UW-Madison CS 400 Final Exam (Fall 2024)
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
Prim's Algorithm Runtime Complexity
O(E * log(v))
- E = number of edges in the graph
- v = number of nodes in the graph
Kruskal's Algorithm Runtime Complexity
O(E * log(v))
- E = number of edges in the graph
- v = number of nodes in the graph
Neighbors/Adjacent Nodes
Two nodes connected with an edge.
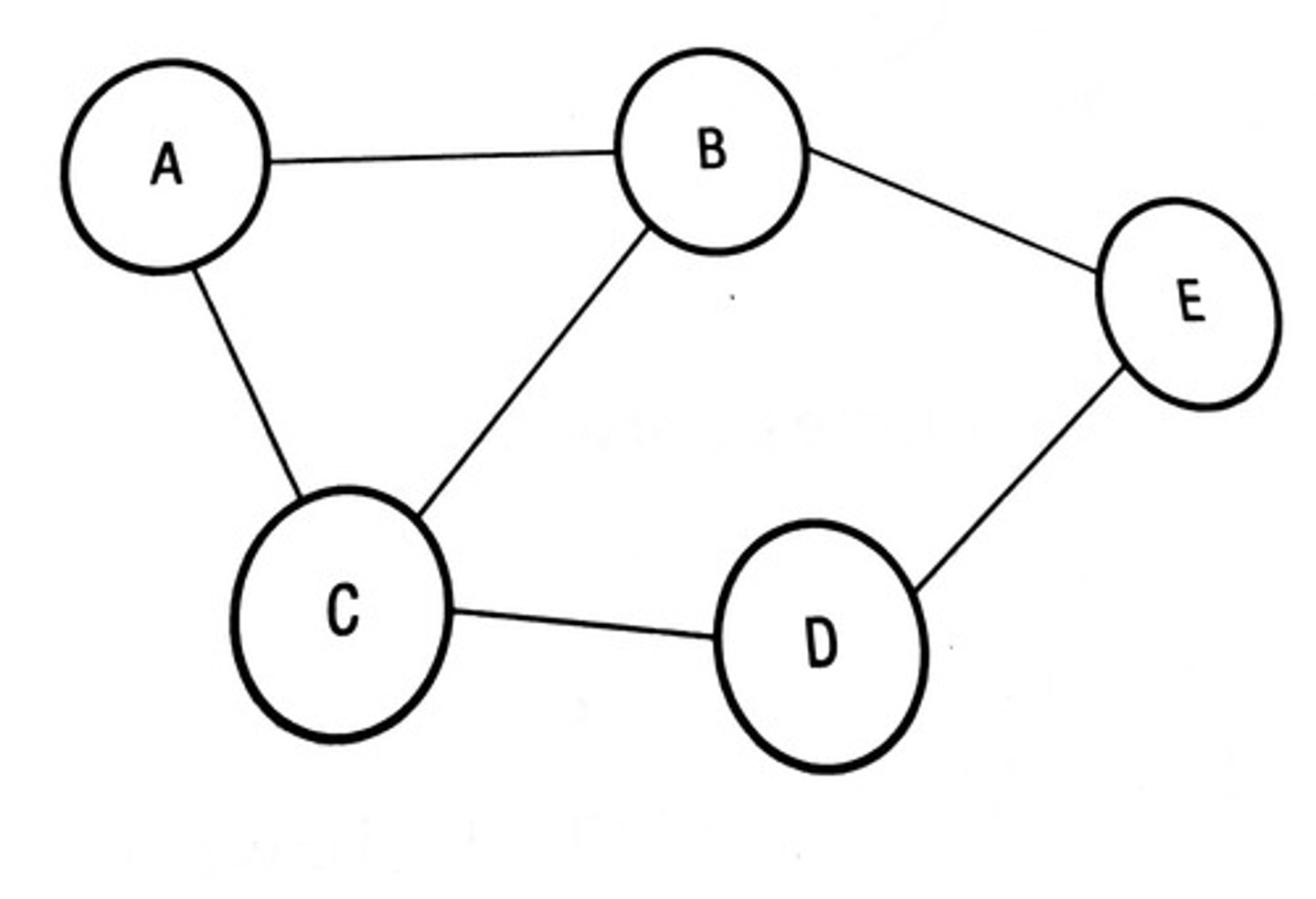
Undirected Graph
You can move through the graph in either direction. The edges do NOT have arrowheads.
