APES- Unit 7: Air Pollution
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
air pollutants
gases and particulate material added to the atmosphere
primary pollutants
pollutants that are directly harmful & can react to form other harmful substances
(ex. NOx, SOx, PM, CO)
secondary pollutants
pollutants that form when primary pollutants interact or react with components of the atmosphere
(ex. tropospheric ozone O3 & sulfuric acid H2SO4)
residence time
time a pollutant stays in the atmosphere
brief residence time exerts localized impacts over short time period (ex. smog, acid rain)
long residence time exerts regional or global impacts (ex. climate change, ozone depletion)
what are the effects of pollution?
reduced visual quality (reduced range, quality, & alteration in color or contrast)
damage to vegetation (leaf tissues, needles, fruits, reduction of growth rates & germination, increased susceptibility to disease & pests)
soil & water contamination (deposition of airborne chemicals & particles can toxify soils, alter pH, & reduce productivity)
human health effects (irritation of eyes, nose, throat, & increased lung disease, asthma, emphysema, COPD, pneumonia, bronchitis)
clean air act (1970)
identified the EPA is required to set acceptable limits for 6 criteria pollutants → later CO2, CH4, GHGs,& 200+ were added
1) sulfur dioxide (SOz)
formed from coal combustion → causes respiratory irritation, smog, & acid deposition
2) nitrogen oxides (NOx)
formed from fossil fuel combustion → causes O3 formation, smog, & acid deposition
3) carbon monoxide (CO)
formed from incomplete combustion of fossil fuels (engines & biomass) → causes smog, O3 formation & human death (lethal b.c it binds to hemoglobin → suffocation)
4) particulate matter (PM2:5 & PM20)
formed from fossil fuel & biomass combustion → causes respiratory irritation, smog, & mercury deposition
5) tropospheric ozone (O3)
formed from photochemical oxidation of NOx → causes respiratory irritation & smog
