Genetics M1
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
What are the 3 components of DNA?
deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
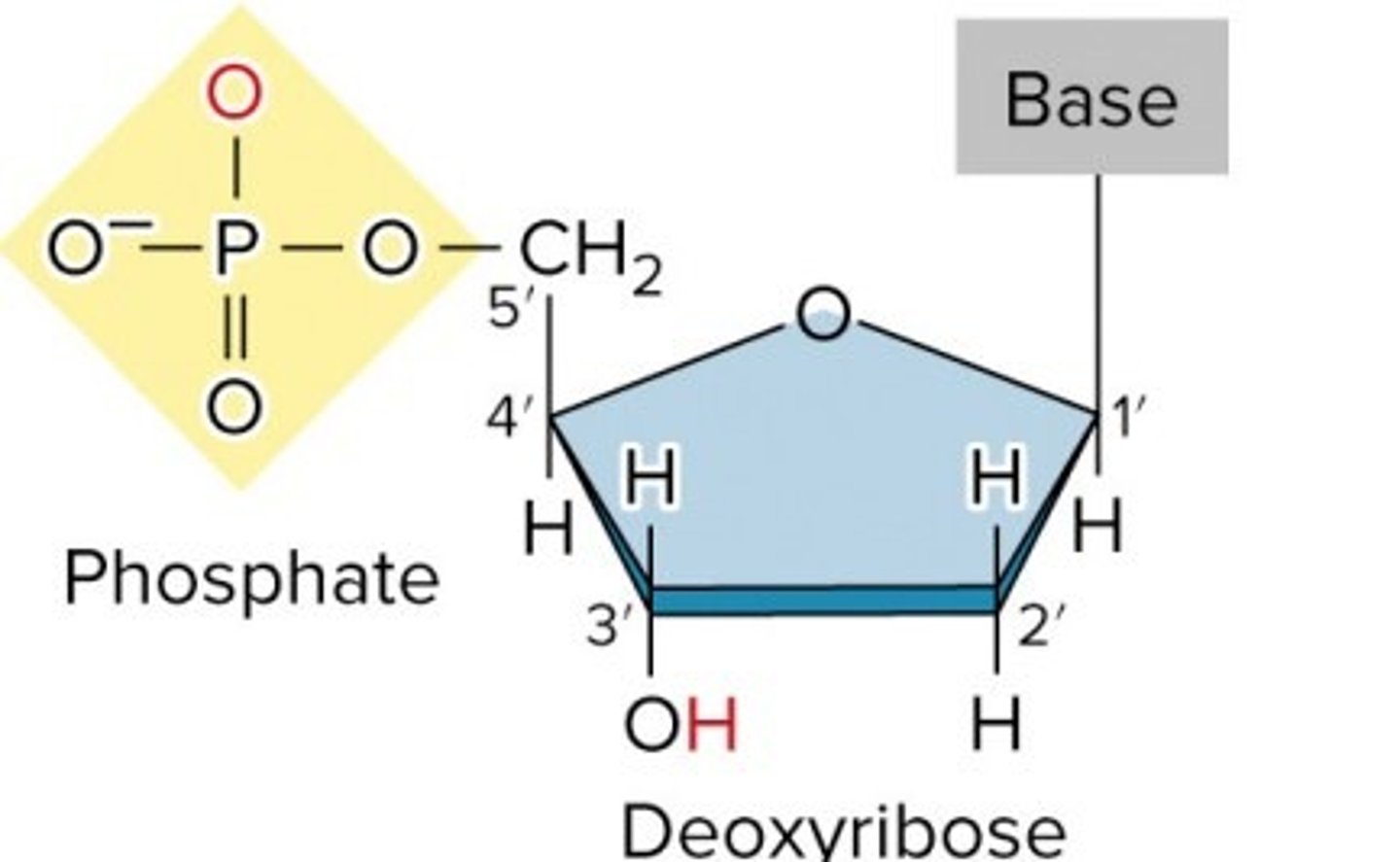
3' = ?
OH
2 multiple choice options
5' = ?
Phosphate
2 multiple choice options
Oxygens Present
DNA = ?
RNA = ?
RNA = 2, DNA = 1
dNTP
Nucleotide Triphosphates, which are reactants used as the sources of A, C, T, and G for a new strand of DNA.
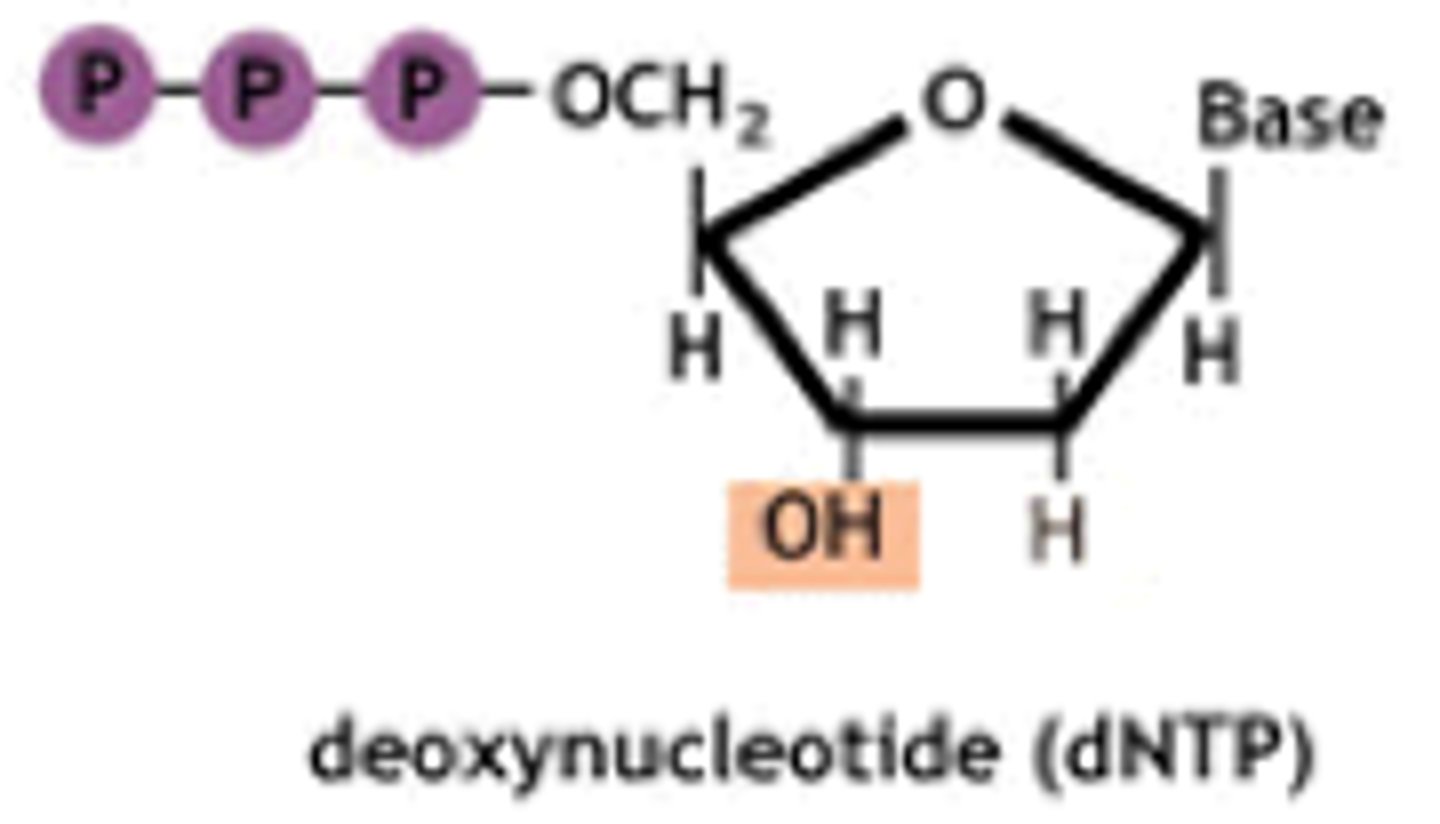
dNTPs combine their 5' ____ with the 3' ____ of another dNTIP to form...
