Digital Merchandise Exam 1
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Digital
"the convergence of multiple technology innovations enabled by connectivity"
Promotion
"any communication used to inform, persuade, and/or remind people about an organization's or individual's goods, services, image, ideas, community involvement, or impact on society"
Merchandising
the activity of promoting the sale of goods, especially by their presentation in retail outlets
Traditional Media-- Media Buying
The simple act of the transaction between media owners and companies
•Ex: Newspapers
Mass Media -- The stage of planning
The practice of determining how, when, and where to deliver a message to an audience
•Ex: Radio & Television
Passive Media consumption
Customers absorbed the given messages
Push Media
Where people passively consume content
•Newspaper, magazines, TV, direct emails
•ads/promotional offers/emails filling inboxes with content
Pull media
Where people actively engage with content
•Web surfing, streaming videos, product search, connecting on social media
•Content that people feel is specifically targeted for them.
•People find themselves "pulled" to a brand's website and products.
Customer dialogue
•Businesses have to learn how to have a meaningful conversation with their customers, through diverse (digital) media
Role of digital merchandiser
•to initiate the conversations
•to figure when and where the conversations are taking place and become a part of it.
Digital Merchandising
All about driving customer conversion and satisfaction across all digital touchpoints
The layers of business challenges
Societal (pre vs post pandemic)
Economic
Technological (Ex: GenAI)
Political (ex: tariffs)
Digital disruption
the effects of digital technologies and business models on a company's current value proposition and its resulting market position
Digital Transformation
1. Rise of Innovation---> Rise of innovative digital technology
2. Digital disruption --> Turbulences caused by emerging digital tech and business models
3. Digital Transformation--> A process where people and tech collaborate to transform existing processes/services or create new ones
“You don’t need a digital strategy. You need ........
a better strategy, enabled by digital ”
Media entertainment as a digital disruptor and its transformation
The creation of a subscription business model to stream shows, movies, etc
Digital Vortex
The inevitable movement of industries toward a "digital center" in which business models, offerings, and value chains are digitized to the maximum extent possible.
-Close to the center: significant impact by digital transformation + Data intensive
Farther out: Slower change + asset-intensive
Digitalization
•Standardizing business processes
•An operational necessity
Digital!
•A host of powerful and accessible technologies (social, mobile, cloud, analytics, IoT, cognitive computing, etc.)
- not advanced digitalization
"becoming digital"
Transformation of a company - rethinking a company's value proposition
Digital Intelligence
•The set of key capabilities needed to succeed in a world driven by technology and changing at breakneck speeds
•Think of digital intelligence as a way of working, not just as knowledge of any one technology
Digital Mindset
the ability to see and make the most of the opportunities that digital change offers.
•An excitement to continuously learn
•A desire to make decisions and adopt technology based on data about customer needs
•A habit of staying knowledgeable about emerging technologies
Metcalfes Law
•A measure of network effects
- The value of a communication network is proportional to the square of the number of its users
Participation "Tipping Point"
•After a certain number of people get on to a platform, it starts to become more attractive
•"Network effects" lead to participation "tipping points"
Milgram's Small World Hypothesis
"We’re all connected by just “six degrees”
•People in their personal relationships were tightly enmeshed in networks.
•Ideas, messages, brands and value can be transmitted very quickly through very densely meshed networks
Power Law Distribution/90-9-1 Rule
•“90% of people are observers who read or observe only, 9% of members are contributors who edit or respond, and 1% of people actively create new content.”
Customer network strategies
Access--> Seeking immediate, simple and fast access to data
Engage--> Seeking engaging content that is relevant
Customize--> Seeking varied, customized experiences that are relevant
connect--> Seeking digital experiences that allow communication and expression
collaborate--> Seeking to work together towards a shared goal
Survey
systematic gathering of information from respondents for the purpose of understanding some aspects of the behavior of the population of interest
•Through survey, we want to ...
