Nervous System and Hormonal Responses to Exercise: Key Concepts and Mechanisms
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What are the two main branches of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
What is the function of dendrites in a neuron?
They conduct impulses toward the cell body.
What is the role of the axon in a neuron?
It carries electrical impulses away from the cell body.
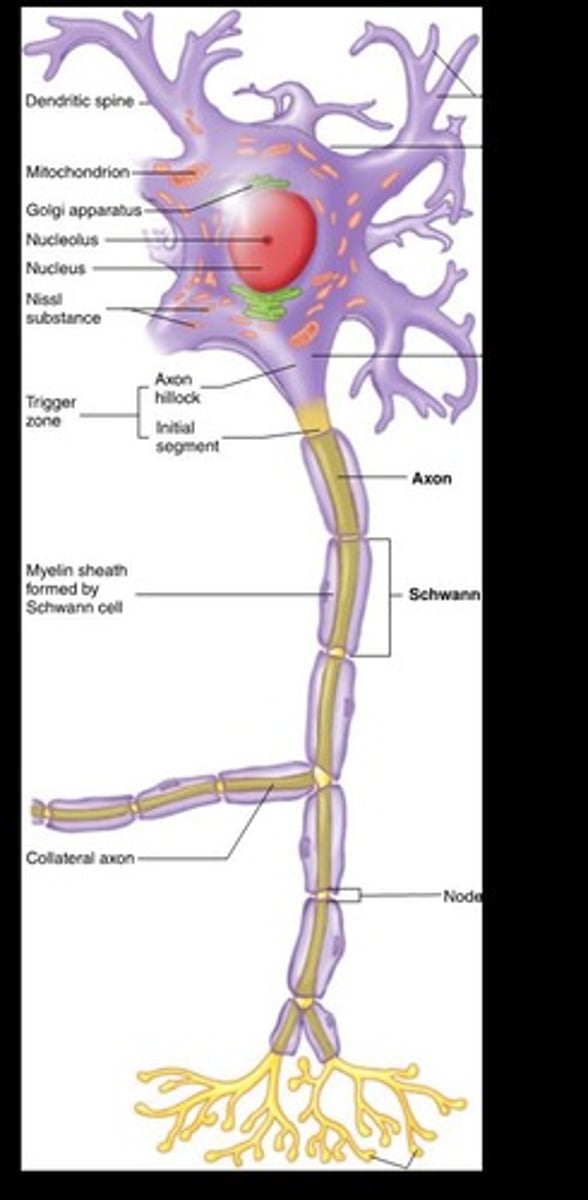
What is a synapse?
Contact points between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron.
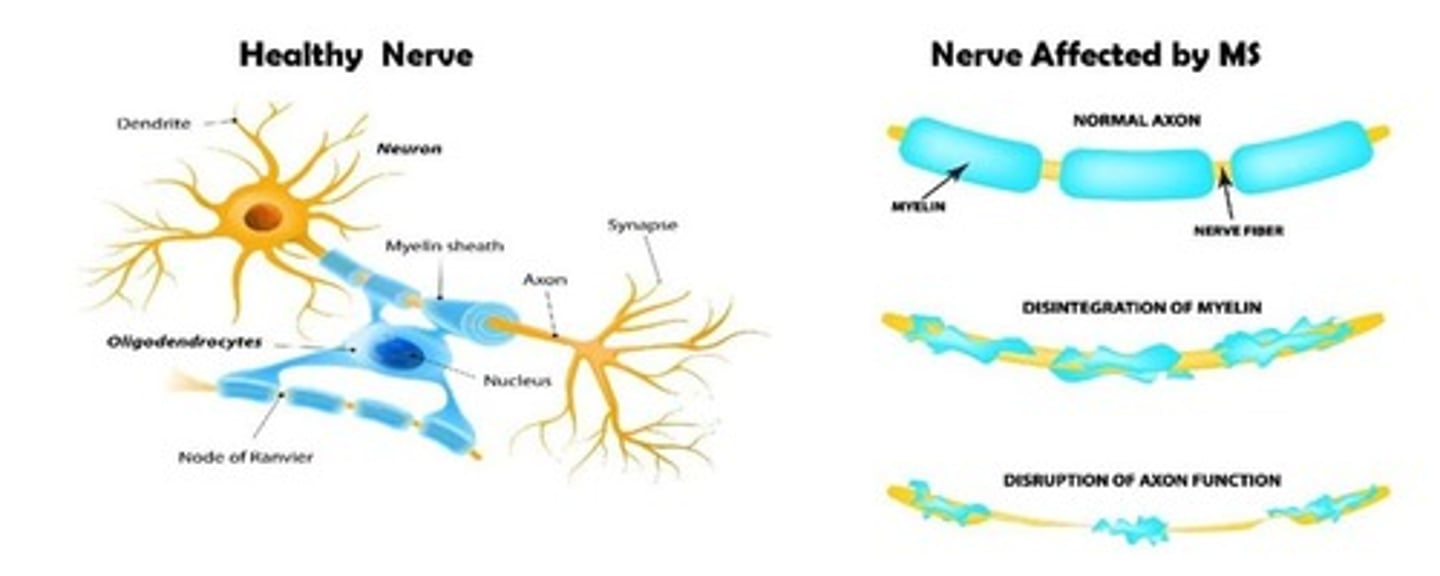
What neurological disease destroys myelin sheaths of axons?
