Lecture 10- Classical Greek Art
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Timeline: Mycenaean
Beginning of greek culture
Developed the first greek language
Established the greek religious traditions, common in greek mythology
Original forms of art and architecture
Victim of bronze age collapse→ dark ages
Timeline: Dark Ages
Began w bronze age collapse until 800 BCE
Timeline: Archaic
800-480 BCE
Transition from monarchical to republican system bc of Polis- city states
Poleis = indp from each other but maintained diplomatic relations with each other and other non-greek countries
Over 100 poleis
Timeline: Classical
480-323 BCE
Alliance of poleis against Achamenid empire
Greco persian wars
Early Classical
High Classical
Late Classical→ Hellenistic
Timeline: Hellenistic
323-31 BCE
General facts abt ancient greek art
contains some visual traditions of which go all the way back to the minoans
by the end of the archaic period, greek artists can build architectural decoration if required to sculpt realistic human figures with naturalistic body language and movements and to paint pottery with equally convincing figures moving in the illusion of a 3D space

Ancient Greek Art: Archaic Art and Architecture- Three Revelers
Naturalistically posed bodies
Movement
vessel - looks like a vase
Figures are in proportion
even tho it looks like the figures are in movement, they are still in proportion, indicating a high level of skill

Ancient Greek Art: Archaic Art and Architecture- Anavysos Kouros, from Anavysos, Attica, c. 530 BCE
kouros
predominant large scale free standing sculpture type
one of the most naturalistic looking kouros figures that we have
looks like a real human body
smirking, archaic smile
Made towards the end of the archaic period
High degree of naturalism
Anatomy and musculature of human body
Art is beginning to imitate nature
Posture is stiff but still hint of movement
Looks like he’s about to take a step forward
Ancient Greek Art: Archaic Art and Architecture- Kouros
young, nude male that were made to serve as grave markers or votive figures for the gods
Ancient Greek Art: Archaic Art and Architecture- Aim of greek art
art = imitates nature
greater move towards naturalism

