ARCH 214: World History of Arch- Exam 2 Keywords
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Vedas
ancient indian stories in the language sanskrit; originally oral transmission and later written down

Ghats
“river landing stairs” or “mountain pass,” providing access to riverbanks for bathing
Brahmins
a member of the highest hindu class, that of the priesthood
Buddha, Buddhism
“enlightened,” utilizing morality, mediation, and wisdom
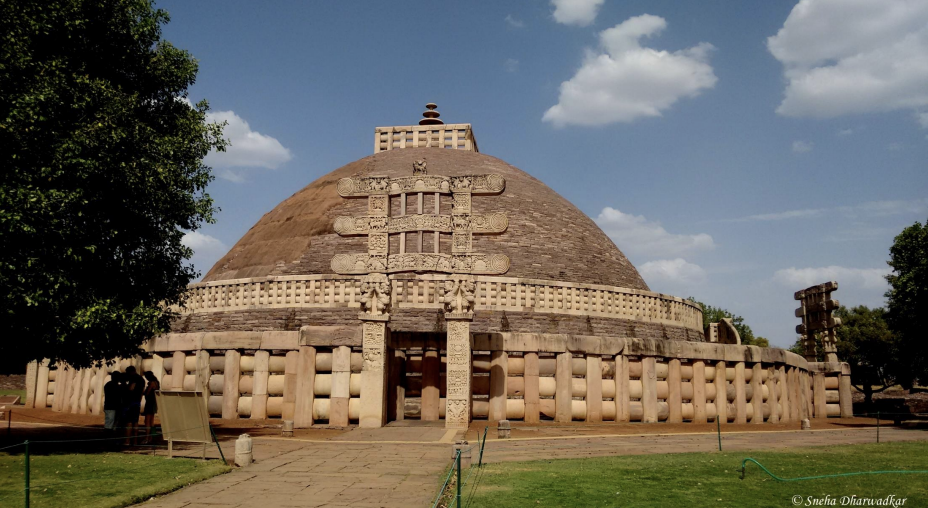

Stupa
dirt burial mound faced with stone; shape of stupa represents the buddha, crowned and sitting in meditation posture on a lion throne

Chaitya, Vihara
a place of worship, shrine, prayer hall and a place of living for the buddhist monks
Chhatri
semi-open, elevated, dome-shaped pavilions used as an element in indo-islamic architecture and indian architecture
Pradakshina-patha
clockwise circumambulation of sacred entities, walking around in a “circle” as a form of worship in hindu ceremonies in india
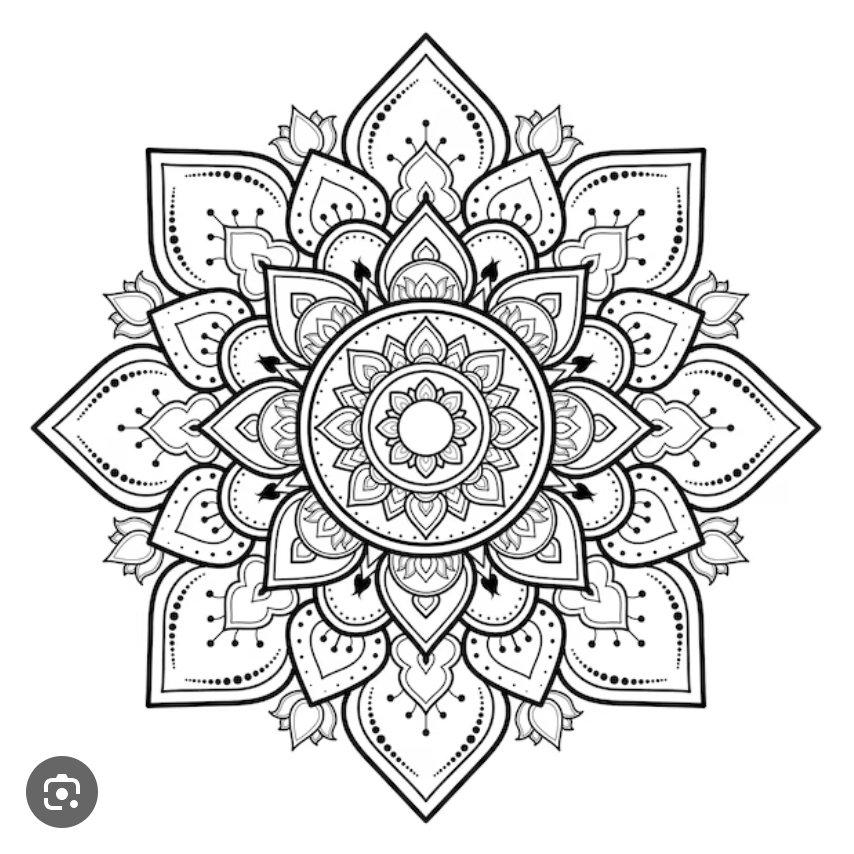

