RMHS - lecture 1 - Introduction to research perspectives, research objective and research questions
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
name a few of the current complex health issues
climate crisis
opioid crisis
access to medicine
anti-microbial resistance
food insecurity / food deserts
shortage of public health workers
public trust (social media misinformation)
data modernization and privacy
name 2 misclassification
differential → The probability of misclassification is different for different groups
non-differential → The probability of being misclassified is the same for all groups.
external versus internal objective
external → societal benefit, why is this research being done
e.g. To contribute to a societal dialogue between the public and nanotechnology developers.
internal → how will you do this, what will the research produce / study
e.g. To explore and analyze the attitudes, perceptions, and concerns of the general public toward nanotechnology.
what makes current issues complex
globalization
fuzzy, instead of rigid boundaries
internalized rules drive action
agents (people) within the system change
systems are embedded in other systems and co-evolve
what is needed to solve these complex issues
a range of methods,
methodologies,
theoretical perspectives and
epistemologies.
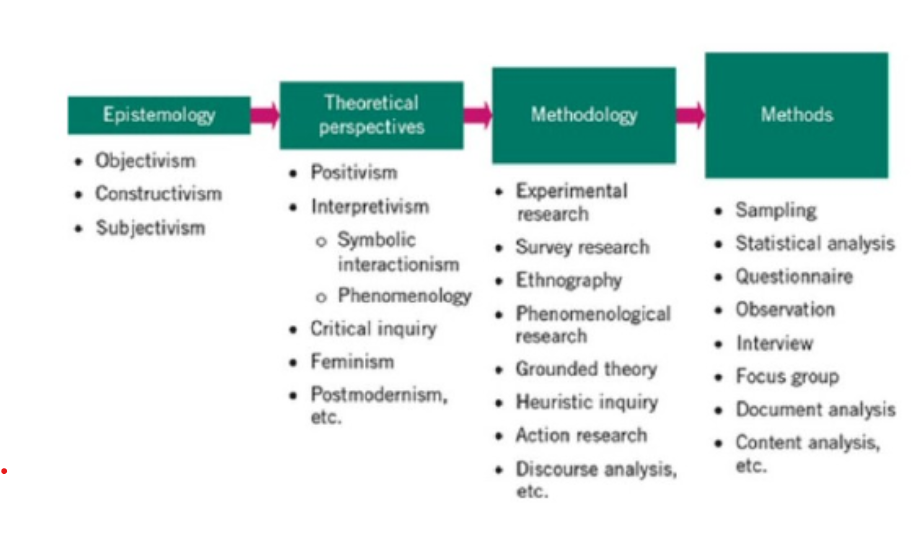
explain the research paradigm framework
how theoretical perspectives connect to methodology and methods.
epistemology → how we know what we know
theoretical perspectives → the philosophical stance (the lens through which researchers view the world)
methodology → the overall research design / strategy
methods → specific techniques / procedures used to collect + analyze data
what is epistemology
It is the study of knowledge.
The study of what constitutes valid knowledge.
theory of knowledge
everything has one (developed around 5 years old) starts by the question how do you know certain things?
why is epistemology important?
a knowledge of research philosophy will help the researcher to recognize which designs will work (for a given set of objectives) and which will not.
it can help clarify issues of research design (but also misunderstanding / tensions) especially in interdisciplinary teams.
important to know that an individuals theory of knowledge and positionality influence the way you set up a study.
objectivism
there is only 1 reality
reality exists independently of consciousness.
research is about discovering this objective truth. researchers should strive not to include their own feelings and values
connected to positivism; there is only one reality / truth. reality can be measured. knowledge can be formulated into laws.
this view has been challenged → post positivism; we can only approximate the truth.
constructivism
there is not one truth
truth and meaning are created by the subject’s interactions within the world.
knowledge is constructed not discovered.
connected to interpretivism; multiple contradictory but equally valid accounts of the world can exist. knowledge is contextual.
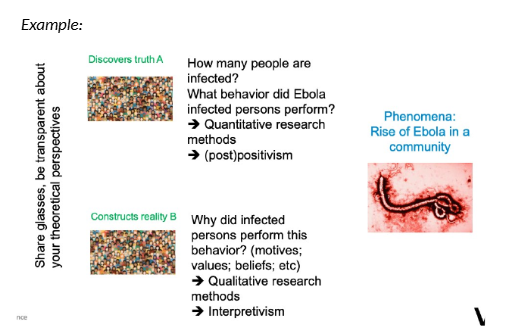
example objectivism versus constructivism
subjectivism
knowledge and truth depend on individual perspectives, feelings and/or beliefs.
meaning is imposed by the subject (researcher) on the object.
Postmodernism can be taken as an example of a theoretical perspective linked to subjectivism.
Postmodernism emphasis multiplicity, ambiguity, ambivalence and fragmentation.
critical inquiry
a way of approaching questions, problems that emphasize careful questioning, evidence, reasoning and reflection.
you understand and question values and assumptions. and want to bring a change.
feminism
dynamic field that aims to address gender relations, power dynamics and socia justice. feminist theories take the view that what a person knows is largely based on their social position.
epistemic injustice
injustice related to knowledge.
exclusion, silencing, misrepresentation, undervaluing because of prejudice or power imbalance.
global health / health sciences is a field where there is still the tendency to disregard local, disabled, children and indigenous knowledge, and refuses to learn from people often deemed to be lesser.
gaslighting is epistemic injustice on an individual level.
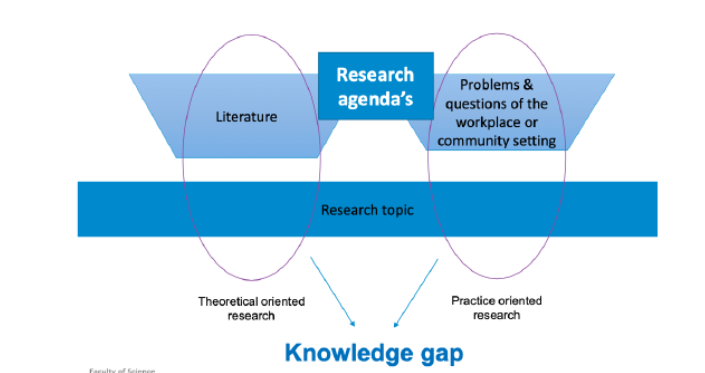
how to find a good research topic
literature + problems and questions of the workplace or community setting leads to the research topic
also really need the practical and theoretical relevance.
however, you need to really identify the knowledge gap.
how to get a research topic
own previous research
experiences from fieldwork (e.g. patients dying from complications whilst doing fieldwork abroad).
(money) donor informed (e.g. sometimes a donor identifies that there is a region in the world where little research is being done).
patient / patient organization informed
interviewing experts and develop a new research agenda
things in research to avoid
unethical
too big
too trivial
lack in resources, materials and people
dependent on the completion of a other project
how to go from topic to the objective and reseach question
What is the broad area of research
What is known/done about it
What is not known/done about it (Why is this a problem)
Therefore, the aim of this study is ..... (I am going to make known about it) = Objective
Research questions (plus sometimes hypotheses)
→ Format for an introduction
external versus internal objective
External objective = contribution of your research project to solution of the problem / what results can be expected.
Internal objective = the way in which this will be done / the insights, information, knowledge needed = very similar to your research question.
formulate the research objective
one or more research questions
tight connection between literature / theories and the research questions
deining the investigations
establish boundaries
concise and unambiguous