Phosphate; OH; DNA
3 multiple choice options
Polarity in terms of genetcis
Having 2 distinct ends of something (like a leg)

DNA runs in a ___________ fasion
antiparallel
3 multiple choice options
Adenine and Thymine form ___ hydrogen bonds
2
3 multiple choice options
Guanine and Cytosine form ___ hydrogen bonds
3
3 multiple choice options
Purines definition
Nitrogenous bases with 2 rings
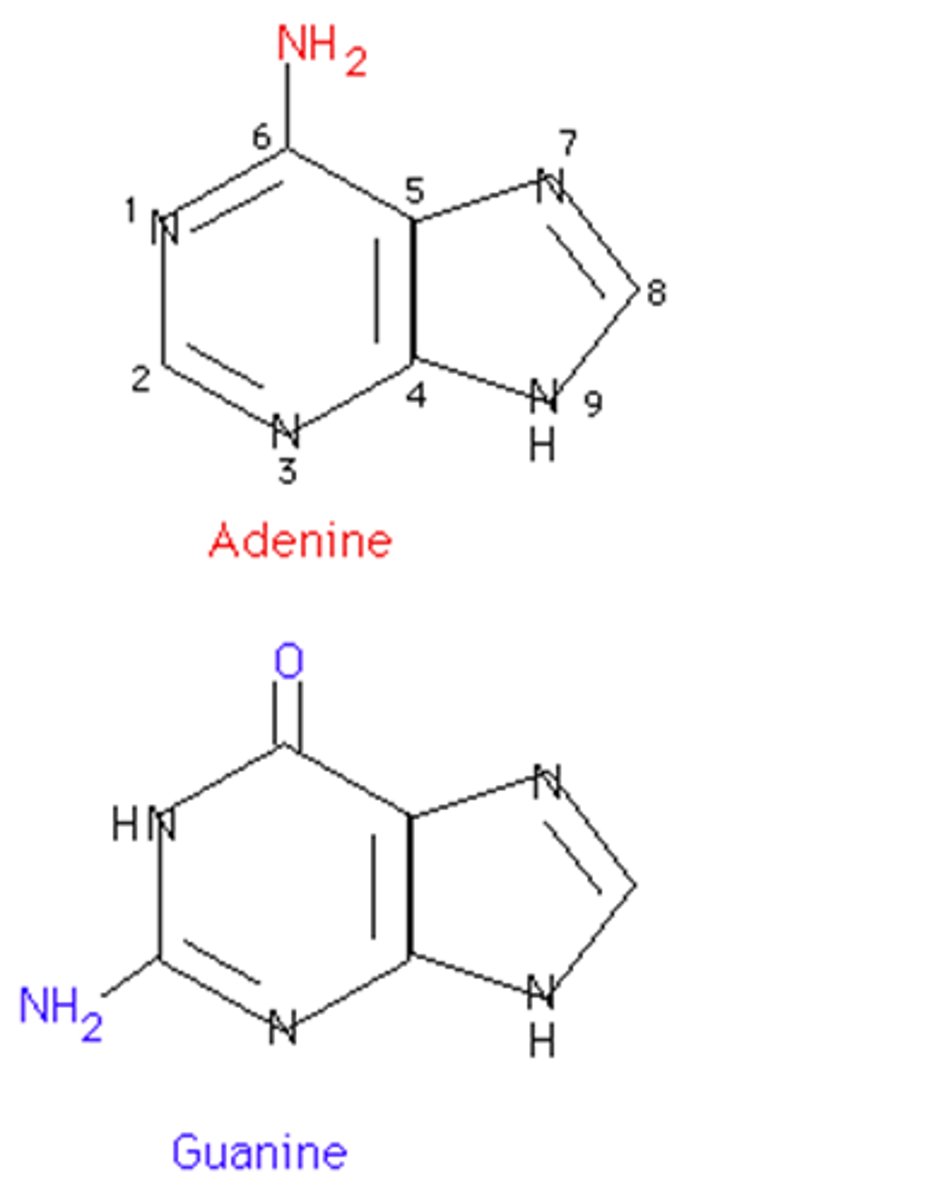
Purines example
Adenine and Guanine
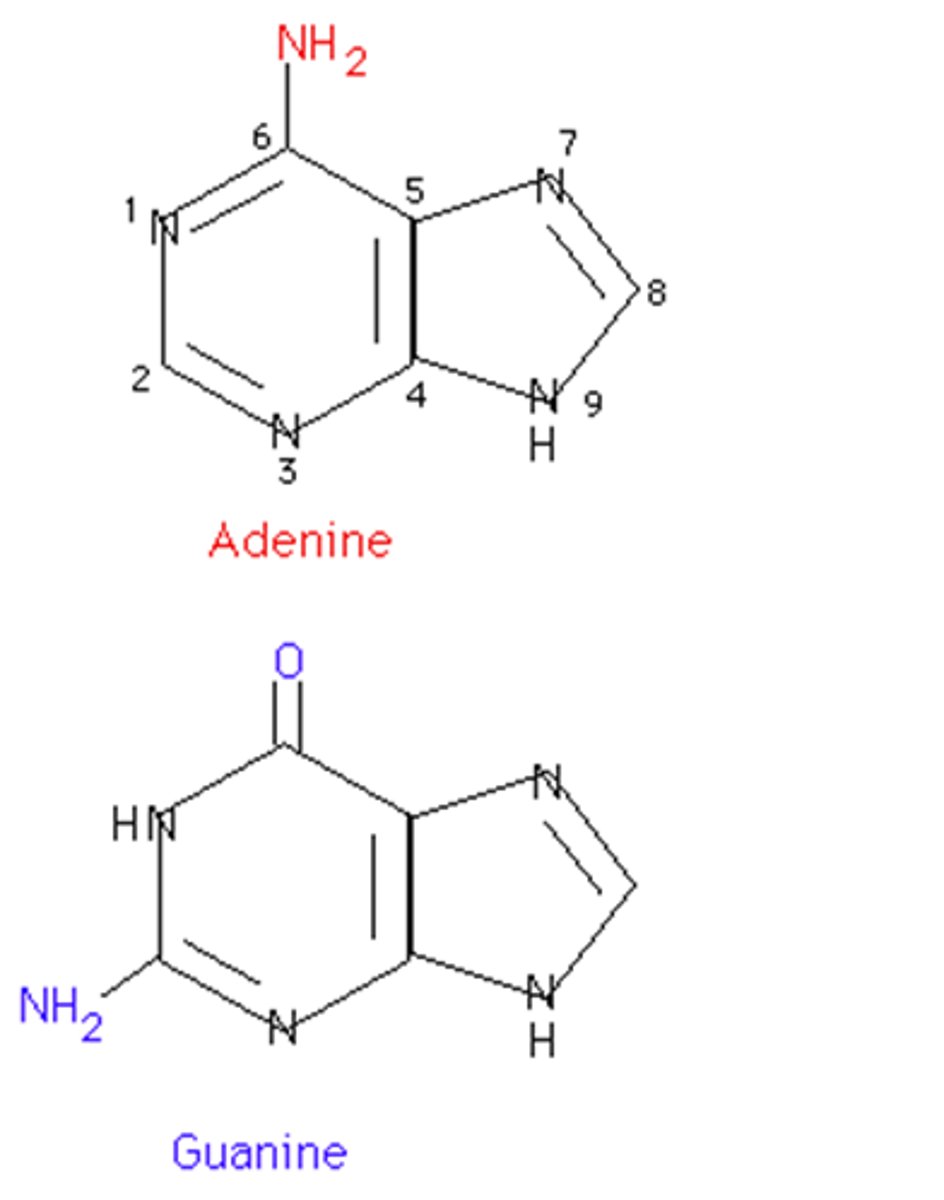
Pyrimidines example
Thymine, Cytosine, and Uracil
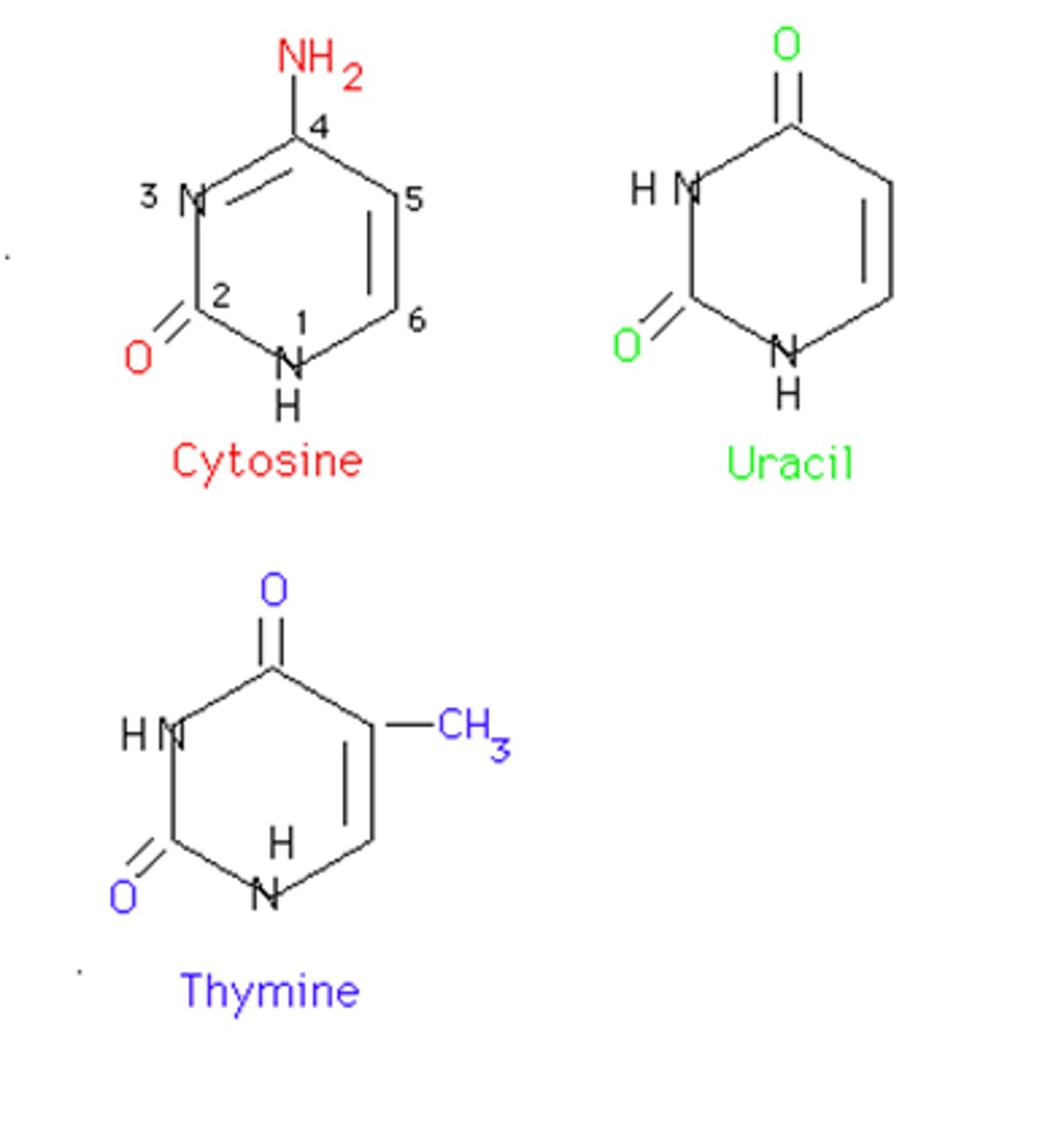
Pyrimidines definition
Nitrogenous bases with only 1 ring
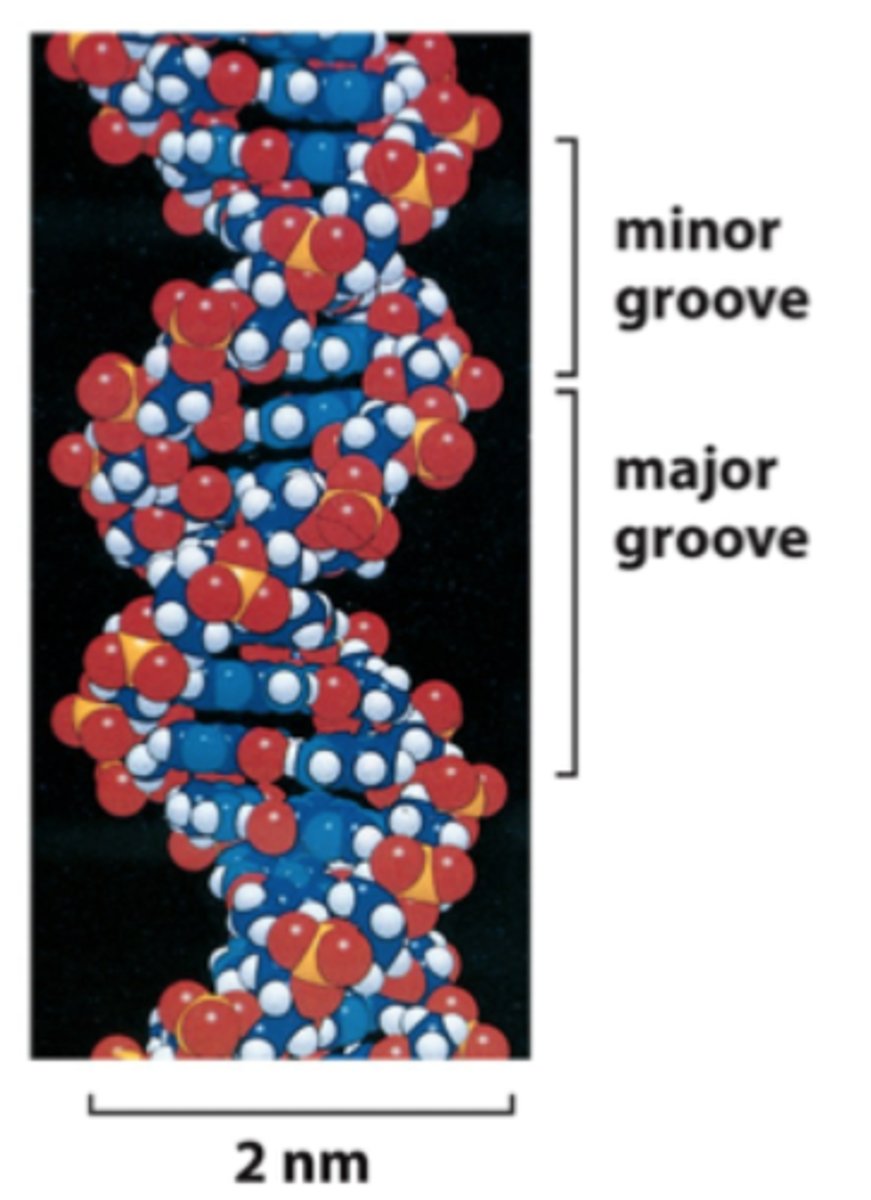
Major Groove
Larger gap present within DNA
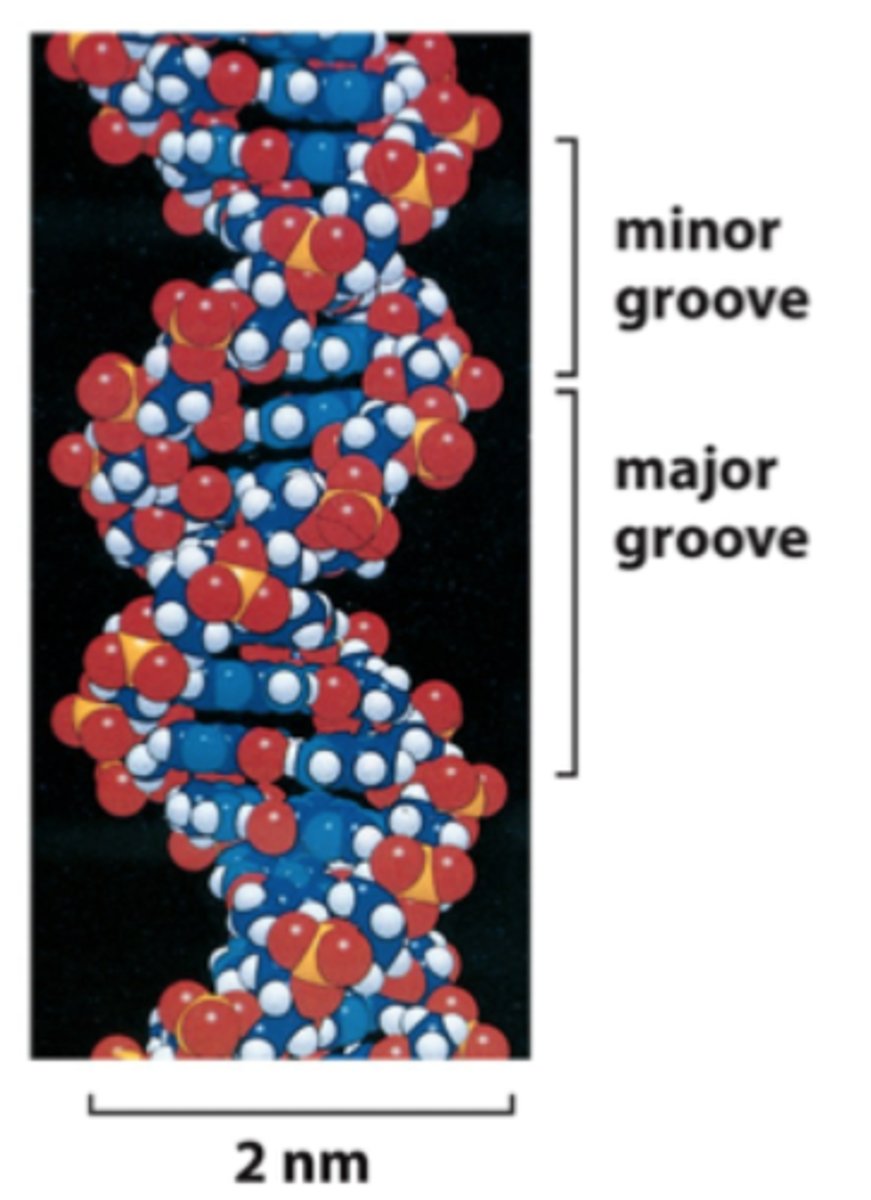
Minor Groove
