Lyba Meiosis Quiz
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Asexual reproduction
reproduction without the involvement of gametes or a partner, produces genetically identical offspring (clones)
Sexual reproduction
a complex process where genetic information from two parents combines to create a genetically distinct, new organism with a unique combination of traits, involves gametes.
somatic cells
any biological cells that can form a body of a multicellular organism, excluding sperm and egg cells
reproductive cells
sperm and egg cells, specialized cells that combine during fertilization to form a new organism
gametes
a mature haploid male or female germ cell which is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote.
parent/daughter cell
original cell that divides to form two or more new cells
zygote
the single cell created when a sperm and an egg fuse during fertilization, forming the first genetically unique individual of a new organism
fertilization
the union of a male sperm and a female egg (ovum) to create a zygote, the first cell of a new individual, and it initiates pregnancy and the development of an embryo
haploid
has a single set of unpaired chromosomes
diploid
two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
synapsis
the fusion of chromosome pairs at the start of meiosis.
homologous
pairing at meiosis and having the same structural features and pattern of genes.
genetic variation
the diversity of DNA sequences within a population, leading to differences in inherited traits
chromosomes
a thread-like structure made of DNA and proteins (like histones) found in the nucleus of cells that carries genetic information in the form of genes.
sister chromatids
two identical strands of a replicated chromosome, joined by a common centromere
chromatin
the material of which the chromosomes of organisms other than bacteria are composed. It consists of protein, RNA, and DNA.
centromere
a specialized region on a chromosome that serves as the attachment point for spindle fibers during cell division, ensuring that genetic material is accurately divided between daughter cells
centrosomes
an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing centre (MTOC) of the animal cell
spindle fibres
protein structure that separates chromosomes during cell division
nucelus
a dense organelle present in most eukaryotic cells, typically a single rounded structure bounded by a double membrane, containing the genetic material.
