Clinical Experience I- Ch 48- Complete
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
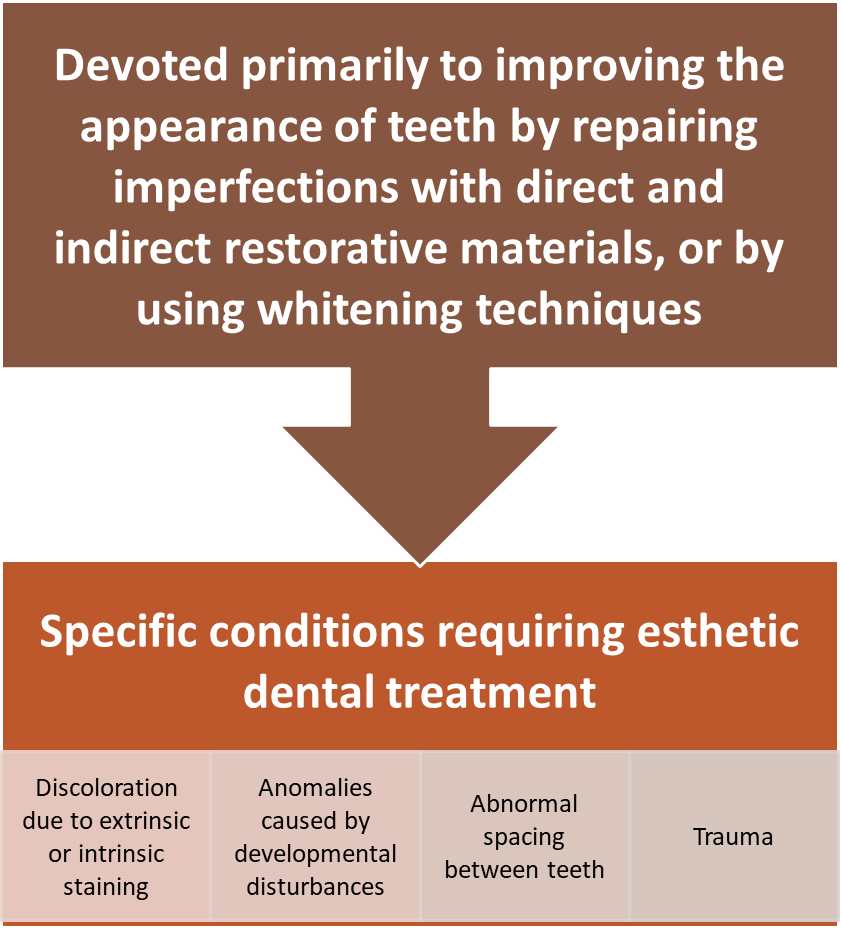
Restorative Dentistry

What types of materials are used for esthetic dentistry?
Direct and indirect restoration materials, along with whitening materials
restorative dentistry
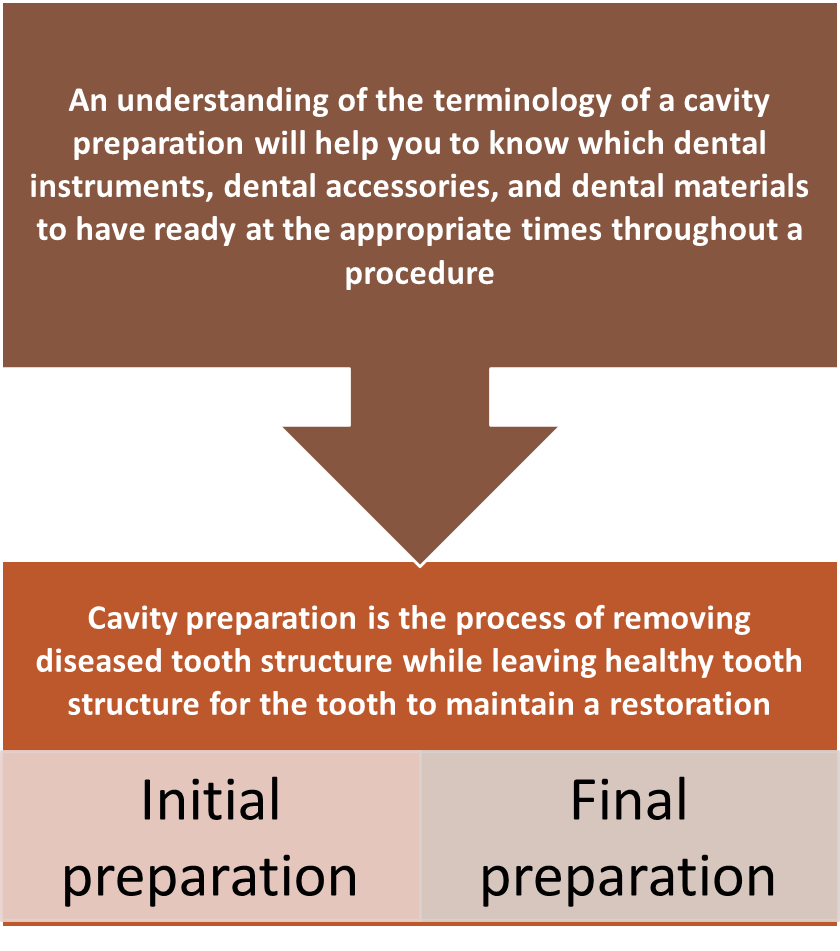
Cavity Preparation
When preparing a tooth for a permanent restoration, the dentist has the acquired knowledge about the:
Direction of the enamel rods
Thickness of the enamel
Body of the dentin
Size and position of the pulp
Crown of the tooth as it relates to the gingival tissues
standardized plan of a restoration
Initial Cavity Preparation
1. Outline form
Design and initial depth of sound tooth structure
2. Resistance form
Primary shape and placement of cavity walls
3. Retention form
To resist displacement or removal
4.Convenience form
Accessibility in preparing and restoring the tooth
