Alimentary 4: Diseases of the The Salivary Glands, Tonsils, Tongue, and Esophagus
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
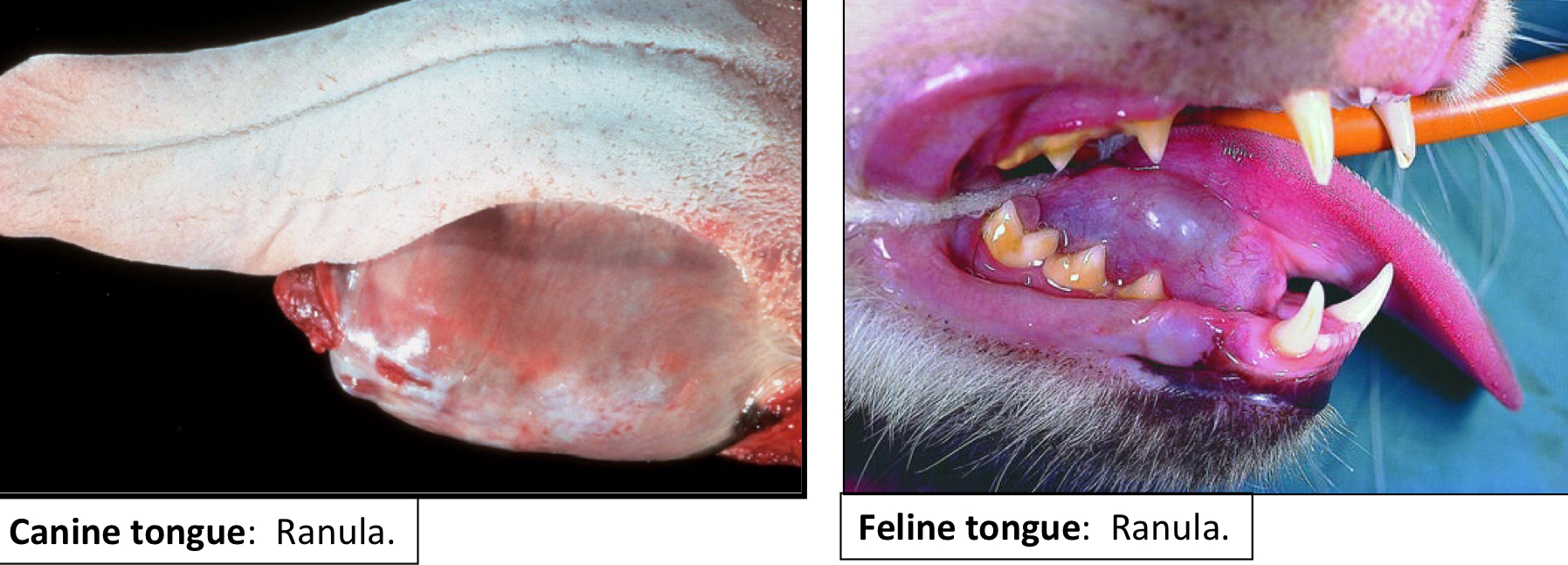
What is the difference between a True Salivary Cyst and a Ranula?
