Introduction to ANOVA: One-Way and Two-Way Analysis of Variance in Applied Statistics
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What is the main objective of using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)?
To test for differences among the means of several groups.
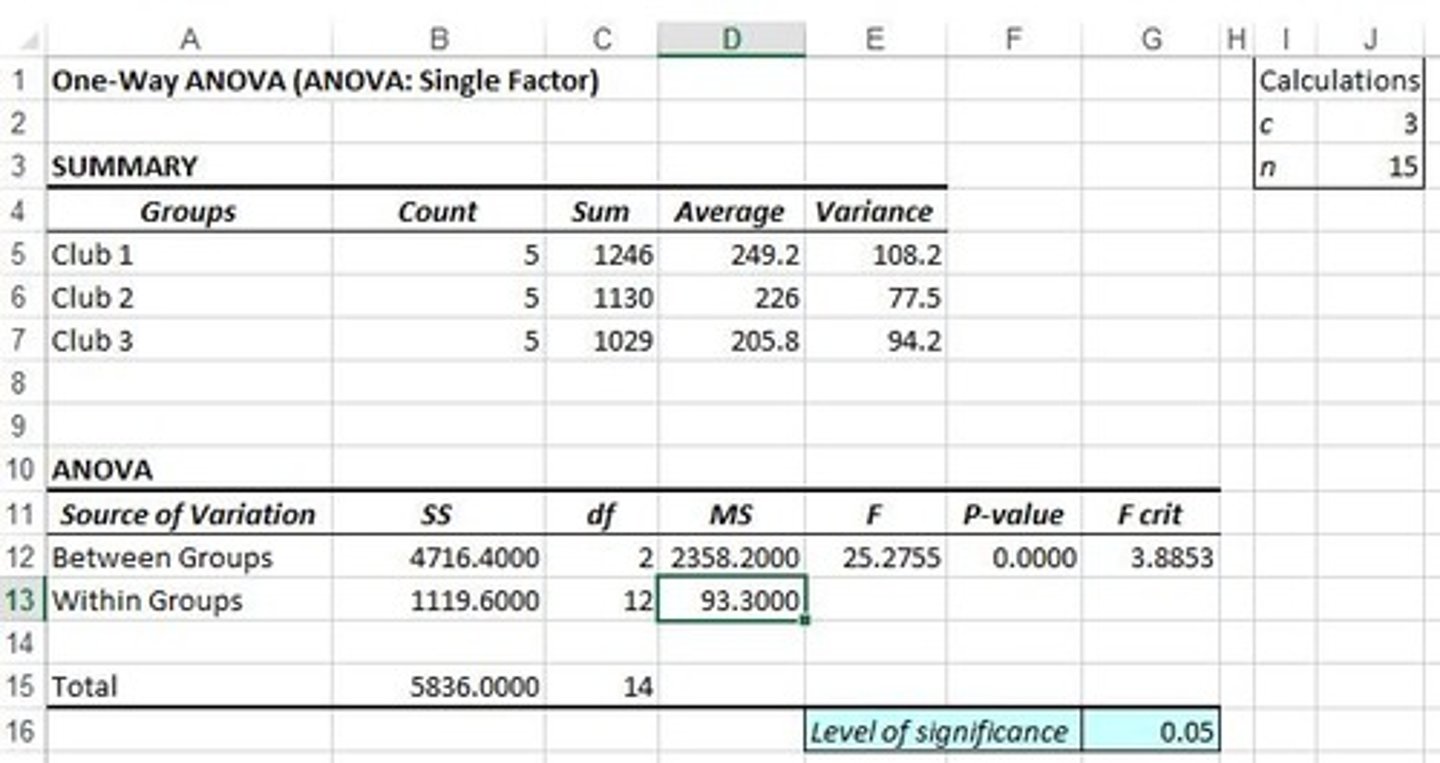
What type of experimental design involves random assignment of subjects to groups?
Completely Randomized Design.
What are the assumptions of one-way ANOVA?
Populations are normally distributed, have equal variances, and samples are randomly and independently selected.
What does the null hypothesis (H0) state in one-way ANOVA?
All population means are equal; there is no factor effect.
What does the alternative hypothesis (H1) state in one-way ANOVA?
At least one population mean is different; there is a factor effect.
What is the formula for total variation (SST) in ANOVA?
SST = SSA + SSW, where SST is Total Sum of Squares, SSA is Sum of Squares Among Groups, and SSW is Sum of Squares Within Groups.
What is the purpose of the F-test in ANOVA?
To compare the variance among group means to the variance within groups.
What does a significant F-statistic indicate in ANOVA?
It suggests that at least one group mean is different from the others.
What is the formula for Mean Square Among Groups (MSA)?
MSA = SSA / (c - 1), where c is the number of groups.