Final Cavity Preparation
Includes:
Removing enamel, diseased dentin, or old restorative material (or a combination)
Inserting additional resistance and retention notches, grooves, and coves
Placing protective dental materials (lining agents, bases, desensitizing, or bonding agents)
Standardized Plan of a Restorative Procedure
Communicate with the patient about the procedure and what to expect
Position the patient correctly for the dentist and have ready the type of procedure
Dentist will evaluate the tooth
Dentist administers local anesthesia
Assistant readies the means of moisture control
Dentist prepares the tooth
Dentist determines the type of dental materials to be used
Dentist burnishes, carves, or finishes the dental material
Dentist checks the occlusion of the restoration
Dentist finishes and polishes the restoration
Dental Assistant’s Role in a Restorative Procedure

Permanent Restorations

Class I Restorations

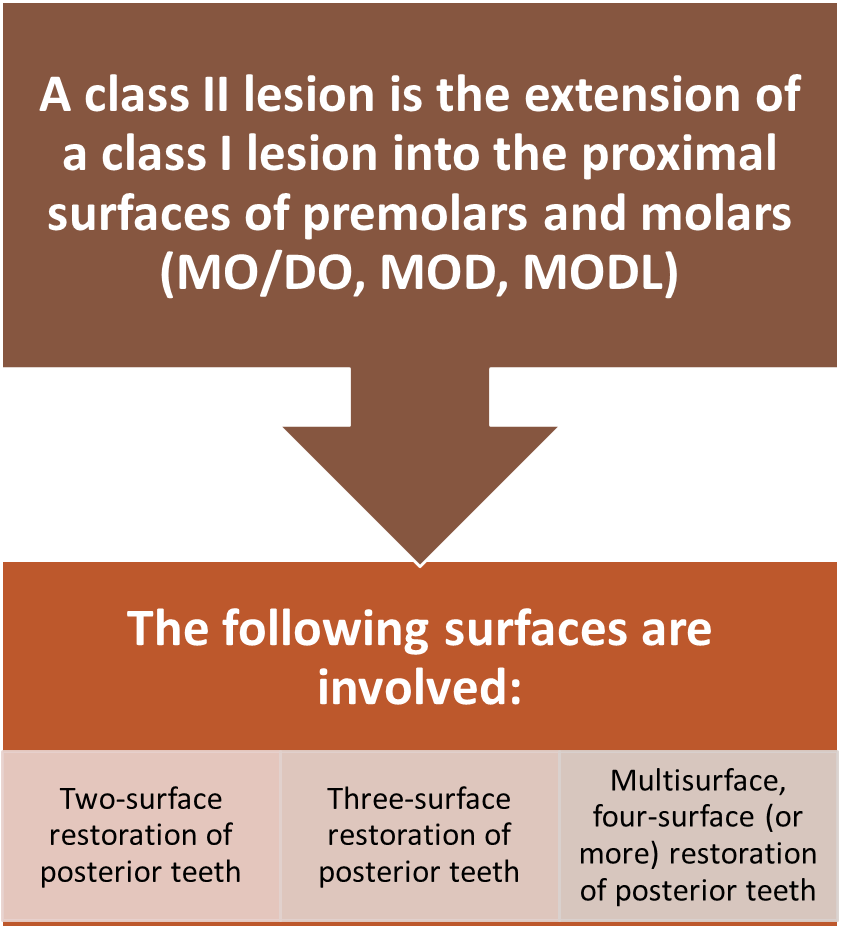