6) lead (Pb)
pollutant from metal plating & waste incineration (previously from adding tetramethyl & tetraethyl to leaded gasoline) → is a neurotoxin
what are the leading sources of most major air pollutants?
extraction, refining, & combustion (coal & gas for electricity, gasoline & diesel in engines)
what pollutants are associated with fossil fuels?
CO, CO2, CH4,VOCs, PM2:5, NOx, N2O, SO2, O3, PAN’s, HNO3, H2, SO4
carbon dioxide (CO2)
formed from combustion of fossil fuels, respiration, & decomposition of organic matter → causes global warming, extreme heat, severe storms, flooding, expanding ranges of tropical diseases, ocean acidification
how is particulate matter formed?
fire (→ matter + gas)
volcanoes (→ ash & gas)
dust storms
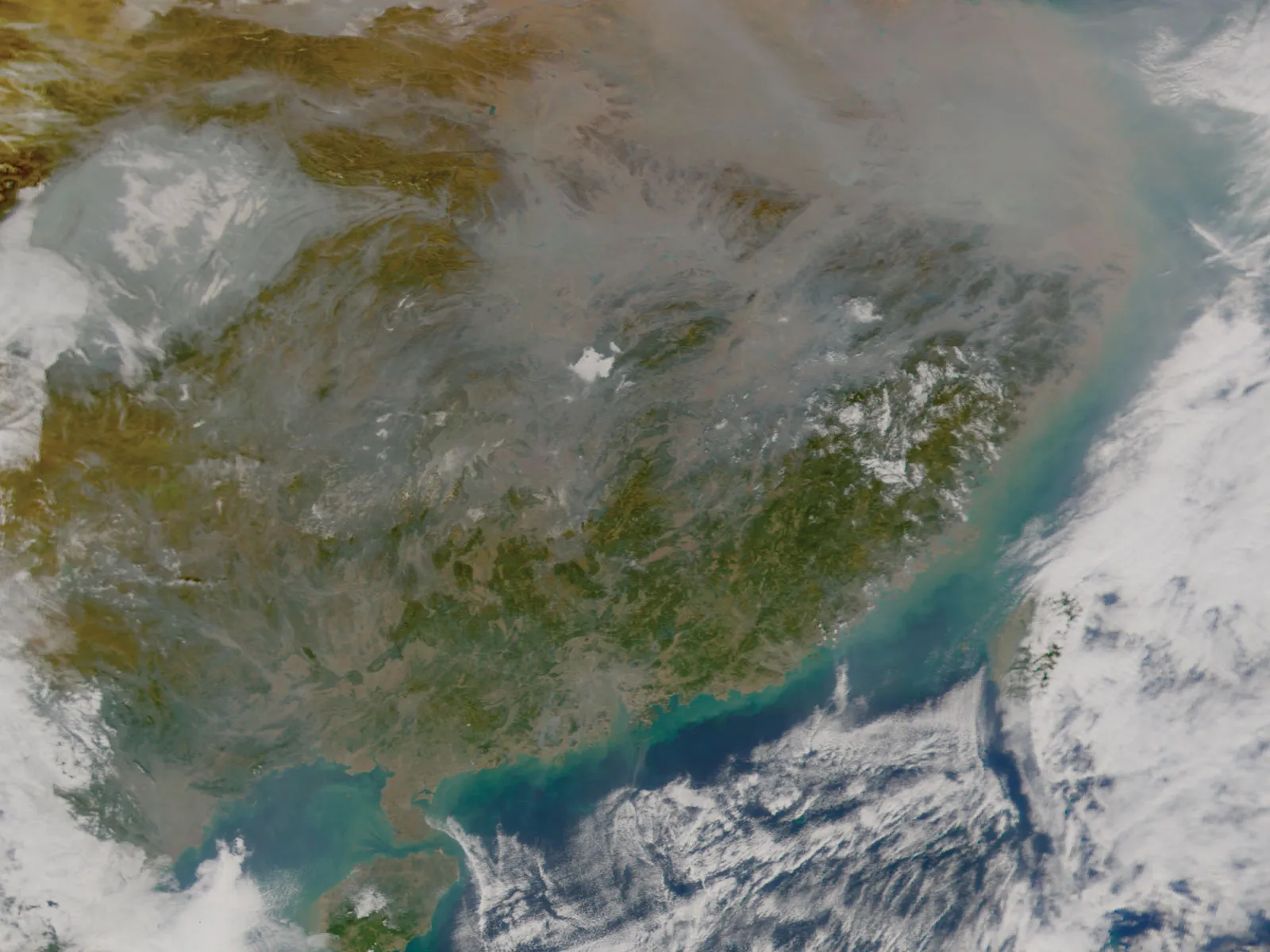

asian brown ring
result of economic growth but little environmental regulation; a 2-mile thick haze of pollution in the dry season that reduces sunlight reaching Earth’s surface → premature death
smog
unhealthy mixture of air pollutants which typically form over urban areas
1) industrial smog 2) photochemical smog
industrial “sulfurous” smog
forms primarily as a result of unregulated coal burning from industry & electricity production (combustion of coal & crude oil) → produces carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, & particulate matter
formation of aerosolized particles in smog
sulfur + water → sulfuric acid → condenses into particulate matters → forms aerosolized particles that are main components of smog
photochemical smog
forms primarily as a result of automobile exhaust during hot, sunny weather & when sunlight drives a series of reactions involving primary pollutants
***traffic releasing NO2 & VOCS + sunlight (intensity & duration summer afternoons in warm climates & urban areas) = conditions that increase smog
what are primary pollutants in photochemical smog?
NO2, VOC’s, CO, PM
what are secondary pollutants in photochemical smog?
