Unit 2: Energy, Enzymes & Digestion
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Exergonic Reaction
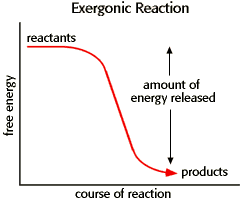
A chemical reaction which releases energy
Endergonic
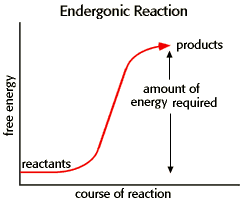
A chemical reaction that requires an input of energy
Enzyme
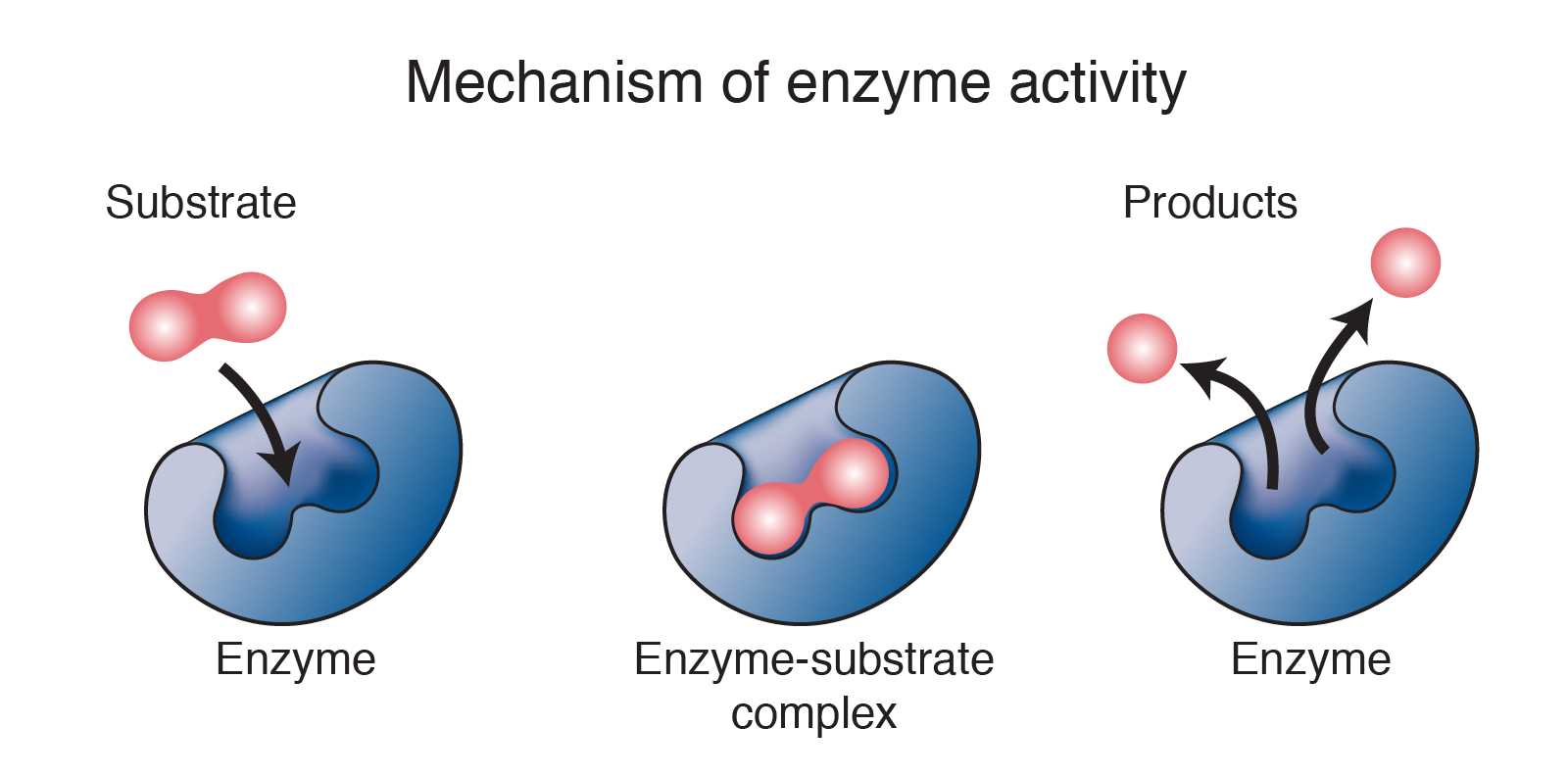
A molecule that can speed up chemical reaction by lowering the amount of energy needed
Substrate →specific molecule enzyme acts on
Active site →Area on surface that an enzyme acts
Inhibitor
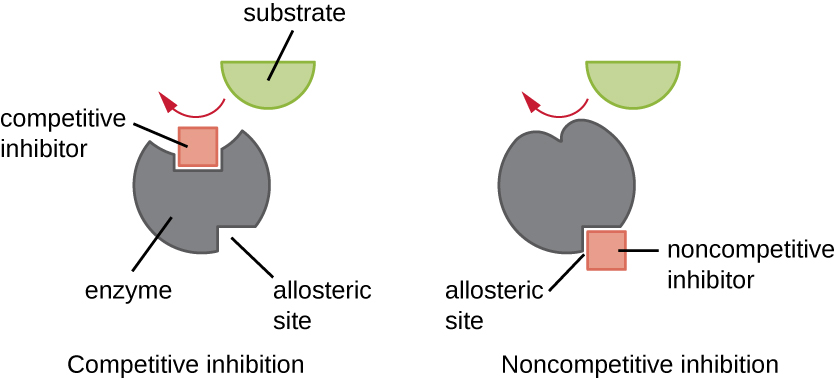
A molecule that can interfere with an enzymes ability to bind to its molecule
Competitive inhibitor - binds to portion of active cite
Noncompetitive inhibitor - Bind to another portion of the enzyme and cause shape change that alters the active site
Digestive tract
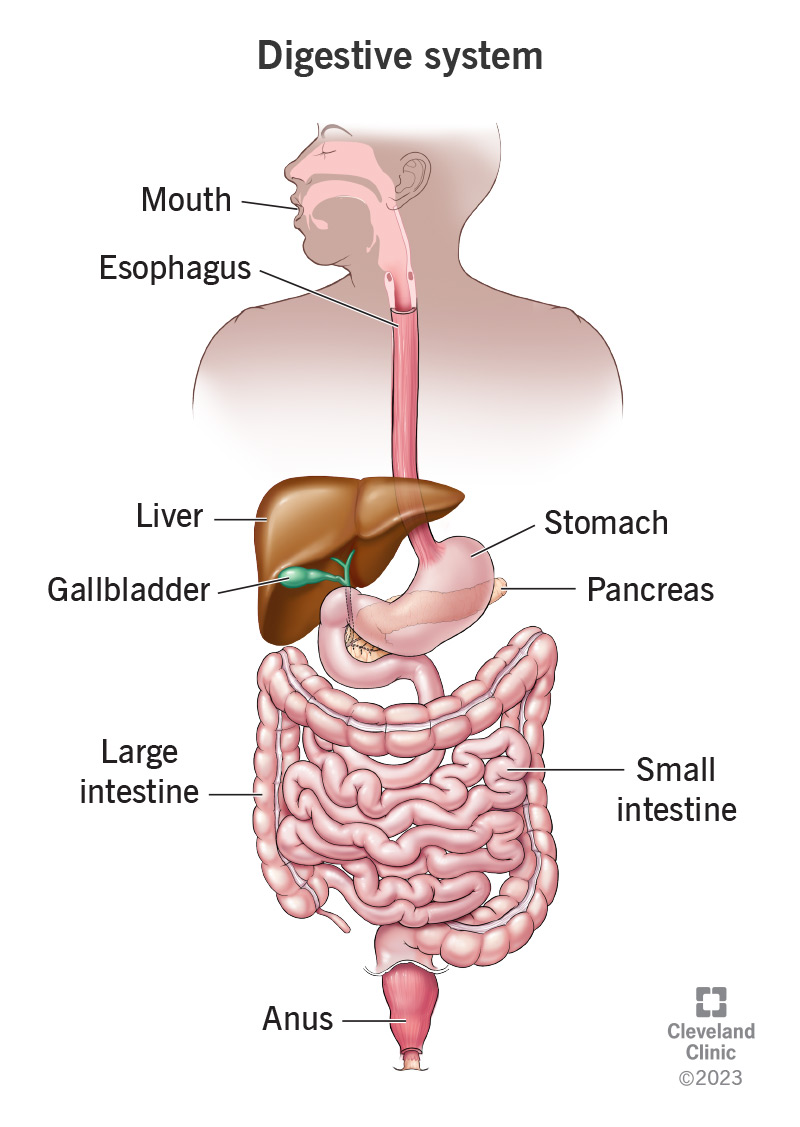
Mouth → Esophagus → Stomach →Gallbladder →Small intestine→Large Intestine →Rectum →Anus
Mouth
Mechanical →Chewing and swallowing
Chemical →amylase and lipase breaking down carbs, lipids
Stomach
Turns food into chyme and transports to small intestine
Mechanical →turns and breaks food down
Chemical digestion → Hcl+Pepsin breaks down proteins
Lipase breaks down lipids
High PH levels are optimal conditions for pepsin and helps breakdown food
Small intestine
Breaks food into smaller molecules
Carbs →amylase, maltose, sucratose, lactace
Lipids → lipase, bile
Proteins →peptides
Nucleotide → Nuclease
Villi outlining the surface area absorbs nutrients, water, and electrolytes
Large intestine
Absorbs water, vitamins, electrolytes
Rectum + Anus
Waste is stored until eliminated out of body
Coenzyme
Changes the shape of active sites to help substrates fit e
EX: drugs
Gallbladder
Stores bile
Liver
Makes bile
Pancreas
Makes amylase, lipase, nuclease
Length of digestive tract
Carnivores have a shorter digestive tract than herbivores and omnivores