Mandala
represent time and space, complex circle
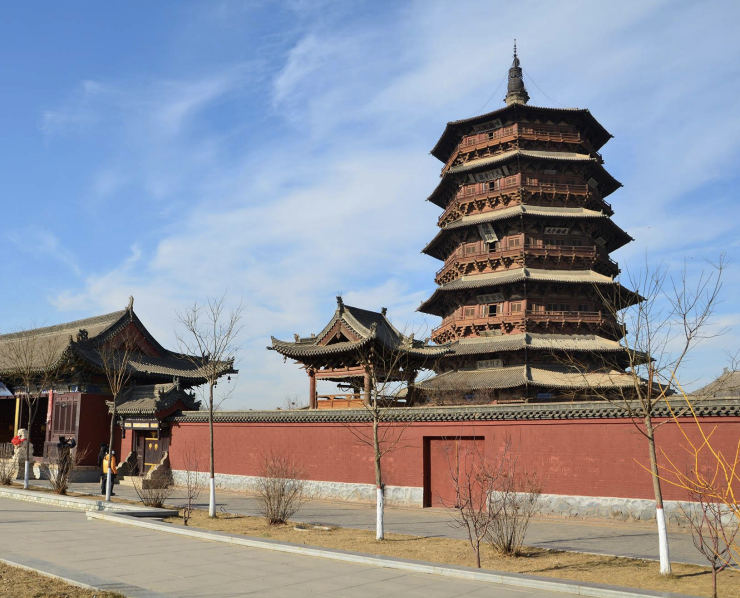

Pagoda
originated from indian stupa buildings, known to chinese architecture as a tiered tower with roofs curving upwards; eaves and tower pavilion style
Cosmic ocean
“ocean of milk,” vishnu convinces the gods to “churn” the ocean to bring forth amrita, the nectar of immortality, so that they can live forever
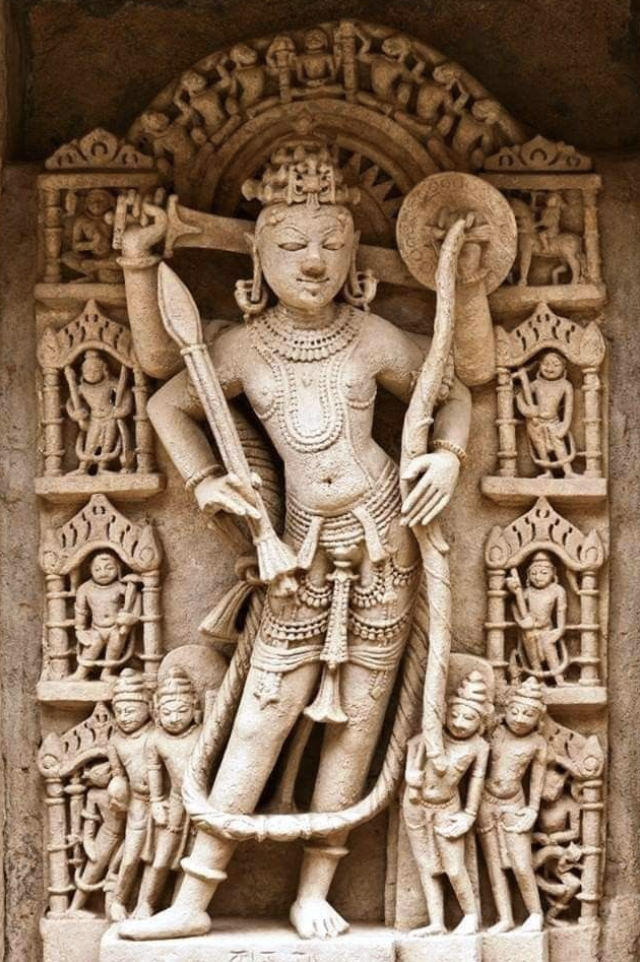