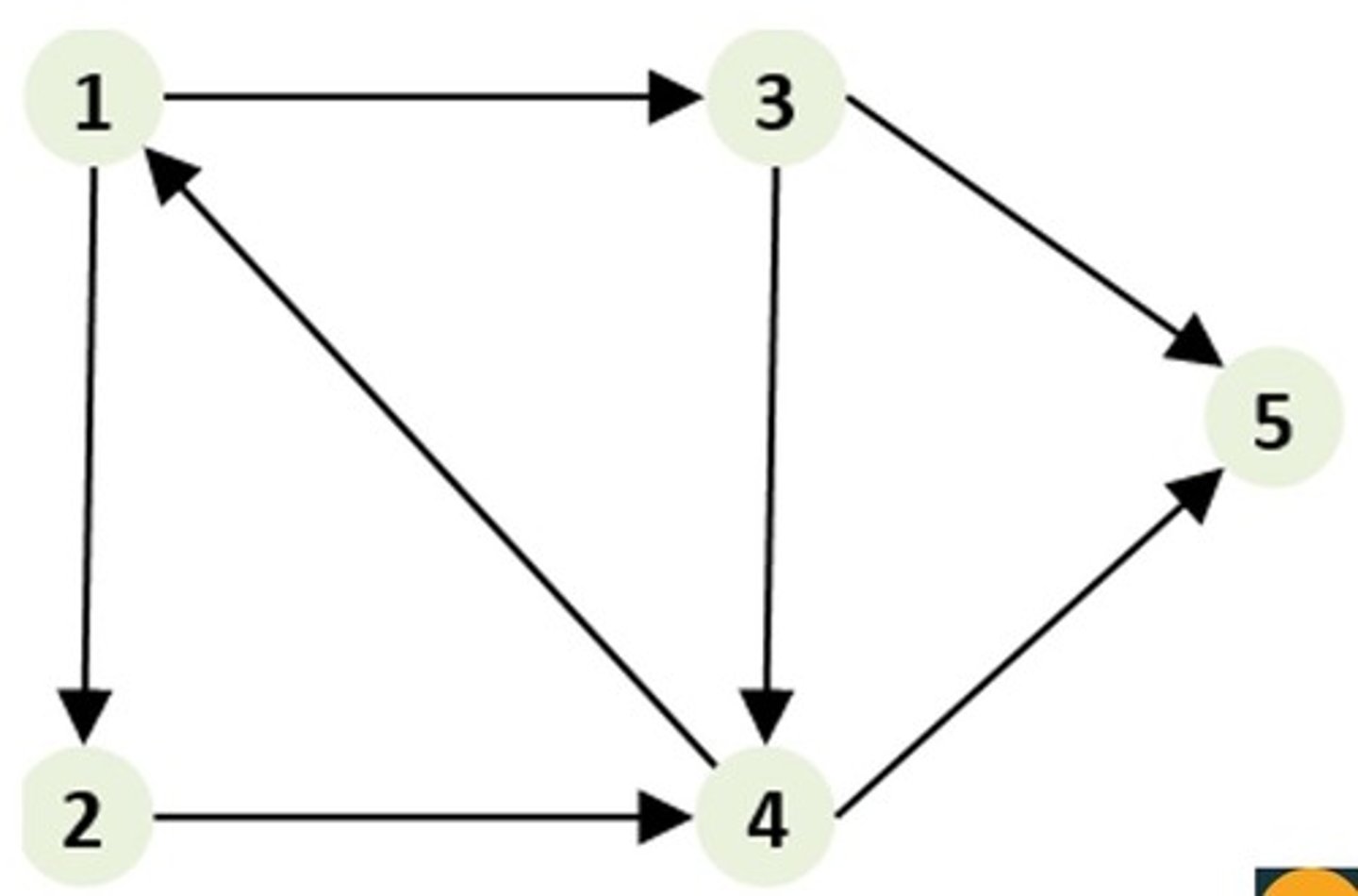
Directed Graph
You can only cross each edge in one direction. The edges DO have arrowheads.
Degree (of a Node)
The number of edges connected to a node.
In-Degree (of a Node)
The number of edges pointing towards a node.
Out-Degree (of a Node)
The number of edges pointing away from a node.
Cycle
A path in a graph that returns to a previously visited node.
Cyclic Graph
A graph that contains at least one cycle.
- Every undirected graph with at least 1 edge is a ________ graph.
Acyclic Graph
A graph that contains no cycle.
- No path that we could possibly take returns to a duplicate node.
Adjacency Matrix
A matrix that holds nodes and their connections.
Adjacency List
Lists outgoing edges for each node.
Spanning Graph
A subgraph of a graph that has all of the nodes of the original graph.
Under what condition will a target of a Makefile be achieved?
- The dependency is younger than the target.
- Both the dependency and target are files.