True Salivary Cysts
Distention/dilation of a salivary gland
Ranula
True Salivary cysts on the floor of the mouth or along the side of the tongue
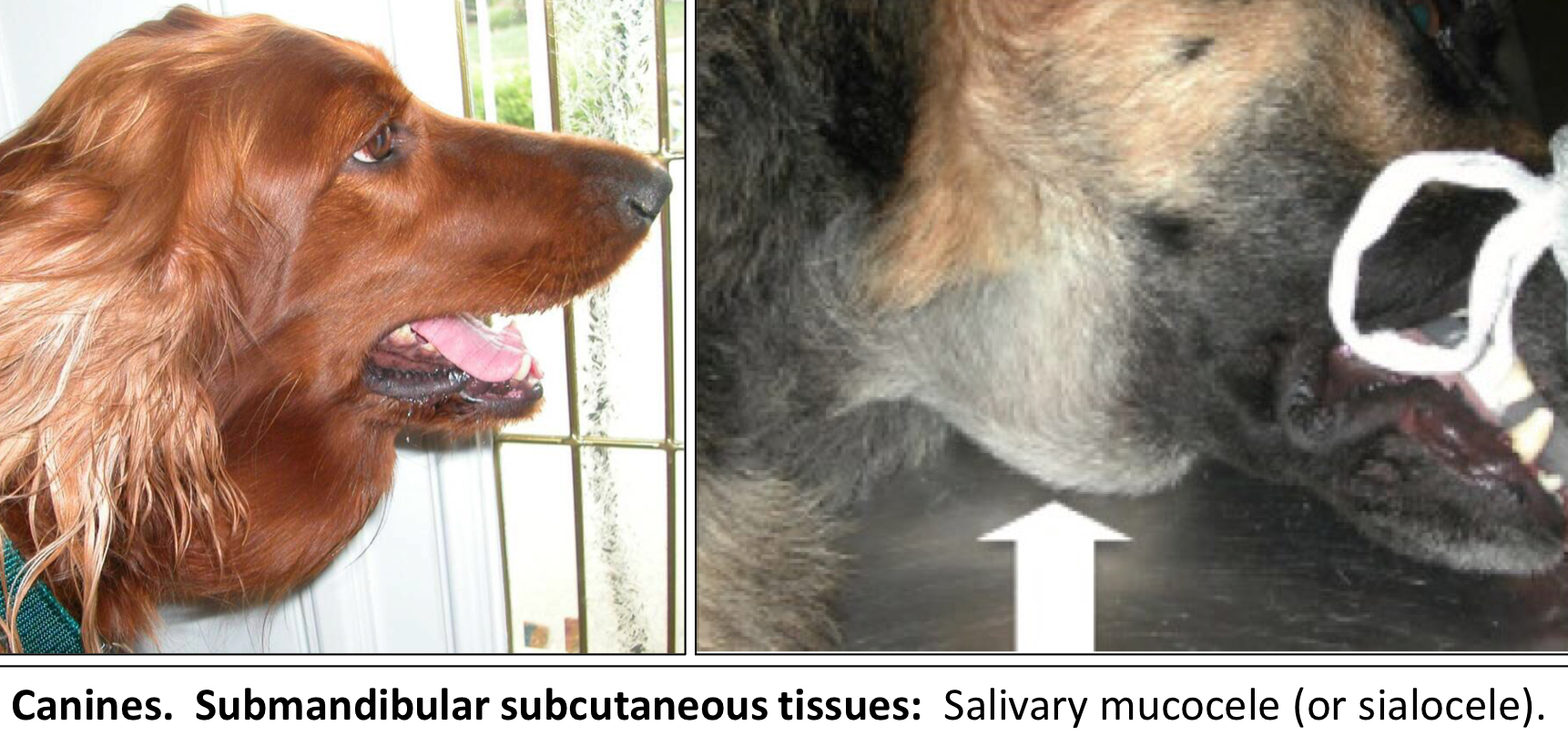
What is Mucocele or sialocele?
A pseudocyst of the Salivary Gland
It occurs as the result of accumulation in the submucosa or subcutaneous tissue after damage to the salivary duct
It is a pocket of saliva in the submandibular soft tissue