Vishnu
the preserver
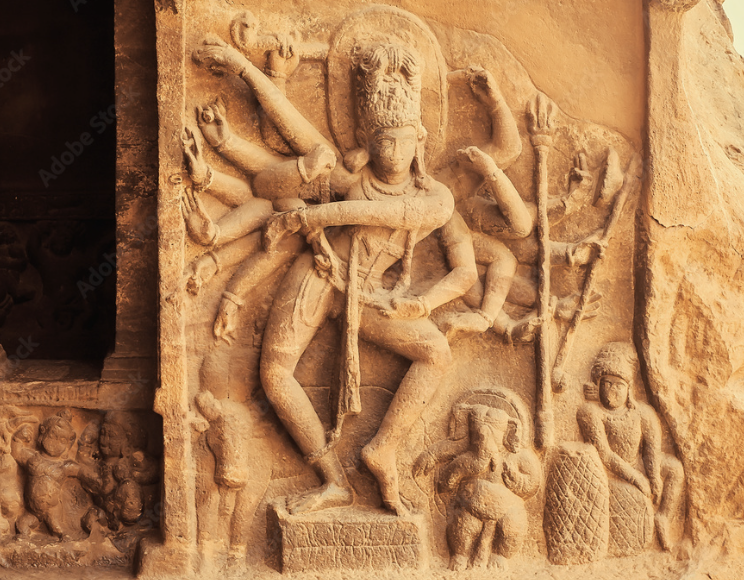

Shiva
the destroyer, swallows the poison that comes out of the “ocean milk”
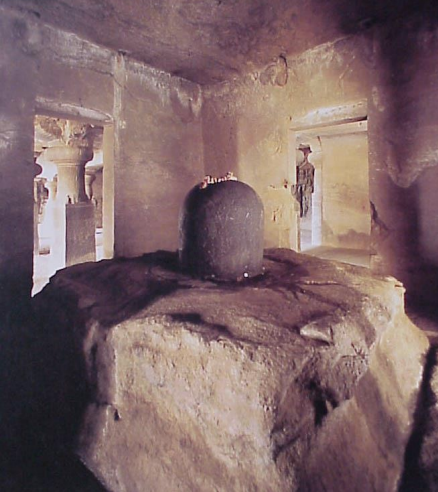

Lingam
symbol of divine generative energy, sacred phallus as a symbol of god shiva
Hindu Renaissance
response to the emergence of many social and religious vices in the hindu society to india; a revival that was to reawaken its devotees to their ancient faith, expose them to christian and muslim ideas, and finally to make its influence felt as far afield as america
Grabha-griha
womb house, sanctum sanctorum, innermost sanctuary of hindu temples
Shikhara
depiction of a mountain, “mountain peak,” topmost pointed portion of a temple
Mandir
freestanding hindu temple, bringing hindus and gods together through worship, sacrifice, and devotion
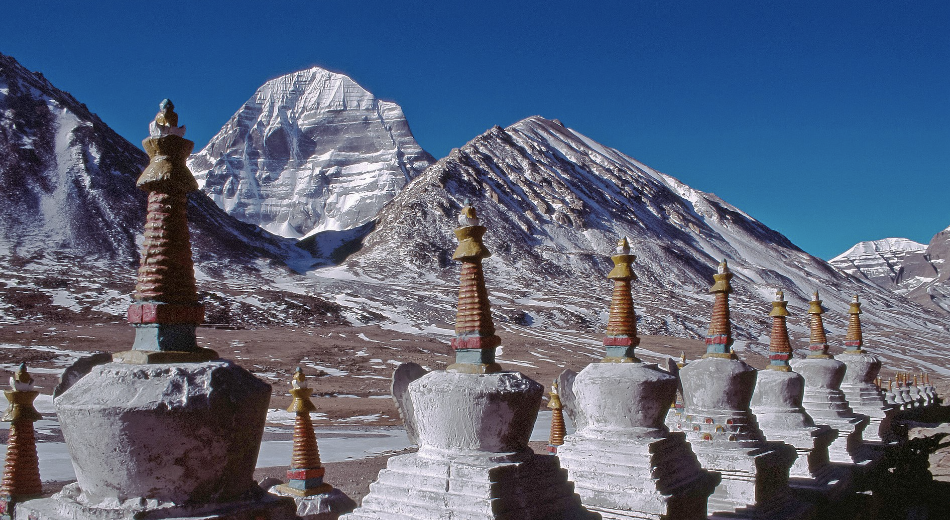