Depth First Traversal (DFT)
Go as deeply into the graph as we can.
Breadth First Traversal (BFT)
Exhaustively visit all neighbors of a node before moving on.
document.querySelector(
Selects one matching element in the HTML document based on the ID, class, or element.
document.querySelectorAll(
Selects all of the matching elements in the HTML document based on the ID, class, or element.
innerHTML
A field of an element. A String representing an HTML element.
- Can also change the contents of an element.
getBytes()
A method that gets the decimal values of each character in the response.
write()
Converts the decimal values into a character.
fetch("http://
A globally available method for .html files.
- Represents the request
Promise
An object returned by a call to fetch().
- Represents the future results from the web server.
then()
Does something with the object/Promise we're getting back (i.e. the response).
- The parameter is a lambda expression that implements what we want to do with the Promise.
encodeURIComponent()
Takes a String and encodes it into a URI form.
- Deals with special characters
- Ex: spaces become %20
Lambda Expression Syntax for JavaScript
(parameter) =>
Lambda Expression Syntax for Java
(parameter) ->
Depth First Traversal Runtime Complexity (Adjacency Matrix)
O(v^2)
- v = number of nodes in the graph.
Depth First Traversal Runtime Complexity (Adjacency List)
O(v + e)
- v = number of nodes in the graph.
- e = number of edges in the graph
Breadth First Traversal Runtime Complexity (Adjacency Matrix)
O(v^2)
- v = number of nodes in the graph.
- e = number of edges in the graph
Breadth First Traversal Runtime Complexity (Adjacency List)
O(v + e)
- v = number of nodes in the graph.
- e = number of edges in the graph
Weighted Edge
Assigns a cost to each edge.
Cost of a Path (Weighted Edges)
Sum of edge weights along a path.
Cost of a Path (Unweighted Edges)
Length of the path (# of edges along the path).
Connected Graph
A path exists between every pair of nodes.
- From any node, you can get to any other node using edges.
Strongly Connected Graph
A path exists between every pair of nodes with edge directions respected.
- Any node in a graph can get to any other node, respecting directionality.
Weakly Connected Graph
A path exists between every pair of nodes with edge directions ignores.
- Change edges to undirected. If the new graph is connected, the original graph is _______ _____________.
Subgraph
G' is a ________ of G if:
- The set of nodes of G' is a subset of the nodes of G, AND
- The set of edges of G' is a subset of the edges of G
Dijkstra's Algorithm
Finds the shortest path between two nodes in a graph.
Web Server
A piece of software that allows us to publish our HTML pages and point a browser to the address of the machine running the server (and to the HTML document on there) so that we can access it from anywhere on the Internet.
Order of the Insets Constructor Parameters
Top, Right, Bottom, Left
consume()
A JavaFX method that prevents the event from moving further upwards.
- The code in the EventHandler with the consume() call will still run in entirety.
Data Source Operation
Puts data onto a Stream.
- T represents the type of data we want to process on that Stream.
Intermediate Operations
Do some sort of operation on a Stream
- Requires a terminal operation to run in the first place.
- Called on the initial stream being created by the data source operation
- Usually instance methods of type Strema
Terminal Operation
Generally returns a different object representing the results (rather than another Stream).
- Usually instance methods of type Stream.
java.util.stream.Stream.generate(Supplier
Every object returned by the get() method of the parameter interface will be put onto the Stream
- Data source operation
java.util.stream.Stream.of(T ... items)
Puts all items passed as arguments onto the Stream.
- Data source operation
java.util.stream.Stream.concat(stream1, stream2)
Allows us to combine multiple Streams.
- The first parameter's contents is added to the Stream, then the second parameter's contents
- Data source operation
java.util.stream.Stream.empty()
Returns a stream with no contents.
- Data source operation
java.nio.file.Files.lines(path)
Returns a new Stream of type Integer, onto which it will put the lines in a given file (as Strings).
- Useful for reading in and processing text files
- Data source operation
filter(Predicate
Filters the incoming Stream based on a certain criteria. The interface parameter ahas one boolean method that is called on each data item.
- True: data moves onto the outgoing stream
- False: data does NOT move onto the outgoing stream
- Intermediate Operation
map(Function
Applies a transformation to the data passed as input.
- T: type of data on the incoming Stream
- R: type of data on the outgoing Stream
- Intermediate Operation
limit(n)
Processes the first n items on the input Stream.
- Closes the Stream after the first n items.
- Intermediate Operation
skip(n)
Bypasses the first n data items on the input stream, and then processes the rest.
- Intermediate Operation
findFirst()
Waits until the first data item coming out of the Stream arrives, and returns the first data item.
- The Stream is then closed.