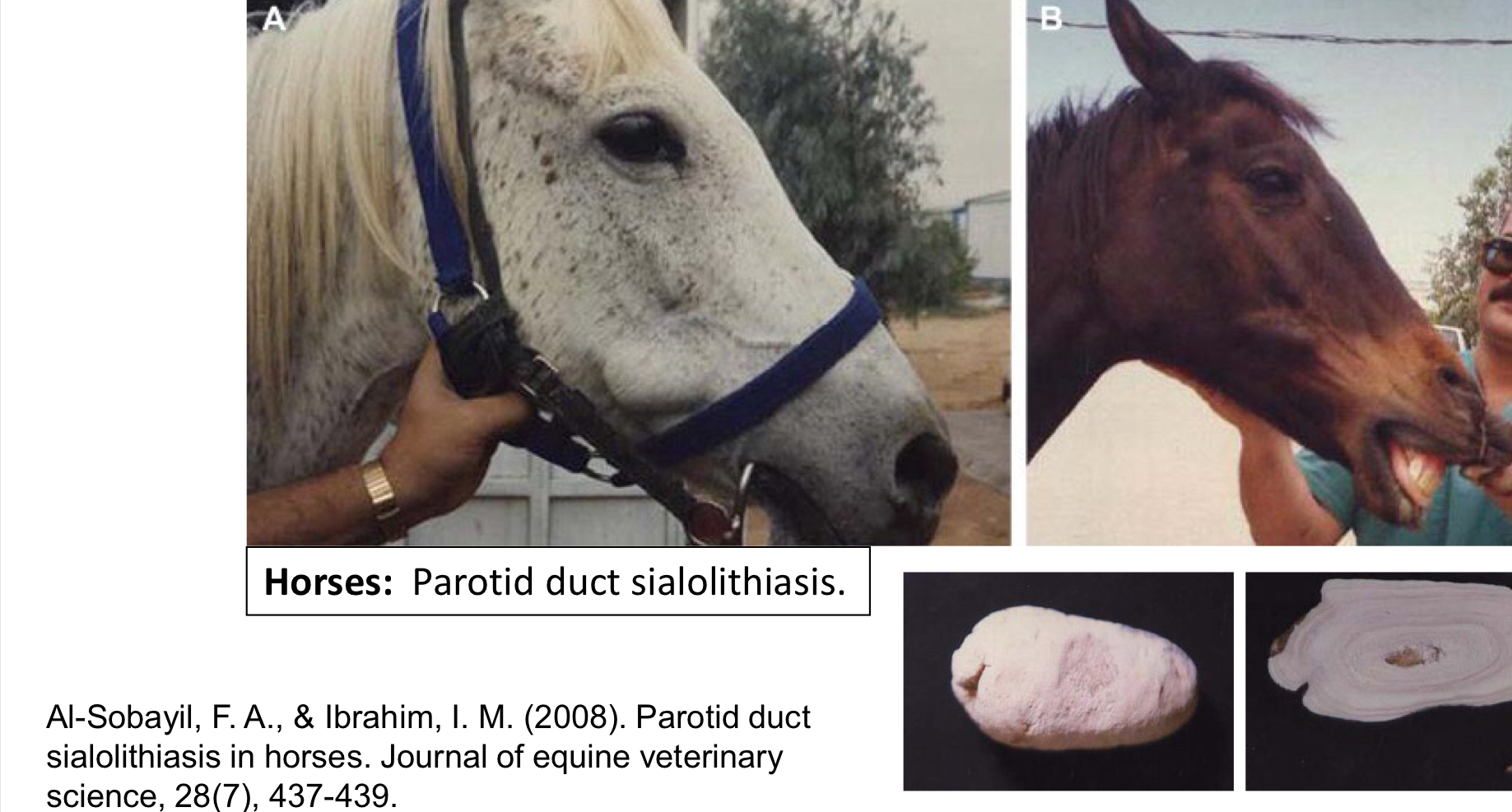
Define Sialithasis
Calculus or stones that form within the salivary gland
Define Sialadenitis
Inflammation of the Salivary Gland
What are some diseases that can cause Sialadenitis in animals?
Canine Distemper
Salmonellosis in pigs
Rabies
What is Epitheliogenesis imperfecta?
The incomplete development/formation of the epithelium
What is the Etiology of Actinobacillosis (aka Wooden Tongue)?