Multiple Sclerosis
What is the resting membrane potential range in neurons?
-40 to -75 mV
What maintains the resting membrane potential?
The sodium-potassium pump.
What occurs during an action potential?
A stimulus depolarizes the cell, opening Na+ channels and allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell.
What is the all-or-none law in relation to nerve impulses?
Once a nerve impulse is initiated, it will travel the length of the neuron.
What are excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP)?
They cause depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron.
What is the difference between temporal and spatial summation?
Temporal summation is the summing of several EPSPs from one presynaptic neuron, while spatial summation is from several different presynaptic neurons.
What do proprioceptors do?
They provide the CNS with information about body position.
What is the function of muscle spindles?
They respond to changes in muscle length and are involved in the stretch reflex.
What does the Golgi tendon organ (GTO) monitor?
Tension developed in muscle and prevents muscle damage during excessive force generation.
What is the role of muscle chemoreceptors?
They are sensitive to changes in the chemical environment surrounding a muscle and provide information about metabolic rate.
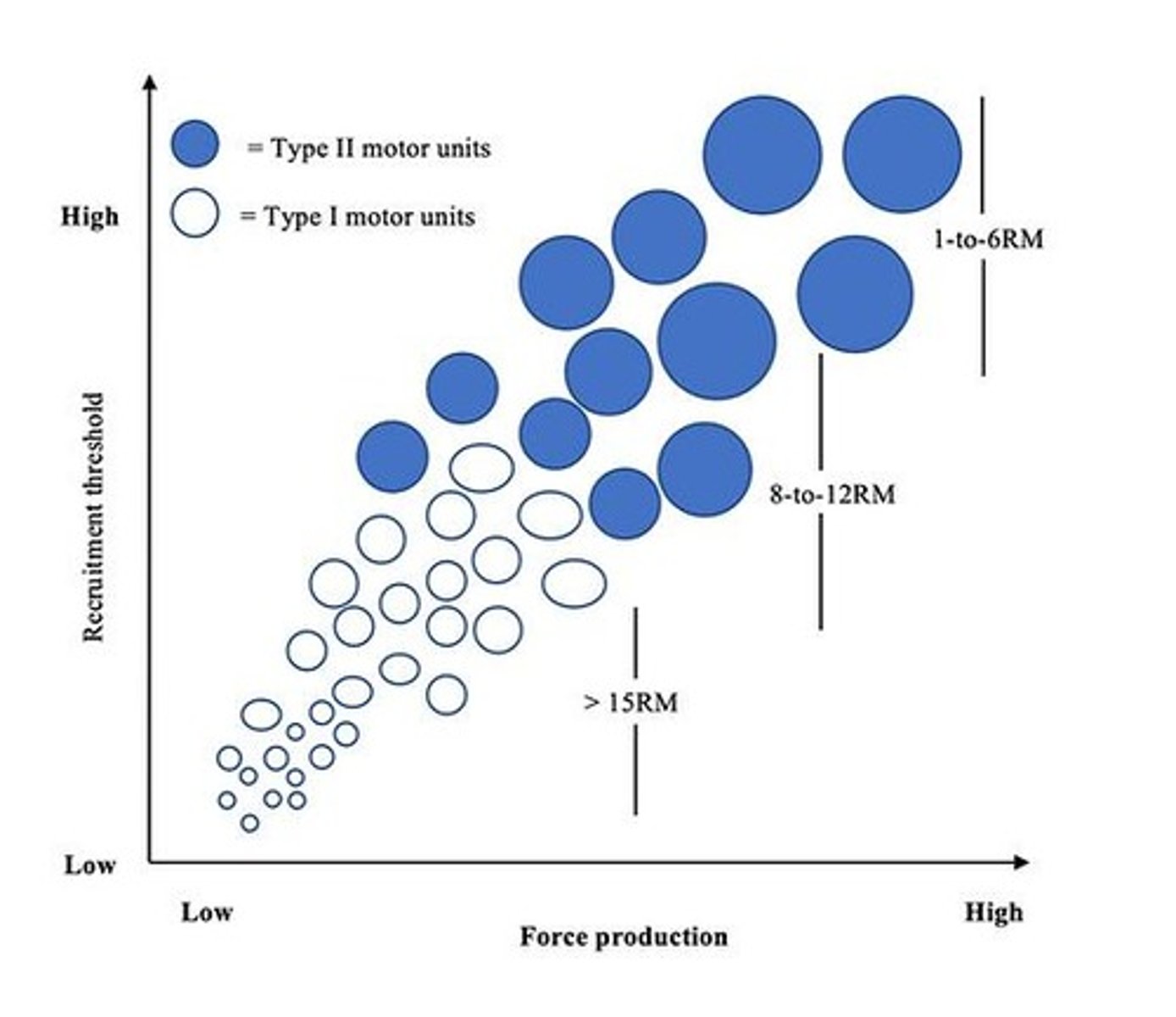
What is motor unit recruitment?
