Macroeconomics, starred = key terms [Incomplete]
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
budget deficit
amount by which government spending is greater than government revenue
macroeconomics
study of large economic systems such as those of a whole country or area of the wold
national income
value of income, output, or expenditure over a period of time
Gross domestic product (GDP)
Market value of all final goods and services produced in a period (usually yearly), an internationally recognized measure of national income
boom
The peak of the economic cycle where GDP is growing at its fastest
downturn
period in the economic cycle where GDP grows, but more slowly
depression
bottom of the economic cycle where GDP starts to fall with significant increases in unemployment
recession
period of temporary economic decline during which trade and industrial activity is reduced, generally identified by a fall in GDP in two successive quarters
recovery
a rise in economic activity following a recession or slump
overheat
demand rises too fast, causing prices to and imports to rise, a situation the government may try to correct by raising taxes and interest rates
unsustainable growth
economic growth that is not possible to sustain without causing environmental problems
aggregate demand
total demand in the economy including consumption, investment, government expenditure, and exports minus imports
deflation
period where the level of aggregate demand is falling
inflation
rate at which prices rise, a general and continuing rise in prices
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
measure of the general price level (excluding housing costs)
retail price index (RPI)
measure of the general price level, which includes house prices and tax
demand-pull inflation
inflation cased by too much demand in the economy relative to supply
cost-push inflation
inflation caused by rising business costs
interest rates
price paid to lenders for borrowed money; it is the price of money
monetarists
economists who believe there is a strong link between growth in money supply and inflation
purchasing power of money
amount of goods and services that can be bought with a fixed sum of money
shoe leather costs
costs to firms and consumers of searching for new suppliers when inflation is high (time)
menu costs
cost of firms having to make repeated price changes
hyperinflation
very high levels of inflation; rising prices get out of control
unemployment
when those actively seeking work are unable to find a job
How can unemployment be measured?
Survey
cyclical or demand deficient unemployment
unemployment caused by falling demand as a result of a downturn on the economic cycle
laying off
to stop employing someone beacuse there is no work for them to do
structural unemployment
unemployment caused by changes in the structure of an economy such as a decline in industry
sectorial unemployment (structural)
when people are laid off because of the decline of the industry they work in
technological unemployment (structural)
when people are laid off because technology replaces their jobs
regional unemployment (structural)
when a specific region in a country faces changes in structure of the economy leading to unemployment
seasonal unemployment
unemployment caused when seasonal workers, such as those in the holiday industry, are laid off because the season has ended
frictional unemployment
when workers are unemployed for a short period of time as they move from one job to another
monetary policy
use of interest rate and the money supply to control aggregate demand in the economy
money supply
amount of money circulating the economy
Why might the interest rate vary between banks? (4 points)
Competition, mortgage or not, savers, credit cards
List the role of central banks (4 points)
Implementing monetary policy and regulating the banking system, acting as a lender of last resort to commercial banks, controlling inflation and stablizing currency, setting interest rates
List the 3 things that affect how interest rates affect balance of payments
income elasticity of imports, strength of link between interest rate and exchange rate, PED for exports and imports
quantitative easing
buying of financial assets, such as government bonds from commercial banks, which results in a flow of money from the central bank to commercial banks
List the business activities that damage the environment
mining, power generation, chemical processing, agriculture, construction
List the ways businesses damage the environment
visual, noise, air, water (pollution)
income inequality
differences that exist between the different groups of earners in society, that is, the gap between the rich and poor
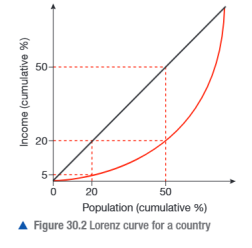
Lorenz curve
graphical representation of the degree of income or wealth inequality in a country
absolute poverty
where people do not have enough resources to meet all of theit basic human needs
relative poverty
poverty that exists relative to existing living standards for the average individual
progressive taxation
where the proportion of income paid in tax rises as the income of the taxpayer rises
regressive taxation
tax system that places the burden of the tax more heavily on the poor
policy instruments
tools governments use to implement their policies, such as interest rate, rates of taxation, levels of government spending
budget
government’s spending and revenue plans for the next year
fiscal policy
decisions about government spending, taxation and levels of borrowing that affect aggregate demand in the economy
direct taxes
taxes levied on the income earned by firms and individuals
indirect taxes
taxes levied on spending, such as VAT
value-added tax (VAT)
tax on some goods and services - businesses pay value-added tax on most goods and services they buy and if they are VAT registered, charge value-added tax on the goods and services they sell
fiscal deficit
amount by which government spending exceeds government revenue
fiscal surplus
amount by which government revenue exceeds government spending
national debt
total amount of money owed by a country
expansionary fiscal policy
fiscal measures designed to stimualate demand in the economy
contractionary fiscal policy
fiscal measures designed to reduce demand in the economy
aggregate supply
total amount of goods and services produced in a country at a given price level in a given time period
supply side policies
government measures designed to increase aggregate supply in the economy
offset
if something such as a cost of sum of money offsets another cost it has the effect of reducing or balancing it, so that the situation remains the same
Two ways supply side policies improve productivity
Improving flexibility, training & education
List the impacts of supply side policies on macroeconomic objectives
Privatization, deregulation, education and training, boosting regions with high unemployment, Infrastructure spending, Lower business taxes to stimulate investment, Lower income taxes to encourage working
austerity
official action taken by the government to reduce the amount of money that it spends or the amount that people spend