Ancient Greek Art: Archaic Art and Architecture- First Temple of Hera, Poseidonia, Italy, c. 540 BCE
Greek colony in Italy: Poseidonia
Hera: greek goddess
Ancient Greek Art: Early Classical Period
480 to 450: Transitional Period from archaic period, peak of archaic art AJA early classical period
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- Doric
archaic period
most simple
chunky column
rests on the stylobate, which rests on the stereobate
capital
2 parts: echinus and abacus
joins column to the entablature
entablature
architrave
frieze
metope
triglyph
cornice
pediment
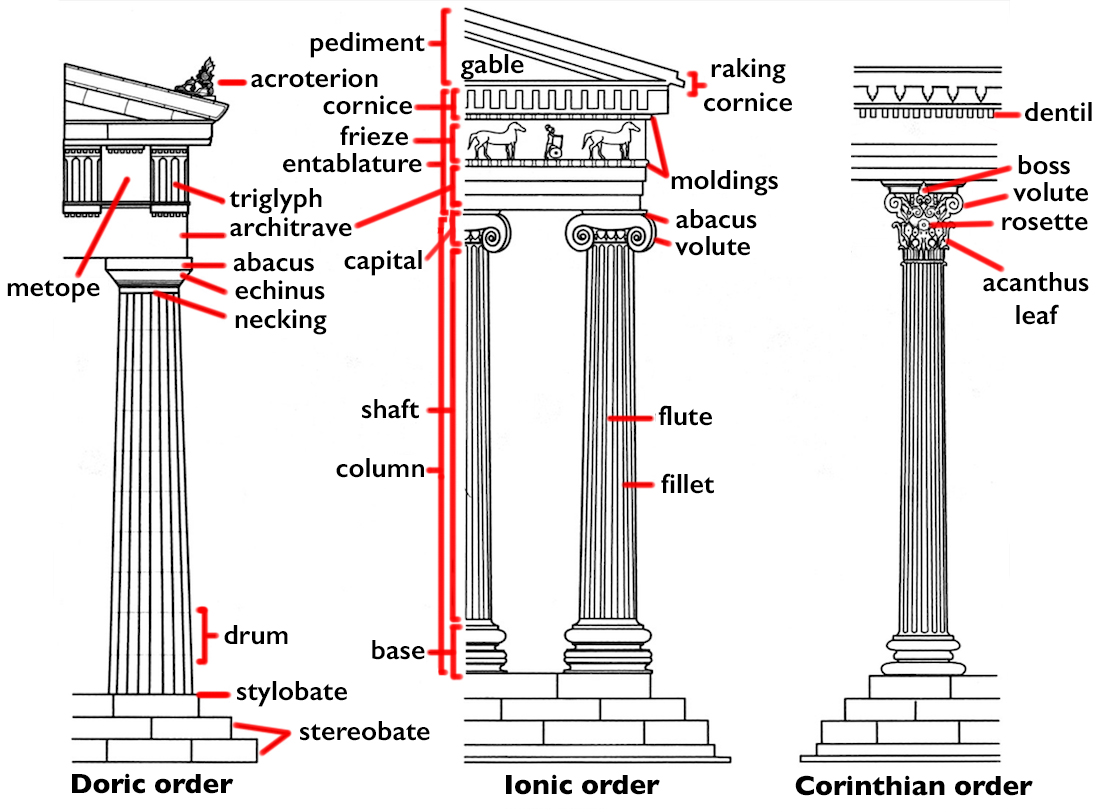
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- Orders
a design system that governs every aspect of a building’s plan, elevation, and decoration
distinguished based on the columns’ capitals
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- Ionic
archaic period
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- Corinthian
more depiction of nature
most complex
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- External Elevation
plan for the appearance, construction, and proportion of the building’s exterior facade
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- Echinus
part of the capital
circular base
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- Abacus
part of the capital
square top part
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- Architrave
beam that lies on top of the column
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- Cornice
upper most strip of molding that lies on the entablature
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- Frieze
almost always consists of alternating triglyphs
between the triglyphs are the metopes
metopes usually contain sculptural relief
Ancient Greek Art: Three Orders of Ancient Greek Architecture- Pediment
triangular space
usually contains more depictions of sculptural relief decorations
Ancient Greek Art: Early Classical Period- Temple of Aphaia
doric columns
East and west pediments contain sculptures from the Sacking of Troy
Center: sculpture of the goddess of athena
Each side of her are sculptures of decreasing size
Crouching archer
Dying warrior
Hierarchical scale used
Athena, goddess, is slightly bigger than the others
Originally painted
Pristine whiteness we associate w greek art is actually false
Polychrome
Visual impact
Allows ppl to see the level of detail carved into the figures
Why significant?
Gives scholars more technical insight on how colors were applied→ preservation treatments
In addition to form, colored was valued as a way to convey meaning for greeks
Harmony and simplicity in greek art
Showed visual drama and realism through color
Corrects centuries old bias of art misconceptions associated with pristine whiteness x purity in greek art
Ancient Greek Art: Early Classical Period- Temple of Aphaia- Polychrome
Polychrome: painted, printed, or decorated in several colors for a decorative effect
Symbolism
Distinguished gods from mortals
Making ppl stand out via patterns and levels of details
Tells a narrative

Ancient Greek Art: Early Classical Period- Kritios Boy, from Acropolis, Athens
Contrapposto
Represents last of kouros tradition and leads way to art displaying new movement of body
New form of posture compared to archaic art
Right hip slightly lowered
weight = mostly shifted onto left leg
Shoulders are slightly lowered
Human looking pose
Physics of human body is detailed in this pose
realism
Still nude male, but more relaxed pose
Subtle rounded transitions instead of hard planes
More lifelike and naturalistic visual
Greater degree of naturalism → hallmark of development of sculpture
Mimesis
Modeling
Humanism
Ancient Greek Art: Early Classical Period- Contrapposto
italian for counterpoise, a posture of the human body that shift most weight onto one leg, suggesting ease and potential for movement
Ancient Greek Art: Early Classical Period- Mimesis
Imitation of reality in art
Emphasized humanism
Ancient Greek Art: Early Classical Period- Modeling
sculptural treatment of the figure’s form— how the artist shapes and transitions the surfaces to create volume and the illusion of flesh, bone, and muscle beneath the skin
Ancient Greek Art: Early Classical Period- Humanism
Man is the measure of all things
Central emphasis of human reasoning, individuality, and potential rather than the gods and supernatural forces
Celebrated for its beauty