The process of recruiting more muscle fibers through motor unit activation.
What is the size principle in motor unit recruitment?
Smallest motor units are recruited first, producing larger EPSPs and resulting in action potentials sooner.
What is central fatigue?
Fatigue that arises from higher brain centers and/or motor neurons, often due to depletion of excitatory neurotransmitters.
What does the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system do?
It prepares the body for 'fight-or-flight' responses by releasing norepinephrine.
What is the function of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system?
It promotes 'rest and digest' activities by releasing acetylcholine.
How does exercise enhance brain health?
It enhances learning and memory, stimulates formation of new neurons, and improves brain vascular function.
What are the effects of regular exercise on cognitive decline?
It reduces peripheral factors such as inflammation, hypertension, and insulin resistance.
What is the role of the endocrine system?
The endocrine system releases hormones into the blood to circulate to tissues.
How do hormones exert their effects?
Hormones bind to specific protein receptors to exert their effects.
What are the two main classes of hormones based on chemical makeup?
Polypeptides/proteins (non-steroid) and steroids.
What is a characteristic of non-steroid hormones?
Non-steroid hormones are unable to cross cell membranes and have receptors on the membrane.
What are the two groups of non-steroid hormones?
Protein or peptide hormones and amino acid-derived hormones.
What are common second messengers activated by non-steroid hormones?
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), cyclic guanine monophosphate (cGMP), inositol triphosphate (IP3), and diacylglycerol (DAG).
What is the source of steroid hormones?
Steroid hormones are derived from cholesterol.
What determines the effect of a hormone on a tissue?
The effect is determined by the plasma concentration of the hormone and the number of active receptors.
What is upregulation in hormone-receptor interactions?
Upregulation is the increase in receptor number in response to low concentration of hormone.
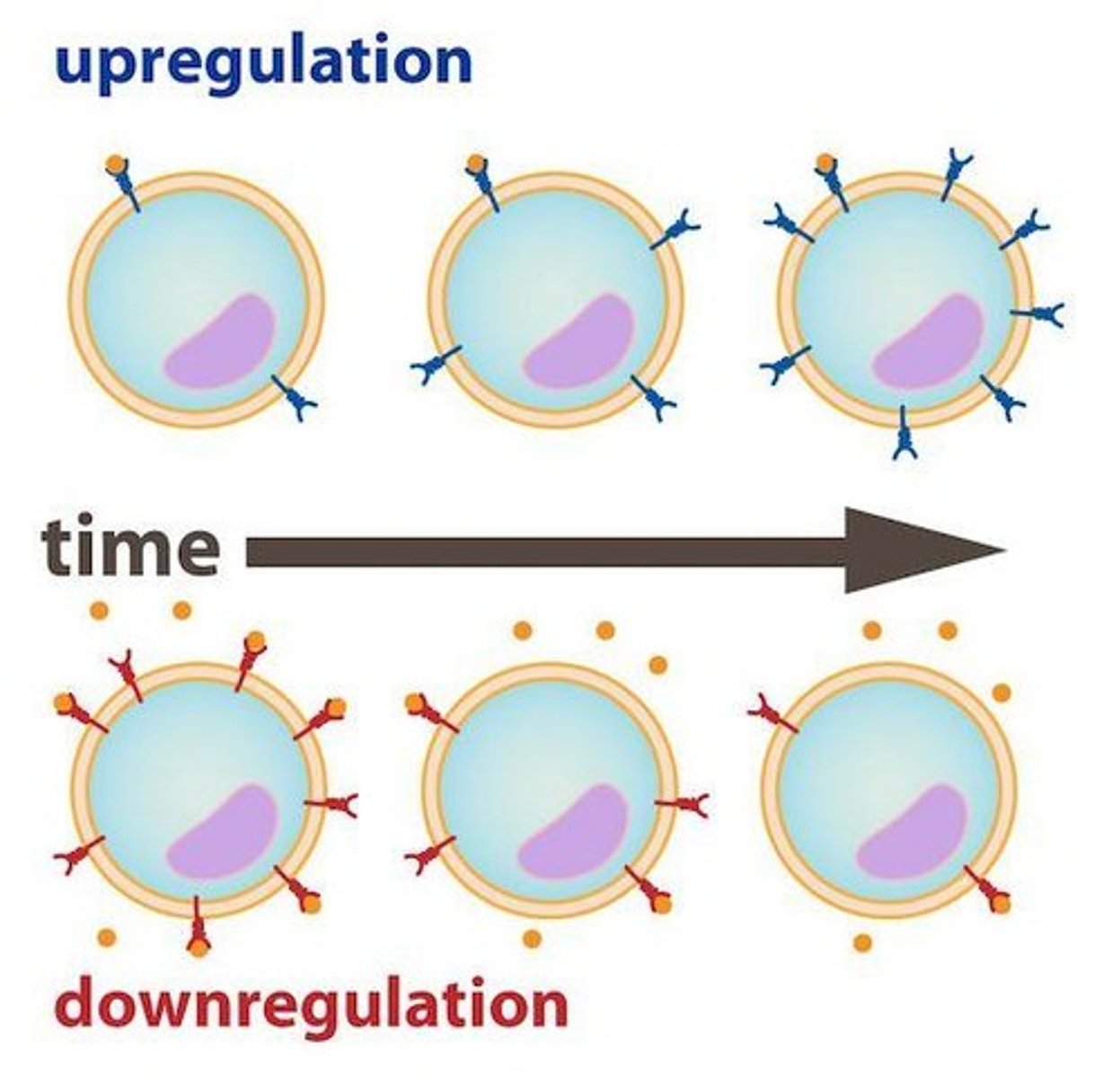