O3, Nitric Acid (HNO3), PAN’s
how is nitrogen dioxide (NO2) formed?
forms from combustion of gasoline in cars (N2+ O2 → 2NO 2NO+O2→ 2NO2)
formation of tropospheric O3 in photochemical smog
exhaust from morning traffic releases NO2 & VOC’s
day-time temperature rises → splits NO2 to form NO & O
O atoms react with O2 → O3
afternoon commute begins & NO2 & VOC levels increase as O3 peaks
formation of nitric acid (HNO3) with photochemical smog
nitrogen dioxide (NO2) from exhaust also reacts with water vapor → forms additional NO & nitric acid (HNO3)
3NO2 + H2O → 2HNO3 + NO
nitrogen dioxide gas + water → nitric acid + hydrogen monoxide
formation of peroxyacyl nitrates (PAN’s) in photochemical smog
NO2 + VOC’s → PAN’s → powerful eye & respiratory irritant, can cause damage to vegetation, very stable & persistent in atmosphere
thermal inversion layers
forms when cold air gets trapped beneath a layer of warm air → traps pollution close to the ground, especially particulate matter & smog → higher concentration of pollutants
coastal inversions
air over land heats faster than air over the ocean (land is warm & warms air faster) → cool ocean air blows onshore under layers of warm air → coastal mountains prevent cool, ocean air from spreading inland
mountain inversion
cold air sinks into valleys at night → when warm front approaches, it moves over top of mountains, capping cold air trapped in valleys
enviromental impacts of smog
particulate matter reduces sunlight & limits photosynthesis
O3 enters stomata & interferes with photosynthesis + cellular respiration
H2SO4 & HNO3 result in acid deposition
human health impacts of smog
PAN’s & O3 are eye & respiratory irritations that cause/worsen asthma, bronchitis, COPD & pneumonia
economic impacts of smog
increased healthcare costs for acute & chronic respiratory conditions
lost productivity due to missed work days
decreased agricultural yields
methods to reduce smog
reducing cars (especially older ones) → increasing public transit, carpools, biking, & more walkable cities
requiring vapor recovery nozzles
requiring emission control catalytic converters
indoor air pollution
air pollution within workplaces, schools and homes: in developed nations, greatest pollution comes from exposure to synthetic materials
furniture: adhesives, paint, foam, flame retardants
building materials: adhesives, paints, insulation, flooring
cigarette smoke
particulates (PM10 & PM2:5)
common indoor pollutant, such as smoke from indoor biomass combustion or cigarettes, dust, & asbestos
asbestos
long, silicate particle previously used in insulation & linked to lung cancer (phased out with clean air act but remains in older buildings); not dangerous until insulation is disturbed & particles enter air then respiratory tract → removed by removing ventilation from area & using plastic to seal it off from the rest of the building
carbon monoxide (CO) as indoor pollution
in developed nations, is released into homes by malfunctioning natural gas furnace ventilation or vehicle left running in the garage
in developing nation, is released from indoor biomass combustion for heating/cooking
volatile organic compounds (VOC’s)
diverse group of chemicals used in variety of home products that easily vaporize & enter the air → causes eye, nose, & throat irritation, dizziness, nausea, lightheadedness, damage to the liver, kidney, central nervous system, suspected/known carcinogen
examples of indoor VOC’s
furniture: foam, adhesives, upholstery treated with flame retardants or stain guards
building materials: adhesives, wall paint, insulation, particle board/OS13/MDF/plywood, vinyl flooring
cleaners: common household cleaners, deodorizes, moth repellents, aerosol sprays, dry cleaning chemicals, pesticides
office supplies: printer & copper ink/toner, permanent markets, liquid white out, carbon paper
plastics: just about everywhere
formaldehyde
common VOC released by adhesive in manufactured wood products & carpet glues → rashes, changes in lung function,systemic toxicity
radon gas (radon-222)
radioactive gas released by decay of uranium naturally found in rocks underground → enters homes through cracks in the foundation & spreads + can seep into groundwater sources → enter body
sealing cracks in foundation can prevent it from entering + increasing ventilation can disperse it
dust & mold
natural indoor air pollutants that can worsen asthma, bronchitis, COPD, emphysema; settles in homes naturally → disturbed by movement & enters air then respiratory tract
fungi, molds, & mildews develop in damp, dark, poorly-ventilated areas → removed physically & water leak/ventilation issue is fixed
lead (Pb) as indoor pollutant
paint chips off walls/windows & is eaten by small children or inhaled as dust + can be released into drinking water through lead water pipes → damages central nervous system of children
what are acids?