What is the formula for Mean Square Within Groups (MSW)?
MSW = SSW / (n - c), where n is the total number of observations.
What is the decision rule for rejecting the null hypothesis in ANOVA?
Reject H0 if FSTAT > Fα; otherwise, do not reject H0.
What does the Levene Test assess in the context of ANOVA?
It tests for homogeneity of variances across groups.
What is the Tukey-Kramer method used for in ANOVA?
To perform multiple comparisons between group means after finding significant differences.
What is the significance of partitioning variation in ANOVA?
It helps to understand how much variation is due to the treatment (factor) and how much is due to random error.
What is the role of experimental design in ANOVA?
It is the plan used to collect data and control factors of interest.
What is the difference between one-way and two-way ANOVA?
One-way ANOVA tests one independent variable, while two-way ANOVA tests two independent variables and their interaction.
What does the term 'interaction effect' refer to in two-way ANOVA?
It refers to how the effect of one independent variable changes depending on the level of another independent variable.
What is the purpose of performing multiple comparisons in ANOVA?
To determine which specific group means are different after finding a significant F-statistic.
What is the grand mean in the context of ANOVA?
The mean of all data values across all groups.
What does the term 'homogeneity of variance' mean?
It means that the variances among the different groups are approximately equal.
What is the significance of the degrees of freedom in ANOVA?
They are used to determine the critical value of F for hypothesis testing.
What is the formula for calculating the Sum of Squares Among Groups (SSA)?
SSA = Σ(nj * (Xj - X)²), where nj is the sample size from group j, Xj is the sample mean from group j, and X is the grand mean.
What does SSW represent in ANOVA?
SSW represents the Sum of Squares Within Groups, indicating variation within each group.
What is the importance of random assignment in experimental design?
It helps to eliminate bias and ensures that the groups are comparable.
What does it mean if the null hypothesis is not rejected in ANOVA?
It suggests that there is no significant difference among the group means.
What is the relationship between F-statistic and variance in ANOVA?
The F-statistic is the ratio of the variance estimate among groups to the variance estimate within groups.
What is the purpose of a One-Way ANOVA?
To determine if there are statistically significant differences between the means of three or more independent groups.
What is the significance level used in the example?
0.05
What does H0 represent in hypothesis testing?
H0 represents the null hypothesis, which states that there is no difference between the group means.
What is the formula for the F-statistic in ANOVA?
FSTAT = MSA / MSW
What does MSA stand for?
Mean Square Between Groups
What does MSW stand for?
Mean Square Within Groups
What is the critical value for rejecting H0 in the example?
3.89
What conclusion can be drawn if FSTAT > Fα?
Reject H0, indicating that at least one group mean is different.
What assumptions must be met to use the ANOVA F test?
Randomness and independence, normality, and homogeneity of variance.
What is the Tukey-Kramer procedure used for?
To determine which specific means are significantly different after rejecting H0 in ANOVA.
What does a significant interaction in a Two-Way ANOVA indicate?
The effect of one factor on the dependent variable depends on the level of another factor.
What are the degrees of freedom for the numerator in a One-Way ANOVA?
c - 1, where c is the number of groups.
What are the degrees of freedom for the denominator in a One-Way ANOVA?
n - c, where n is the total number of observations.
What does the term 'homogeneity of variance' refer to?
The assumption that the variances of the different groups are equal.
What is the formula for calculating SSA in One-Way ANOVA?
SSA = Σ(n * (X̄ - X̄overall)²) for each group.
What is the purpose of Levene's Test?
To test the homogeneity of variance assumption in ANOVA.
What is the meaning of 'interaction effect' in Two-Way ANOVA?
An interaction effect occurs when the effect of one independent variable on the dependent variable changes depending on the level of another independent variable.
What is the formula for calculating SSW in One-Way ANOVA?
SSW = Σ(X - X̄)² for all observations.
What does a non-parallel line segment in cell means plots indicate?
The presence of a significant interaction effect between factors.
What is the total degrees of freedom in ANOVA?
n - 1, where n is the total number of observations.
What does the term 'mean response' refer to in ANOVA?
The average outcome for a specific group or condition.
What is the purpose of a normal probability plot in ANOVA?
To assess the normality assumption of the data.
What does 'n' represent in the context of ANOVA?
The total number of observations across all groups.
What is the formula for calculating the Mean Square Error (MSE)?
MSE = SSE / (n - c), where SSE is the sum of squares for error.
What is the effect of unequal sample sizes on ANOVA assumptions?
Unequal sample sizes can seriously affect inferences if variances are also unequal.
What is the main focus after determining a significant interaction in Two-Way ANOVA?
Further analysis will focus on the interaction effects.
What does the term 'cell means plots' refer to?
Graphs that display the means for each combination of factor levels in a Two-Way ANOVA.