Ancient Greek Art: Early Classical Period- Artemision Zeus, or Poseidon, from the Sea near Cape Artemision, c. 460-450 BCE
Looks like he’s doing yoga
Weight slightly shifted towards front leg
Moment right before poseidon/zeus throws a weapon
Moment of the most potential→ gives the sculpture a pent up energy
Empty eyesockets
Originally inset with bone
Bronze became favored medium for sculpture
Allowed for greater naturalistic detail in sculptures cuz it is less fragile
Freedom came with the use of bronze
better depiction of human body and humanism
Bronze sculpture also commonly painted
Color is used to aliven the artwork
greater strength and versality allowed humans to be depicted in greater detail
Inset
Keypoint of bronze sculpture
Allowed new exploration of human form
Human forms are now depicted in greater detail
More naturalistic and better representation of greek humans
Now bronze is now the new medium of sculpture
Ancient Greek Art: Early Classical Period- Inset
Inset: technique where a separate object, material, or section is set into a larger surface or framework
Ancient Greek Art: High Classical Art and Architecture
alliance of greek poleis AKA city states defeated the invading Persian Achaemenid army in decisive battles
athens emerged as the leader of the greek world
center of greek art and culture
restoration and rebuilding of athens, which had been sacked by the persians in 480 BCE, embody the spirit of humanism:
emphasis on order, symmetry, and balance
consideration of the veiwer’s experience
the use of naturalism, mathematical proportions, and idealized figures to represent harmony and perfection
Ancient Greek Art: High Classical Art and Architecture- Age of Pericles
named after the powerful statesman, Pericles, who came to power in Athens around 461 BCE
promoted arts, literature, and philosophy in Athenian culture
Pericles = proponent of democracy (only for male citizens)
most important project he took on was the rebuilding of the parthenon on the athenian acropolis

Ancient Greek Art: High Classical Art and Architecture- Age of Pericles: The Acropolis and Parthenon
manifests the importance of humanism
ritual center of Athens that was devoted to Athena
rebuilt by Pericles
central piece = parthenon
designed by Iktinos and Kallikrates
project overseen by Phidias
doric temple w some elements of the ionic order also incorporated
ionic elements that we see
continuous inner frieze
opisthodomos
rectangular temple surrounded by a peristyle
within peristyle, you have rooms of the temple
main space = cella
smaller space that flanks it= opisthodomos
cella contained a massive statue of Athena made out of ivory and gold
topped by a marble tiled wooden roof
highly advanced mathematical measurements of the parthenon’s architecture
emphasis on balance, order, and symmetry
humanism
barely any straight 90 degree angles or lines because Iktinos and Kallikrates wanted to make the parthenon seem like it was perfectly made; optical illusion
each column has a slight bulging in the middle called entasis
gives the impression that the structure is rising above the ground rather than sitting static or worse, drooping
3 main sculptural groups- more geared towards exemplifying athenian power and dominance and hegemony (dominance of one group over others)
metopes
depicted scenes from Greek mythology
common portrayal of greeks or their divine allies like Athena, overcoming peoples that they perceive to be barbaric or uncivilized
thought to be a rep of the greco-persian wars
pediments
west side:
mythological contest btwn the god Poseidon and the goddess Athena who were competing to see who would become the patron god of athens
this contest was said to taken place on the Acropolis where it’s then celebrated in the west pediment
east side:
birth of athena
popped out of zeus’ head in full armor and fully grown
each pediment celebrates athena
her approval was important for continued prosperity
ionic frieze
continuous scene
depicts pan Athenaeia, which was thought to be the most important event because it’s a festival that celebrates Athena’s bday
dated all the way back to the Archaic period
most sacred point: pan-athenaic procession
large number of people walking in procession bringing offering and gifts to athena
emphasizes athenian dominance
most powerful of the city states
celebration of the height of athenian power
Ancient Greek Art: High Classical Art and Architecture- Age of Pericles: The Acropolis and Parthenon, Opisthodomos
ionic
set of inner columns
used as a treasury for the remainder of the gold that he plundered from the alliance of city states
Ancient Greek Art: High Classical Art and Architecture- Age of Pericles: The Acropolis and Parthenon, Peristyle
peristyle: row of columns
Ancient Greek Art: High Classical Art and Architecture- Age of Pericles: The Acropolis and Parthenon, Entasis
bulging center of a column, constructed to correct the optical illusion that may otherwise make the column’s shaft appear to curve inward