•Understand who the consumer is
•Know what their behavior is
•Gather numerical/quantifiable data for insights to make better decisions
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
A market research metric that takes the form of a single survey question asking respondents to rate the likelihood that they would recommend a company, product, or a service to a friend or colleague
NPS Formula
Promoters - detractors = NPS % (EX: 2/13- 1/13)= 7.69%
13 -- total number of participants
-- > 2 + 1 à the number for each Detractors and promoters
•Questionnaire
a research instrument containing questions and other types of measurement items designed to solicit information appropriate to data analysis
Analyze questionnaire data to..
•Develop products
•Improve retail environment
•Assist customers with ease of access
•Innovate customers' experience
Questionnaire design process
1. Determine research objectives
2. Identify research questions
3. Determine a data collection method
4.Determine question types
5.Check question writing techniques
6. Establish questionnaire flow and layout
7. Evaluate the questionnaire
Pre-Test
testing a questionnaire (or any research component) with a small number of people before conducting the main survey to test reliability and validity of the questionnaire
•Pilot study
examining the entire survey process with a small set of a study sample that you will include in the main study.
•Small-scale version or trial-run of the research
What is analytics?
•Using mathematical models and algorithms that simplify a company's view of its customer base and the behavior of individual customers
•Analytics vs. Analysis
•Number-oriented vs. not
digital analytics
the process of collecting, measuring, and analyzing data from digital sources such as websites or mobile apps
Analytics -- an accurate description of customers
•Classification
•Estimation
•Clustering
•Prediction
Predictive Analytics
Making predictions about future outcomes.
•Forward-looking
•uses historical data combined with statistical modeling, data mining techniques, and machine learning.
4 types of predictive analytics
1.Product-Affinity Model
2.Segment-Migration Model
3.Response Model
4.Attrition Model
Product-Affinity Model
"What are customers purchasing in one basket?
Segment-Migration Model
"who will be more likely to behave in a certain way?"
Market segmentation
The process of dividing a broad consumer market consisting of existing and potential customers into sub-groups of consumers based on shared characteristics.
Response Model
"who will respond to our promotional campaign?"
Attrition Model
who wants to leave our company
Value of Retail Analytics
improve sales productivity; reduce marketing costs
Conversion
When a consumer completes a desired goal, such as making a purchase, filling a form, signing up, ... .
Conversion rate
the % of total visitors that convert
Blurred Boundaries (Lee and Cho) (2020)
"... The rapid change in the media landscape brought about by digital transformation has blurred the boundaries between and domains of diverse advertising media ... a holistic view of business strategy and new ways of thinking to transform businesses to upgrade the strategic mindset
..."
Customer Journey
: The path of interactions a customer has with a brand, product and/or services
Customer Journey Map
A visual storyline of every experience a customer has with a service, brand, or product across various mediums.
Components in Customer Journey Map
Touchpoints
Customer actions
pain points
opportunities
Touchpoints
A contact point or interaction between a customer and a brand
•Customer actions
Actions a customer takes to achieve objective
•Pain points
: Issues/problems that a customer faces in interacting with a brand
Opportunities
: Ways for the brand to improve overall experience
2 types of customer journey maps
Retrospective maps
Prospective maps
Retrospective maps
where you map out how customers currently do stuff (typically based on research findings)
•Prospective Maps
where you map how you expect users to behave with a new product idea or future events
phases of the customer journey
What is the customer's need/awareness (objective)?
What product research has been done?
What did or does the customer take into consideration?
What is the purchase decision?
What is the support for renewal/future purchase?
First Moment of Truth (FMOT)
when consumers stand in front of store shelf and decide whether to buy a P&G brand, or a competing product"
(Shelf)
Second Moment of Truth (SMOT)
"when consumers use a product and it delivers a delightful & memorable experience - or not and then decides whether to buy it again"
(Experience)
Zero Moment of Truth (ZMOT)
the moment in the consumer's decision-making process when a consumer researches a product and all options prior to purchase
Moment of Truth
When a customer interacts with a process and forms an opinion (positive, negative, or indifferent) about that process.