Actinobacillus lignieresii

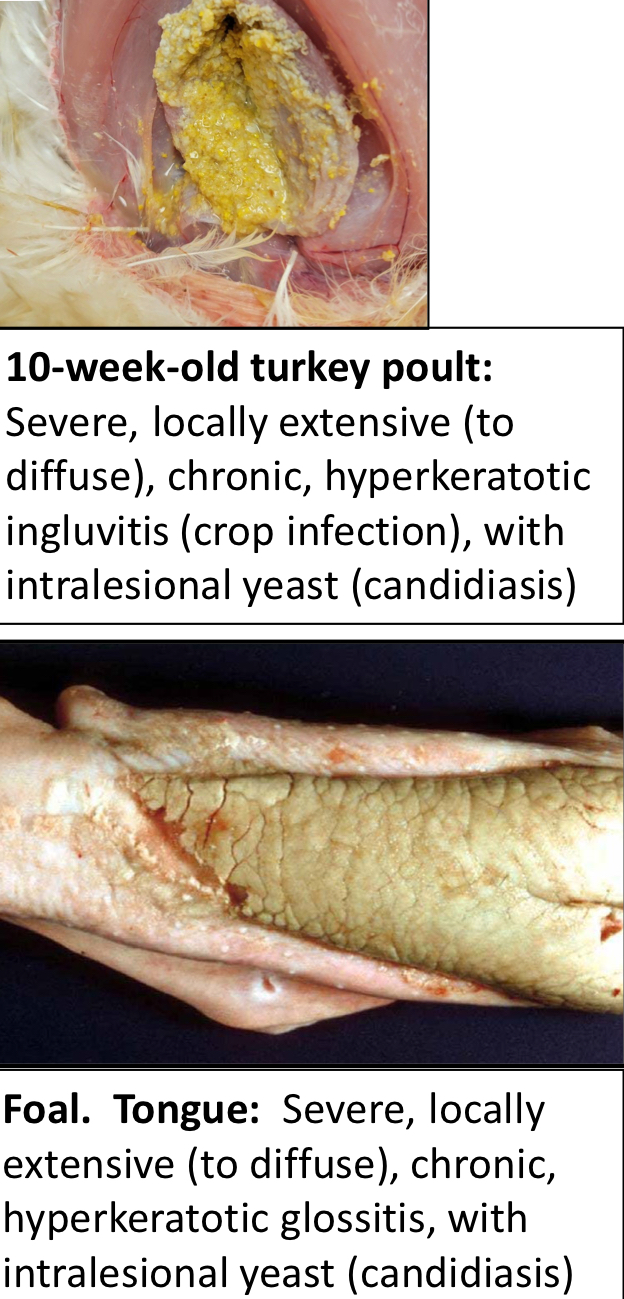
What is Thrush? What is its Etiology?
A disease of the tongue
An infection of the keratinized epithelium of the tongue
Presents as a yellow/grey/green pseudomembrane
Can be easily scraped off
Etiology
Candida Albicans
For diseases of the esophagus, what are their general C.S?
Regurgitation
Dysphagia
Odynophagia (painful swallowing)
Multiple swallowing attempts\Excessive salivation

Provide the Etiology
BVD
Bovine Papular stomatitis virus
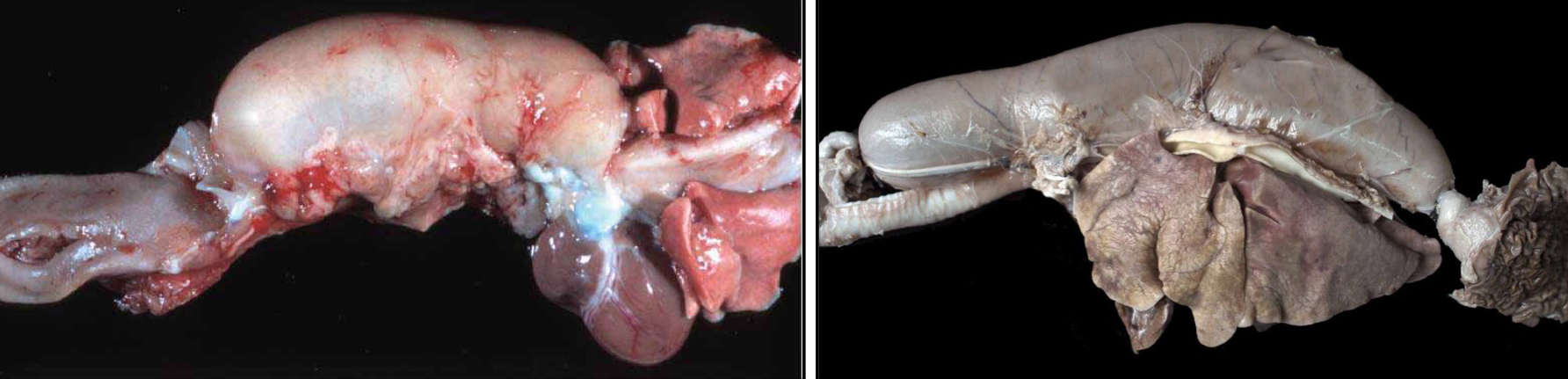
What is Megaesophagus, what are the 2 different forms?
Dilation of the esophagus due to insufficient/uncoordinated peristalsis
Congenital
Acquired
What are the 3 causes of Congenital Megaesophagus?
