immunity
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
what is the bodys first line of defense
skin/mucus membrane
urticaria
hives
raised bumps
puritis
itching
innate immunity
in your body since birth
adaptive/aquired immuity
something we’ve been exposed to
active immunity
actively fighting
passive immunity ex
breast feeding
immune system is
self-regulated
must be able to distinguish self from non-self so immune system can work normally!
antigens
foreign agents
things that are presenting on cells
major actions for the immune system
defending and attacking
two types of defenses
innate and adaptive
innate
neutrophils (1st responder)
mast cells- release histamine (connective tissue)
macrophages- eating invaders
adaptive
b cells - memory, antibody
t cells include
t helper (CD4)
t killer (CD8)
t helper cell
CD4
t killer cell
CD8
order that cells work for immune system in adaptive
t helper (CD4)
b cells
t killer (CD8)
innate defense barrier
from birth
has immediate response distinguish self from non-self
external defense/barrier for innate defense is primary
not completely impenetrable
surface- skin, mucous membrane
chemical- saliva, sweat, vaginal bacteria/pH
bloodborne innate defenses for innate defense is secondary
WBCs!
imflammatory response
pyrogens (adjusts body temp)
complete proteins (relates to inflammatory response)
what manifestations may we expect with an inflammatory response
swelling, erythema (redness), warm to touch
inflammatory response s triggered by
mast cells- histamine (causes inflammation and capillary permeability) and prostaglandins
vasodilation
sends blood to site to dilute/send immune cells like neutrophils, monocytes/macrophages nutrients and o2
pyrogens
fever producing molecules
produced by bacteria exposed macrophages
fever creates bad environment for bacterial growth and improves healing
macrophages are
WBC
severe/life threatening temperature
105
can change with age
interferons
do not protect infected cells, they stop the spread of the virus to new cells
proteins released from virus-infected cells
complement proteins
is a plasma protein that enhance antibodies
is activated by antigens
has to do with inflammatory process
plays an enhancement role