Smaller gap in DNA
RNA
commonly single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
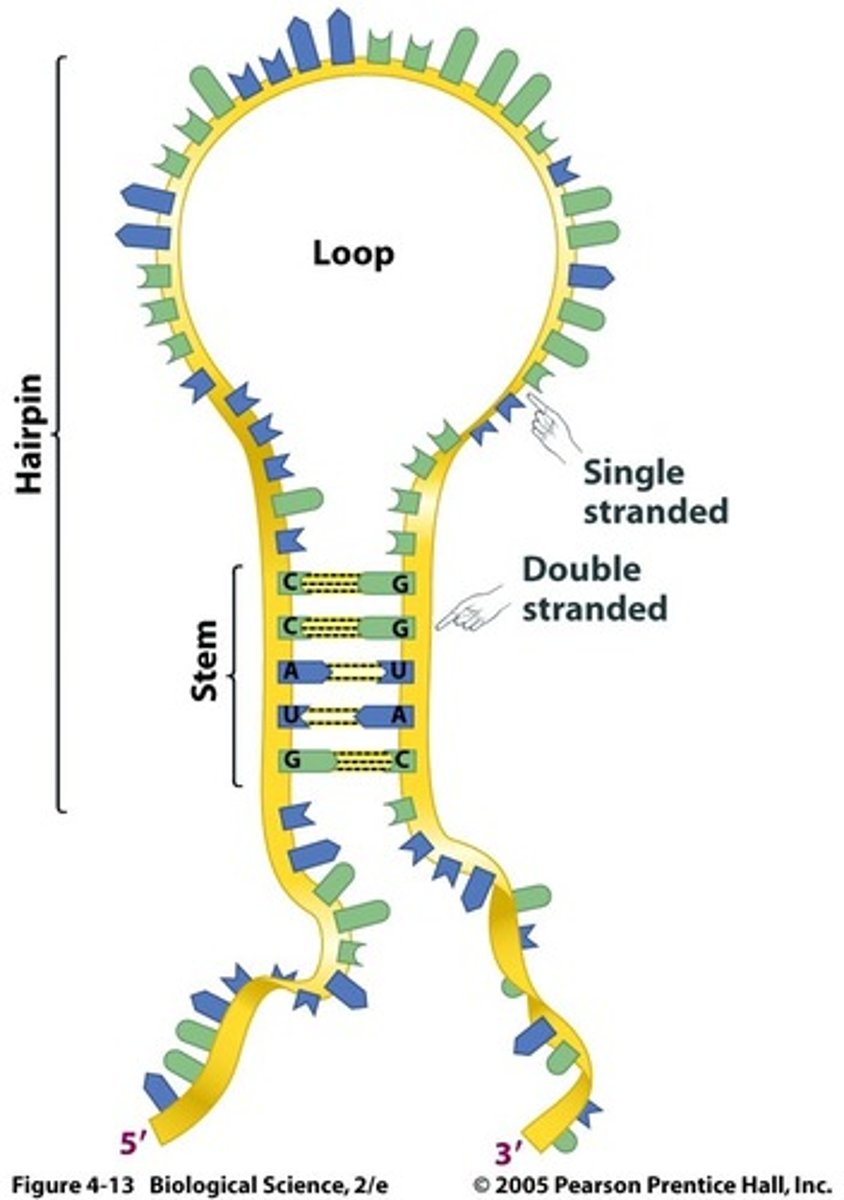
RNA secondary structure
circular structure that arises in a single stranded RNA molecule due to complementary base pairing
%A =
%T
%C =
%G
Genetic info is stored within DNA's ________ __________
base pairs
3 multiple choice options
Major and Minor grooves allow ___________ to interact with regions of base pairs
Proteins
Hybridization/Annealing
The process from which single-stranded DNA/RNA bind to one another to form a double stranded structure.
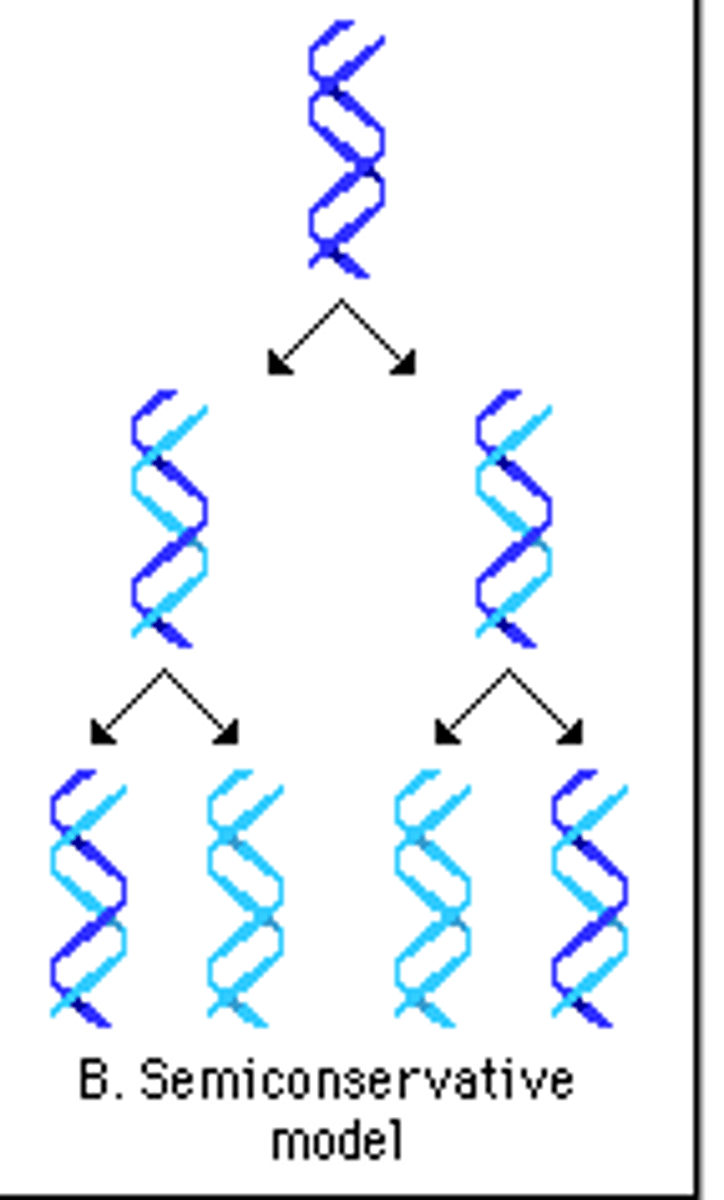
Meselson-Stahl Experiment
Used isotope of nitrogen to change the weight of DNA N15 & N14, demonstrated that the semi-conservative model is the best description of replication.