What is downregulation in hormone-receptor interactions?
Downregulation is the decrease in receptor number in response to high concentration of hormone.
What hormone does the hypothalamus stimulate the release of from the anterior pituitary gland?
Growth hormone.
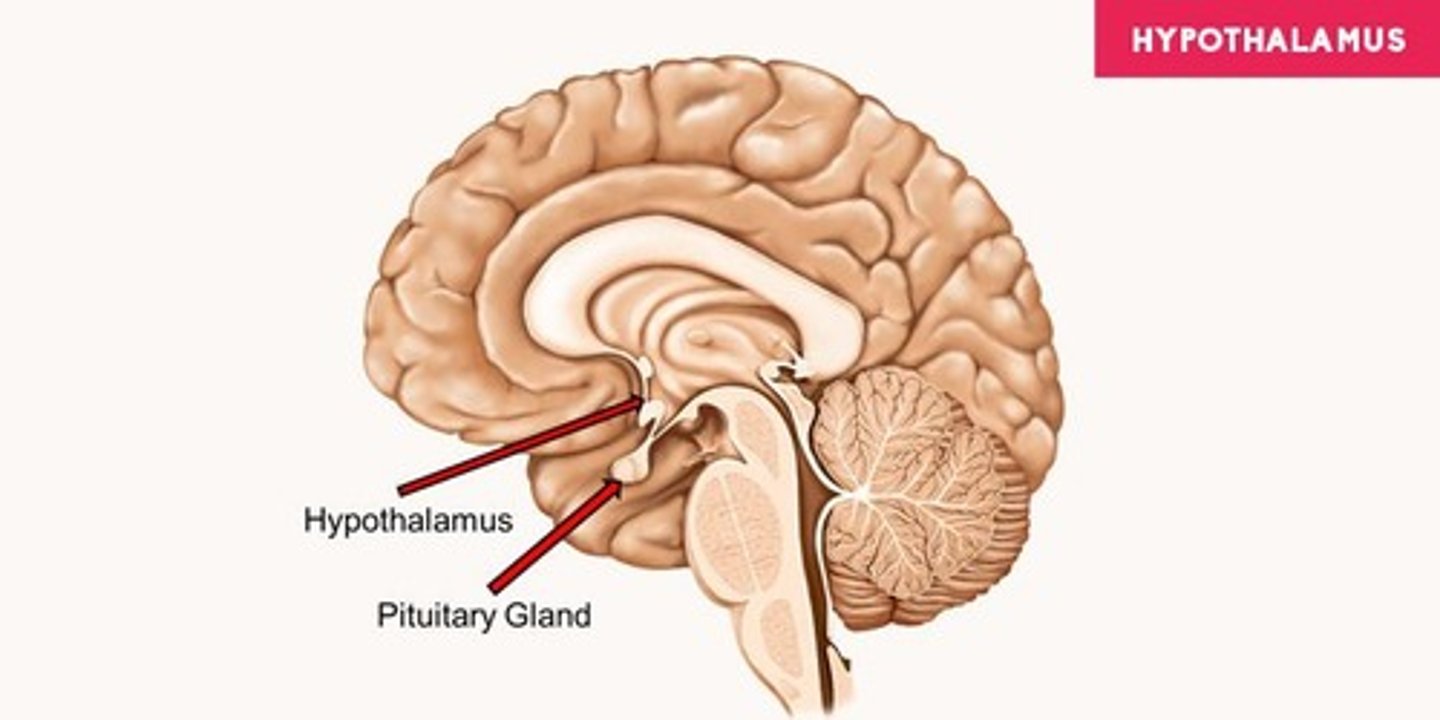
What is the role of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs)?
IGFs stimulate muscle growth and are essential for the growth of all tissues.
How does growth hormone affect plasma glucose levels?
It decreases glucose uptake by non-working tissues and increases fatty acid mobilization.
What hormones are released from the posterior pituitary gland?
Oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
What is the effect of epinephrine and norepinephrine during exercise?
They maintain blood glucose levels by mobilizing muscle glycogen and increasing liver glucose mobilization.
What is the role of aldosterone?
Aldosterone controls sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion, regulating blood volume and pressure.
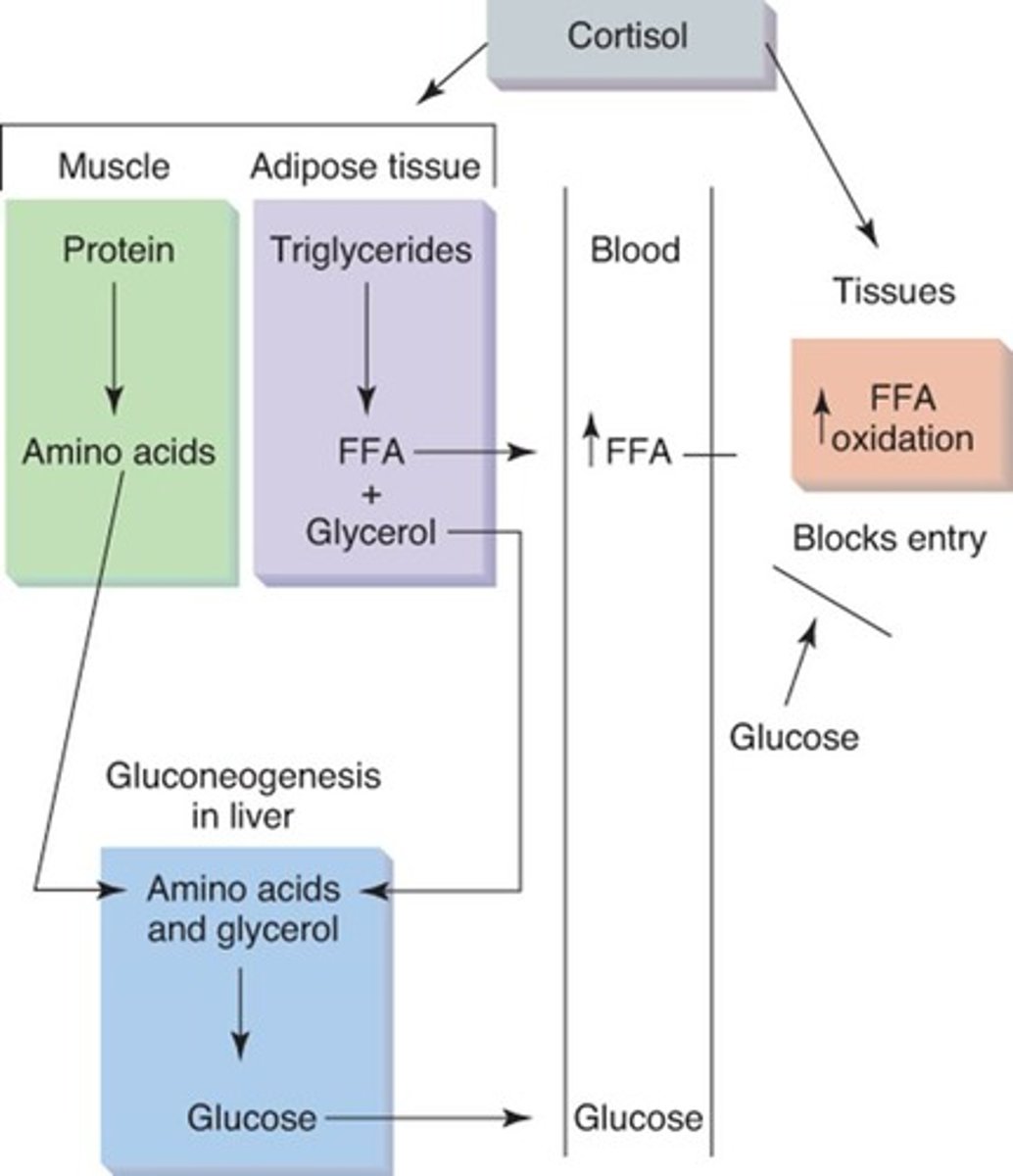
What is cortisol's function during exercise?
