Cell Transportation and Membrane
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Osmosis
Movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from high to low water concentration.
Why Cells Are Small
Smaller cells have higher surface area-to-volume ratio allowing faster nutrient and waste exchange.
Function of Cell Membrane
Controls what enters and leaves the cell, maintaining homeostasis.
Cell Theory
States that all living things are made of cells.
Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes flexible, dynamic membrane structure made of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Made of two layers of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
Cholesterol Function
Regulates membrane fluidity; prevents stiffness at low temps and excess fluidity at high temps.
Integral vs Peripheral Proteins
Integral span the membrane for transport; peripheral sit on the surface and act as enzymes or anchors.
Glycoproteins and Glycolipids
Aid in cell recognition and communication (e.g., CD4 glycoprotein targeted by HIV).
Diffusion
Net movement of particles from high to low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
Energy Requirement of Diffusion
No energy required; it is passive transport.
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive movement through membrane proteins for large or polar molecules.
Factors Affecting Diffusion Rate
Distance, temperature, solvent density, molecular size, membrane properties, concentration gradient.
Importance of Diffusion
Allows oxygen and nutrients in, and carbon dioxide and waste out of cells.
Passive Transport
Movement from high to low concentration without energy use.
Types of Passive Transport
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis.
Simple Diffusion Molecules
Small, nonpolar molecules like O₂ and CO₂.
Facilitated Diffusion Molecules
Large or polar molecules like glucose or ions.