Semiconservative Replication
Method of DNA replication in which parental strands separate, act as templates, and produce molecules of DNA with one parental DNA strand and one new DNA strand
2 multiple choice options
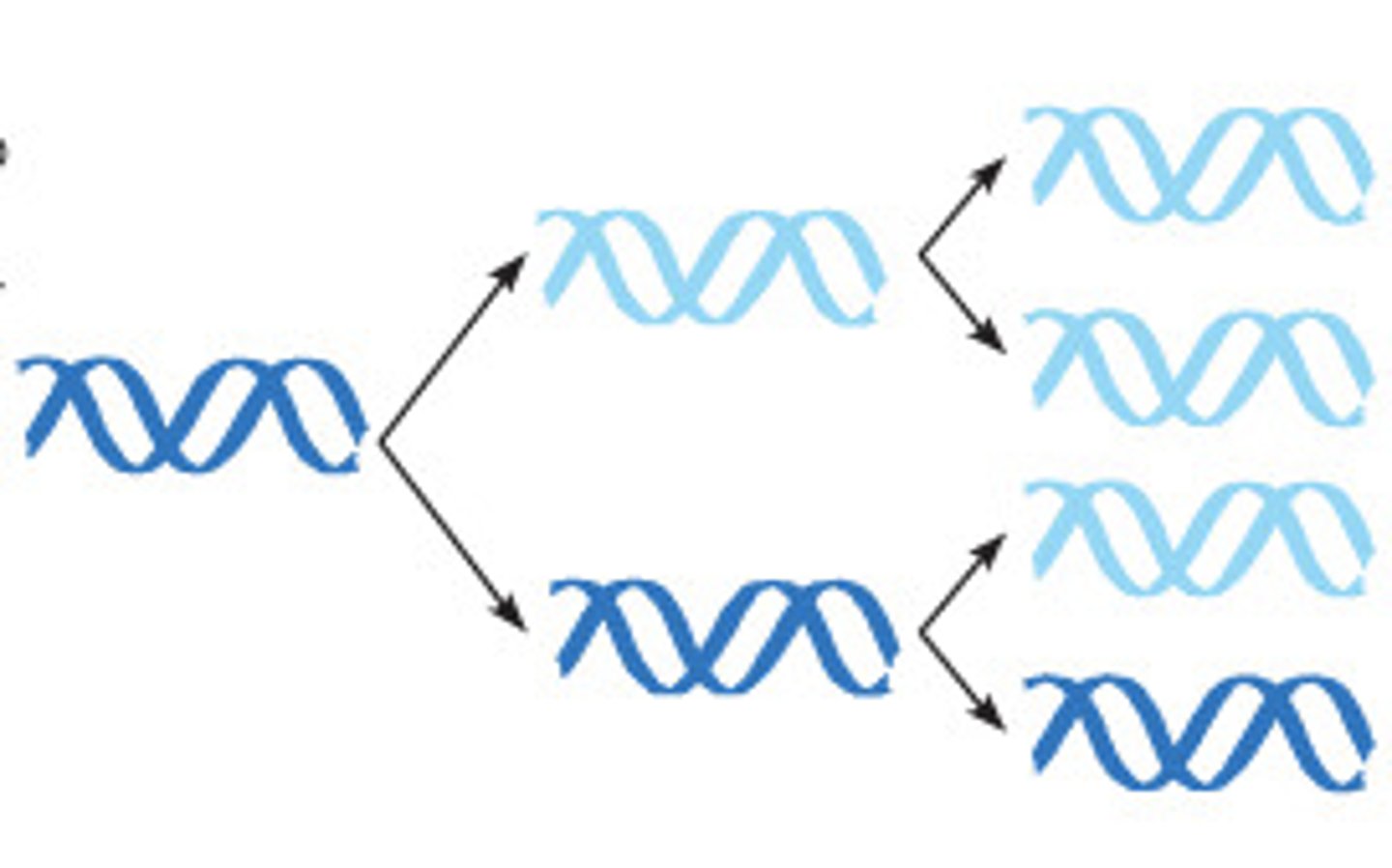
Conservative Replication
the parental molecule serves as a template for the synthesis of an entirely new molecule
2 multiple choice options
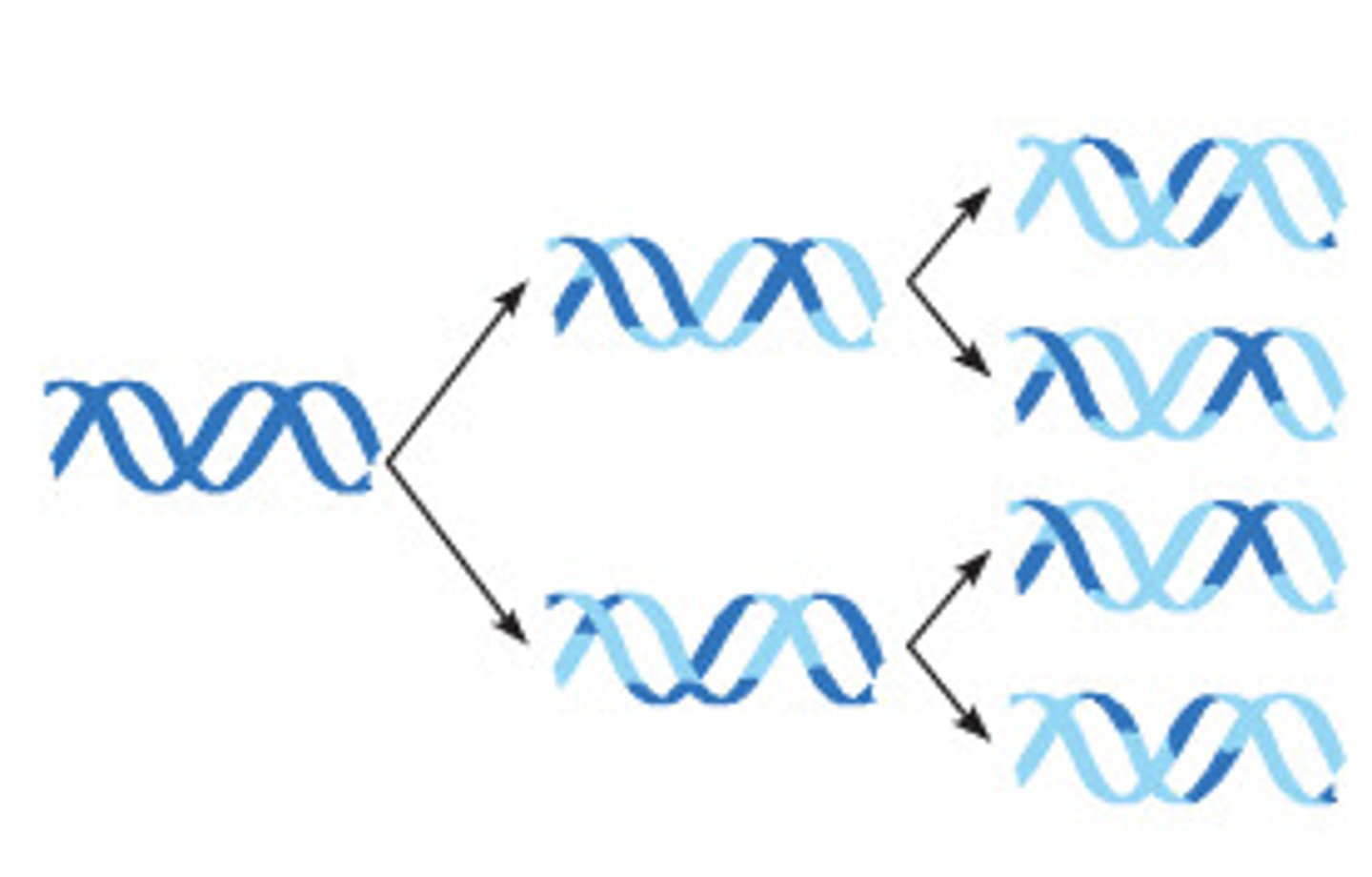
Dispersive Replication
a disproved model of DNA synthesis suggesting more or less random interspersion of parental and new segments in daughter DNA molecules
2 multiple choice options
Initiator proteins
bind to the origin of replication, separate the strands of DNA, and recruit other replication proteins
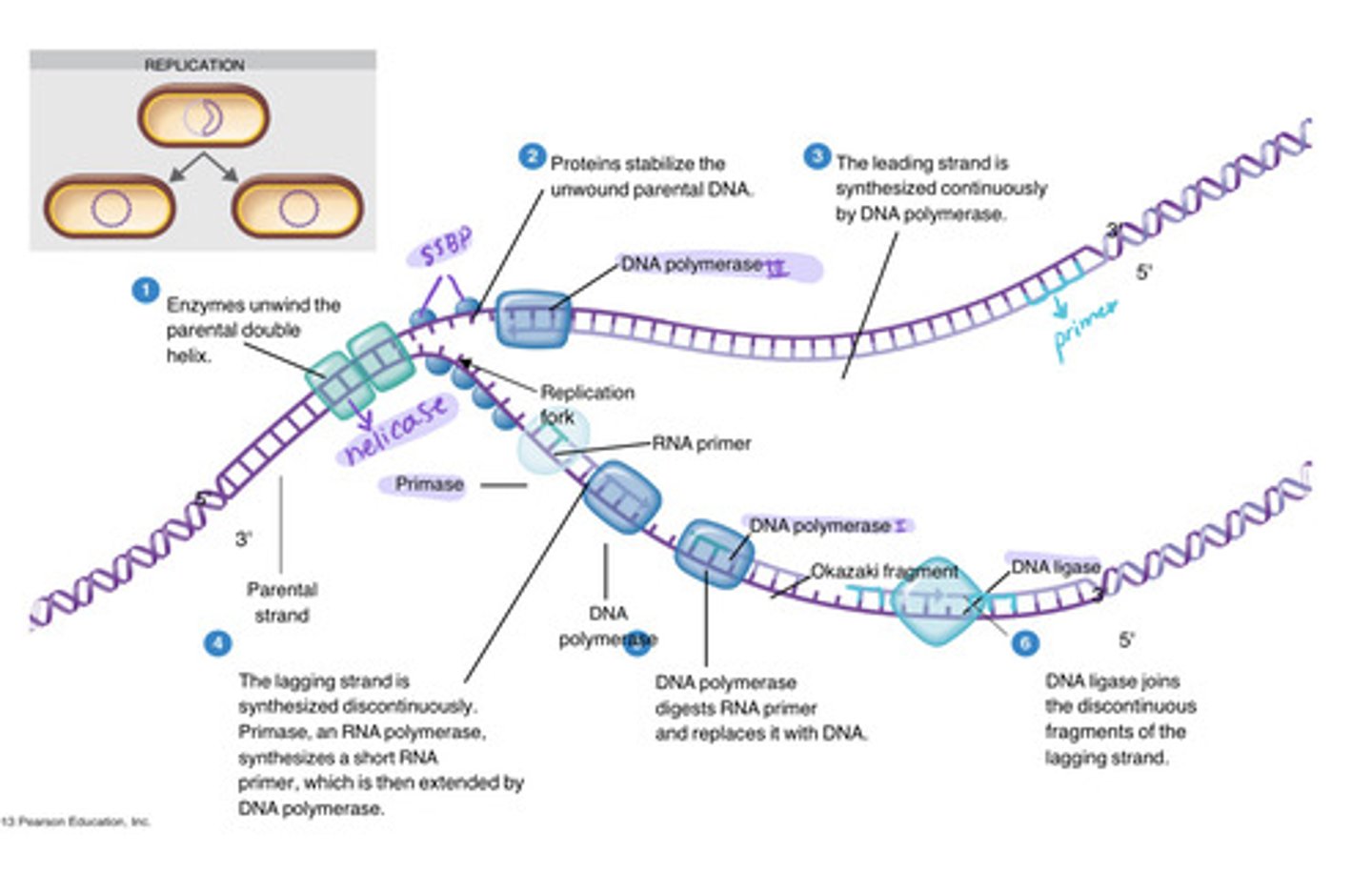
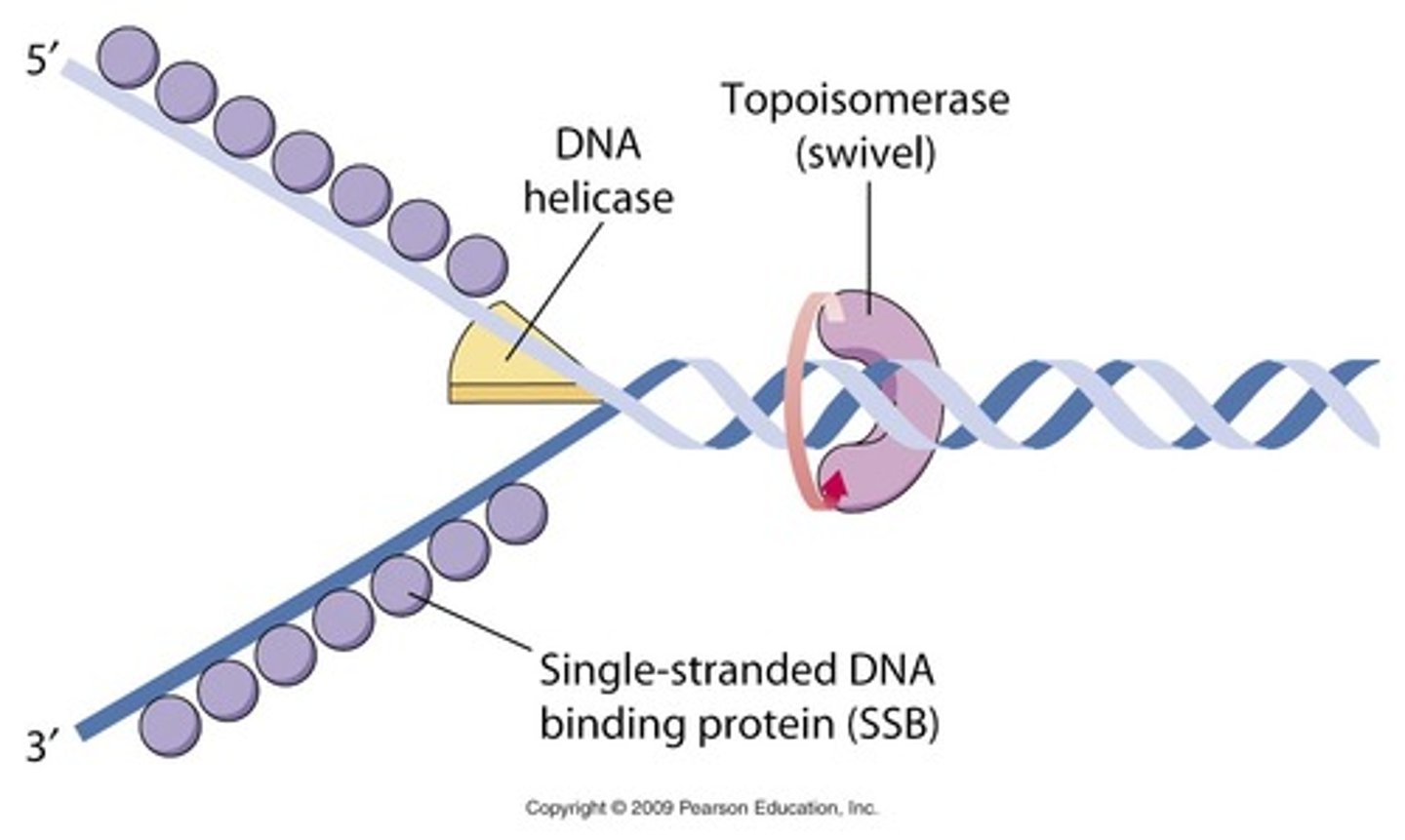
DNA Helicase
continues "unzipping" the DNA.
Single-Stranded Binding proteins (SSBP)
protects the unzipped DNA until it is replicated
Topoisomerase
Relieves supercoiling in DNA when it is being unwound
DNA grows when a 5' triphosphate of a dNTP reacts with the ______ of another molecule
3' OH
DNA Polymerase III
synthesis new DNA
What does DNA polymerase III need in order to do its job?
1. dNTPs (building blocks of reaction)
2. A DNA template (old strand that determines which dNTP is added)
3. A 3' OH to add new dNTPs onto
What provides the 3' OH for DNA polymerase III to add a dNTP?
primer
What makes DNA primers?
Primase
DNA Polymerase I
removes RNA primers and replaces them with DNA
DNA Ligase
connects the backbones of adjacent strand fragments
AZT drug was approved for _________ therapy
HIV
What does the AZT drug do?
stops further replication by replacing the 3' OH with a N3 group
Leading strand