adaptive/acquired defenses
specific
developed over time after exposure to disease (vaccine/get it)
uses memory system (body can response faster 2nd time exposed)
distinguishes self from non-self AND between pathogens
2 approaches to adaptive defenses
cellular immunity
humoral immunity
cellular immunity
job: destroy antigen
t cells
humoral immunity
job- produce antibodies against again
B cells
cellular immuniy
mediated by T CELLS on recognition of antigen
T Cells in cellular immunity
T cells are produced in bone marrow & mature in thymus
protect against viruses and cancer
responsible for hypersensivity reactions and transplant rejections
two types of t cells in cellular immunity
regulatory- t helper, t suppressor
effector/killer
cells in order for crime
1) t helper (CD4)- identify (detective)
2) B cells- antibodies (officer)
3) Killer T (swat team)
more info about what T cells do
recognize the antigen (t helper)
bind t the antigen
trigger a response by the immune system
helper t cells activate and call up b cells to produce antibodies
humoral immuiy
mediated by b cells
antibodies take longer to produce after initial antigen exposure compared to innate immunity
b cells in humoral immunity
mature in bone marrow
2 types of b cells in humoral immunity
memory cells
immunoglobulin-secreting cells
memory cells in humoral immunity
recall the trigger and quickly triggers a response leading to acquired immunity
2 types of acquired immunity
active immunity
passive immunity
active immunity (type of acquired immunity)
acquired by having the disease and/or by taking vaccination
long lasting but takes a few days to become effective
passive immunity (type of acquired immunity)
passed down
short lasting
receiving antibodies from external sources (material fetal transfer/breastfeeding
hypersesitivity
exaggerated immune response to a feign substance
leads to inflammation
can be immediate or delayed
autoimmune
mistakes self as non-self
immunodeficiency
inadequate immune reaction
four types of hypersensitivty
type I: IgE mediated
type II: cyototoxic hypersensitivity reaction
type III: immune complex-mediated
type IV: delayed hypersensitivity reaction
to remember hypersensitivities
A- allergies= IgE