Cortisol maintains plasma glucose by promoting protein breakdown and stimulating fatty acid mobilization.
What is the primary function of insulin?
Insulin promotes the storage of glucose, amino acids, and fats.
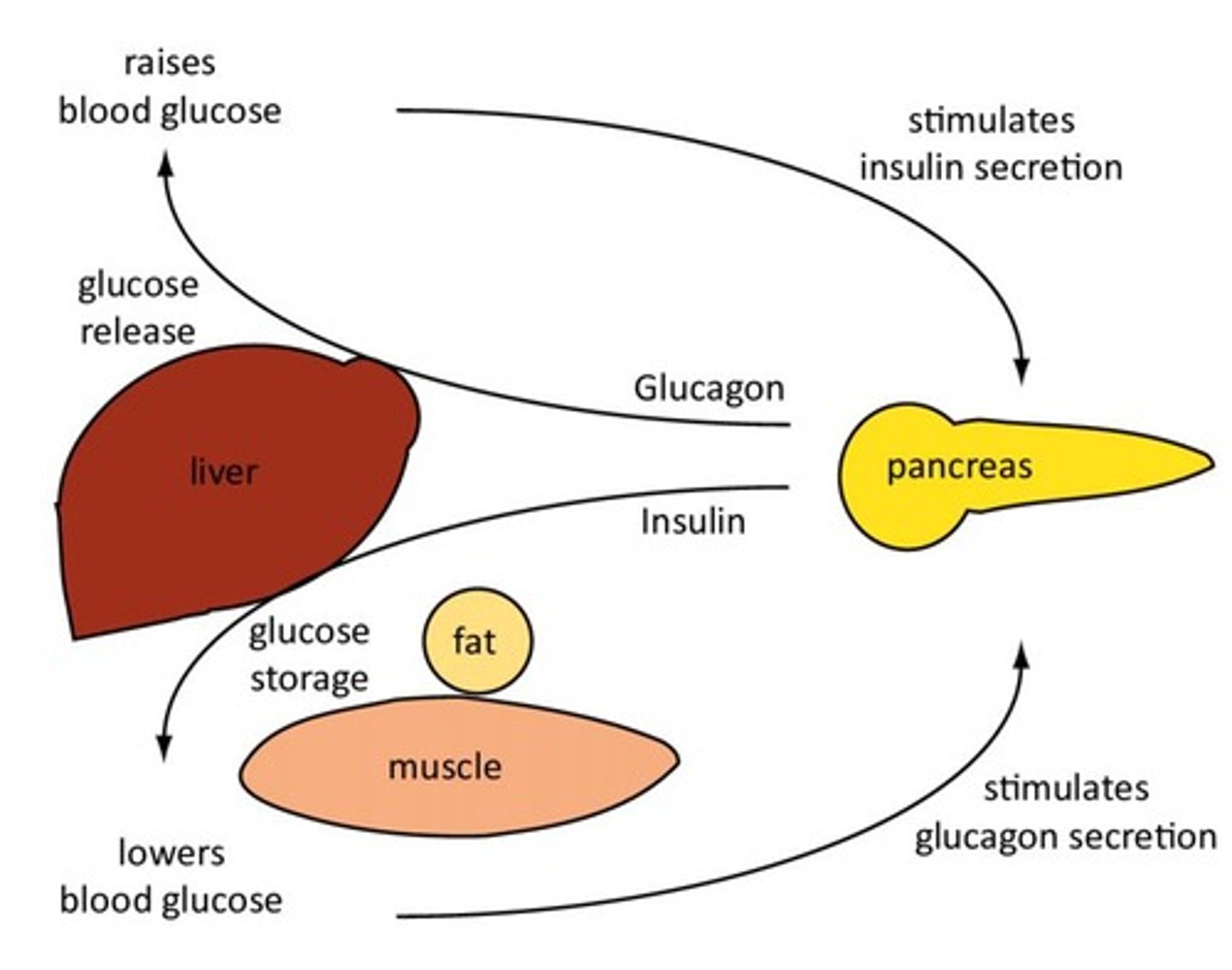
What does glucagon do?