Class II Restorations
Class III and IV Restorations
Anterior Teeth: Class III lesion
Affects the interproximal surface of incisors and canines
(M or D)
Anterior Teeth: Class I lesion
Involves a larger surface area, including the incisal edges and interproximal surface of incisors and canines
(MI/DI)
Class V Restorations
Class V restoration
Classified as a smooth surface restoration, occurs more in older patients
Decayed lesions occur at:
Gingival third of the facial or lingual surfaces of any tooth
Root of a tooth, near the cementoenamel junction
(F)
Complex Restorations
In certain situations, during tooth preparation, the loss of tooth structure will become greater than what is remaining of the natural tooth structure
The dentist must decide whether to:
Restore the tooth with a direct restoration
Change the treatment plan and advise the patient that an indirect restoration would be more suitable
Retention Pins
It may be necessary for the dentist to use a stronger system for retaining and supporting the restoration other than retentive grooves or bonding materials
In general, when using retention pins, one pin is placed for each missing cusp
Pins are available in several diameters (widths) and styles
The retention pin has deep threads that grip the dentin when screwed into tooth structure
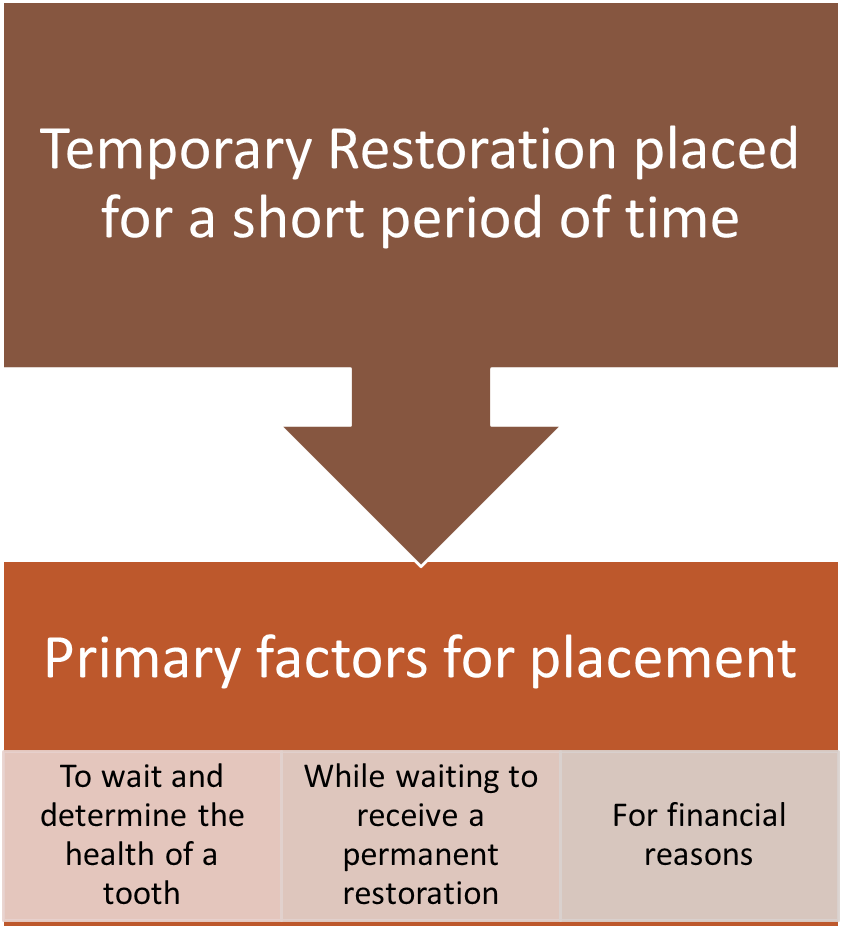
Intermediate Restorations
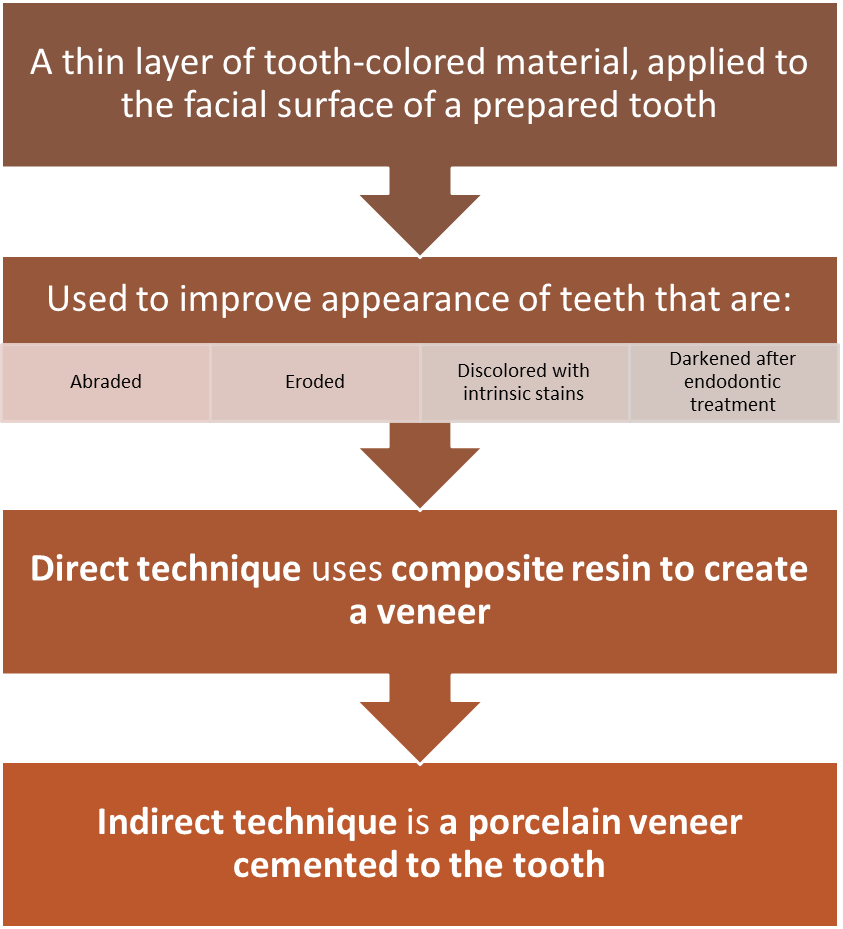
Veneers
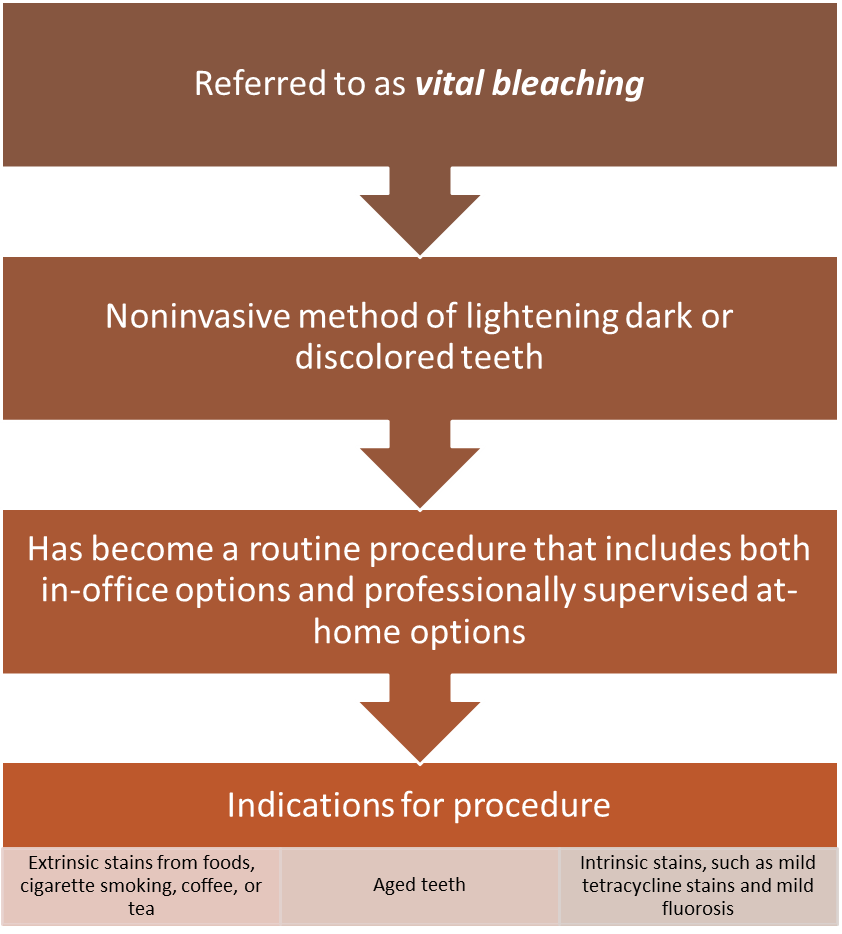
Tooth Whitening
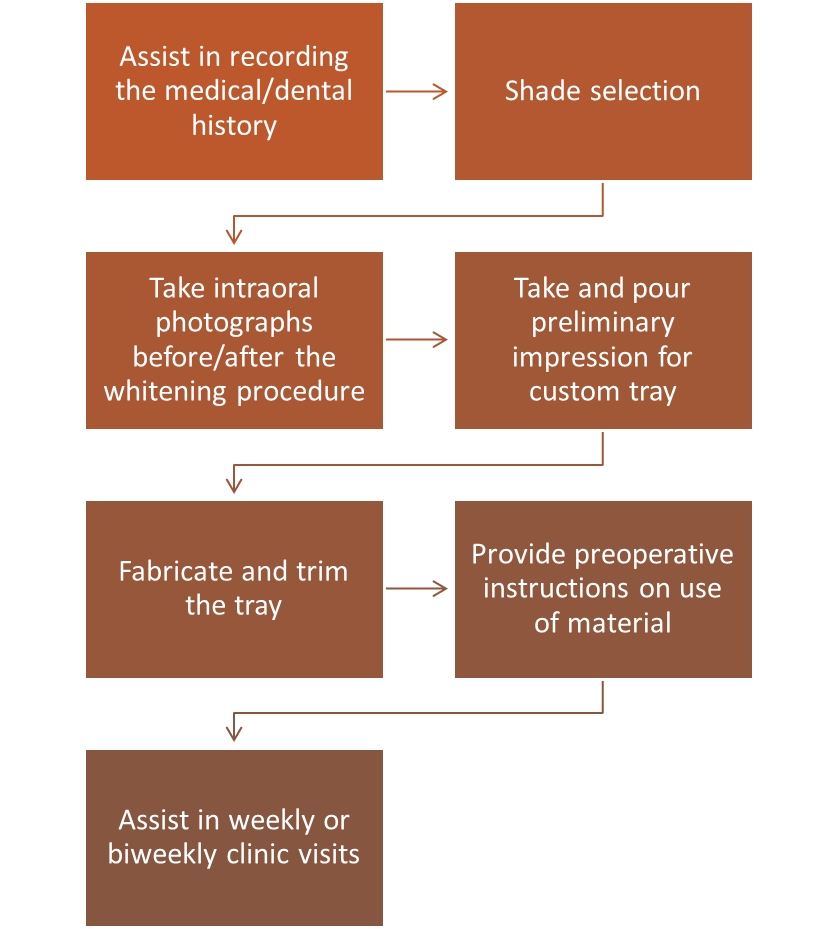
Treatment Options
In-office treatment
At-home treatment
Over-the-counter options
In-Office Treatment

At-Home Treatment

Over-the-Counter Options

Dental Assistant’s Role in Tooth Whitening
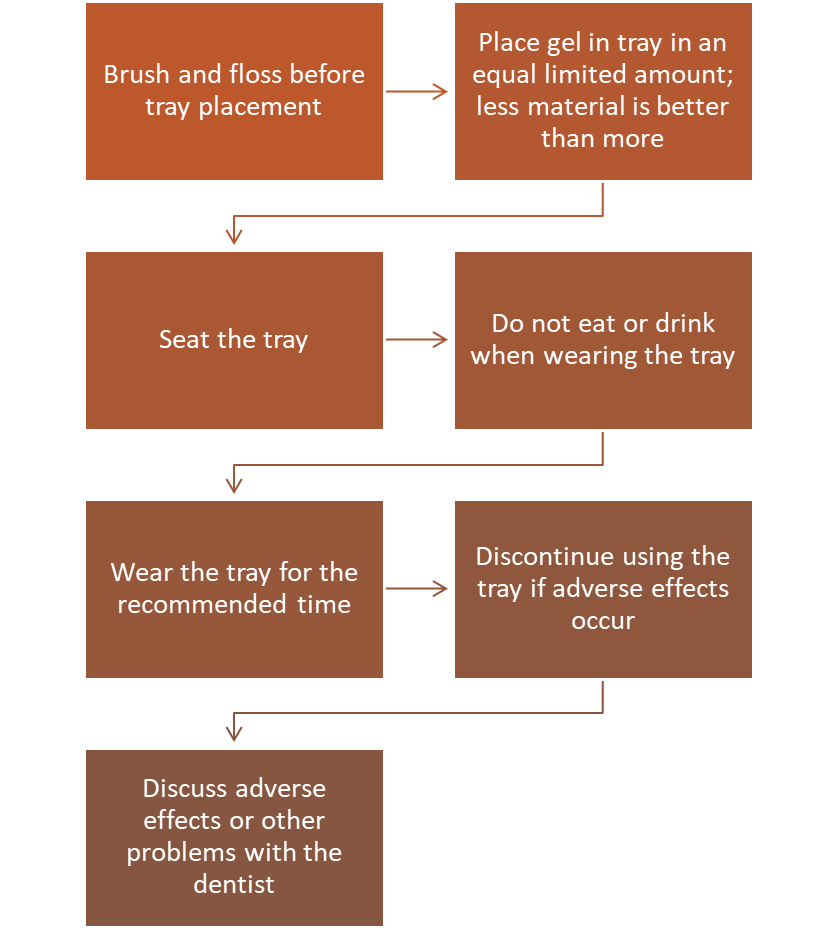
Patient Instructions in Tooth Whitening
Abuse of Whitening Products
With at-home and over-the-counter whitening products, the patient may have greater potential for abuse
