Energy - energy
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy stored in moving objects
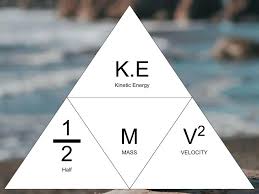
What is the equation for kinetic energy?
Ek=0.5 x m(Kg) x v2(
Kinetic image(J) = 0.5 x m(Kg) x v2(M/s)
What is elastic potential energy?
When a spring is stretched, a force is applied to change the length of the spring and it the spring extends
The stretched spring is storing this energy and this is the elastic potential energy
How is the extension plotted on a graph?
The extension is directly proportional to the force so staight line is drawn on the graph
However if too much force is applied, the spring has reached the limit of how far it can extend which is called the limit of proportionality
When the limit of proportionality is met, what are the affects on the spring?
It can no longer return to its original length if the force is taken away
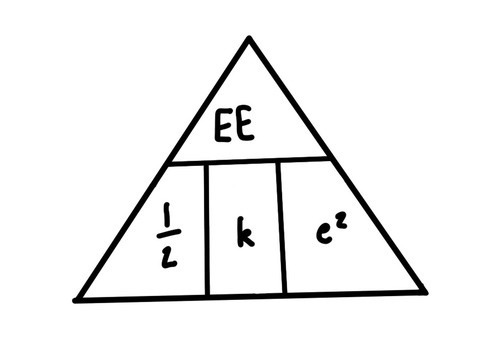
What is the equation for elastic potential energy?
Ee= 0.5 x K x e2
Elastic potential energy(J) = 0.5 x spring constant(N/m) x e2(m)
What is applying a force called?
Doing work
What is gravitational energy?
The energy stored in an object due to its position above the earths surface which is due to the force of gravity acting on an object
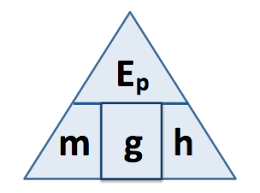
What is the equation for gravitational potential energy?
Ep = m x g x h
Gravitational potential energy(J) x mass(Kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg) x height (m)
Measures the force of gravity
What are the units for mass?
Kilograms
What are the units for height?
Meters
What is thermal energy?
The energy stored due to a objects temperature
What is specific heat capacity?
The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg substance by 1’c
What is the equation to calculate the specific heat capacity?
△E = m x c x △θ
Change in thermal energy(J) = mass(Kg) x specific heat capacity(J/kg ‘C) x temperature change (‘C)
What is the law of conservation of energy?
Energy can be transfered usefully, stored or dissipated but it cannon be created or destroyed
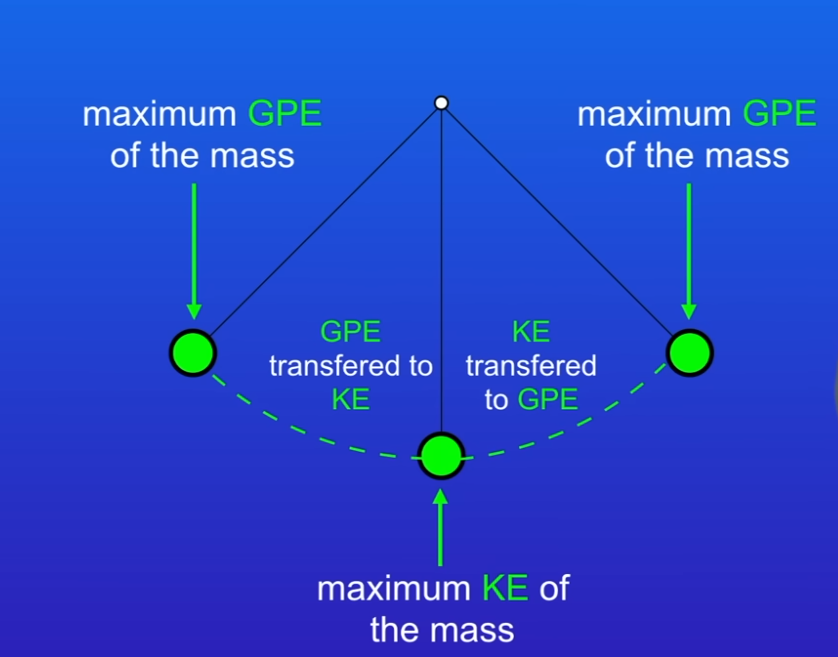
What is a pendulum?
A mass attached to a string attached to a fix point
This set up is called a system
What is a system?
A system is an object or a group of objects
What is a closed and opened system?
In a closed system, no energy can enter or leave
In a opened system, energy can enter or leave
How does energy transfer in pendulum?
What is a problem with the pendulum?
It does not consider friction
Friction causes energy to be transfered to thermal energy which are less useful which means the energy have been dissipated (wasted)
It is wasted as the energy is not used for its intended purpose
This causes the pendulum to gradually swing with less energy and eventually stop
How do we reduce unwanted energy transfers?
Unwanted energy transfers can be reduced by reducing friction
How can we reduce friction in the pendulum?
Use a lubricant on the fixed point
Remove the air particles from around the pendulum
What are the energy transfers in bungee jumping?
Standing on the platflorm
As the jumper falls
When the rope starts to tighten
When its fully extended
The bungee jumper starts by standing on a platform and all the energy stored in the system is gravitational potential energy
As the jumper falls, energy is transferred from the gravitational potential energy store to the kinetic energy store
When the bungee rope starts to tighten, the kinetic energy store is now at its maximum
When the rope is fully extended, the kinetic energy is at 0 as the jumper is not moving and all the energy has transferred to the elastic potential energy store
The rope recoils and energy is transferred from the elastic potential energy back to the kinetic energy stor e
During the ascent up, energy transfers from the kinetic energy store back to the gravitational potential energy store
At the top, all the energy is gravitational potential energy
What is the key idea of the bungee jump?