Caused by a persistent right aortic arch → caused segmental esophageal dilation
Idiopathic denervation of esophagus → Diffuse esophageal dilation
Congenital Myasthenia gravis → Diffuse esophageal dilation
What is the only congenital cause of Megaesophagus that results in Segmental Esophageal Dilation?
Persistent right aortic arch → caused segmental esophageal dilation

What are the 2 causes of Acquired Megaesophagus?
Idiopathic
Muscle Disease
Myasthenia Gravis
Hypoadrenocortisism
Hypothyroidism
Esophagitis
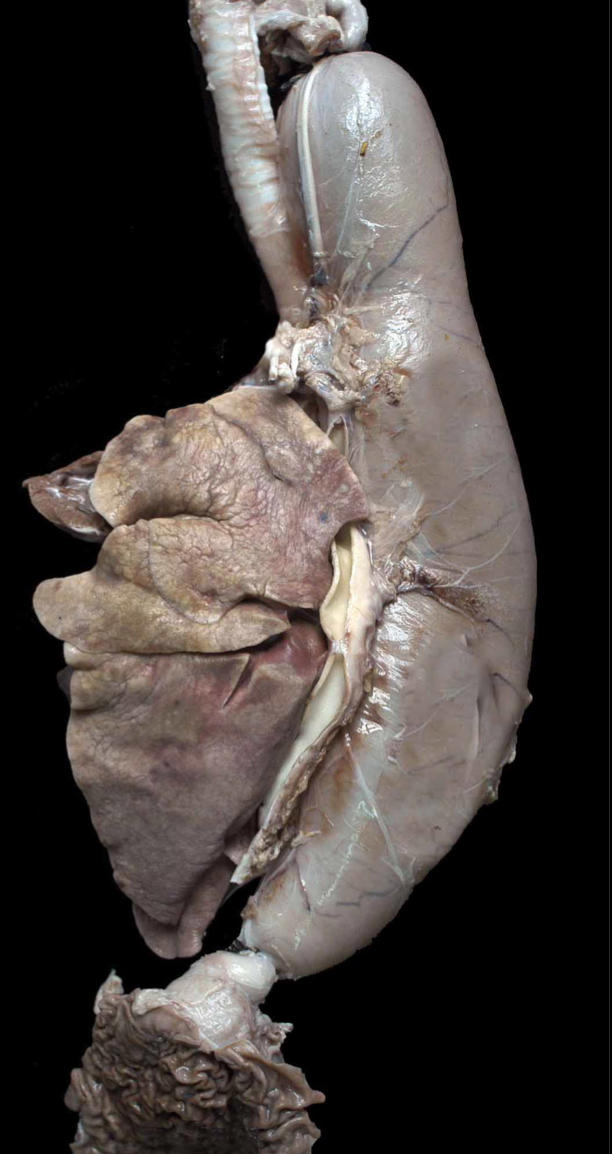
Most acquired forms of Megaesophagus are _____ (Diffuse/Segmental)
Diffuse
What is the Iatrogenic cause of Esophageal rupture?
