Feline BEHAVIOR + RESTRAINT + PE
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Common Behavior concerns
Inappropriate elimination
Urine marking
Scratching
Increased aggression (toward people and other animals)
Fear and Anxiety at the vets office
Defense cascade
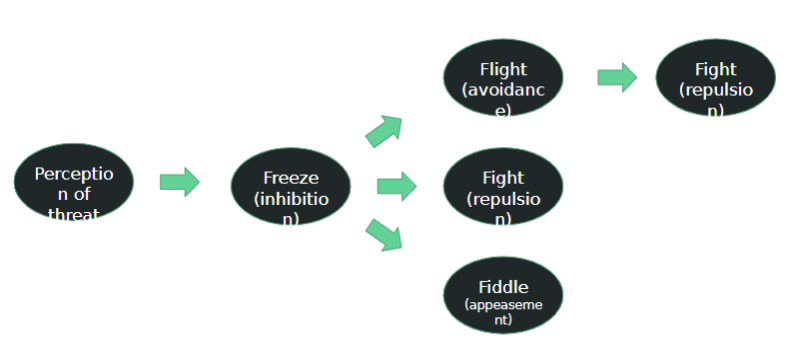
To help make feline vet visits better
Get the owner involved! Desensitization training starts at home
destigmatize the carrier
Create a cat friendly environment at the clinic
Usage of medication
Relaxed Feline
Ears: up and forward
Eyes: normal pupils, eyes may be closed
Mouth: closed mouth
Whiskers: forward
Body position: back flat, sitting/standing/laying loosely, looking around
Tail: up or relaxed, gentle back and forth movements
Stressed Feline
Ears: back and/or flattened
Eyes: Dilated pupils
Mouth: open mouth - may be panting, hissing, spitting, vocalizing or lip licking
Whiskers: back
Body Position: Back arched, fur standing up, crouched or tense, may be fixated on you or refuse to look at you
Tail: tucked, fur bristled, rapid and intense movements
Relaxed/content/happy
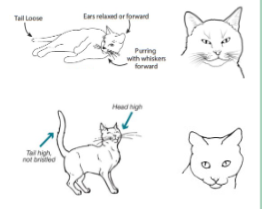
Curious/interested/engaged
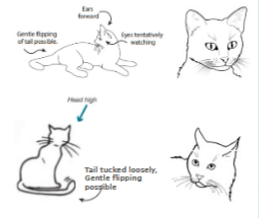
Fearful/Anxious/stressed

Towel restraint
tuck front limbs up first, then wrap one side, then the back, and then finish the burrito by wrapping the other side

Cat Bag
Muzzles
Velcro secured, nylon material
Tie or buckle secured. Leather or plastic material
long part goes over the head

Cat gloves

Snake hold
From behind, place the first and middle finger on top of the cats head, with the thumb and ring finger on either side of the head under the jaw. You can then use that arm to keep light pressure along the back of the cat

Ring grip
From the front, cup under the cat’s jaw with the first finger and thumb on either side (making a “c”)
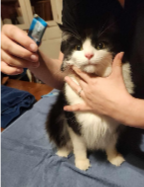
Triangle Hold
From behind, place thumbs behind head on either side and first fingers under the chin. Keep other fingers curled into hand
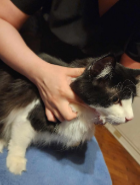
Standing Restraint
Commonly used for examination
standing beside or behind the cat, use one hand to maintain loose control of the head by using a relaxed ring grip. The other hand can be used to provide more restraint if needed by reaching over the back and under the abdomen. Keeping the cat tucked in close to your body will help prevent excessive squirming
Sitting Restraint
Commonly used for Exams, jugular or cephalic venipuncture, cephalic IV catheter placement, SQ injections/fluids, ear cleaning
Use one hand to maintain control of the head, and the other hand can be placed along the back/tail base, applying light pressure to encourage the cat to remain sitting. Keeping the cat tucked in close to your body will help prevent squirming
Sternal Restraint
Commonly used for cephalic or jugular venipuncture, SQ injection/fluids, ear cleaning
The “cat press” Standing beside the cat, make a “c” with on hand and use it to cup over the back of the neck near the shoulders. Use the other hand to apply light to medium pressure along the low back/tail base to encourage the cat to remain laying
Lateral Restraint
Commonly used for saphenous venipuncture, IM injections, cystocentesis
The “cat stretch”
The “pretzel”
Some cats may better tolerate this restraint if their front half is allowed to remain sternal
Cat stretch

Dorsal Recumbency Restraint
Commonly used for cystocentesis, FAST scan
One or Two person
Can use a trough to help the cat feel more secure and balanced
Ear Cleaning
Need: Otoscope, Cotton balls/cotton tip applicator, Ear cleaning solution
Technique: Use the otoscope to visualize the overall and confirm the tympanic membrane is intact. Take swab for cytology before cleaning. Saturate a cotton ball with ear cleaning solution and squeeze that into the ear. Massage bass of ear. Clean
Nail Trim
Need: Trimmers, Clotting agent like Kwik Stop, Moistened cotton tip and a paper towel
Technique: Comfortably restrained, grasp the paw and gently squeeze to extend out the nail, Identify the quick and cut at least 2mm below it.
Body Condition Scoring
Small changes in a cats weight can indicate underlying illness
Weigh EVERY patient