The jumper never returns back to the original position
This is because energy is dissipated as thermal energy
This is due to:
Friction with air particles
Stretching effects in the bungee rope which is not fully elastic (some thermal energy is dissipated)
What happens when a car brakes?
The brake presses against the wheel causing friction
This means the kinetic energys store of the car is transferred to thermal energy store in the breaks
This means the temperature of the breaks increases and the car slows done and stops
What does ‘work done’ mean?
Work done is whenever energy is transferred from one store to another
What is mechanical work?
Using a force to move an object
What is electrical work?
Energy transferred in a current
What is the equation for work done?
Work done(J) = force (N) x distance (m)
This tells us the energy transfer between to stores
What is power?
The rate at whuch energy is transferred or the rate at which work is done
Measured in watts
What are the two equations for power?
Power(W) = energy transferred(J) / time(S)
Power(W)= work done(J) / time (S)
What is power in watts directly proportional to?
1 watt is an energy transfer of 1 J per second
What does efficiency tell us?
Efficiency tells us what fraction of the energy we put into a appliance is transferred to useful forms of energy
What are the two equations for efficiency?
Efficiency = useful output energy transfer / total input energy transfer
Efficiency = useful power output / total power input
These must be calculated in this exact order or you will get a value greater then 1 or 100%
How do we calculate a decimal to a percentage to get the percentage of efficiency?
Times by 100
How can we increase the efficiency of a energy transfer?
Use a pan with a wider base and lid
Place the heating element inside the water
What does conductivity mean?
How efficient a material is at keeping thermal energy/heat in
High conductivity = allow a lot of thermal energy out
Low conductivity = reduces the amount thermal energy passing through
How are houses kept warm?
Houses have a internal breezeblock wall and a external brick wall that have a gap inbetween called a cavity
The cavity if filled with insulating material which has a low thermal conductivity which helps keep heat in
Houses also have loft insulation
How are windows designed to keep heat in?
Windows are double glazed to have a low thermal conductivity
Required pratical 1: specific heat capacity
Place a beaker onto a balance and press zero
Now add oil to the beaker and record the mass of the oil from the balance
Place a thermometer and an immersion heater into the oil
Read the starting temperature of the oil
Add insulating foam to reduce thermal energy transfer to the surroundings
Connect a joulemeter to the immersion heater (this tells us the how many jewls of electrical energy passes through the immersion heater)
Leave for thirty minutes
Read the total number of joules of energy that passed into the immersion heater and the final temperature of the oil
What to do with the specific heat capacity required pratical results?
Change in thermal energy = mass x specific heat capacity x temperature change
Rearrange this equation for find the specific heat capacity
Specific heat capacity = change in thermal energy / mass x temperature change
Why may result of the specific heat capacity required pratical be inaccurate?
Thermal energy passing out of the beaker into the air
Use an insulator with a lower thermal conductivity
Not all thermal energy passing into the oil
Ensure that immersion heater is fully submerged
Incorrectly reading of the thermometer
Use on electronic temperature probe
Thermal energy may not be spread through the oil
Stir the oil
What are examples of use of energy in the modern world?
Transport
Generating electricity
Heating
What are the three main fossil fuels?
Coal
Oil
Gas
What are the advantages to fossil fuels?
Reliable
Fossil fuels release a great deal of energy
Abundant
Cheap
Verstile (can use for many things)
Portable
What are the disadvantages of fossil fuels?
Release large amounts of carbon dioxide
Non-rewnable (not being replaced as we use them and will one day run out)
Can release of pollutants eg sulfur dioxide
What are the features of nuclear power?
Non-rewnewable
Run on uranium and plutonium
What are the advantages of nuclear power?
Does not contribute to climate change
Reliable
What are the disadvantages of nuclear power?
Highly dangerous radioactive material
Decommissioning (take down) a nuclear power plant takes many years
Extremely expensive
Produces large of amounts of highly dangerous radioactive waste
What big changes ocurd that made the use of coal fall?
The use of nuclear power increased
The uk began to become a producer of oil and gas which started to replace coal
What were the advantages to switching from coal to gas?
Burning gas produces less carbon dioxide
Gas-fired power stations are flexible and can be switched on quickly in demand
What are the disadvantages of renewable resources?
Expensive
Unreliable
How do we fix the problem of renewable resources being unreliable?
Baseloads can be used which is a constant supply of electricity thats on all the time
Gas-fired power stations can be used to provide emergency power
What is renewable energy?
A renewable energy resource is one that is being or can be replenished as it is used
What are the advantages of all renewable energy resources?
Renewable
Do not add carbon dioxide to the atmosphere
What is wind power? What is the disadvantage of wind power?
Wind power harnesses the kinetic energy of moving air to generate electricity
Unreliable
What is solar power? What is the disadvantage of solar power?
Solar power converts energy from the sun into power
Unreliable
What is hydroelectric power? What are the advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric power?
Hydroelectric power uses the energy of moving water to generate electricity
Reliable
But
Requires rivers
Causes damage to habitats
What is the advantage of tidal power?
Reliable
What is geothermal energy? What are the advantages?
Geothermal energy uses heat from the earth to generate electricity and heat buildings
Reliable
What is a problem with renewable resources only generating electricity?
A lot of energy used in the Uk is for cars which run of petrol or diesel which are fossil fuels
What is biofuels? What are the advantages and disadvantages ?
Biofuels are produced from plant materials
Burning biofuels does not add extra carbon dioxide to the atmosphere
Can be used to power vehicles
But
Using land to grow crops for fuel could push up the price of food as less land is being used to grow it