substances that release H+ into solutions
in water, HNO3 → H+ + NO3-
in water, H2SO4 → H+ + HSO4-
**pH scale is logarithmic, so one decrease in one unit = 10x increase in H+
acid deposition
deposition of acid or acid-forming pollutants from the atmosphere onto earth’s surface; orginates from emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2) & nitrogen oxides (NOx)
dry deposition
particulate matter containing acids forms compounds or gaseous compounds that bind to surfaces
acid precipitation
rain, snow, sleet, hail, fog with pH below 5.6
how ae sulfuric acid (H3SO4) & nitric acid (HNO3) formed?
compounds react with water vapor, oxygen, & oxidants
3NO2 +H2O → 2HNO3 + NO
2SO2 + O2 → SO3 → SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
H20 + NO, SO2 CO2 = acid
water + nitrogen dioxide (produced by lighting), sulfur dioxide (produced by volcanoes), carbon dioxide (produced respiration & aerobic decomposition) = forms acids
sources of sulfur dioxide (SO2)
combustion of coal in power plants to produce electricity, production of metals, diesel combustion
sources of NOx
vehicle emissions, coal power plants, gas power plants
effects of acid rain
directly harmful to human health
soil & water acidification (directly with acid precipitation or when dry deposition interacts with water in aquatic ecosystems)