- Terminal Operation
forEach(Consumer
Takes every item coming out of the Stream and calls the interface parameter's method on each.
- Useful for doing something (i.e. printing) with every data item.
- Terminal Operation
count()
Returns an int telling us how many data items from the Stream reached the terminal operation.
- Terminal Operation
min(Comparator
Returns the minimum of the data items as a result of the Stream
- Terminal Operation
max(Comparator
Returns the maximum of the data items as a result of the Stream
- Terminal Operation
Redirection Operator (>)
Overwrites the contents of a file (after the >) with the result of the command before the >.
Redirection Operator (>>)
Preserves the old contents of a file (after the >), appending the result of the command (before the >) to the end of the file.
wc
A Bash command giving us three different numbers related to the file.
- First number: # of lines
- Second number: # of words
- Third number: # of characters
grep "
Uses regular expressions to filter through a file.
sort
Sorts the lines of a file in alphabetically ASCENDING order.
- Case sensitive (capital letters come first, lowercase letters come second)
sort -f
Sorts the lines of a file in alphabetically ASCENDING order.
- NOT case sensitive
sort -r
Sorts the lines of a file in alphabetically DESCENDING order.
- Case sensitive (capital letters come first, lowercase letters come second)
head -n
Allows us to to look at the the top n lines of a file.
tail -n
Allows us to look at the bottom n lines of a file.
Pipe Redirection Operator (|)
Takes the output of the command on the left side and uses it as the input of the command on the right side.
Contains/Search (Balanced BST) Runtime Complexity
O(log(n))
Add/Insert (Balanced BST) Runtime Complexity
O(log(n))
Remove (Balanced BST) Runtime Complexity
O(log(n))
Contains/Search (General BST, not necessarily balanced) Runtime Complexity
O(n): Linear Time
Add/Insert (General BST, not necessarily balanced) Runtime Complexity
O(n): Linear Time
Remove (General BST, not necessarily balanced) Runtime Complexity
O(n): Linear Time
Red Black Tree Properties
1. Each node is either red or black
2. The root node is black
3. No red nodes have red children
4. Every path from root to null child has the same number of black nodes (black height of the tree)
- Null children are black
Red Black Tree Insertion Repair #1 Runtime Complexity
O(1): Constant Time
Red Black Tree Insertion Repair #2 Runtime Complexity
O(H): Linear Time
- H = height of the tree
Red Black Tree Deletion Repair #1 Runtime Complexity
O(1): Constant Time
Red Black Tree Deletion Repair #2 Runtime Complexity
O(H): Linear Time
- H = height of the tree
Red Black Tree Deletion Repair #3 Runtime Complexity
O(1): Constant Time
Red Black Tree Search Runtime Complexity
O(log(N))
- N = number of nodes in the tree
Red Black Tree Insert Runtime Complexity
O(log(N))
- N = number of nodes in the tree
Red Black Tree Delete Runtime Complexity
O(log(N))
- N = number of nodes in the tree
JUnit Test Properties
1. @Test annotation above the method header
2. Public method
3. Void return type
4. Instance (non-static) method
Unit Test
A test that focuses on a single unit of code (i.e. a single method/class block)
- Advantage: easy to isolate bugs
- Disadvantage: bugs can also develop when we use other Java structures
Integration Test
Taking 2+ units of code and seeing if they run together as expected.
Opaque-Box Test
Focuses solely on publicly available methods/fields.
- Advantage: we can use the exact same test code for any implementation (portability)
- Disadvantage: the test cases may not be as fine-grained as we'd like them to be.
Clear Box Test
Accessing the internals of the class we're testing.
- Advantage: very in-depth and fine-grained tests
- Disadvantage: not as portable across different implementations
Input-Output Test
Testing specific inputs for expected outputs
- Ex: testing insertions into BSTs
Property test
Generating random sequences of values and checking an implementation using those values.
- Advantage: looping the process allows us to gather a lot of data
- Disadvantage: it is hard to debug an implementation because we're using random values that only cause issues in very specific cases.
Securely copying a file from the local laptop to the VM
scp
Securely copying a file from the the VM to the local laptop
scp
Height of a B-Tree
H = logm(N)
- N = number of nodes
- m = branching factor (the number of children nodes have in a given tree)
.
Indicates a class in HTML
#
Indicates an ID in HTML
Indicates an element in HTML.
InetSocketAddress(
Specifies the port number to use with a web server.
HttpServer server = new HttpServer(new InetSocketAddress(8080), 0)
Creates a new instance of HttpServer.
- The first parameter specifies the port that we want to use.
- The second parameter specifies the length of the request queue (0 for OS default)