1. Food preservation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Preservation methods
Traditional methods
Thermal methods
Concentrating
Packaging
Combinations/other
Process concepts
Fluid flow
Reactions-Reactors
Heat transfer
How to control microorganisms and enzymes
Slow down deterioration reactions
Change conditions for undesired m.o.
Remove m.o.
Inactivate m.o. and enzymes
Food Preservation mechanisms
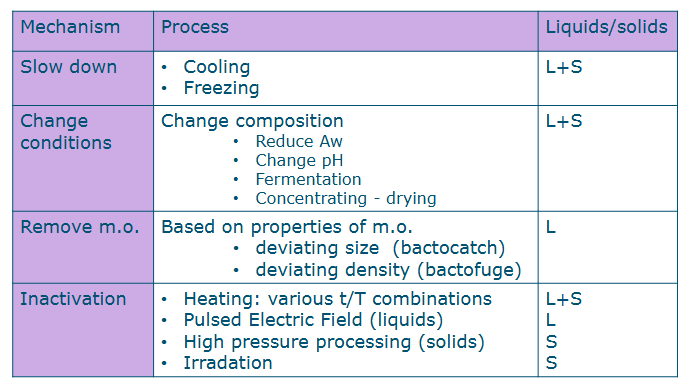
Food preservation mechanisms for milk, fruit juices & alcholic drinks
PEF = pulse electric field
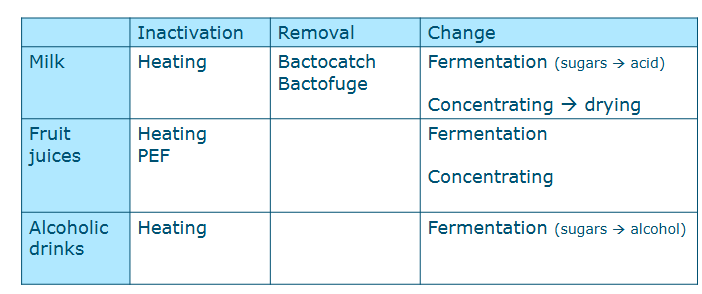
Food preservation mechanisms for semi-solid foods
(Heat treatments) Thermisation
Gets rid of psychrotrophic bacteria
65-72 C, 15-22 seconds
(Heat treatments) LTLT, low temperature; long time
62-65 C, for at least 30 min
(Heat treatments) Pasteurization
72-75 C, for 15-40 seconds
(Heat treatments) Flash pasteurization
85 C
1-2 seconds
(Heat treatments) UHT, ultra-high temperature
Sterilization
135-140 C, for 1-2 seconds
Aim of bactofugation & bactocatch
Used for milk/dairy
Aim:
prolonged shelf life
Preserve taste and nutritional value
Remove Clostridia sporeformers from milk for cheesemaking
Can be achieved by doing this instead of heat treatments
Process of bactofugation
Increase temp for fat removal
Centrifugation: separation of fat fraction
Bactofugation: separate stream with bacteria
Sterilization of stream with bacteria
Recombining + mild pasteurization of recombined stream
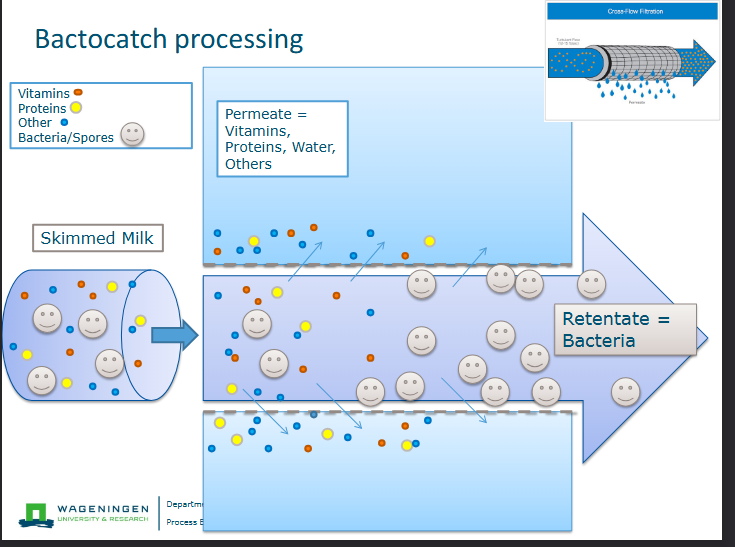
Process of bactocatch
used for ESL milk-milk with extended shelf life
Membrane process; Microfiltration (membrane 1.4 micrometer)
Separation based on size
Effect of treatment on product
The effect can be tested, for example the protein nativity is an indicator for heat treatment
Or measure beta lactoglobulin nativity
Packaging for preservation
Post package treatment (cans)
You have to heat the can
Aseptic packaging
Product is sterilized first, followed by filling disinfected containers under sterile, enclosed conditions
Three categories of operations
Separations: including cleaning, fractionation and purification
Conversions and structuring: such as fermentation, enzymatic/microbial inactivation, and changing ingredient positioning
Stabilizations: involving a preservation treatment to reduce deterioration risk and packaging