Strand of DNA built in the same direction as the replication complex is traveling
Lagging strand
strand of DNA build in the opposite direction that the replication complex travels
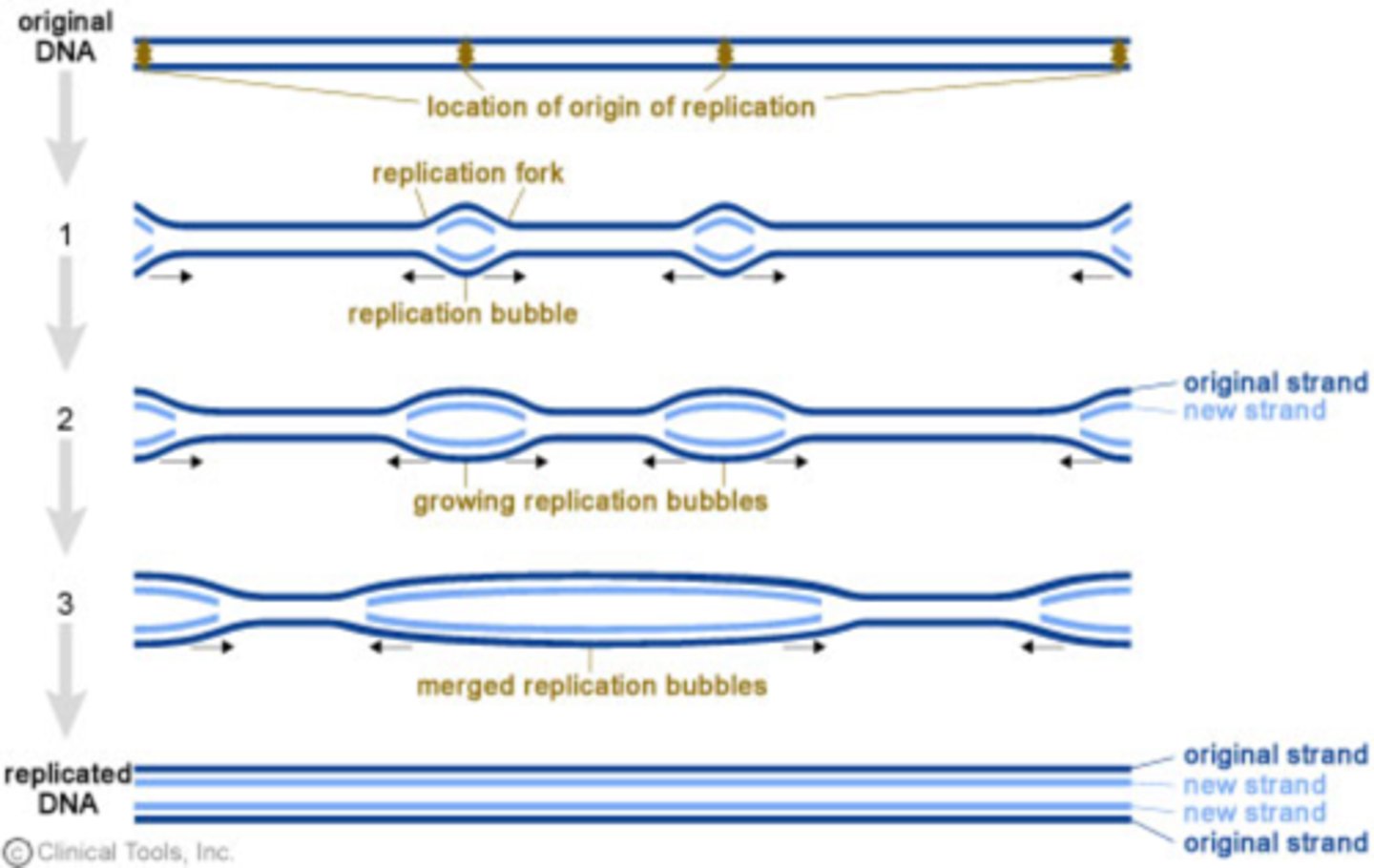
Each replication bubble has _____ replication forks
2
3 multiple choice options
Prokaryotes replicate _______ from a single Origin of replication
once
3 multiple choice options

Eukaryotic chromosomes replicate _______________
bidirectionally
Bidirectional replication
replication at both ends of a replication bubble
PCR steps
1. Denaturing
2. Annealing/Hybridizing
3. Extension
What happens during the denaturing step of PCR?
Reaction is heated to 95°C and double stranded DNA is seperated into single strands when hydrogen bonds break
What happens during the Annealing/hybridization step of PCR?
Reaction temperature is reduced to around 55°C to allow primer annealing
What happens during the Extension step of PCR?
Temperature is raised to 72°C and Taq synthesizes DNA
Taq Polymerase
A DNA synthesis enzyme that can withstand the high temperatures of PCR
Mutations are a source of...
sequence variation
Substitution =
changing one nucleotide to another
Transition
purine to purine or pyrimidine to pyrimidine mutation
Transversion
Purine to pyrimidine or pyrimidine to purine mutation
Insertion/Deletion
bases added or removed
mutations may cause an organism to be more or less ______
fit
Do mutations occur in response to a stimuli or randomly?
randomly
The fluctuation experiment asked what?
will a trait for resistance emerge before its needed
Spontaneous Mutation
mutations resulting from normal biological and chemical processes in a cell with a low chance of it happening.
Induced Mutation
Result of mutagens which cause mutations that wouldn't otherwise occur.
