Muscle Mechanics Video
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What are the three types of muscles in the human body?
smooth muscle
skeletal muscle
cardiac muscle
_____ is the most abundant tissue in the body.
Skeletal muscle
There are approximately ____ skeletal muscles in the body, ____ of which are prime movers.
430; 80
The functions of skeletal muscle include:
facilitate movement
protect the structures that are under them
give our bodies structure
There is constant _____ activity of our muscles.
static and dynamic
Different structural appearance of muscles correlate to their…
different functions and roles
Organization of skeletal muscle from inner —> out
muscle
fascicle
muscle fiber (cell)
myofibril
sarcomere
What is muscle composed of?
muscle cells, blood vessels, and nerves
Muscle is covered by ______.
epimysium (a type of connective tissue)
What is the fascicle composed of?
bundles of muscle cells
The fascicle is surrounded by the _____.
perimysium
What are muscle fibers surrounded by?
endomysium
What is a myofibril?
a complex organelle
Sarcomere
the basic contractile unit of muscle
Filaments
protein strands important during muscle contraction
The structure of muscle correlate to its ____.
function and ability
What is a triad made up of?
a T-tubule and two terminal cisternae (of the sarcoplasmic reticulum)
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is critically important to delivering calcium to…
the muscle fibers during contraction.
The primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the musculoskeletal system is ___.
acetylcholine
Titant molecule
the span of connection between the actin and myosin filaments in a sarcomere
think of it as the superglue that holds the thick and thin filaments together
Sliding Filament Theory
explains muscle contraction as the actin (thin) filaments sliding past myosin (thick) filaments, shortening the sarcomere
Sliding Filament Theory Steps
An action potential triggers the release of calcium
calcium binds to troponin
Tropomyosin moves off the binding sites on actin so myosin can bind
myosin heads pull the actin filaments inward
ATP binds to myosin, causing detachment
ATP —> ADP + P to allow the myosin heads to reset for another cycle
What occurs during the resting phase of the sliding filament theory?
little to no calcium is in the myofibril
no tension occurs
there are few cross bridges
What occurs during the excitation-contraction phase of the sliding filament theory?
the sarcomere is stimulated by calcium release
calcium binds to troponin
this causes tropomyosin to move off the active sites in actin
myosin binds to actin and cross bridges form
What occurs during the contraction phase of the sliding filament theory?
ATP binds to myosin
ATP —> ADP + P
What occurs during the recharge phase of the sliding filament theory?
ATP is restored
calcium is replenished
Myosin ATPase is ready
What occurs during the relaxation phase of the sliding filament theory?
motor nerve stimulation stops
calcium refills in the sarcoplasmic reticulum
no cross bridges form
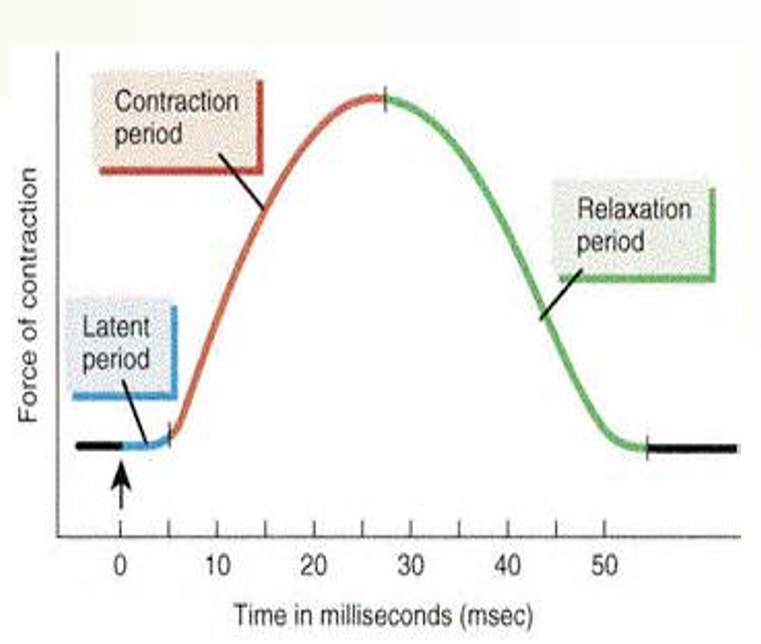
A single stimulus leads to a ____.
muscle twitch
There are three parts of a muscle twitch. What are they?