Mount Kailash, Mount Meru
sacred peak in the himalayas, a golden mountain that stands in the center of the universe and is the axis of the world
Mandapa
pillared hall or pavilion for public rituals, porch like structure used for religious dancing and music
Rammed Earth
compacted natural raw materials such as earth, chalk, lime, or gravel
Mandate of Heaven
idea that there could be only one legitimate ruler of china at a time and that this ruler had the blessing of the gods
Wangcheng Plan
ideal city, a square urban layout based on the well-field system which divided and ruled the land by a grid plan
Confucianism
an ancient chinese belief system, which focuses on the importance of personal ethics and morality
Daoism
“the way” is the natural order of the universe
To Kung (dǒugǒng)
a structural element of interlocking wooden brackets, bracket system
Hip, gable, hip and gable
hip roof that slopes down on all four sides and integrates a gable on two opposing sides
Shintoism
an ancient religion of japan, importance of purity, harmony, respect for nature, family respect, and subordination of the individual before the group
Kami
spirits or holy powers, a divine being in the shinto religion
Torii
sacred gateway of a shinto shrine with two uprights and two cross pieces
Shimenawa
rice or hemp rope found at shinto shrines, dividing the space between the sacred area where gods are enshrined and the outside world
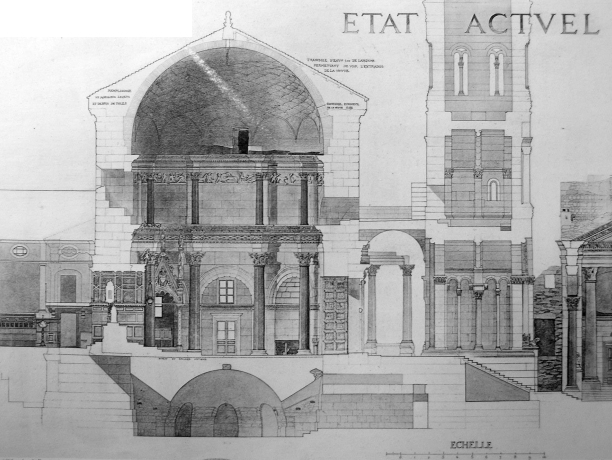
Mausoleum
buildings that holds dead people
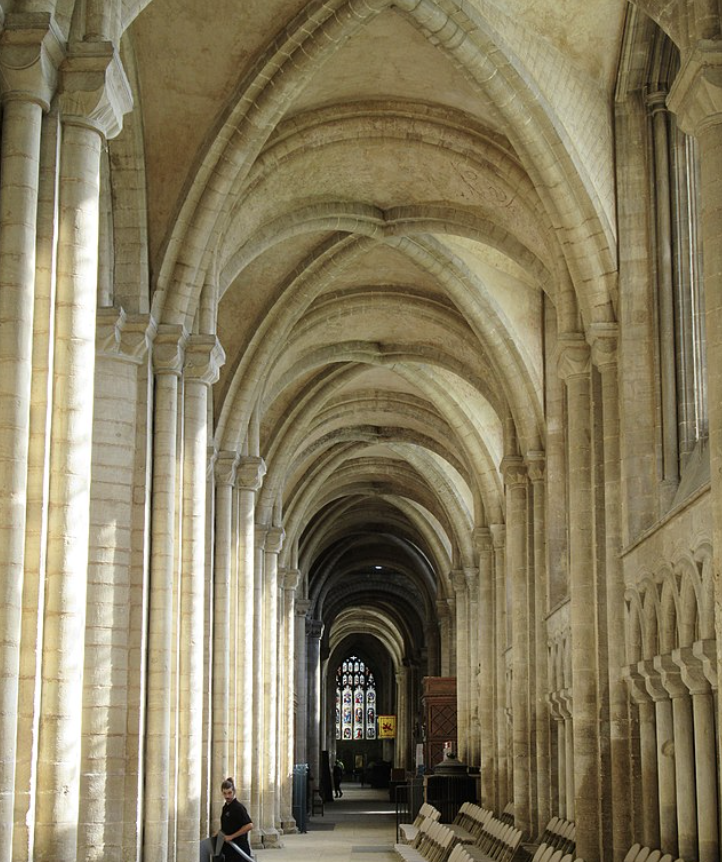