C- cytotoxic= IgG or IgM
I- immune complex
D- delayed hypersensitivity reaction
Type I, IgE mediated
produces an immediate response (2-30 min)
local or system (anaphylaxis)
IgE coats mast cells and basophils, sensitizing them to the allergen (when you’re exposed to an allergy you have a bad reaction, get worse)
ex- seafood allergy, hay fever
anaphylaxis
priority concern
can affect airway
treatment for type I, IgE mediated
includes epinephrine, antihistamines, corticosteroids, and desensitizing injections
type II hypersensitivity, cytotoxic
IgG or IgM antibodies bind to antigen on individuals own cells
causes cell lysis (cell destruction) and phagocytosis (clean up)
reaction takes 5-8 hours to develop
type II, cytotoxic example
mom and baby: mom is A blood type and baby is A+, 1st pregnancy is fine but 2nd causes issues
reason: blood transfusion reaction and erythroblastosis fetalis (hemolytic disease of the newborn)
type III hypersensitivity, immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity reaction
circulating antigen- antibody complexes accumulate and are deposited in the tissue (tissues include kidney, joints, skin, blood vessels)
triggers the complement system, causing inflammation
takes 2-8 hours to develop
examples of type III hypersensitivity, immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity reactions
autoimmune conditions (systemic lupus eruthematosus)
causes glomerulonephritis
type IV hypersensitivity, delayed hypersensitivity reaction
cell-mediated rather than antibody-mediated (only T cell mediated/ran) involving the T helper cells and killer cells
leads to inflammation causing severe tissue injury and fibrosis (scaring) (usually involves skin)
reactions occur 1-3 days after exposure
examples of type IV, delayed hypersensitivity reaction
tuberculin skin testing
transplant reactin
contact dermatitis (nickel- only at ONE site)
type I- allergies picture
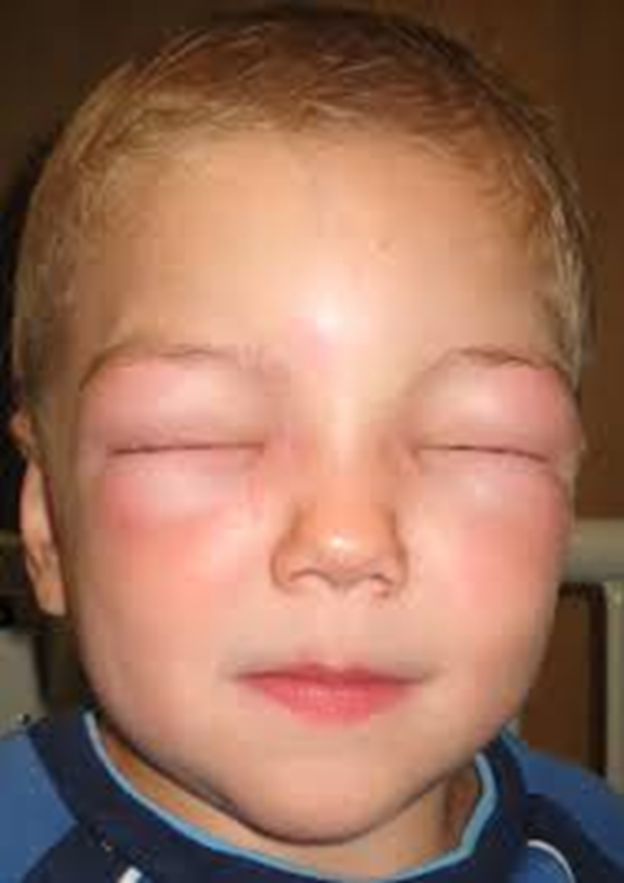
•Whole body reacts
•Sudden itchiness
•Puffy face, itchy eyes/nose
•Difficulty breathing, wheezing
•Anxiety
asthma
allergies
N/V/D
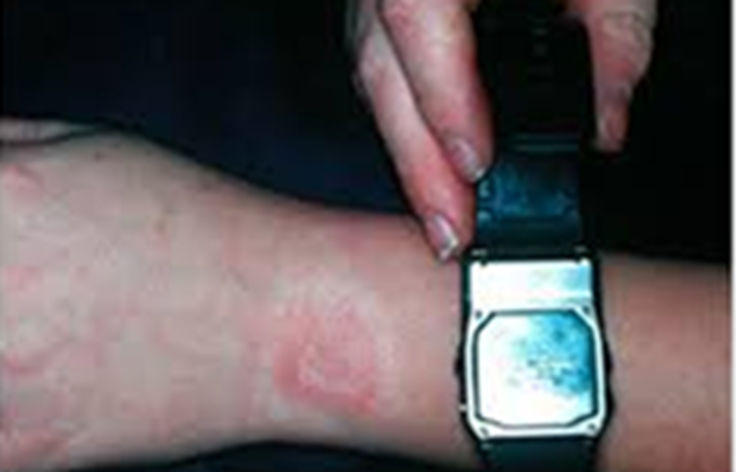
type IV- delayed hypersensitivity reaction picture
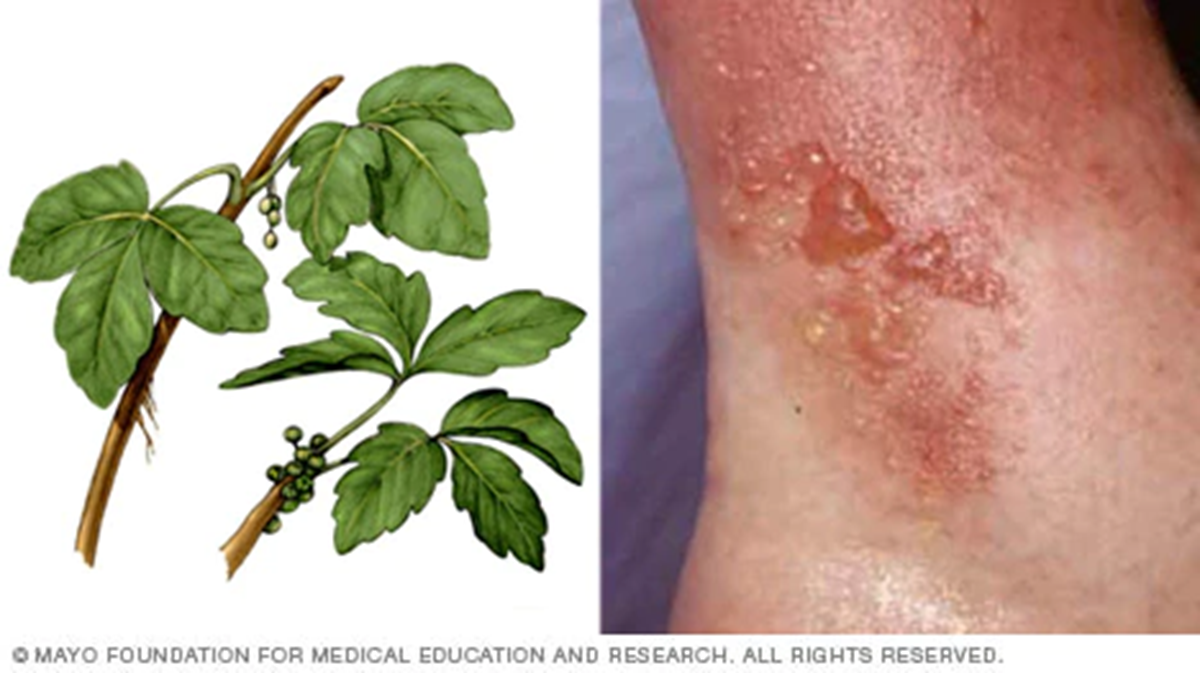