McKinsey's Consumer Decision Journey
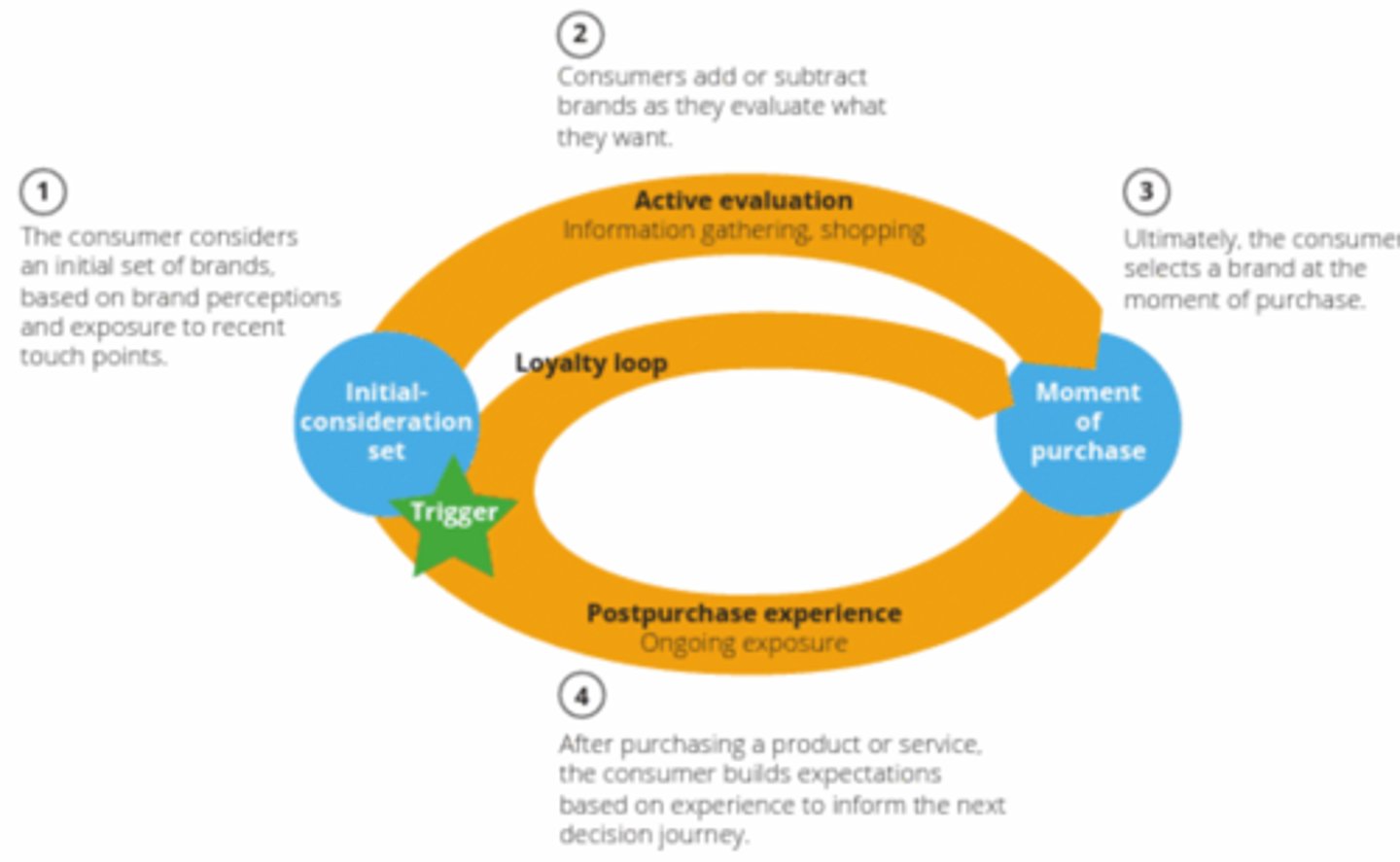
Digital Advertising
promotional messages delivered to consumers through online media outlets
Key Channels for Digital Advertising
Display
Video (+ Audio)
Social Media
Search
Email marketing
-> 4 billion global email users
->Top lead generation tool (the best ROI)
->Shoppers who purchase from emails received spend more
-> Emails can create brand ambassadors (4x more likely to share content on SM)
Bounce Rate
the % of emails that your business has sent and failed to reach the recipient's inbox
Email Marketing Challenges
42%--> promotional emails from brands were useful at least sometimes
33%--> never found brand marketing emails useful
Email Essential 1: Triggers
•Personalization
•Welcome
•Customer actions
•Lack of action
•Abandon Cart
•Time passed
•Deadlines
•Calendar
Anniversary
Win back
Discount
Order Confirmation
What matters most (Emails)
Relevancy
Personal benefits
Opportunity to take some action
what customers want from emails
Deals and discounts (64%)
Requests for product reviews (33%)
Tips and tricks (31%)
Upcoming product news (23%)
Other product suggestions (20%)
Inspirational stories (9%)
Email Essential 2: Mobile First Design Step
Optimizing emails for mobile
- 48% of emails are opened on mobile devices
-Only 11% of email templates are well optimized for mobile
key benefits of email marketing
•Allows you to reach your core audience
•Is highly measurable
•Open rate, click rate, click-to-open rate, bounce rate, unsubscribe rate, ...
•Trustworthy
•Cost-effective
•Is versatile with a number of other digital advertising uses
Display Advertising
advertising that incorporates text, logos, and pictures or images position on a website or search engine
site placement ads
When a company chooses the site they would like to advertise on
Native Ads
Advertising appears on a website with similar content
Remarketing Ads
Advertising changes based on the user's activity on a given websites
•Past visitors see ads while they are browsing the web
•Can keep brand top-of-mind
•Entice visitors to come back
key features of display advertising
