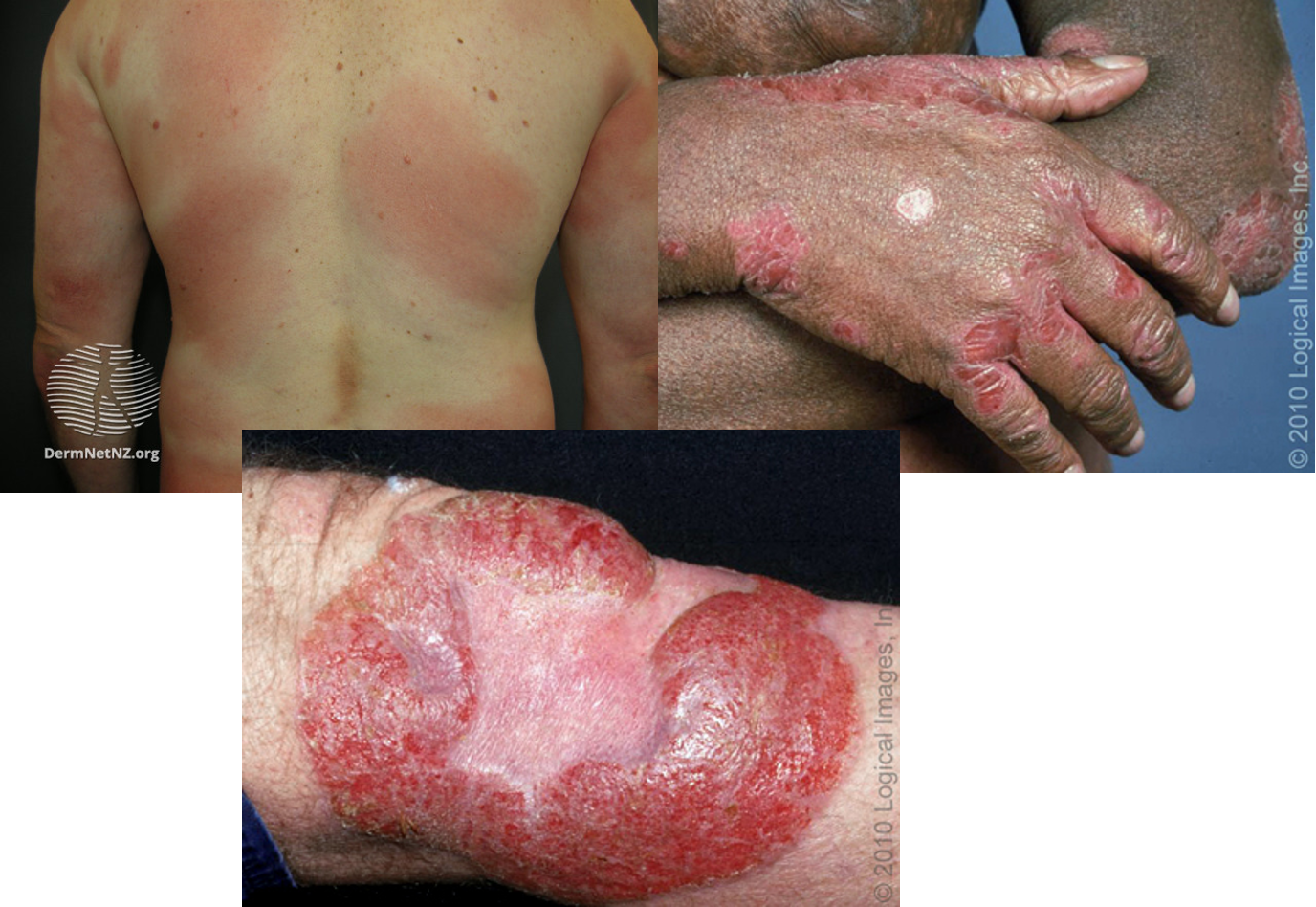
How do you dx mycosis fungoides?
skin bx
what is tx for mycosis fungoides?
UVA phototherapy, TCS, topical chemotherapy, radiation