Intubation of esophagus (tears during endoscopy)
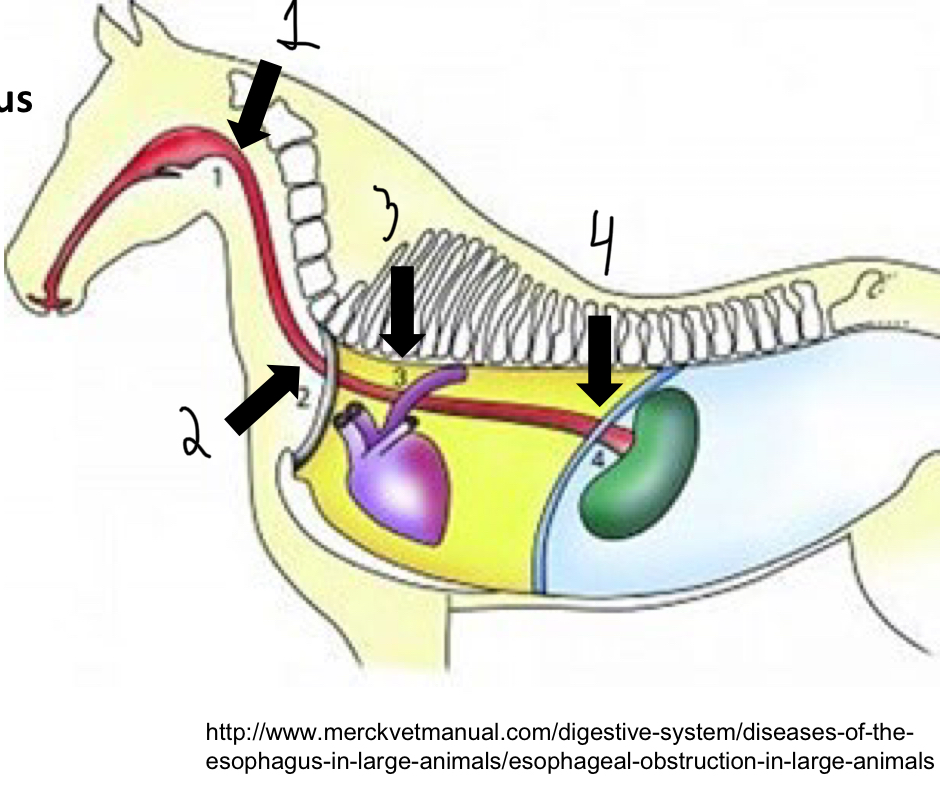
What are the 4 sites in which Esophageal obstruction (choke) and or rupture is most common? Why these sites?
Larynx
Thoracic inlet
Base of the heart
Diaphragmatic hiatus
These are all areas where the esophagus narrows
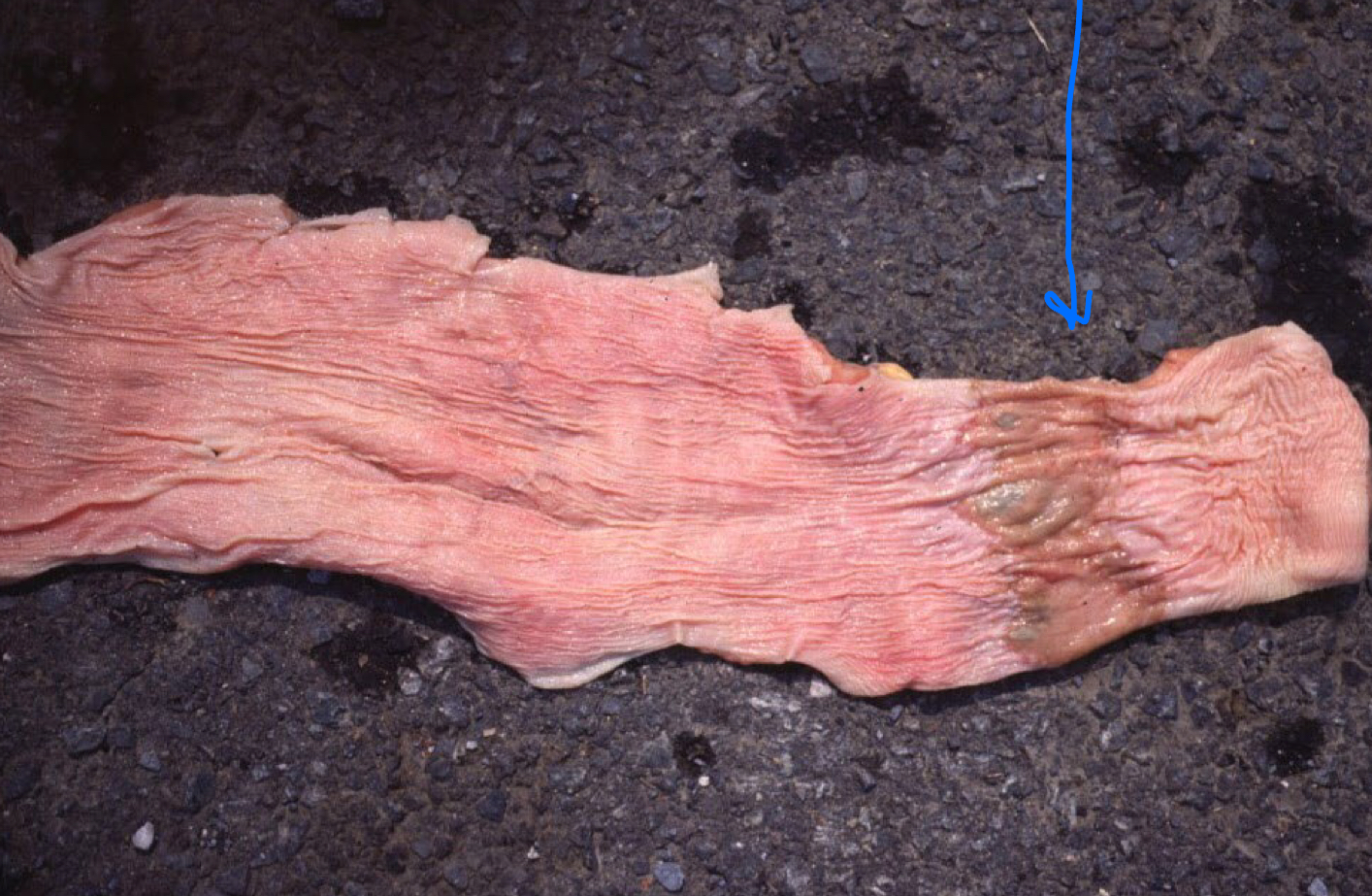
This circumferential damage to the esophagus indicates what?