Groin vault
produced by the intersection at right angles of two barrel vaults
Catacombs
passageways for religious practice, any chamber used as a burial place
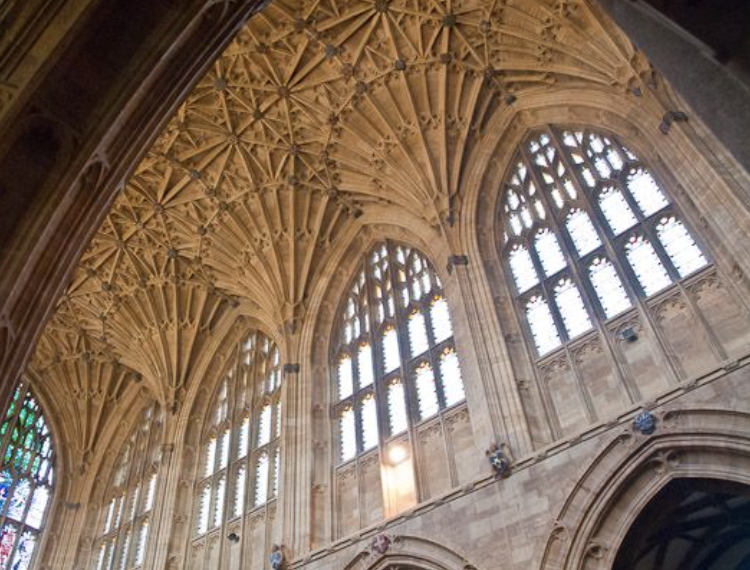