latent period
contraction period
relaxation period
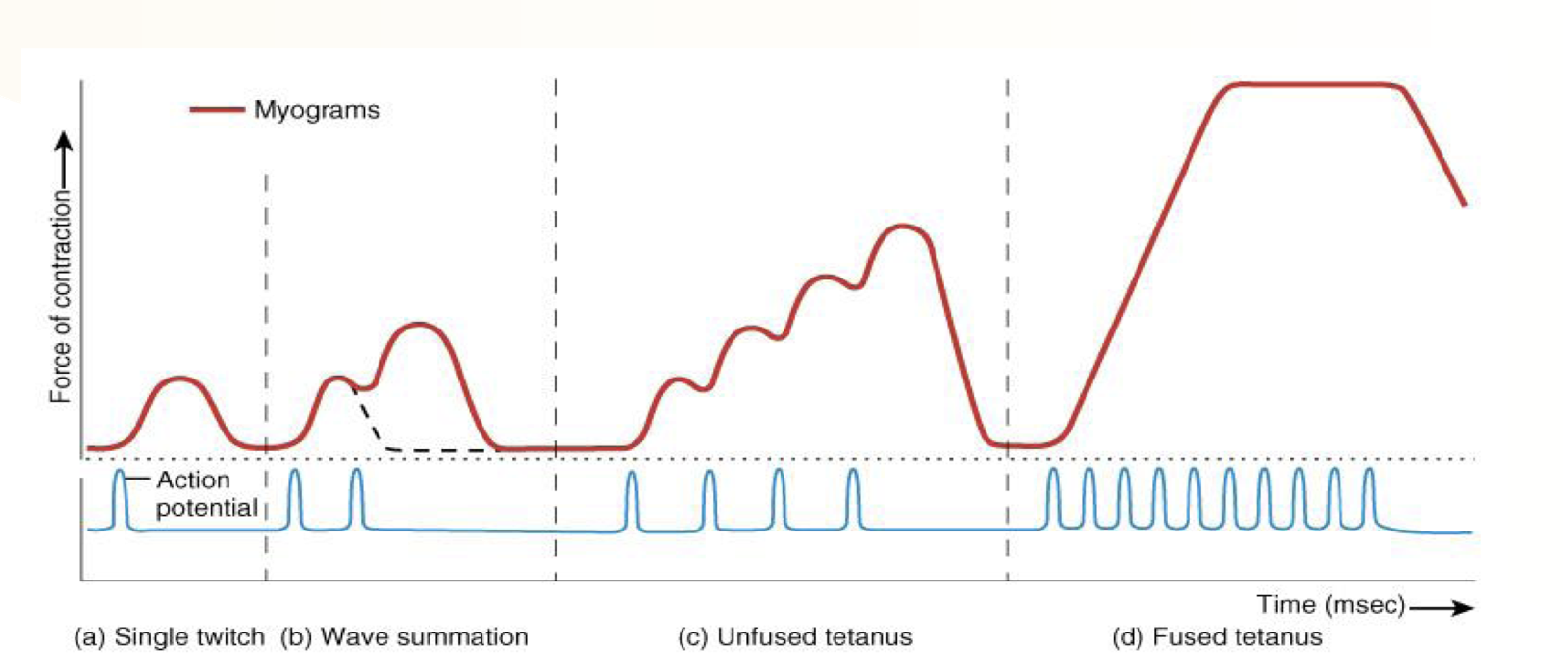
What is going on in parts a-d of this picture?
a. Single twitch: a normal action potential occurs
b. Wave summation: a second action potential is generated near the end of the first, leading to increased force and time of contraction
c. Unfused tetanus: more consecutive action potentials are generated, leading to more force and increased time of contraction
d. Fused tetanus: a smooth even contraction occurs due to rapid generation of multiple action potentials, leading to a plateau force that eventually declines
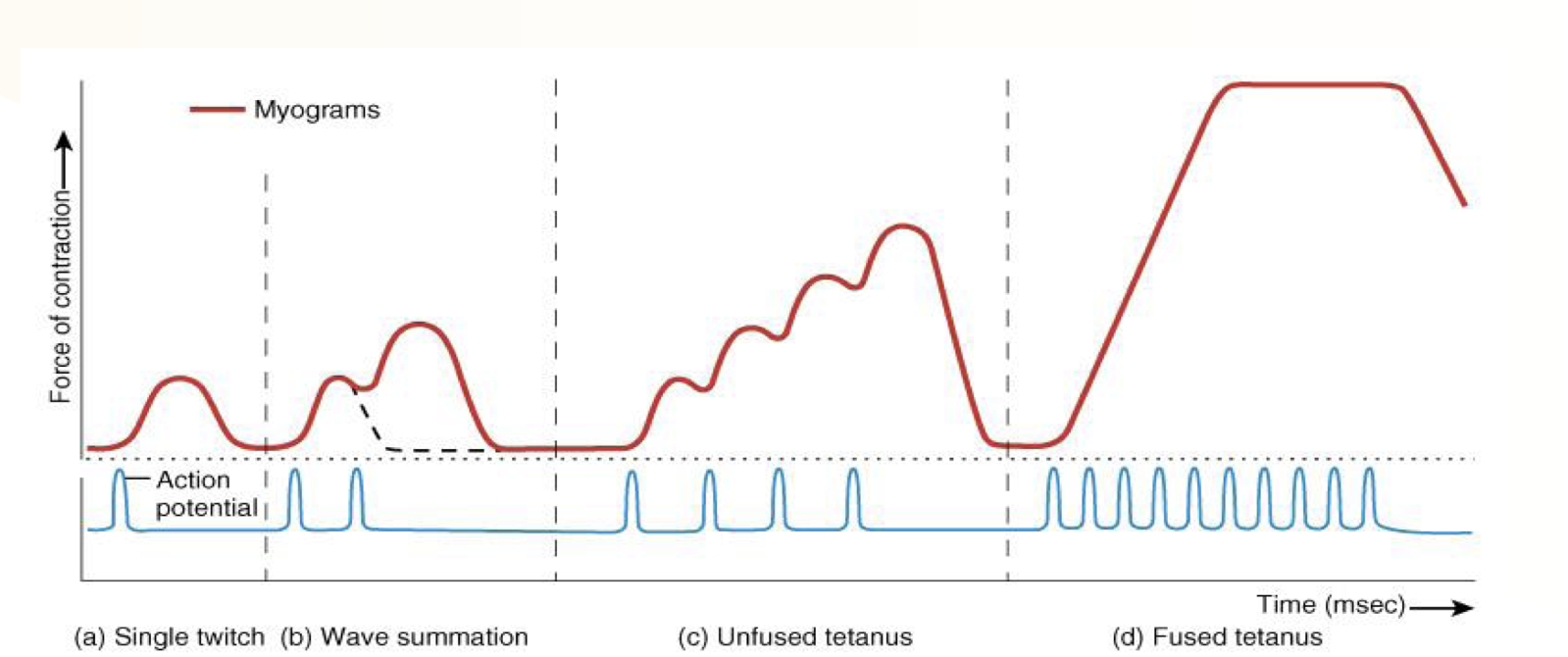
_____ is the normal muscle function.
Fused tetanus
What are the takeaways from the length-tension relationship?
