Translation + Transcription
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
structure of a dna strand
sugar phosphate backbone and a base
purine
double ringed bases include adenine and guanine
pyrmidines
single-ringed bases that include thymine and cytosine
number of hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine
2
number of hydrogen bonds between guanine and cytosine
3
2 strands of dna run in ? direction
antiparallel
stages of dna replication
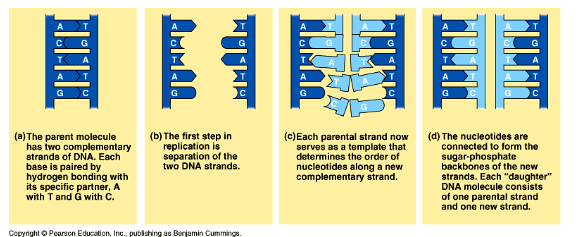
separation of 2 dna strands
each parental strand now serves as a template that determines the order of nucleotides along a new complementary strand
nucleotides are connected to form the sugar oghosphate backones of the new strands. each daighter dna molecule consists of one parental strand and one new strand
topoisomerase
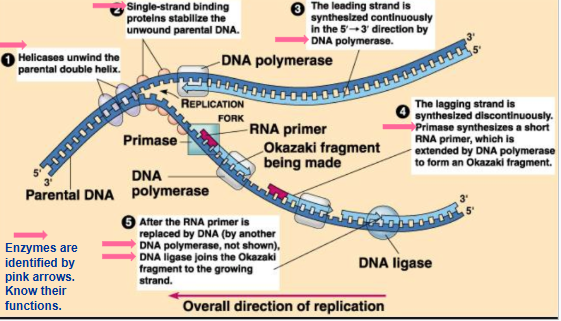
beaks, swiwels, and rejoins the parental DNA ahead of the replication fork, relieving the strain caused by unwinding
helicase
unwinds and separates the aprental dna strands at the replication forks
primase
synthesizes rna primers using the parental dna as a template
single strand binding proteins
stabilize the unwound parental strands
dna ligase
joins okazaki fragments of lagging strand; on leading strand, joining 3’ end of dna that replaces primer to rest of leading strand DNA
origin of replication
a specific DNA sequence where DNA replication begins.
replication fork
a Y-shaped structure formed during DNA replication where the double-stranded DNA helix is separated, allowing for n
5’ end of strand
phosphate group
3’ end
OH side
during replication new nucleotides must be added to an existing ? end of a sugar in DNA
3’
FREE THREE
lagging strand
the strand of DNA that is replicated discontinuously, in short fragments called Okazaki fragments
synthesized away from the replication fork, which is where DNA replication begins
moves from 5’ to 3’
leading strand
the newly synthesized strand that is built continuously in the 5' to 3' direction, moving towards the replication fork
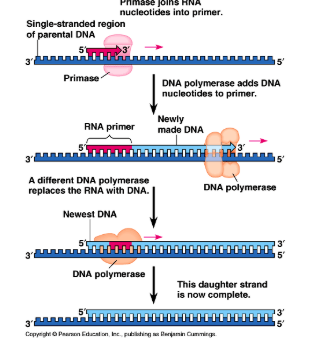
priming dna synthesis with rna
primase joins rna nucleotides into primer
dna polymerase adds dna nucleotides to primer
a different dna polymerase replaces the rna with dna
synthesis of leading and laggin strands during dna replication
? protect the ends of dna
teleomere
transcription
involves turning dna base sequence for a polypeoptide into an rna copy of the sequence
differences in transcription in prokaryotes v eukaryotes
pro:
mrna is made and can immediately be translated in the ribosome
euk:
mrna is made in the nucleus. it undergoes rna processing before leaving the nucleus
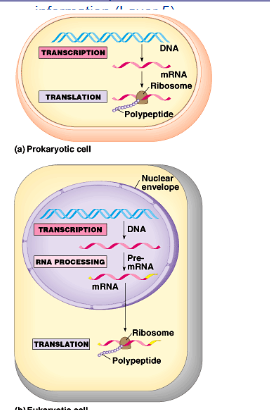
how gene info flows
dna → rna → protein
codon
triplet rna bases
promoter
segment of dna that is that the rna polymerase enzyme binds to. located upstream
rna polymerase
adds new nucleotide bases of rna making an mrnaa molecule in 5’ to 3’ direction
termination
after transcribing the transcription unit, a terminator sequence is reached… the mrna will dissociate from the dna shortly afterward
tata box
he TATA box helps initiate the transcription process by specifying where the RNA polymerase should begin reading the DNA to create an RNA molecule.
stages of transcription
initiation
rna polymerase binds to a specific dna region called a promoter, marking the staert of the gene to be transcribed
elongation
rna polymerase moving along the dna template, synthesizing the complementary rna strand
termination'
occurs when rna polymerase reaches a termination sequence
rna processing
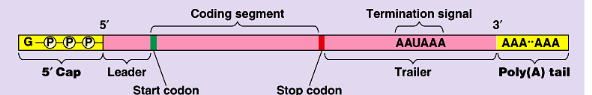
adds a 5’ cap that includes a guanine triphosphate
adds a poly a tail
this is to protect the mrna as it exits the nucleus and aid its exit
rna splicing
introns are removed and exons are spliced together
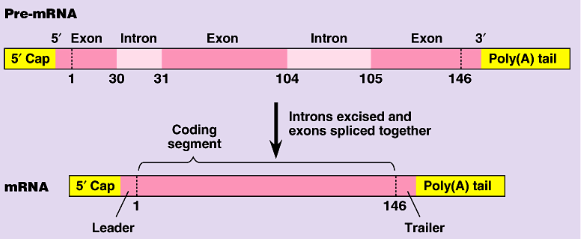
splicosome
a big structure that removes introns and splices exons together
translation
occurs in the cytoplasm in ribosomes
stages of translation
mrna enters and binds to the small subunit of the ribosome
iniation codon (aug) binds to methionine amino acid in the p site
trna will bring in the appropriate amino acids to add in the appropriate position the polypeptide chain
trna
plays catalytic roles and structural roles in ribosomes
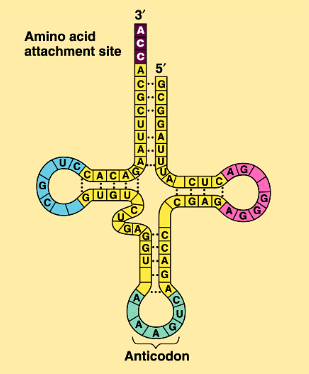
rrna
pl
mrna
carries infromation specifiying amino acid sequences of proteins from dna to ribosomes
point mutation
substitution
deletion
insertion
frameshift mutation
when insertions or deletions of not triplets happen
missense - which codes for the wrong amino acid
nonsense - which codes for an early STOP codon
differences in transcription between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
prokaryotes - no transcription factors or tata box on promoter
eukaryotes - transcription factors, tata box on promoter, mrna editing, 5’ cap and polyA tail, intron removal, spliciing of exons
differences in translation between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
prokaryotes - almost simultaneous transcription and translation
eukaryotes - translation begins after the mrna has been modified and leaves the nucleus