Clerestory
fenestrated (windowed) wall of a room that is carried higher than the surrounding roofs to light the interior space
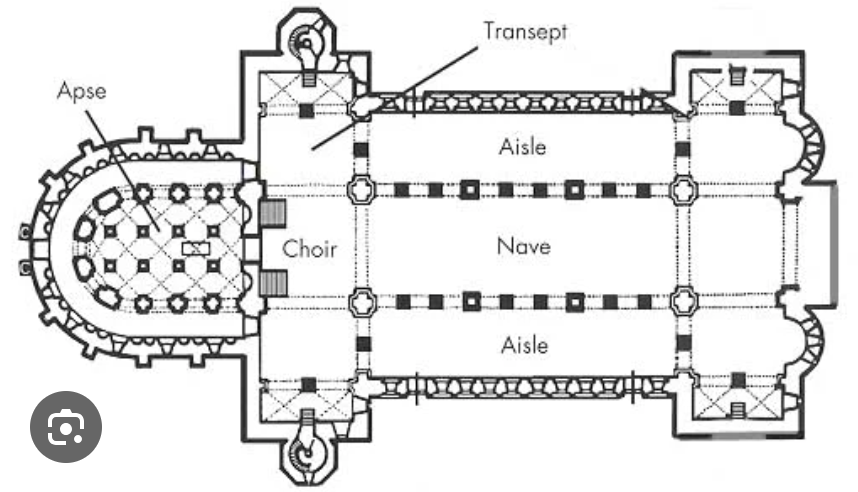
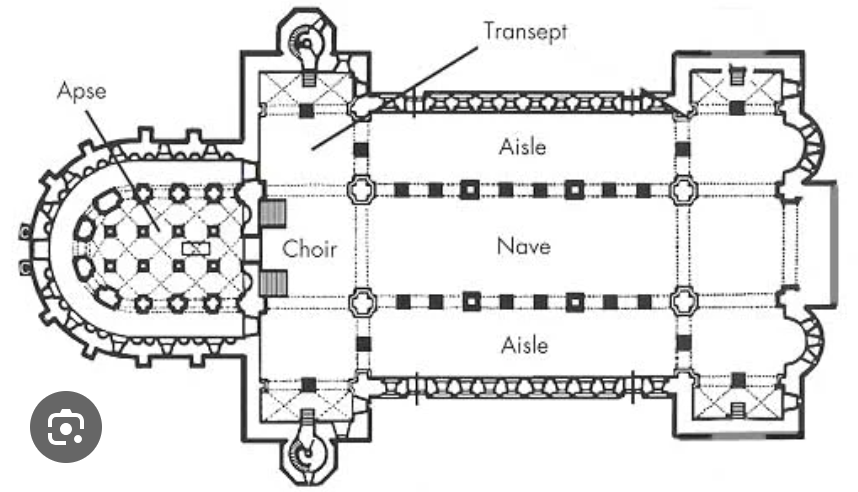
Nave, aisles, chapel
in a basilican church, nave refers only to the central aisle; nave is set apart for the laity
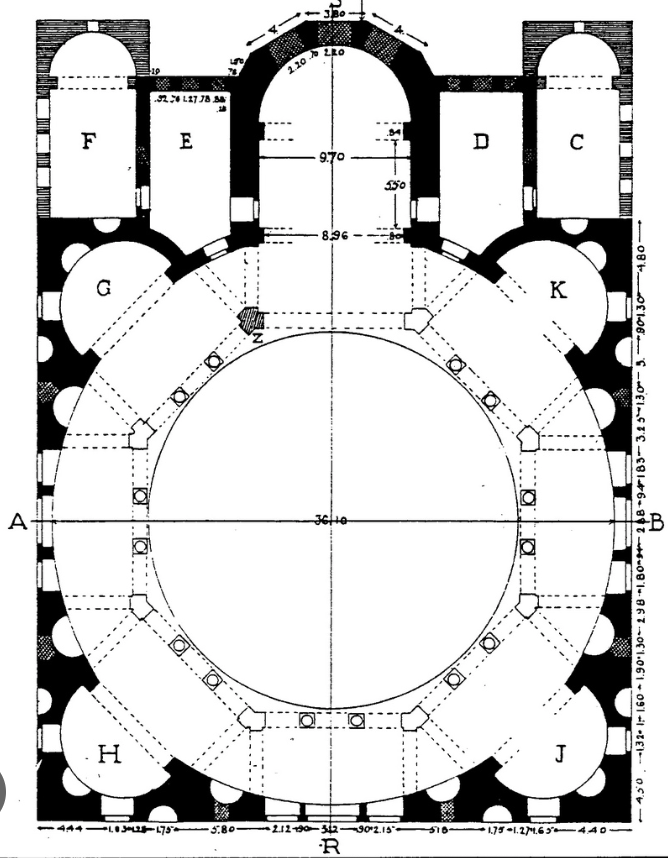
Apse
a part of church that sticks out from one end of the building, is usually semicircular, has an arched roof, and is often richly decorated
Martyrium
building or chamber used by the early christians as a burial place
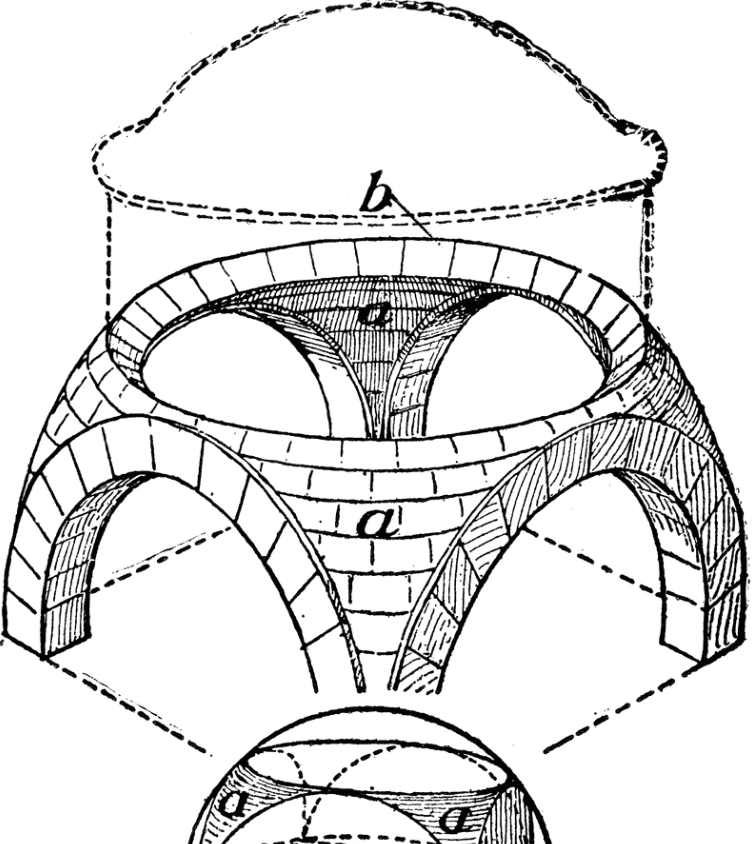
Pendentives
a curved triangle of vaulting formed by the intersection of a dome with its supporting arches