max tension occurs at 100% sarcomere length, meaning that the optimal position for muscle to generate force is from resting length or just beyond
At 75% sarcomere length: the cross bridges are formed and the muscle is in too short of a position to generate optimal force
At 170% sarcomere length: no cross bridges are formed and the muscle is too long to generate forces
____ length maximizes the ability of muscle to contract when stimulated.
Resting
Max tension is generated at muscle ____
resting length
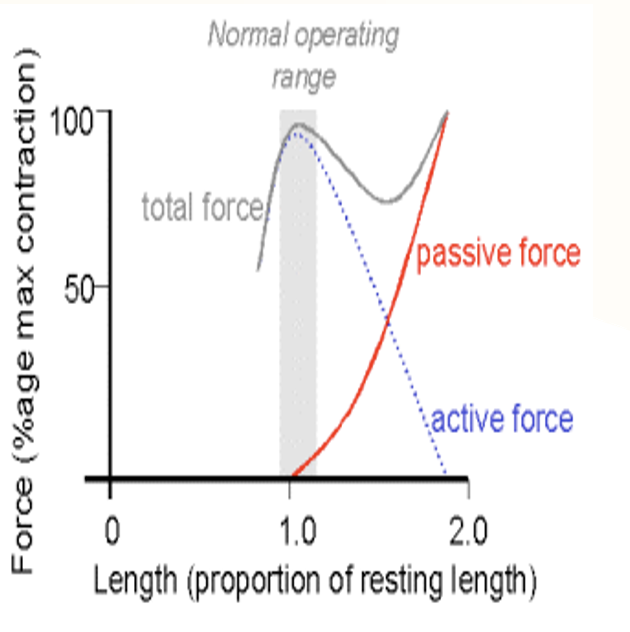
Beyond resting length, ____ components rise and ____ components fall.
passive; active
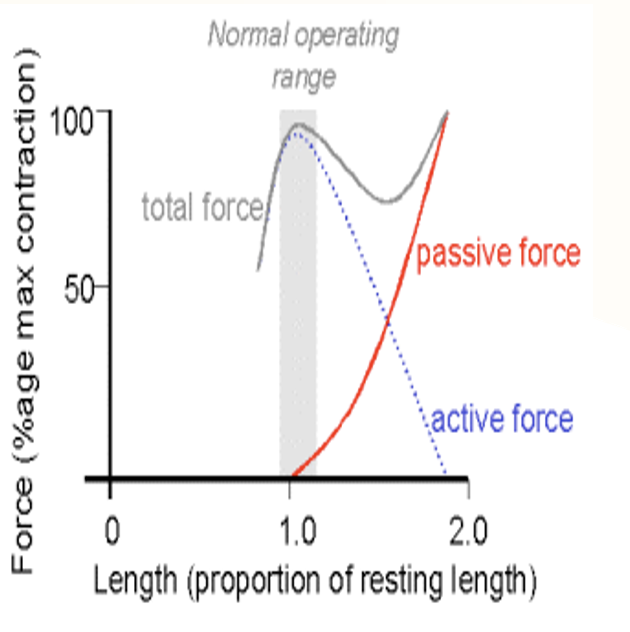
Active Tension
allows for the greatest number of cross bridges to form and greatest potential of active force