-Various standardized sizes and shapes
-Pay per impression
-Price depends on the publisher
-Used for branding, as well as direct response
Interstitial ads
: ads that run full-screen and cover the interface of the app the user is using
expandable ads
ads that launch as banner ads but invite the user to interact to learn more
Banner ads
Advertisements on web pages designed to encourage users to click to reach an advertiser's site
Skyscraper and leaderboard
Rich Media
digital ads with features like video, audio, or other elements that encourage viewers to interact and engage with the content
Key metrics for display ads
Impressions
reach
engagement rate
CTR
site placement ads
•When a company chooses the site they would like to advertise on
•Banner ads
Native Ad*
* "any paid advertising that takes the specific form and appearance of editorial content from the publisher itself"
Look, feel, function (Native ads)
Entertain
inform
inspire
Type of native advertising
•In-feed social ads
•Promoted/Sponsored content
•Recommended content
Why native ads?
Attention ↑
Avoidance ↓
Click Through Rates (CTR) ↑
Google Display Network (GDN)
A collection of over 200 million sites, apps, and videos where Google ads can appear.
•Utilizing cookies, mobile ad identifier (MAID), identifier for advertisers (IDFA)
-Remarketing ads
The VIdeo Matrix
•Numerous pipes & access points
Devices
content producers
distribution network
•Devices (video matrix)
: the options available based on what device viewers are using to view the content
content producers (video matrix)
: the options available based on who owns the content
Distribution network in video matrix
the options available based on who is distributing the content
Linear TV
•The device used when content is delivered over broadcast or cable signals
•Watch linear TV on a television set
Connected TV (CTV)
•The internet-connected device used when content is streamed to a television set
•Watch digital video through an internet-enabled device
•“The device”
•How the content is being delivered
over-the-top (OTT)
: content that is streamed over broadband channels
•“The content”
•Whether it is steamed or delivered live