Tautomerization
when a base flips to another tautomeric state which has different bonding properties.
What causes a sequence to get messed up by tautomers?
When DNA polymerase replicates the strand when the tautomer pairs to the wrong base.
tautomeric shifts (are/are not) mutations
are not
1 multiple choice option
Mutagens
substances that increase the mutation rate above the baseline spontaneous rate
nucleotide mimics
Bases that look like one of the 4 nucleic bases but base pair randomly
Intercalators
molecules that get sandwiched inside the DNA and disrupt replication machinery causing insertions and deletions
Germline Cells
cells whose descendants are gametes
Soma cells
cells that derive from everything else
Germline mutations
occur in germ cells (sperm or ova) and can be passed to one's children at conception
If a person has a mutation in all their cells, it is likely a _________ mutation
germline
Somatic mutations (are/are not) inherited
are not because the mutation wasn't present in the zygote
Mismatch Repair
The cellular process that uses specific enzymes to remove and replace incorrectly paired nucleotides.
How does DNA repair machinery tell which strand is the old or new strand?
the old strand has extra chemical tags that are added after it was fully built.
Base excision repair
Repair mechanism that cuts a large portion of the backbone out and then rebuilds it using DNA polymerase.
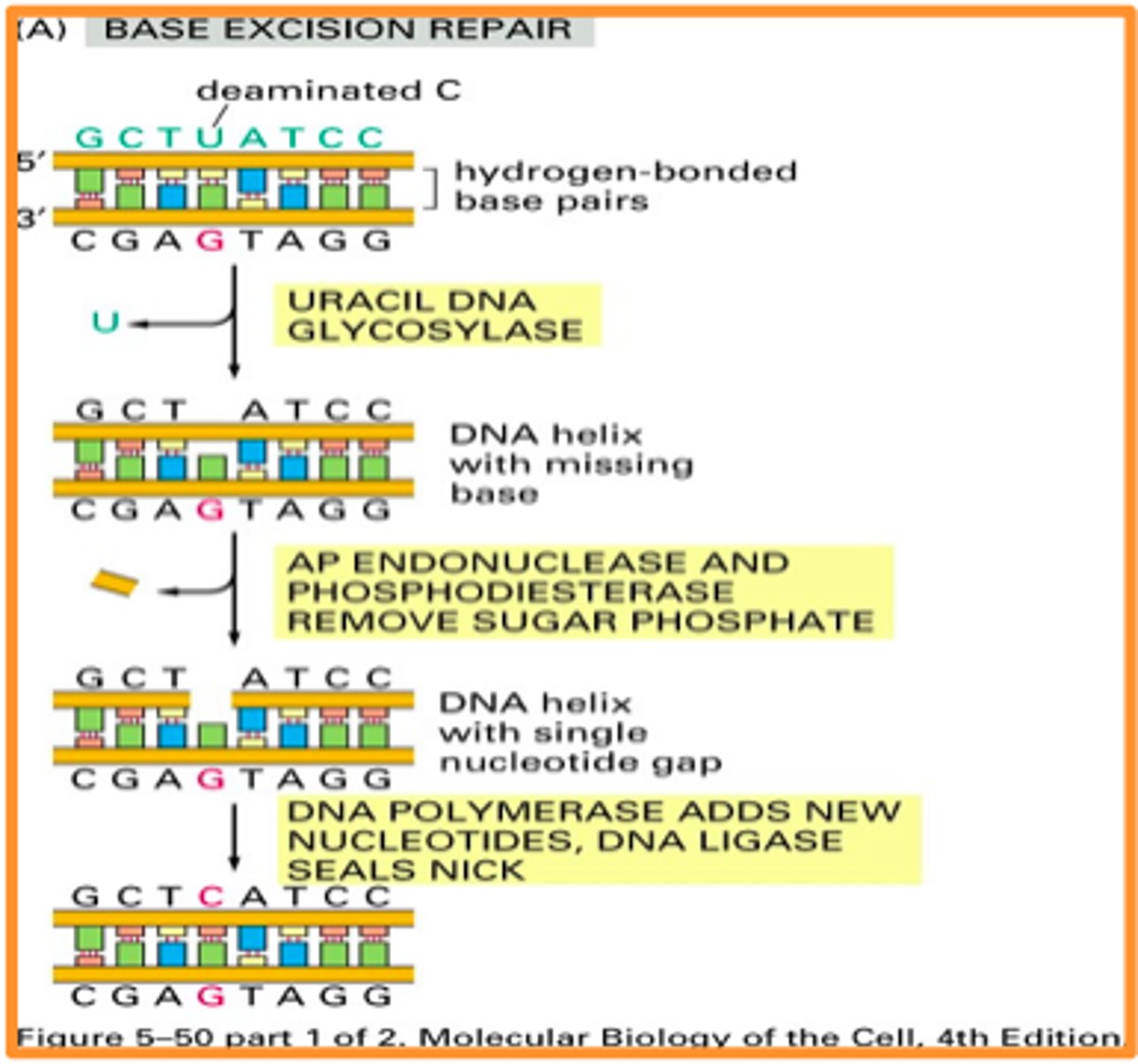
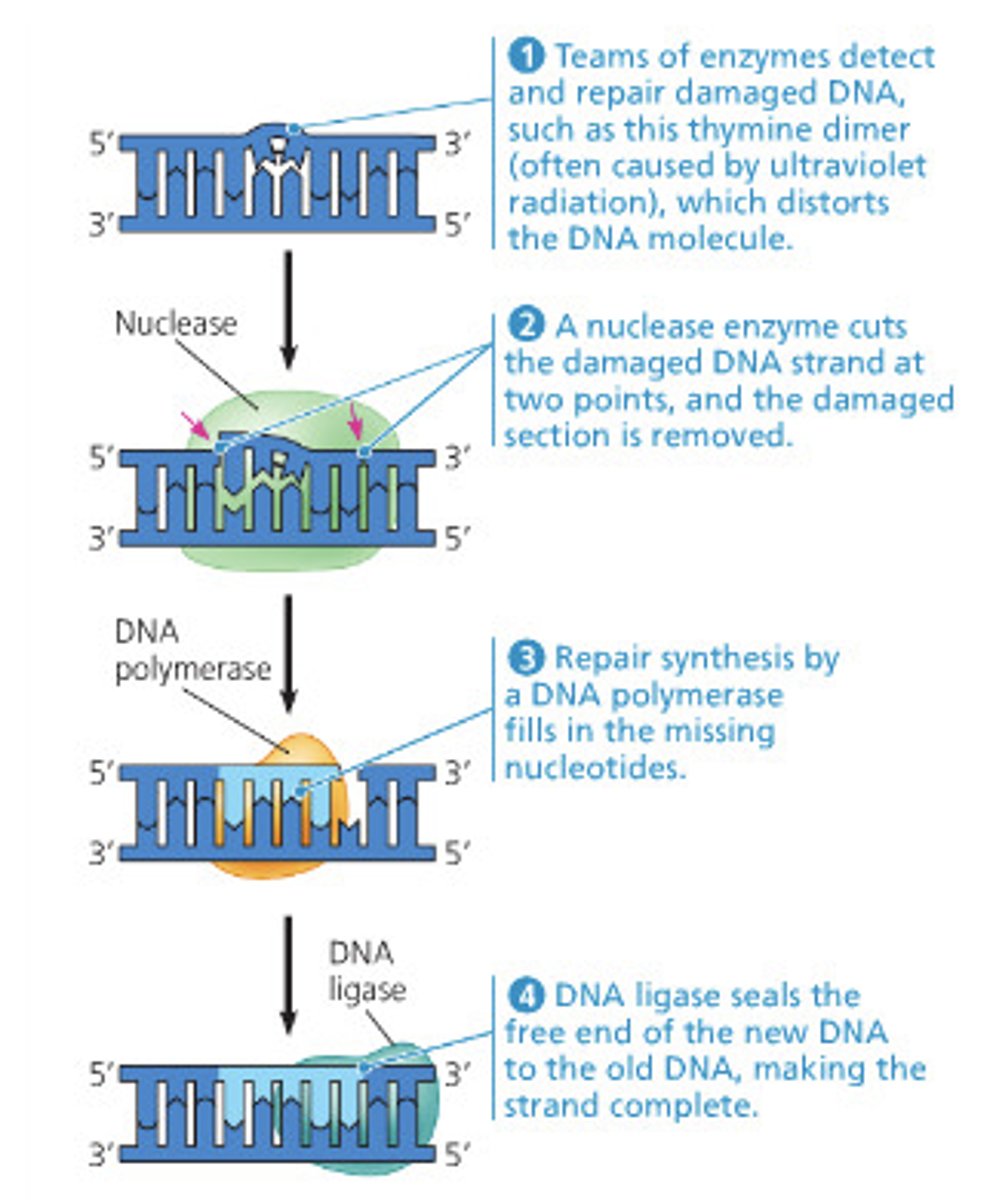
Nucleotide Excision Repair
A repair system that removes and then correctly replaces a damaged segment of DNA using the undamaged strand as a guide.
Double stranded breaks can be repaired using...
Homologous Recombination or Non-Homologous end joining
Homologous recombination
Uses homologous DNA as a template to repair DNA
Non Homologous End-joining
A fast, error-prone DNA repair process that rejoins broken double strands by trimming and ligating the ends, often causing loss of genetic information.