PE - Integument
Evaluate the skin, nails, paw pads, nailbed.
Any matted or unkempt fur?
obesity
Pain, especially if localized
Compulsive behavior/anxiety
Ectoparasite
Fleas, flea dirt, ticks, mites
Masses
Skin disease
Lymph Nodes
Peripheral
submandibular
prescapular
popliteal
Not easily palpable
if you feel them readily, they are probably enlarged
Symmetry
pain

PE - Head
Look for symmetry
Vibrissae are sensitive structures
Evaluate cranial nerves
Evaluate Nasal Planum
thickening, discharge
Mucous Membranes
Color: Pink, pale, white, icteric, cyanotic
Cats are usually a lighter pink than dogs
best evaluated on hard plate
Capillary Refill time (CRT)
Moisture?
Look under tongue (masses, foreign bodies?)
Look at tonsils
PE - Teeth
Commonly get periodontal disease
Stomatitis or gingivitis
Dental tartar or calculus
Tumors
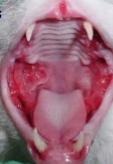
PE - Eyes
External: Symmetry of globes, pupils, etc. PLR and Menace Response
Pupils are elliptical not round
Siamese type cats may have nystagmus normally
Sclera is less visible than in dogs
Internal: Retinal Examination
PE - Pinna/Auricle
Preauricular alopecia is normal
Evaluate for ear mites
Evaluate for Discharge
PE - Ear Canal
Tympanum easily visualized
Evaluate for masses, mites, polyps
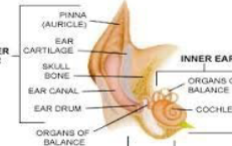
PE - Neck
Palpate for enlarged lymph nodes
Auscultate the trachea for increased upper airway sounds
Palpate for thyroid gland enlargement
Range of motion (any pain?)
PE - Lungs
Cat thorax is slightly compressible
If not, may indicate disease
Auscult lungs first
Bronchovesicular sounds are quiet in cats
10-30 bpm in unstressed cat
Listen in all 4 lung field (crackles, wheezes?)
PE - Heart
Listen to the heart
Sternal then rock the diaphragm to the left and right
Murmurs are best heard parasternal
Heart valve sounds are similar to the dog..
left = pulmonic, mitral, and aortic
Right = tricuspid
Any arrhythmia is significant in cats
PE - abdomen
Liver, stomach, and pancreas generally not palpable in normal cat
Both kidneys are readily palpable
Right - high under the ribcage
Left - caudal to ribs, loose in the abdomen
Palpate small intestines for thickening “ropey”, pain, gas, or masses
Colon - dorsal, tubular structure, usually can palpate feces
Urinary Bladder - Soft and compressible, HARD = BLOCKED
PE - Musculoskeletal
Evaluate for muscle mass - senior cats or debilitated cats often have generalized muscle atrophy
Evaluate joints - Symmetry, Range of motion, pain (osteoarthritis in geriatric cats), Laxity (Patellar luxation)
Evaluate Posture: changes may indicate disease or pain
PE - Genitourinary Female
Vulva is ventral to anus
Mammary tissue on ventral abdomen
palpate for masses
PE - Genitourinary Male
Penis is ventral to the anus not the abdomen
Penile spines are seen in intact males
Testicles may not be fully descended into the scrotum until 5-7 months old
PE - Genitourinary BOTH
Anal sacs, Perineum - look for masses

Relaxed

Stressed

Anxious

Fearful/annoyed

stressed/angry
A cat is approaching you with its tail held high and slightly curved at the tip. This body language indicates:
Confidence and friendliness
A cat that is slow blinking at you is likely:
Expressing affection and trust
A cat’s tail puffed up and fir standing on end generally indicates:
The cat is scared or trying to appear larger to a perceived threat
If a cat’s whickers are pulled back against its face, it likely indicates:
the cat is nervous, scared, or feeling threatened
A cat that is “kneading” with its paws is:
Displaying a sign of affection or comfort
A cat that is vocalizing loudly with a low, guttural sound is likely
Signaling that it feels threatened or is in pain
What is the normal capillary refill time for a cat
less than 2 seconds
True/False
You should avoid palpating the abdomen if the cat shows any signs of discomfort
False
What would you do if you notice a cat has a heart murmur during the exam
Record the finding and recommend further diagnostics
When assessing a cat’s breathing, which of the following is considered abnormal?
Rapid breathing rate
TPR
100-103 degrees
HR - 160-220
RR - 20-30
Fearful cat typically displays what
aggression
What does a cat’s tail flicking back and forth typically indicate?
Annoyance or agitation
Ears are rotating or twitching indicates what
The cat is trying to listen to sounds around it
What does it mean if a cat suddenly starts to groom itself during an interaction?
The cat is trying to calm itself or diffuse tension