cytokinesis
the cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis, bringing about the separation into two daughter cells.
oogenesis
the biological process of producing the ovum (egg cell) in females, beginning before birth and continuing through puberty and the reproductive years.
spermatogenesis
process of sperm cell development
egg
a single biological cell with a protective outer covering that can develop into a new individual
sperm
male reproductive cells responsible for carrying genetic material and fertilizing a female egg to start a new pregnancy
karyotype
an individual's complete set of chromosomes, visually represented in a laboratory as an image of a cell's chromosomes arranged in order by size and shape
mitosis
the process of cell division in eukaryotic cells that results in two genetically identical daughter cells from a single parent cell
meiosis
special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome.
polar body
a small haploid cell that is formed at the same time as an egg cell during oogenesis, but generally does not have the ability to be fertilized.
viability
ability to survive or live successfully.
fraternal twins
develop from two separate eggs fertilized by two different sperm during the same pregnancy
identical twins
develop from a single fertilized egg that splits into two, resulting in two embryos with the same genetic material
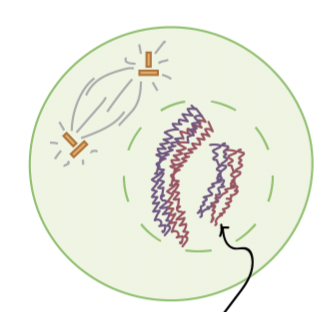
Prophase I
starting cell is diploid (2n=4), homologous chromsomes pair up and exchange fragments (crossing over)
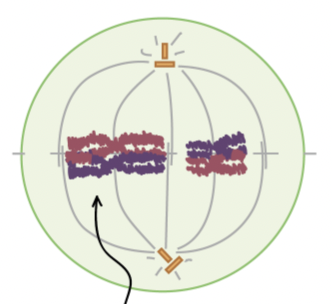
Metaphase I
homologue pairs line up at the metaphase plate
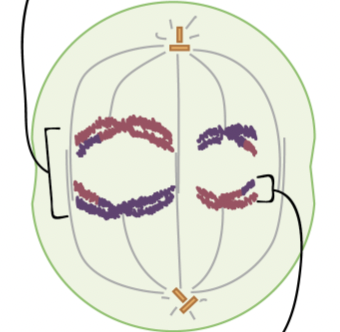
Anaphase I
homologues separate to opposite ends of the cell, sister chromatids stay together
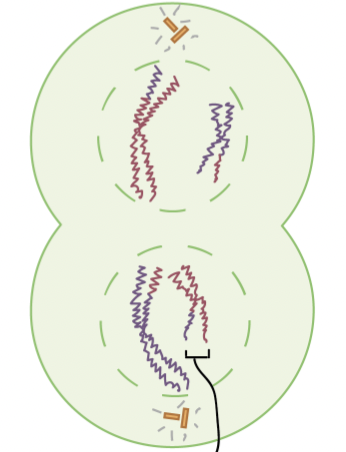
Telophase I
newly forming cells are haploid (n=2), each chromosome has two (non-identical) sister chromatids
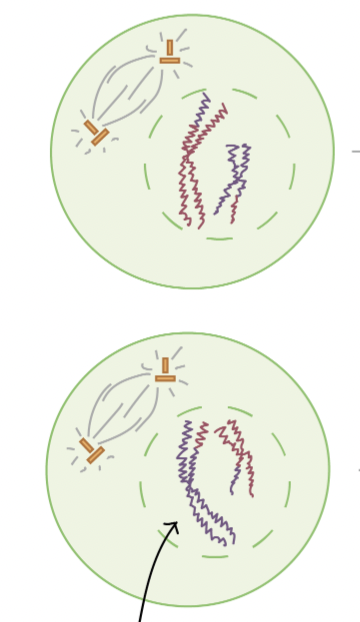
Prophase II
starting cells are the haploid cells made in meiosis I, chromosomes condense
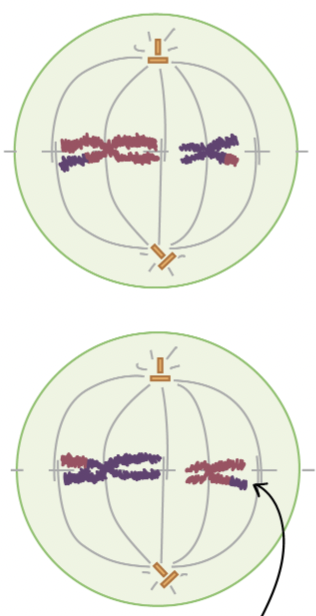
Metaphase II
chromosomes line up at metaphase plate
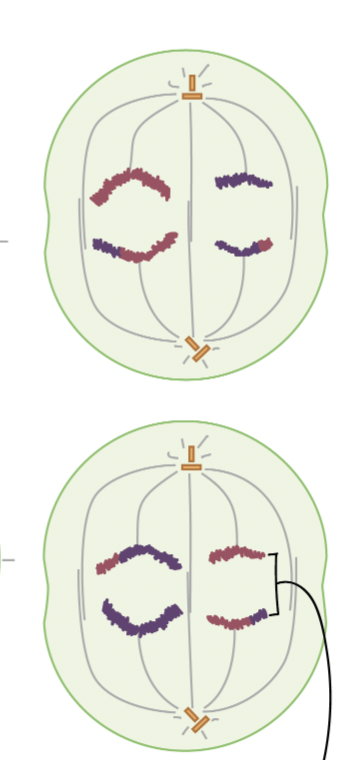
Anaphase II
sister chromatids separate to opposite ends of the cell
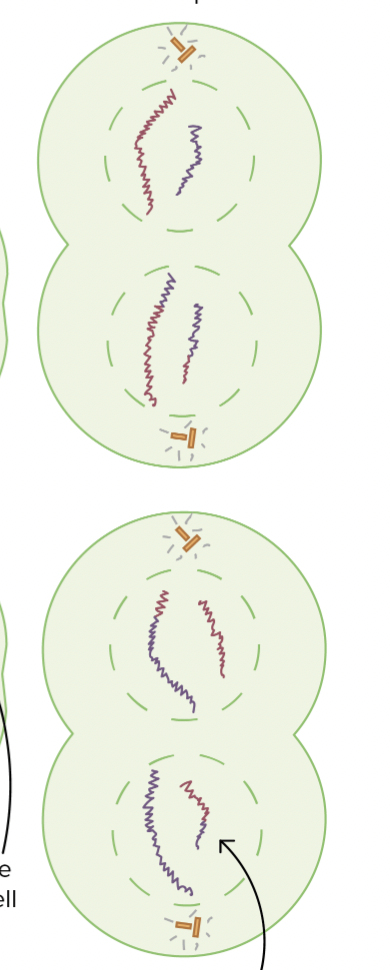
Telophase II
newly forming gametes are haploid, each chromosome has just one chromatid