Glucagon promotes the mobilization of fatty acids and glucose.
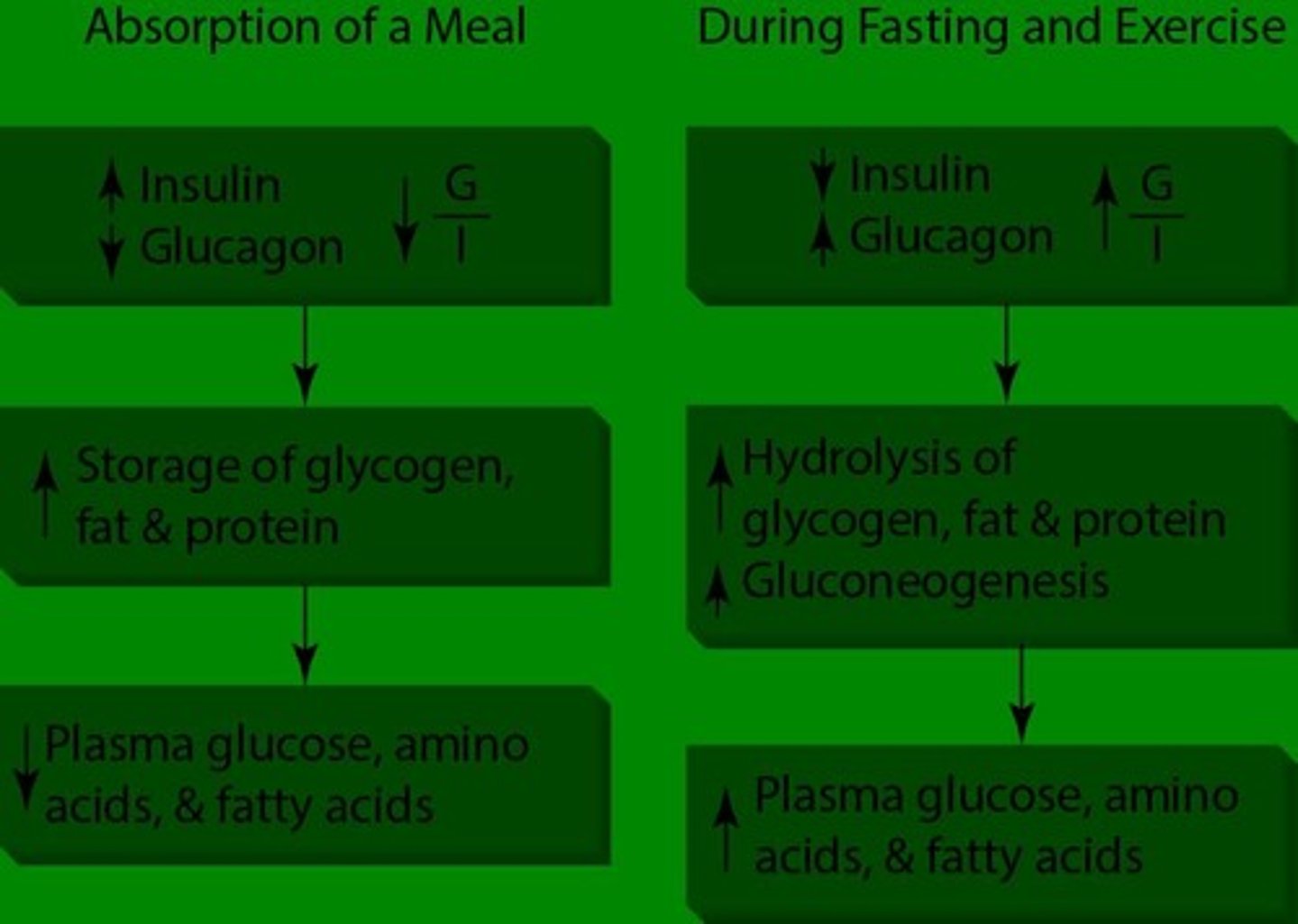
How does exercise affect insulin and glucagon levels?