A blockage
What are some sequelae that can occur as a result of an Esophageal obstruction/Rupture?
Perforation
Aspiration Pneumonia
Stenosis (Narrowing)
Bloat (Cattle)
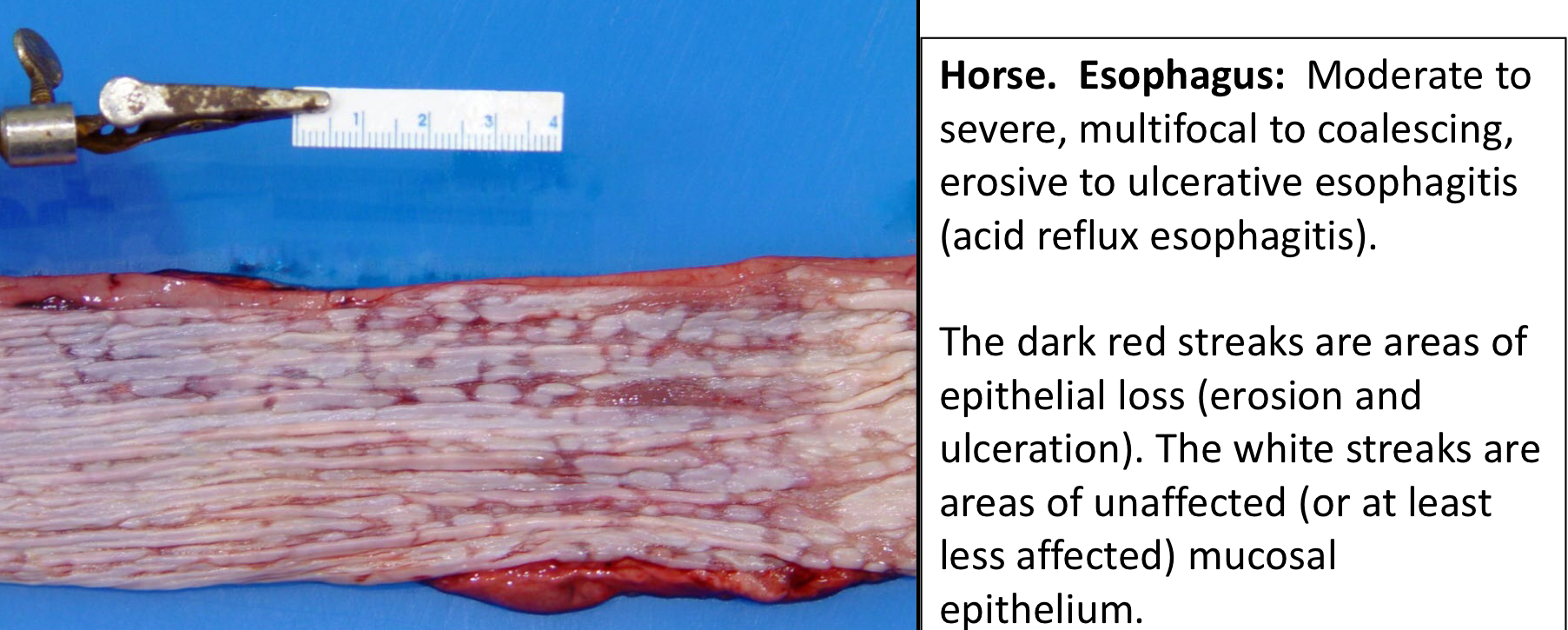
What is Reflux Esophagitis?
