Exam III Practice Exam Questions
2.5(2)
2.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
2
New cards
NAD+
During cellular respiration, what molecule collects the __***MAJORITY***__ \n of the electrons from the food that we eat?
3
New cards
the reduction of NAD+ and FAD.
As a forensic pathologist, you have just completed an autopsy of a poisoning victim. After a thorough examination, you conclude that the victim died of cyanide poisoning. You know that cyanide binds to the cytochrome oxidase complex, and therefore list the official cause of death as suffocation due to cyanide exposure. However, a more technical explanation would be that all of the following aspects of cellular respiration were inhibited except…
4
New cards
Two
How many pyruvate molecules are generated during the oxidation of one glucose molecule during cellular respiration?
5
New cards
L → N
Using a series of arrows, draw the branched metabolic reaction pathway described by the following statements. \n Then answer the question at the end. Use red arrows and minus signs to indicate inhibition. \n L can form either M or N. \n M can form O. \n O can form either P or R. \n P can form Q. \n R can form S. \n O inhibits the reaction of L to form M. \n Q inhibits the reaction of O to form P. \n S inhibits the reaction of O to form R. \n \n Which reaction would prevail if both Q and S were present in the cell at high concentrations?
6
New cards
Competitive Inhibitors
Vioxx and other prescription non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are potent inhibitors of the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzyme. High substrate concentrations reduce the efficacy of inhibition by these drugs. These drugs are…
7
New cards
Competitive Inhibitor
Methyl alcohol, also known as wood alcohol, is a common solvent and paint remover. It is poisonous if accidentally swallowed. The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase in the liver converts methyl alcohol into formaldehyde, which then gets converted into a toxic product. Grain alcohol, ethyl alcohol, is also acted upon by alcohol dehydrogenase. One antidote for methyl alcohol poisoning is to make a person drink a lot of ethyl alcohol. This blocks the active site of the enzyme so that it can't bind to and break down the methyl alcohol. In this capacity, the ethyl alcohol is acting as a/an:
8
New cards
Competitive Inhibition
Sulfa antibiotics damage bacteria by affecting a certain bacterial enzyme. The sulfa antibiotic looks similar to a substrate normally required by the bacterial cells to live. The sulfa antibiotic occupies the active site of the required enzyme and blocks entry of its normal substrate. This prevents the bacteria from making nucleotides that are required for their reproduction and survival. Based on this information, the action of sulfa antibiotics is an example of:
9
New cards
An acidic environment causes bacterial enzymes to fail or work less efficiently.
Preservatives such as citric acid are added to foods to interfere with bacterial growth. This creates an acidic pH in the food. Why does this affect the bacteria that are present?
10
New cards
Is a competitive inhibitor
Triclosan is a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent used in many household products. It is structurally similar to polychlorobiphenylol, a substrate that binds to the active site of the enzyme sulfotransferase. Based on these facts, you can conclude that triclosan most likely:
11
New cards
All of these choices are correct.
Which one of the following can contribute to a protein’s tertiary structure?
a) Ionic bonding
b) van der Waal’s forces
c) Covalent bonding
d) Hydrogen bonding
e) All of these choices are correct.
a) Ionic bonding
b) van der Waal’s forces
c) Covalent bonding
d) Hydrogen bonding
e) All of these choices are correct.
12
New cards
All statements are true.
Which statement is true concerning the structure of proteins?
a) The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids.
b) Alpha helices and beta sheets are examples of secondary structure.
c) Side chains (R-groups) of amino acids can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic.
d) Proteins made of two or more polypeptide chains have quaternary structure.
e) All statements are true.
a) The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids.
b) Alpha helices and beta sheets are examples of secondary structure.
c) Side chains (R-groups) of amino acids can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic.
d) Proteins made of two or more polypeptide chains have quaternary structure.
e) All statements are true.
13
New cards
No; whereas the non-covalent bonds determine the shape of a protein, the peptide bonds are required to hold the amino acids together.
The function of a protein is dependent upon the shape into which the chain of amino acids folds. Many noncovalent interactions are responsible for maintaining the protein’s shape. Assume you have isolated a protein from an organism in its proper shape, and you have treated it with an enzyme that selectively breaks only the peptide bonds in the proteins. Would the protein retain its shape under these conditions?
14
New cards
The ETC cannot establish a proton gradient to drive chemiosmotic production of ATP.
A newly developed insecticide compound steals high-energy electrons from FADH2 and NADH before they can bind to the electron transport chain. Why does this kill insects?
15
New cards
an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized
What kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis?
16
New cards
ATP binds at the allosteric regulatory site of the enzyme that combines acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate and slows the citric acid cycle.
What would be the effect of abundant ATP on the citric acid cycle?
17
New cards
directly enter the citric acid cycle
Fatty acids usually have an even number of carbons in their structures. They are catabolized by a process called beta-oxidation. The end products of the metabolic pathway are acetyl groups \n of acetyl-CoA molecules. These acetyl groups ________.
18
New cards
binds to a site other than the active site, changing the shape of the active site and decreasing the binding of substrate
When a product binds to an allosteric site on the enzyme to inhibit its reaction, it does what?
19
New cards
cytosol/cytoplasm
A drug is designed to make the glycolytic pathway more productive. What part of the cell would the drug need to be delivered to for it to directly affect this pathway?
20
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
Suppose a drug were added to mitochondria that allowed protons to freely pass through the inner membrane. Which of the following mitochondrial activities would most likely be inhibited?