Insulin levels decrease during exercise, while glucagon levels increase.
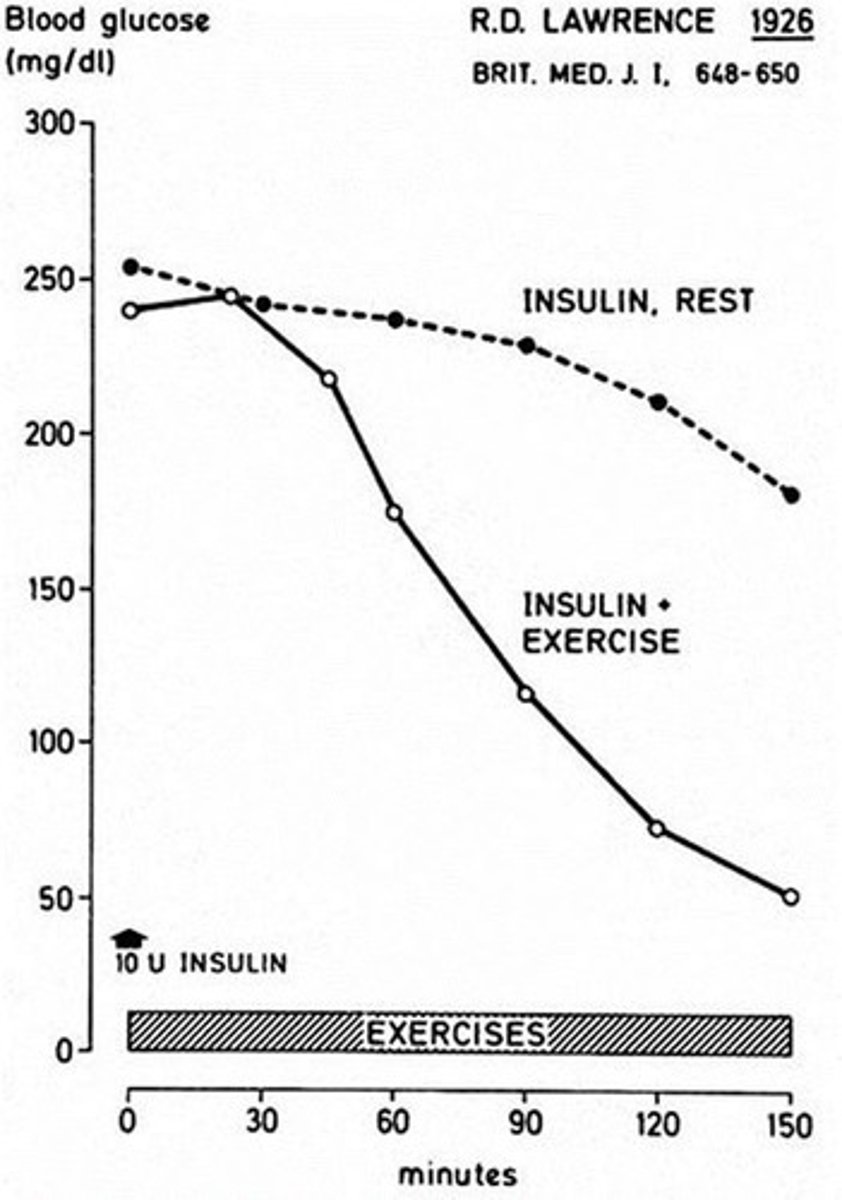
What is the role of skeletal muscle in hormone production?
Skeletal muscle produces myokines that stimulate glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation.
What is glycogenolysis and how is it related to exercise intensity?
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen, which is greater and more rapid during high-intensity exercise.
What is the effect of heavy exercise on free fatty acid (FFA) mobilization?
FFA mobilization decreases during heavy exercise despite hormonal stimulation.
What are the counter-regulatory hormones to insulin?
Epinephrine, glucagon, cortisol, and growth hormone oppose insulin action and promote substrate mobilization.
What hormones are involved in blood glucose homeostasis during exercise?
Thyroxine (T4), cortisol, growth hormone, epinephrine, norepinephrine, insulin, and glucagon.
What is the primary androgen hormone and its role?
Testosterone promotes tissue (muscle) building and enhances masculine characteristics.
What are anabolic steroids and their associated risks?
Anabolic steroids promote muscle growth but are associated with negative side effects and potential for abuse.