Haploid number (n)
number of chromosomes in a gamete
Ploidy
how many homologous "sets" of chromosomes a cell has
Diploid number (2n)
number of chromosomes in a diploid cell
Prophase 1 Meiosis
Chromosomes become visible; nuclear envelope breaks down; crossing-over occurs between non sis chromatids
Metaphase 1 Meiosis
Paired homologous chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
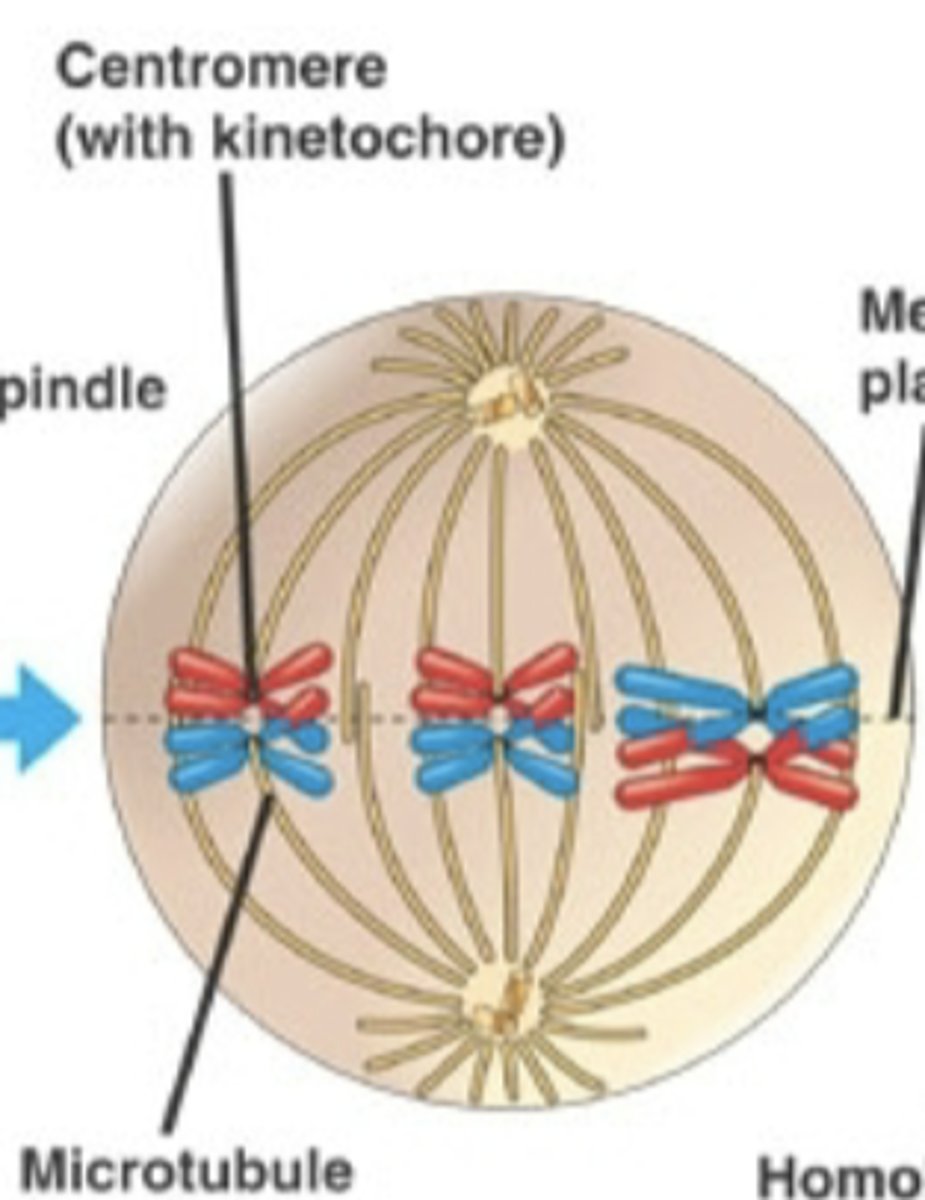
Anaphase 1 Meiosis
homologous chromosomes separate and are pulled to opposite ends of the cell
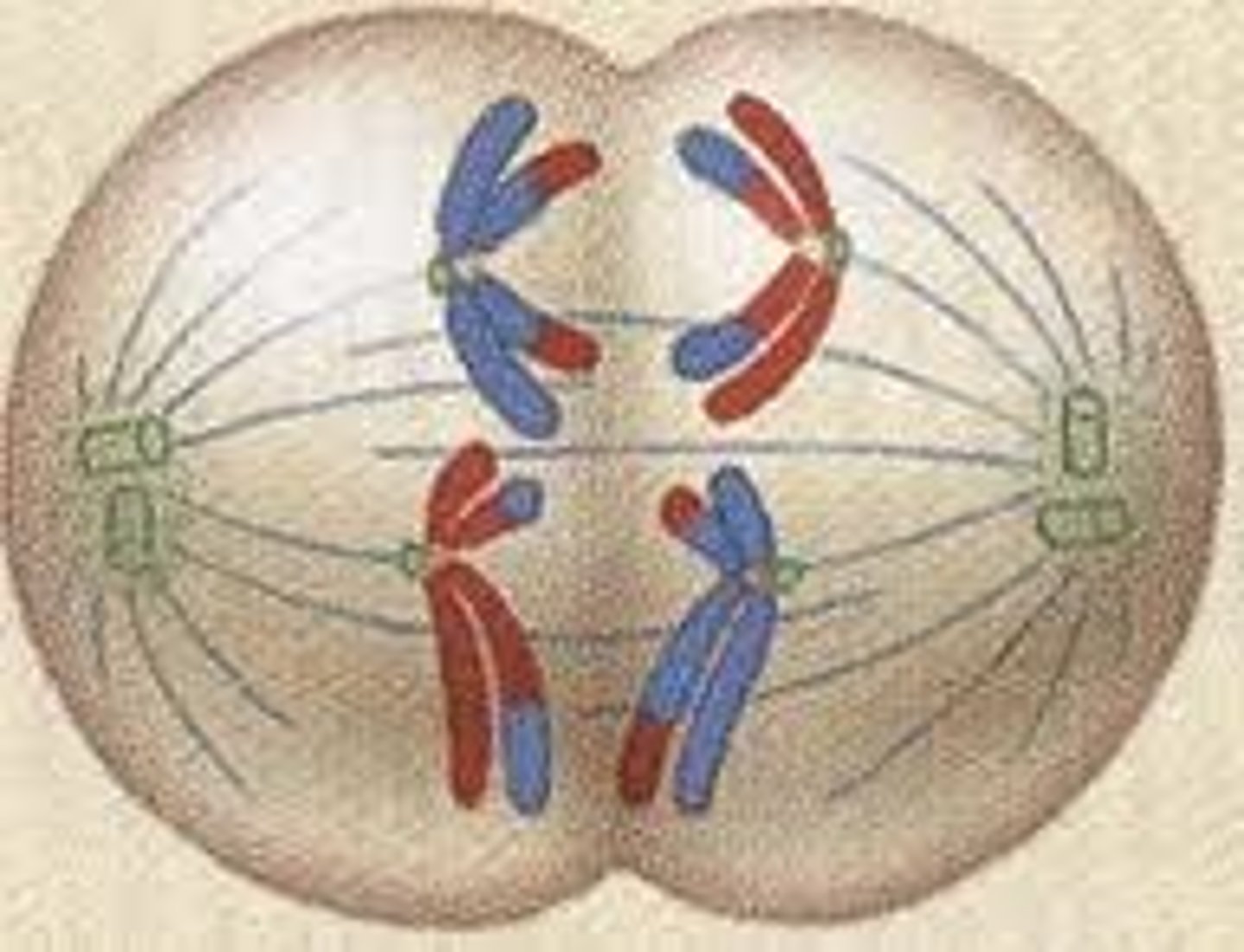
Anaphase 2 Meiosis
sister chromatids separate
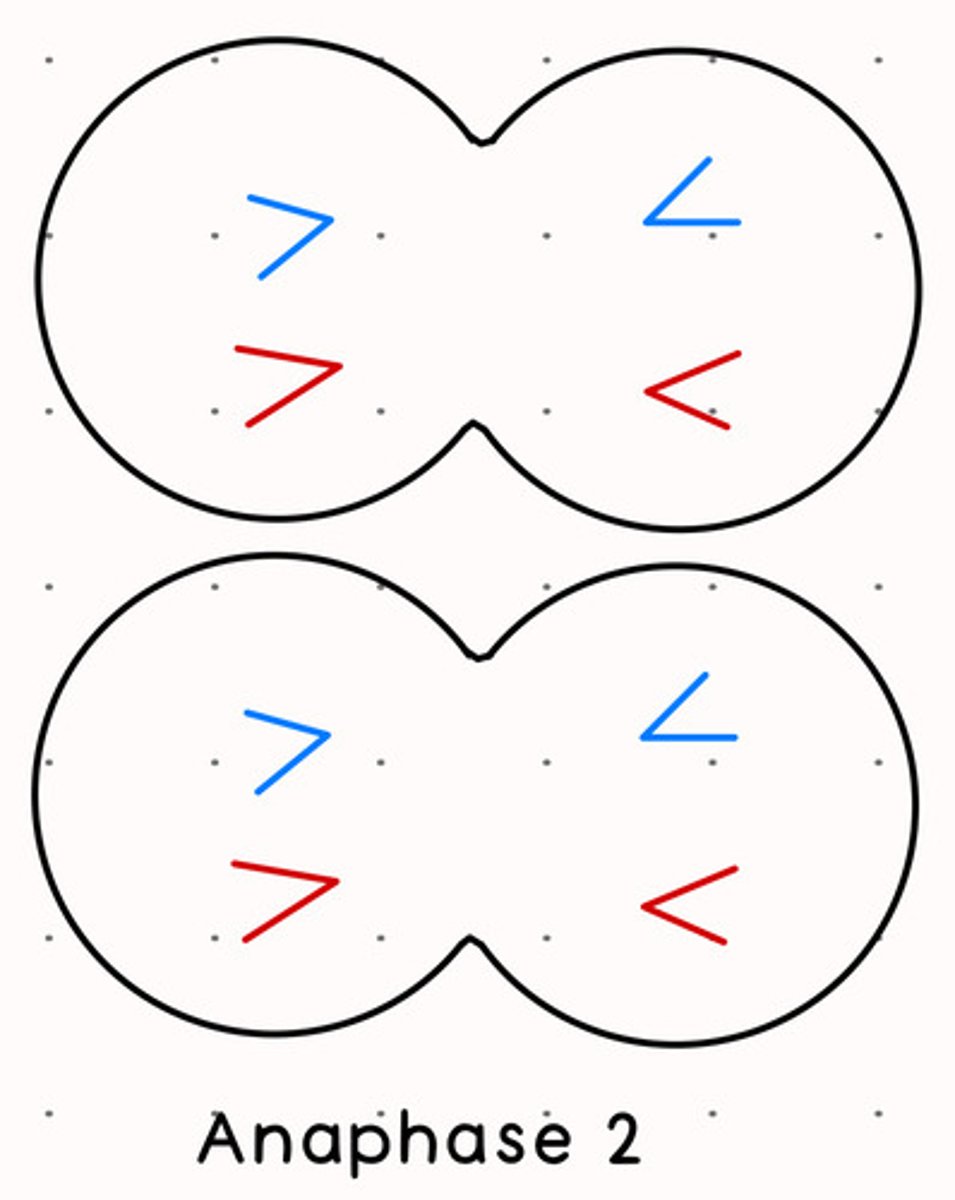
Independent Assortment
generates new haploid sets of chromosomes
The info in each haploid gamete from meiosis depends on...