type II- cytotoxic picture
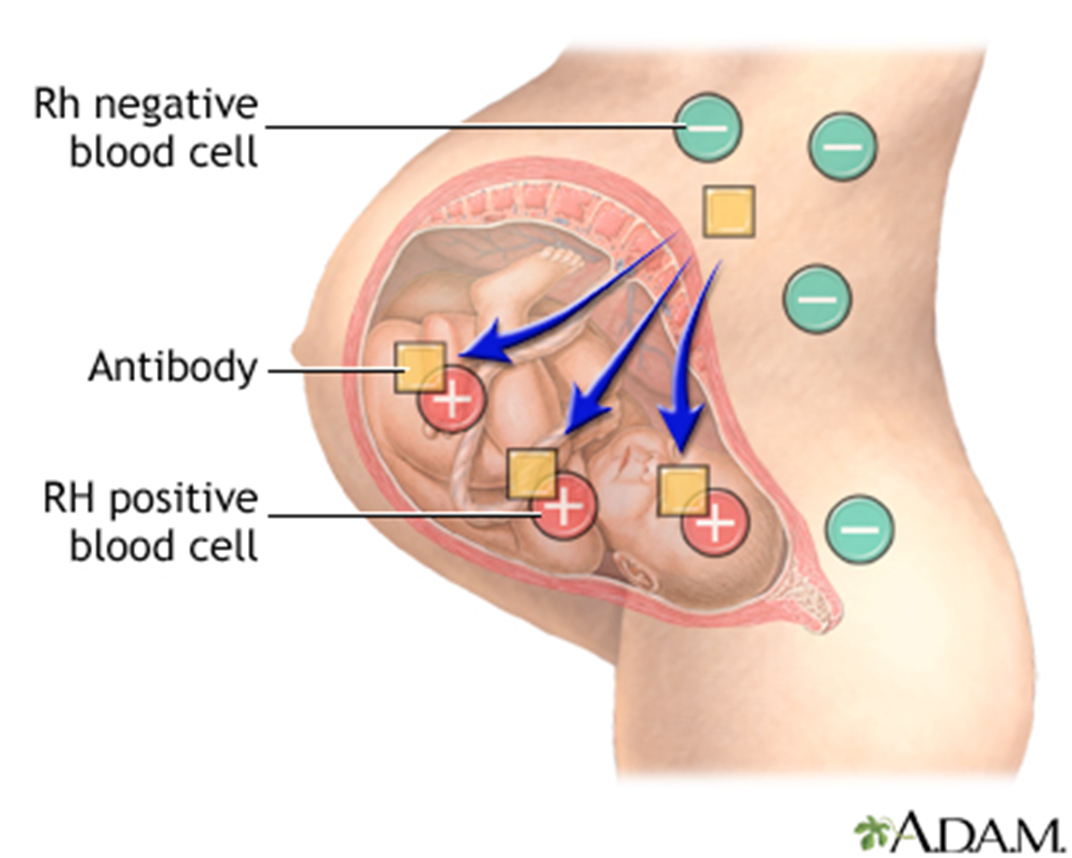
type III- immune complex
autoimmune disorder
self doesn’t recognize self, attacks self
defenses are directed against host
can affect any tissue
could be triggered by stressor or chronic stress
known characteristics of autoimmune disorders
genetics play a role (received from immediate family)
more prevalent in females
onset is associated with abnormal stressor, physical or pschological
has periods of sx getting worse and then sx getting better
Systemic (whole body) lupus erythematosus (SLE)
chronic inflammatory autoimmune condition
stressors influence severity
remission and exacerbations
may affect connective tissue of any body organ
more common in women (estrogen), asians, and african americans
SLE is thought to be caused by
B cells are activated→ produce autoantibodies + autoantigens tha combine to form immune complexes, which attack the body’s own tissues
manifestations of SLE
S erositis (lining of organs)
O ral ulcers
A rthritis
P hotosensitiity (body is sensitive to UV radiation) (gets rash)
B lood disorders (decreased counts)
R enal inflammation (reduces function, leaks protein through urine)
A ntinuclear antibody
I mmunological phenomena
N eurological disorders (seizures/psychosis)
M alar rash (butterfly rash over cheeks)
D iscoid rash (patchy redness that can cause scarring-scaly)
when is lupus normally diagnosed
20s-30s
not kids!
diagnosing SLE
abdominal/chest xray
elevated sedimentation rate from inflammation
C-reactive protein from inflammation
urinalysis (kidneys inflamed, protein in urine)
echocardiogram (inflammation in heart)
skin biopsy (not definitive by itself) (caused by photosensitivity)
blood test complications
treatment for SLE
no sure
sx management
stress management and health promotion behaviors
immunosuppressants
prognosis for SLE
improves with early diagnosis and treatment
discoid rash
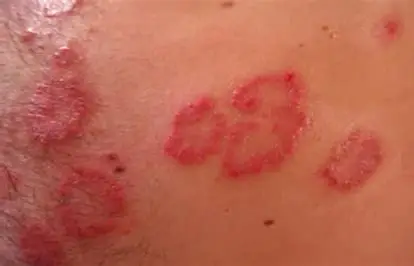
mallor rash

A female client asks the nurse if there are any conditions that can exacerbate systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Which is the best nurse response?
pregnancy is often associate with an SLE exacerbation (estrogen)