Osmosis and Aquaporins
Water moves across membranes quickly through aquaporin channels.
Active Transport
Movement from low to high concentration using ATP energy.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate; releases energy when third phosphate bond is broken.
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Moves 3 Na⁺ out and 2 K⁺ in using ATP.
Bulk Transport
Movement of large materials using vesicles (endocytosis and exocytosis).
Endocytosis
Cell engulfs materials into vesicles.
Types of Endocytosis
Phagocytosis (solid intake), pinocytosis (fluid intake), receptor-mediated (selective uptake).
Exocytosis
Releases materials from a cell, removes waste or secretes proteins.
Exocytosis in Plants
Releases polysaccharides to build cell walls.
Simple Diffusion Summary
High to Low; No energy; No protein; Example: O₂, CO₂.
Facilitated Diffusion Summary
High to Low; No energy; Yes protein; Example: Glucose.
Osmosis Summary
High to Low (water); No energy; Yes (aquaporin); Example: Water.
Active Transport Summary
Low to High; Yes energy (ATP); Yes protein; Example: Na⁺/K⁺ pump.
Endocytosis Summary
Into cell; Yes energy; No protein; Example: Amoeba eating.
Exocytosis Summary
Out of cell; Yes energy; No protein; Example: Polysaccharide export.
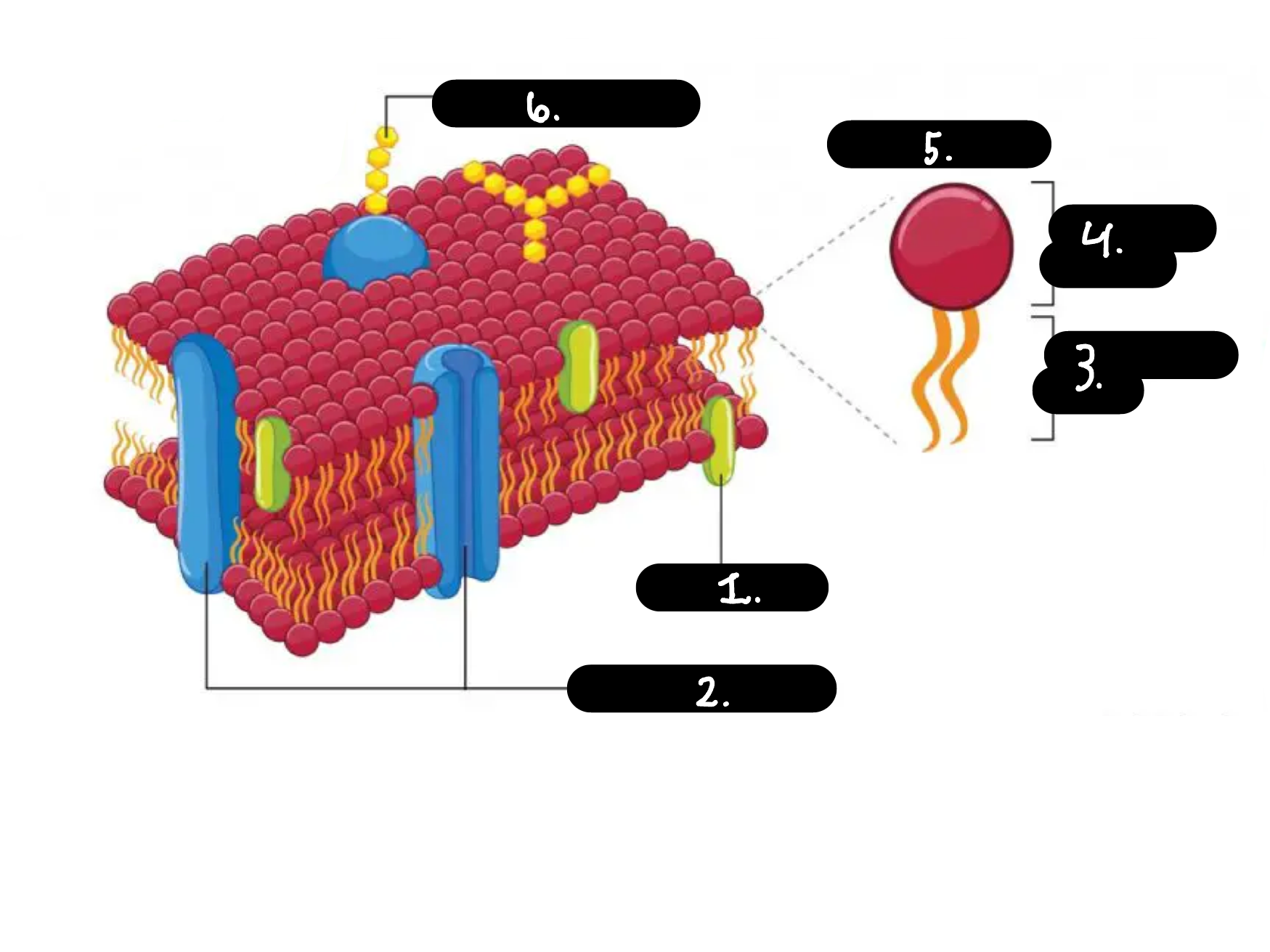
What is 1
Chokesterol
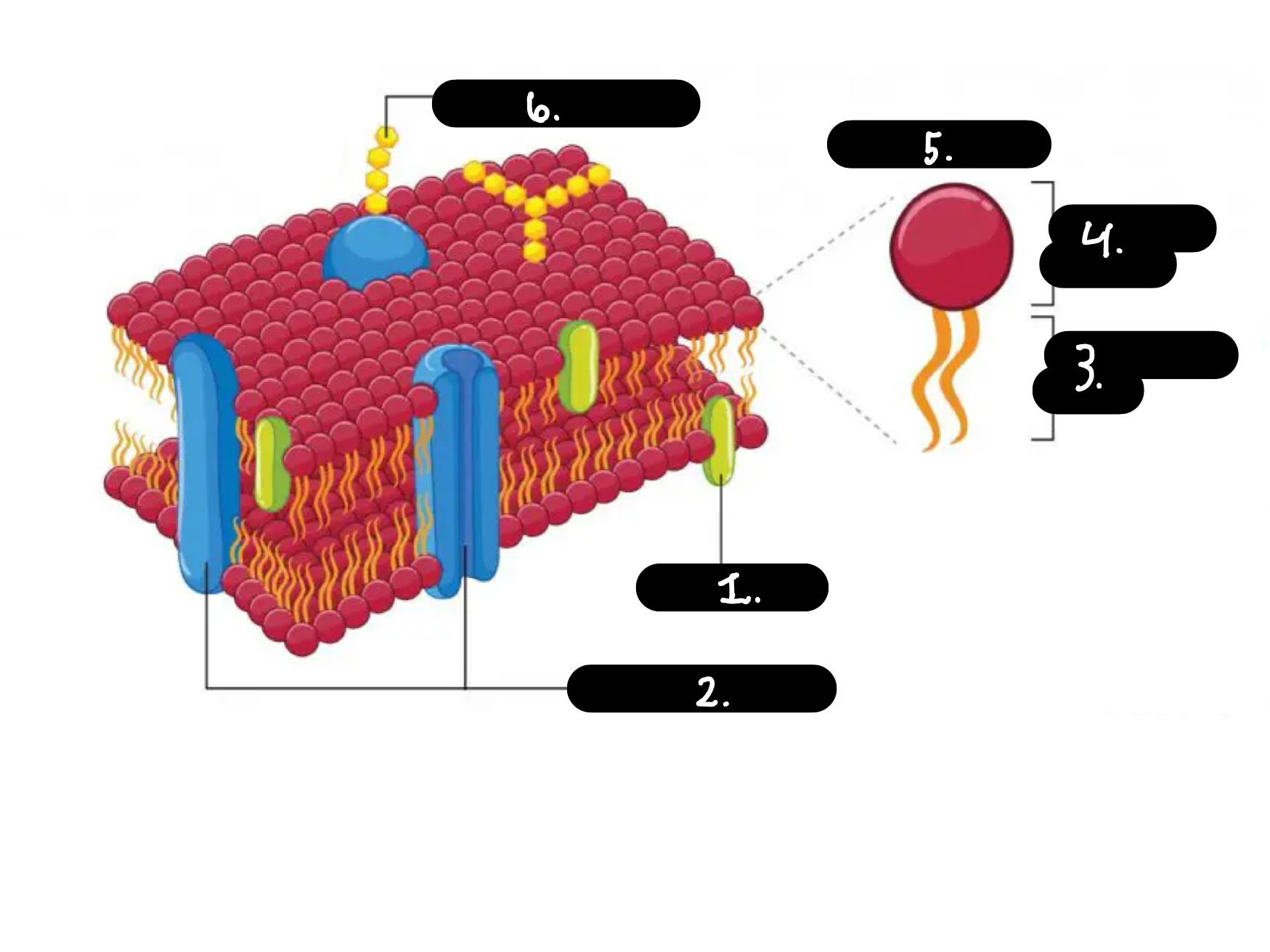
What is 2
Membrane proteins
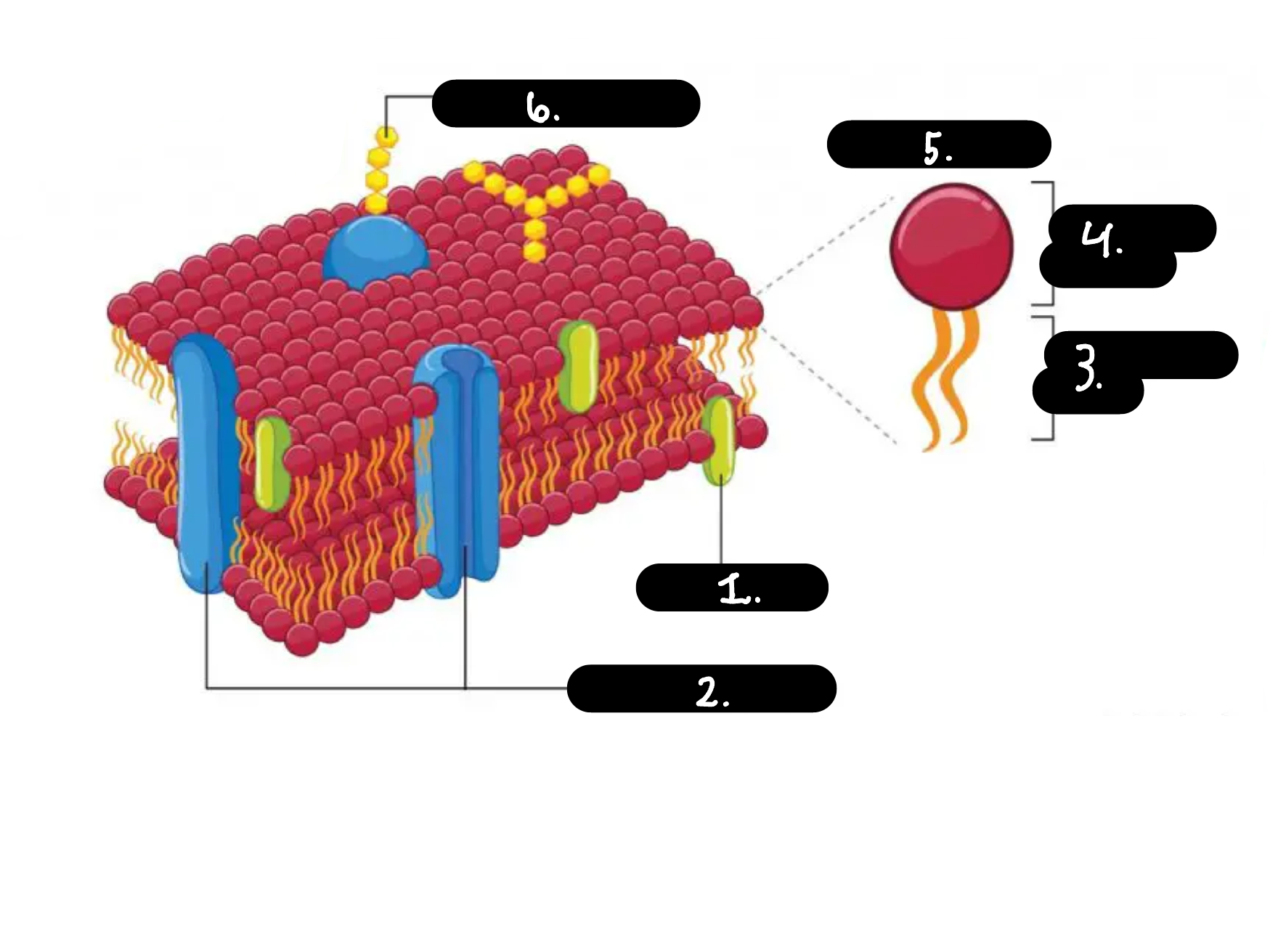
What is 3
Hydrophobic tail
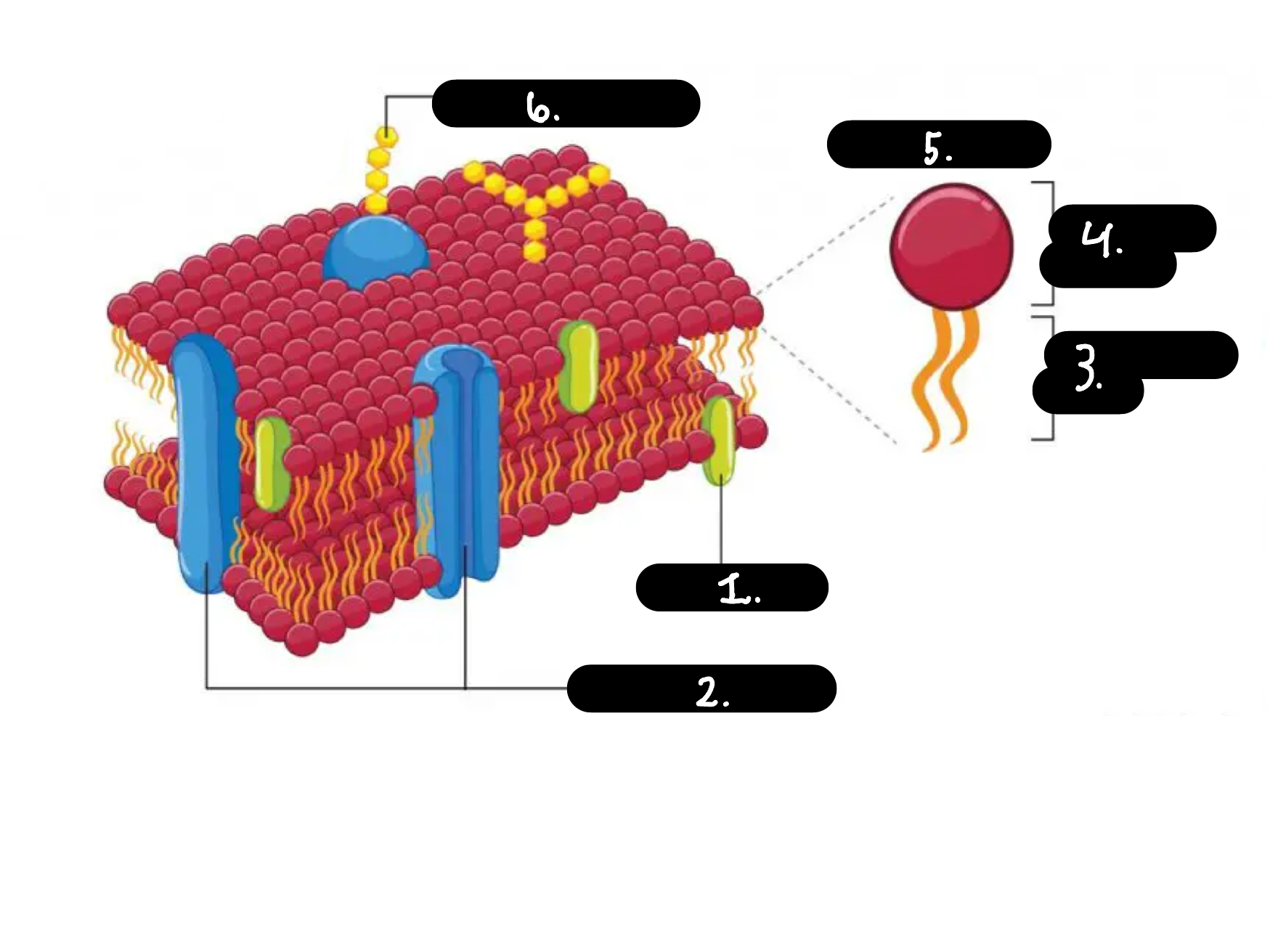
What is 4
Hydrophilic head
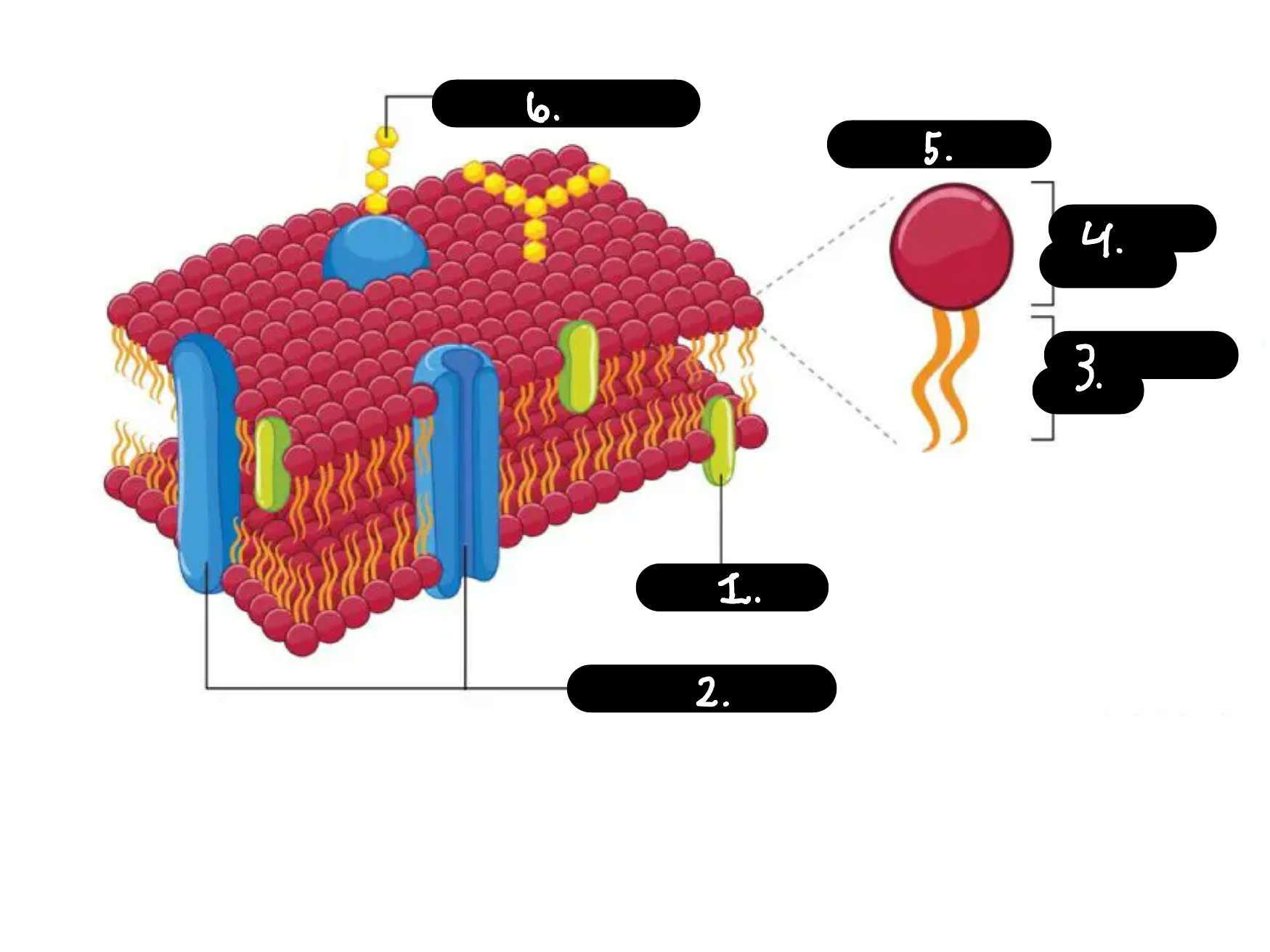
What is 5
Phospholipid
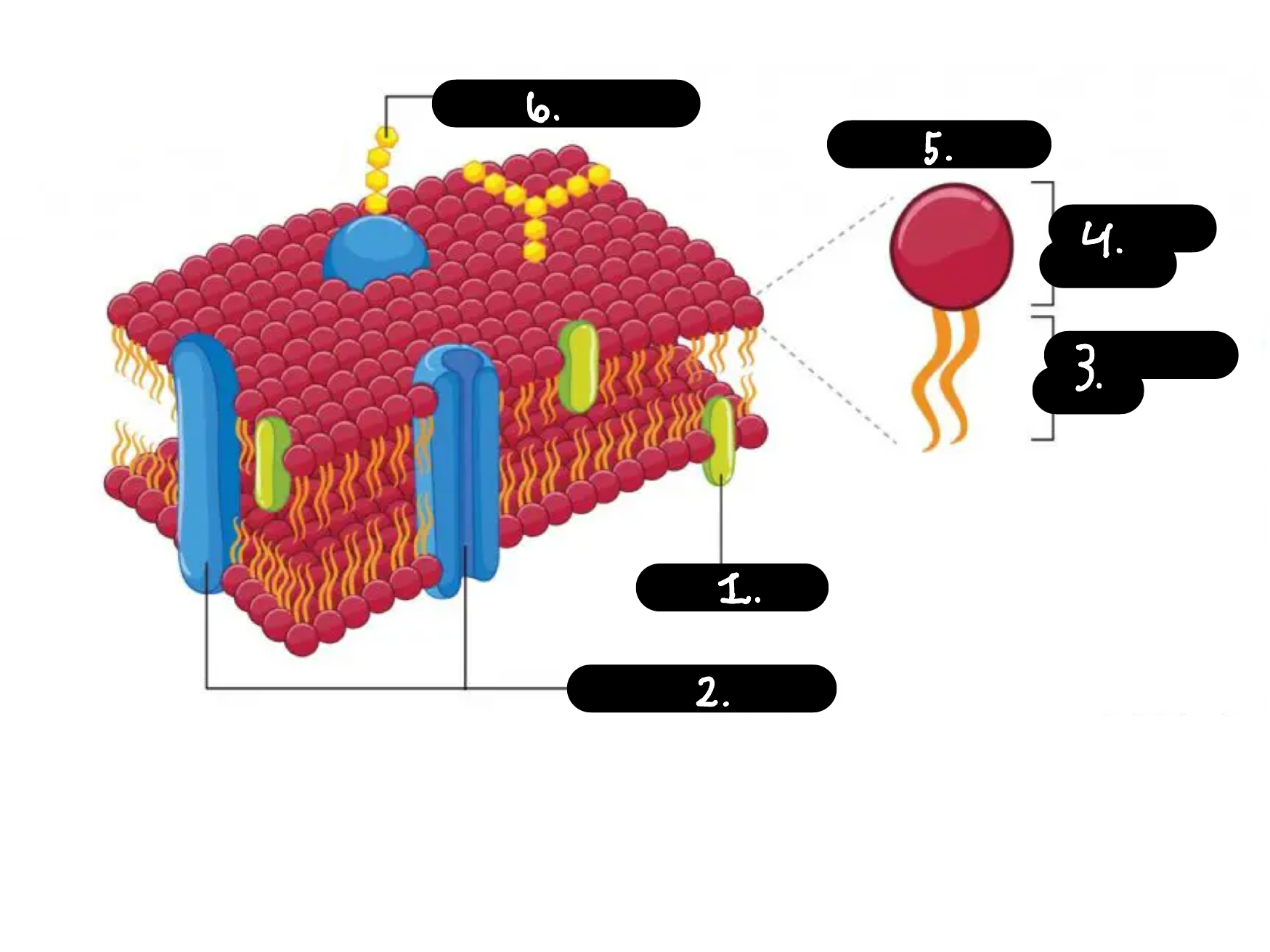
What is 6
Carbohydrate chain
Molecule motion
Constant random motion.
Concentration gradient
Difference in concentration across a space.
Equilibrium
Equal concentration throughout a space.
Permeable
Allows all substances through.
Solution
Solute + solvent.
Hypotonic
Lower solute concentration.
Hypertonic
Higher solute concentration.
Isotonic
Equal solute concentration.
Hypo/Hyper/Iso prefixes
Refer to solute concentration.
Hypertonic environment
causes cells to lose water through osmosis
Hypotonic environment
causes water to move into cells through osmosis, leading to swelling and potentially bursting in animal cells (cytolysis) or turgor pressure in plant cells
Turgor pressure
Water pressure in plant cells.
Cytolysis
The animal version of Turgor pressure
The SHRINKING of plant cells when water leaves so the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall is called
PLASMOLYSIS