21
New cards
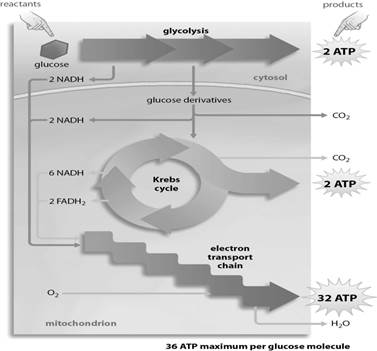
glycolysis and the Krebs cycle
Which stage or stages of aerobic respiration require both NAD+ and ADP as reactants?
22
New cards
ATP, NADH, Pyruvic Acid
The three main products of glycolysis are:
23
New cards
two
How many turns of the Krebs cycle are needed to completely break down one molecule of glucose?
24
New cards
Mitochondria
Oxygen is reduced to water in the cell's:
25
New cards
\n three per NADH and two per FADH2
During electron transport, how many ATP molecules are produced per NADH molecule and FADH2 molecule?
26
New cards
H+ ions flowing across the mitochondrial inner membrane
What is the energy source used to drive ATP synthase to produce ATP?
27
New cards
When we break down our food, the reactions are not 100 percent efficient; therefore, energy is lost as heat.
When we metabolize our food, we produce heat that helps to keep us warm. Which of the following best describes why?
28
New cards
the active site is saturated with substrate
In the graph reaction rate vs substrate concentration, the reason that the curve reaches a plateau, and does not increase any further at high substrate concentration is that:
29
New cards
is a misconception, as energy is transformed, not created, during photosynthesis
“Plants conduct photosynthesis to create energy.” This statement _______.
30
New cards
red and blue
Suppose that you are experimenting with different types of lighting for your indoor green plants. What colors of light will be most effective?
31
New cards
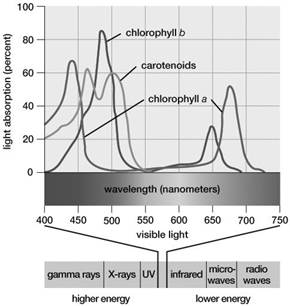
450-500 nanometers
Based on this graph, which wavelengths of light would result in the highest rates of ATP production during photosynthesis?
32
New cards
Red
If you see a red leaf, what color(s) of light in the visible light spectrum is/are being reflected?
33
New cards
Thylakoid
Chlorophyll is found in which part of the plant cell?
34
New cards
Sunlight excites electrons in chlorophyll to a higher energy level.
What function does sunlight perform in photosynthesis?
35
New cards
NADPH
The electron carrier in photosynthesis that will donate electrons to CO2 so that it can be fixed into sugars is:
36
New cards
Cytoplasm.
Glycolysis occurs in the cell's:
37
New cards
Glucose.
Before starch can be used for cellular respiration, it must be broken down into:
38
New cards
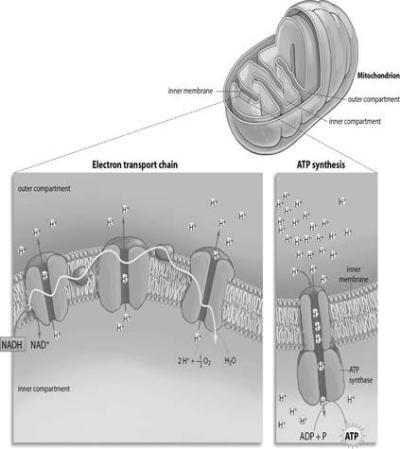
Hydrogen ions are pumped from the inner compartment of the mitochondrion to the outer compartment of the mitochondrion.
As electrons move through the electron transport chain, which of the following occurs?
39
New cards
Three
How many NADH molecules are created during one turn of the Krebs cycle? (Assume the Krebs cycle begins with one acetyl CoA molecule.)
40
New cards
pyruvic acid.
The end products that come out of the Krebs cycle include all of the following *except*:
a) NADH.
b) pyruvic acid.
c) FADH2.
d) CO2.
e) ATP.
a) NADH.
b) pyruvic acid.
c) FADH2.
d) CO2.
e) ATP.
41
New cards
acetyl CoA
Which of the following molecules is produced in the intermediate step between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle?
a) ATP
b) oxaloacetate
c) pyruvic acid
d) acetyl CoA
e) citric acid
a) ATP
b) oxaloacetate
c) pyruvic acid
d) acetyl CoA
e) citric acid
42
New cards
glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport
When glucose is the fuel source, what is the correct sequence of stages in cellular respiration?
43
New cards
in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
The enzymes used by the electron transport chain are located:
44
New cards
True
True or False?
The shortest wavelength of light is the ultraviolet ray, which is the highest in energy.
The shortest wavelength of light is the ultraviolet ray, which is the highest in energy.
45
New cards
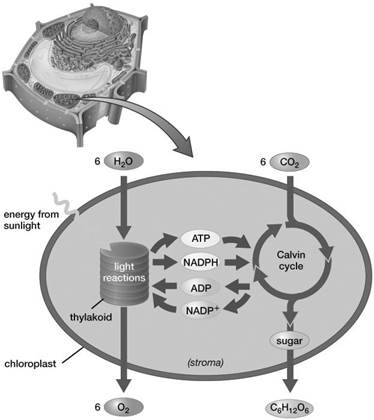
H2O
Based on the information provided in this figure, where does the oxygen gas produced by a leaf come from?