damages buildings & monuments
prevailing winds transport pollutants that cause acid deposition → damages throughout a region
worse in spring after snow melts & releases acidified runoff
buffer
soils naturally contain calcium carbonate (CaCO3) that helps solutions resist changes in pH by reacting with H+ to reduce H+ concentration
CaCO3 ←> Ca2 + CO3²- ←> HCO3-
**some soils contain more calcium carbonate but all can be overwhelmed
cation exchange capacity (CEC)
CEC of soil decreases when pH drops & H+ increases b.c H+ displaces cation nutrients (Ca²+, Mg²+, Na+, K+, NH4+) from clay particles in the soil → leeching of nutrients into deeper soil horizons away from plant roots)
aluminum toxicity
increases when soil pH drops b.c decreasing pH & increasing H+ dissolves the common soil compound AI(OH)3 → produces ion AI3+ which binds tightly to clay particles, displacing ration nutrients
effects of acid rain on aquatic ecosystems
there is some natural buffer but… → lowered pH causes aluminum toxicity, disruption of blood osmolarity (balance of Na+/CL-) & water balance → decreases outside of optimal range for aquatic species → physiological stress & changes in species composition
economic impacts of acid deposition
reduces crop productivity (down cation exchange, up aluminum toxicity)
reduces forest productivity: loss of provisioning (lumber services), loss of cultural services (tourism) economic value, loss of supporting services (biodiversity) that underlie functioning of ecosystems
reduced productivity of freshwater & coastal ecosystems + their ecosystem services
corrodes cars
dissolves stone structure
cap & trade
introduced to clean air act in 1990 as emission trading program for SO2 where pollution is capped at agreed upon level with hefty fines for exceeding & heavy polluters must buy additional allowances from competitors
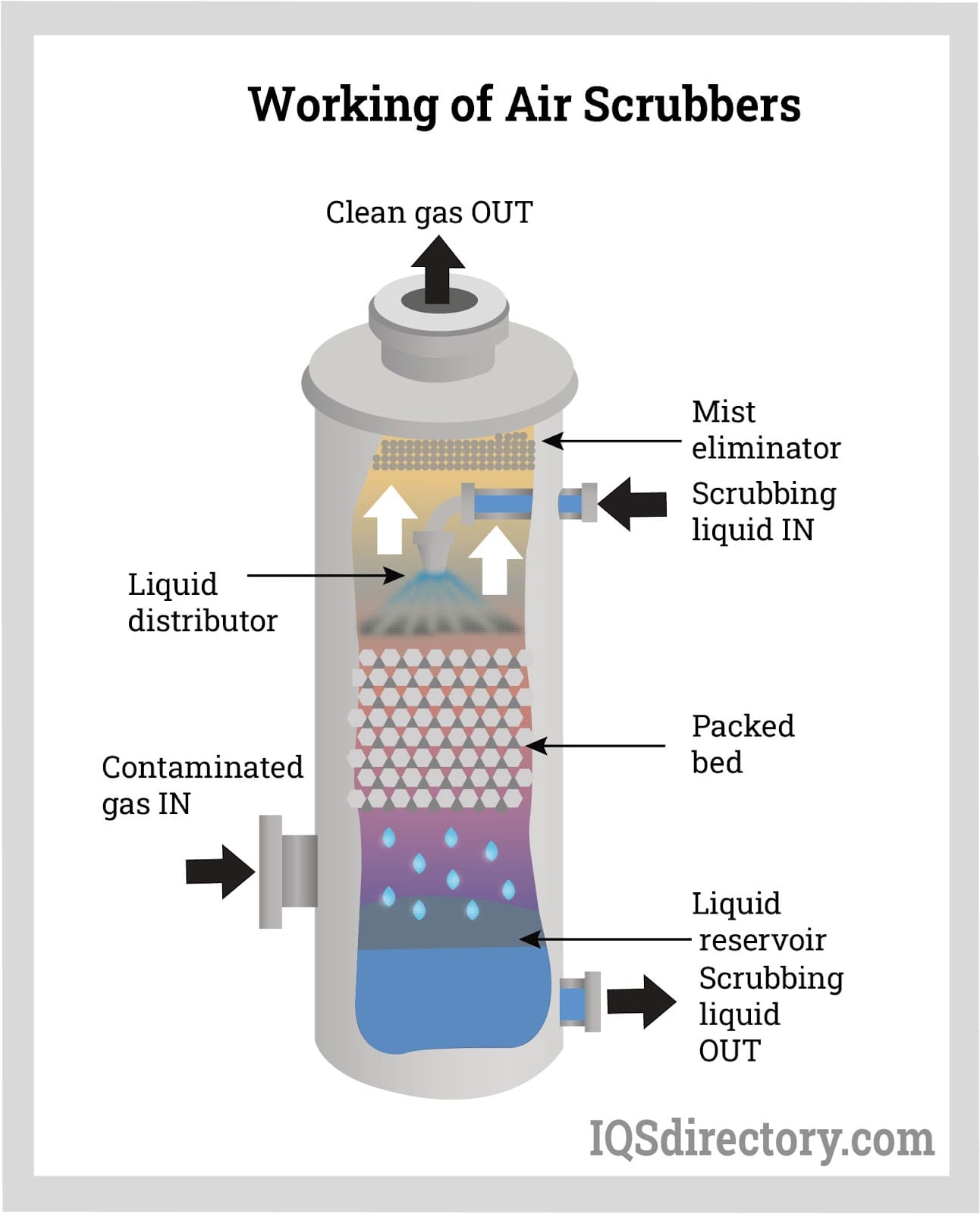
scrubbers
large column/tube/pipe lined with lime (CaO) that absorbs or neutralized oxides (NOx, SOx VOCs) from exhaust streams (emissions) → mist droplets with pollutants & PM trapped in them fall to bottom of scrubber to get trapped at top by mist eliminator
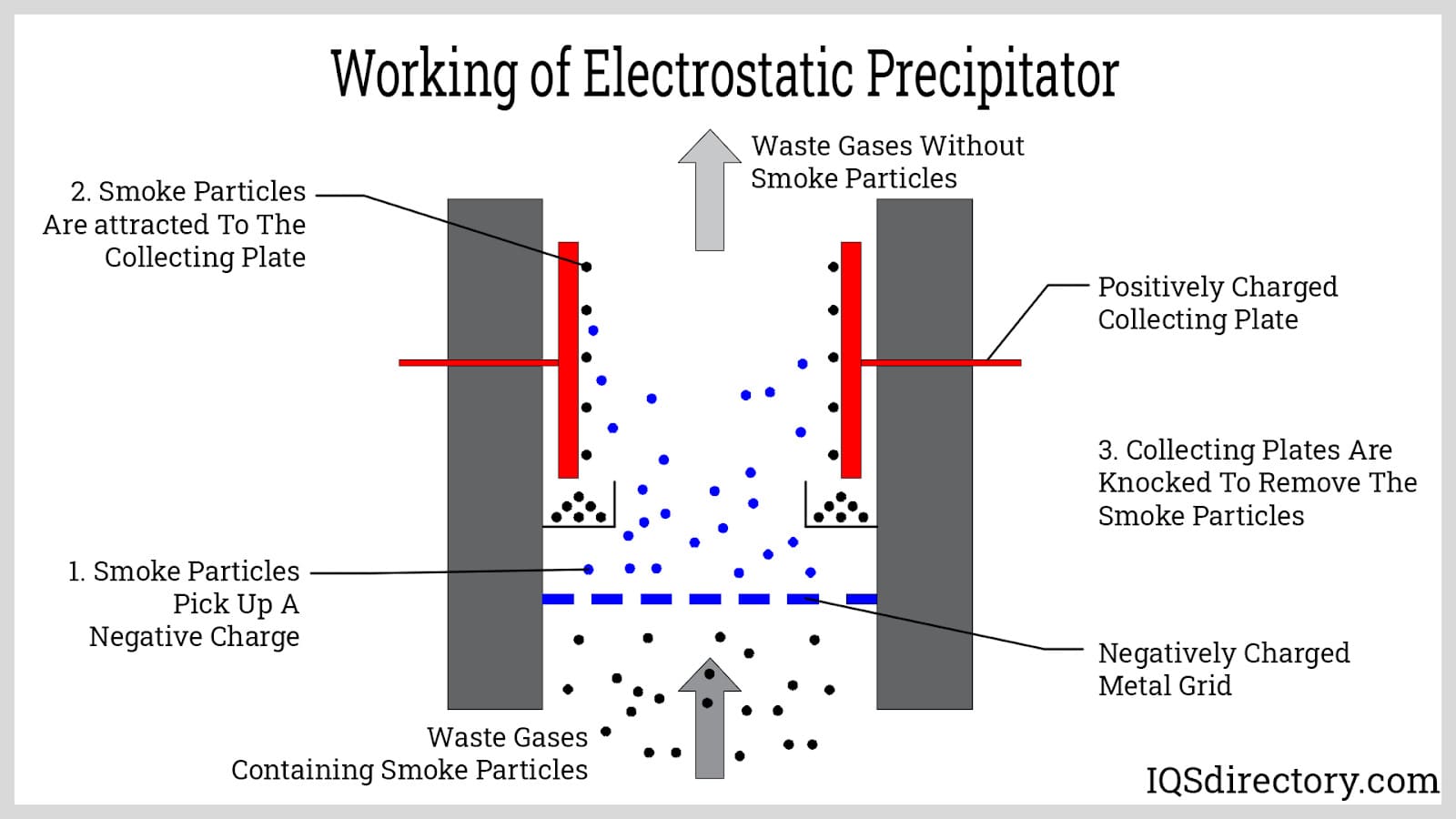
electrostatic precipitators
power plant/factory emissions passed through device with a - charged electrode, giving particles a - charge → stick to + charged collection plates, trapping them → plates discharge occasionally so particles fall down into collection hopper for disposal in landfills