Chemical damage of the epithelium in the esophagus due to repeated gastric acid reflux
What parasite is known to encyst in the esophagus? What type of inflammation does it cause?
Spirocerca Lupi
Chronic granulomatous esophagitis
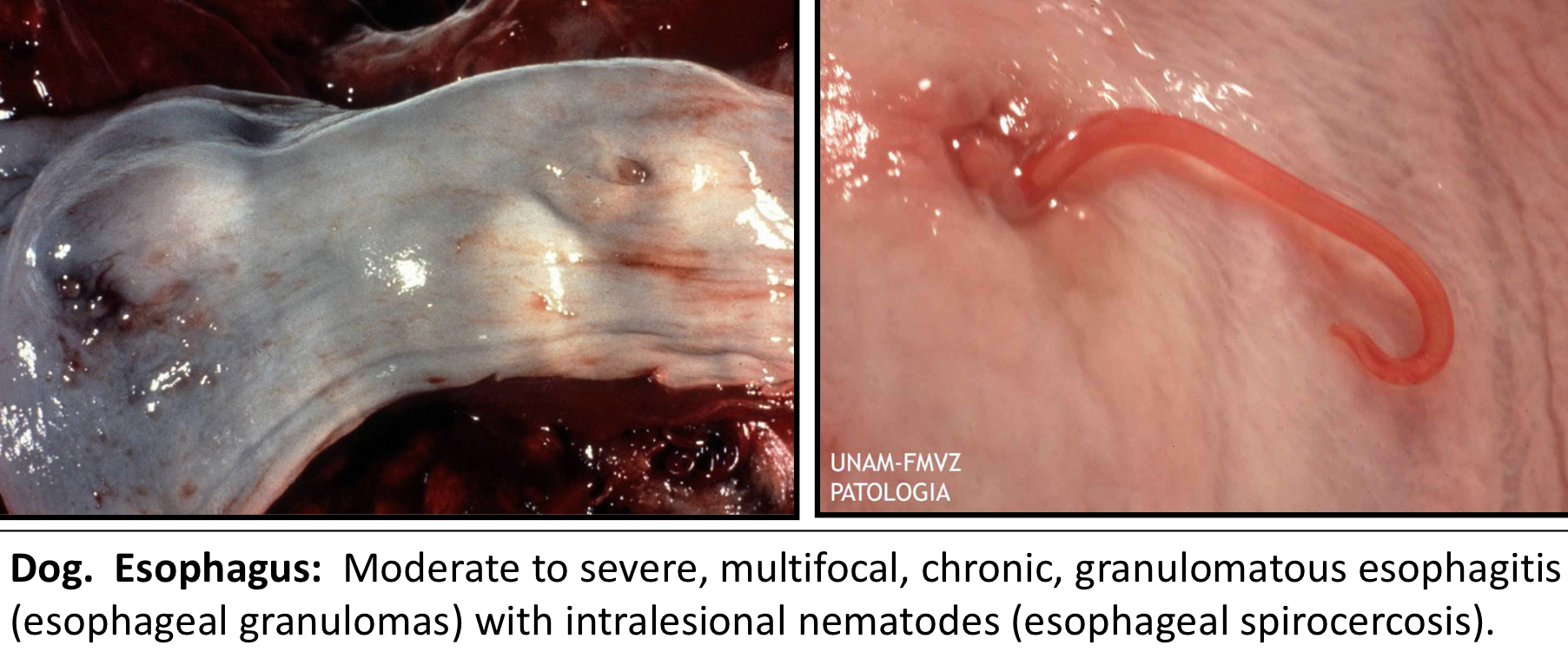
T/F: Spirocerca Lupi can cause a chronic granulomatous esophagitis that can transform into a malignant sarcoma
True!
T/F: Spirocerca lupi can also cause aoirtic aneurysms
True