the alignment of the chromosomes during anaphase
Homologous chromosomes are not/are identical
are not
Crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
Euploidy
complete haploid sets of chromosomes are present
Aneuploidy
having one or more extra or missing chromosomes leading to an unbalanced chromosome amount
Trisomy
3 copies of a chromosome
Monosomy
2n-1
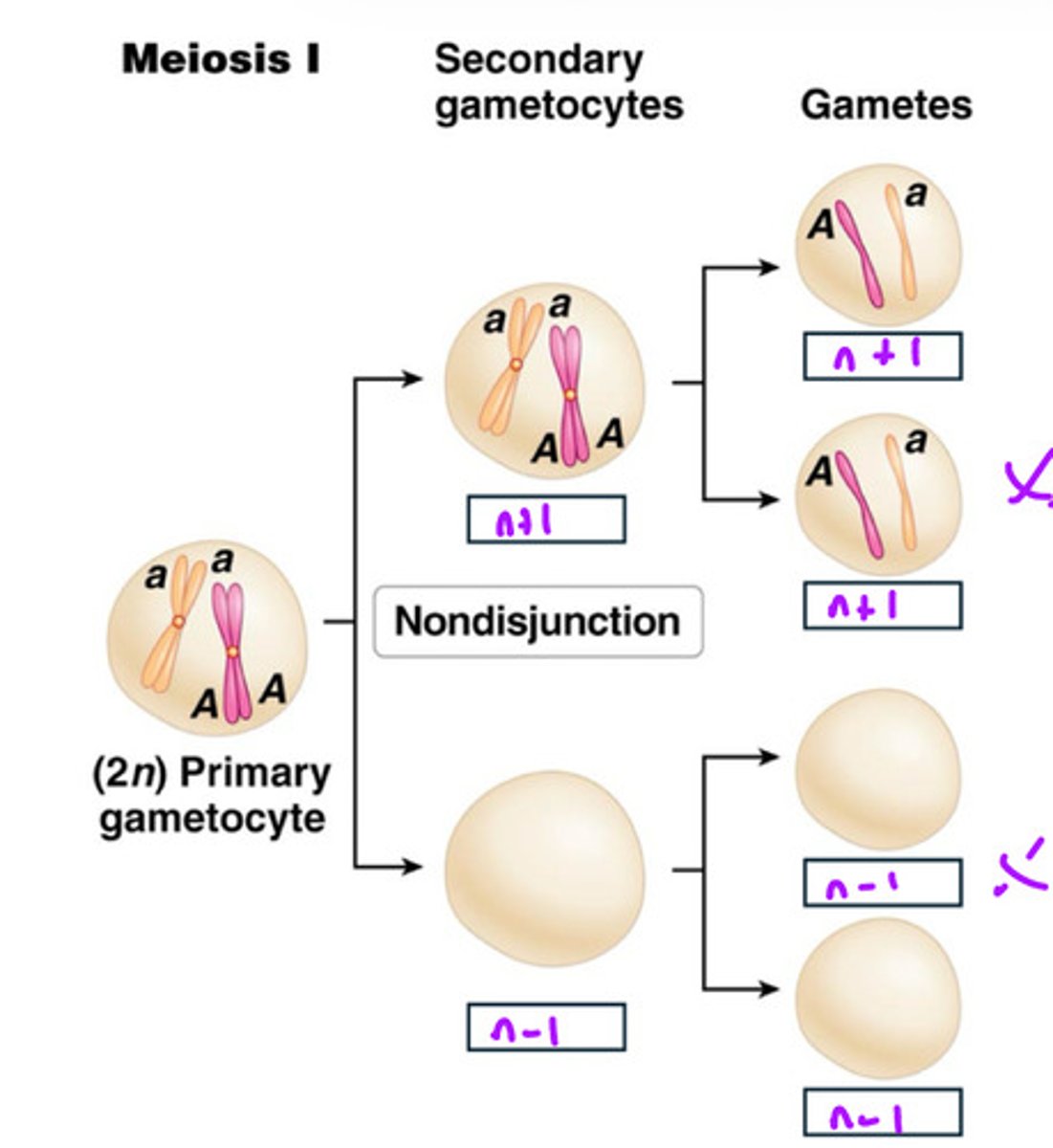
Nondisjunction
Failure of homologs or sister chromatids to separate into different cells
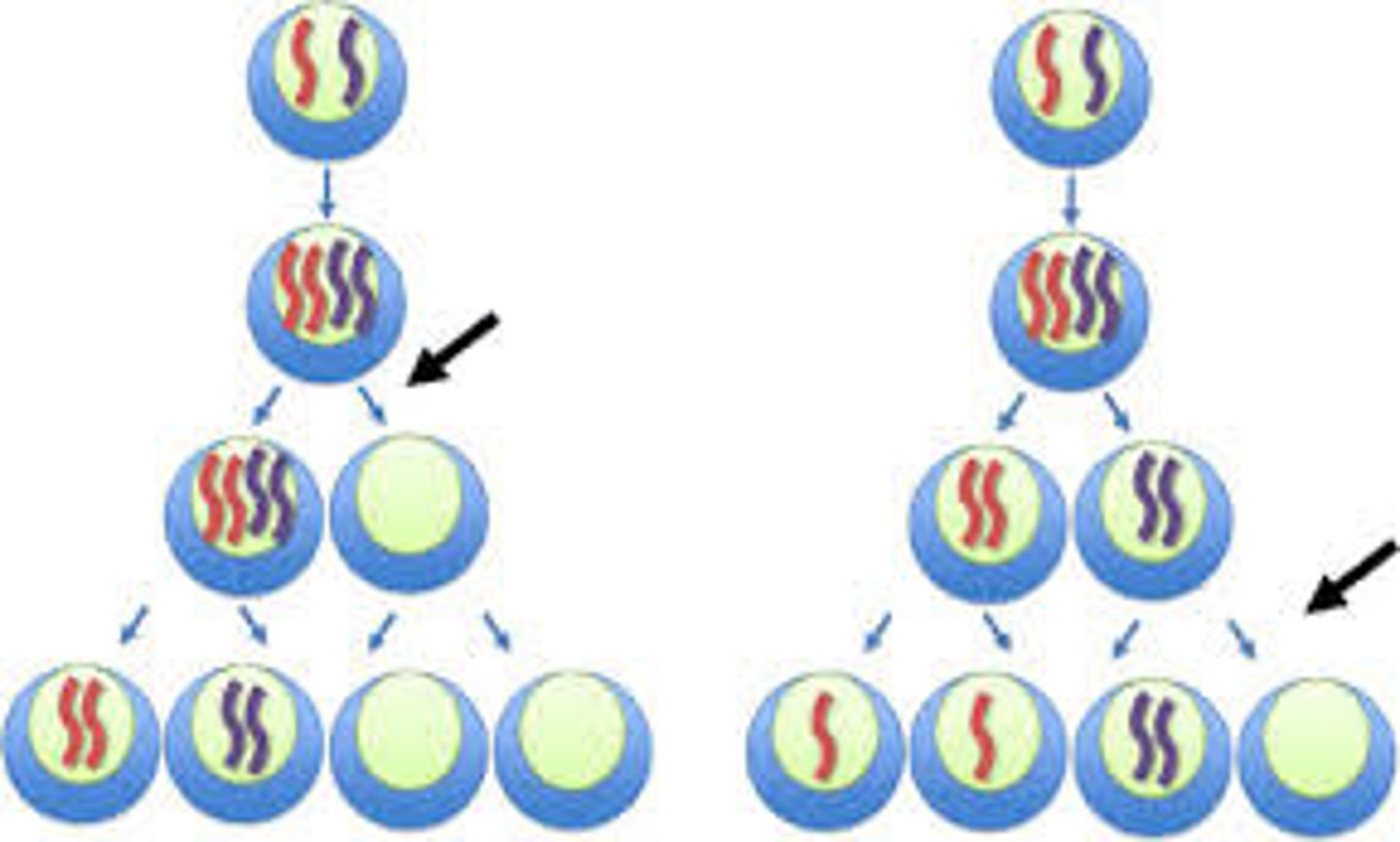
Meiosis I nondisjunction
results in a greater amount of empty cells
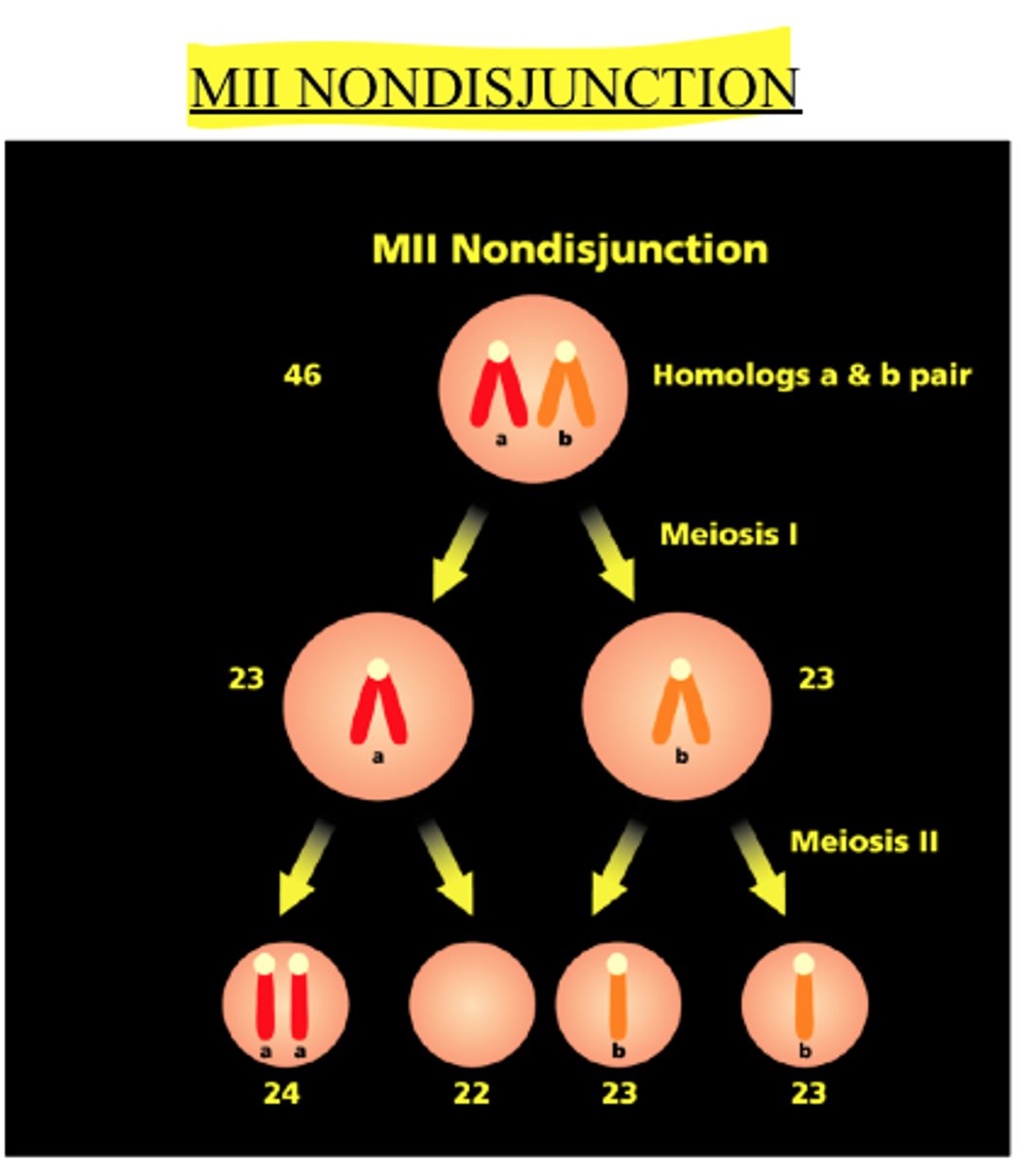
Meiosis II Nondisjunction
Nondisjunction occurring during the second meiotic division.
True-breeding
term used to describe organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves if allowed to self-pollinate
Hybridized
Crossing 2 true breeding organisms to get a sort of "intermediate"

True-breeding lines are...
homozygous for a particular allele