A patient will abuse a whitening product by
1.) not following directions
2.) by overusing it to achieve whiter teeth
Adverse Effects of Tooth Whitening

Veneer
a thin layer of composite resin or porcelain that is bonded or cemented to a prepared facial surface for an aesthetic appearance
diastema
a gap or space between two adjacent teeth, often seen in maxillary central incisors
Which classification involves the incisal and interproximal surface of an anterior tooth?
Class IV (4)
Direct veneers are made of what material?
composite resin
What is the active ingredient in tooth whitening products?
Hydrogen peroxide
What does the inital cavity preparation include?
convenience form
outline and resistance form
retention form
In which teeth are Class II restorations found?
premolars/molars
What is the final step in a cavity preparation?
placing a desensitizing or lining agent
During a Class III or IV restoration, the dentist may use a ___ to help reproduce the correct contact between the teeth.
mylar matrix system
A point angle is the junction of ___walls or surfaces that come from different orientation.
three
Which describes why a composite restoration stays in a tooth?
bonding
class I
Cavities in the pits and fissure surfaces of the molars, premolars, and lingual surfaces of anterior teeth
Class II
Cavities in the proximal surfaces of premolars and molars.
Class III
Cavities in the proximal surfaces of anterior teeth (canines and incisors), excluding the incisal edge.
Class IV (4)
cavities on the proximal surfaces of anterior teeth that involve the incisal edge.
Class V
Cavities located on the cervical third of the facial or lingual surfaces of any tooth.
Class VI (6)
Cavities located on the incisal edges of anterior teeth or the cusps of posterior teeth. (later added to the G.V Black Classification of Cavities as a new category in 1956 but W.J Simon.)