Lecture 10- Quality & Maturity Indices Harvesting Methods
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
what is quality of fruits and veggies
Quality of fruits and vegetables is a combination of various physico-chemical and nutritional characteristics that give them value or wholesomeness as a food item
does quality apply same to all fruits and veggies
Quality can only be defined for a specific commodity and for a specific use
quality is fruits and veggies specific
what are the different components that go into quality?
appearance or visual/esthetic factors
texture or mouth/finger feel factors
flavour (Taste &Smell)
Nutritive value
safety or antinutritional factors
explain appearance and quality
relates to size, shape, color, gloss, defects
explain texture or mouth/finger feel factors AND quality
firmness, hardness, softness, juicyness, toughness, fibrousness, grittyness
explain flavour and quality
Subjective and objective evaluations
explain nutritive value and quality
protein, carbohydrate, fat, vitamins, minerals, etc
what are different types of defects in quality
morphological defects
physical defects
mechanical damages
physiological defects
pathological defects
entomological defects
MMEPPP
explain morphological defects
Sprouting of potatoes, onions & garlic
Elongation & curvature of aparagus
Seed germination in tomatoes & peppers
explain physical defects
Shriveling & wilting as a result of water loss
explain mechanical damages
Puncture, cuts, crushing & abrasion
explain physiological defects
Chilling & freezing injury
Internal breakdown
explain pathological defects
Fungal & bacterial decay (blue & grey mold etc.)
explain entomological defects
Damages caused by insects & pests etc.
who is concerned with quality in the produce chain
Grower, shipper, wholesaler, distributor, retailer, consumer
explain different perspective of qualitues of consumers, everyone, and plant breeders
Appearance factors: everybody’s concern
Plant breeders/farmers: Priority is yield & resistance to disease
Consumer: good appearance, firm, good flavor & nutritive value
why are quality factors important
setting standards specifications
explain grading in US vs Canada
USDA: Quality standards
Fancy, Choice and Standard
Canada:
Grade A, B, C
what are factors that influence quality
genetic factors
environmental factors
temperature
light
cultural factors
explain how genetic factors influences quality
cultivars, rootstocks, selection of specific varieties, GMO
explain environmental factors influence quality
climate: Temperature, Light, Rainfall, Irrigation, Wind
cultural: Soil type, Mineral nutrition, Water supply, Pruning, Thinning, Application of Pesticides, Growth regulators
rainfall
soil texture
wind factors
explain temp and quality
every commodity has a tolerance range for optimal growth
Within TR, higher the temperature, faster the growth
higher temperatures…
earlier the harvest
what is temperature summation
Indicator of harvest maturity (degree-day – Heat Unit)
what is the mean heat unit
(Mean temperature – Reference temperature) (F) x Time (h or day)
expressed as degree hr OR degree-days
what is degree hour
accumulated heat unit equivalent to the exposure of the crop to one degree above the reference temperature for one hour
what is degree day
exposure at one degree above the reference temperature for one day (24 h)
what are ideal conditions for plant growth
warm days and cool nights
warm days: greater photosynthetic activity – better storage of food reserves
cool nights: lower respiration – lower depletion of stored reserve
what is ideal scenario for tropical fruit?
night temperature ~ day temperature
Produce fruit quality is generally different –higher accumulation during the day and higher depletion of stored reserve during nigh
give example of temp can affect citrus fruits
Oranges from Texas & Florida receive more than double heat units than the ones from California
Quality differences: Florida & Texas oranges are sweeter
explain different components of how light influences quality
duration of light
intensity
quality
explain duration of light and quality
Longer day, shorter nights better than converse
More photosynthetic and less depletory activity
Results are reflected in the composition
explain intensity and quality
Higher the intensity, higher the sweetness and lower the acidity in the fruit
Higher intensity also results in fading of colors
Density of planting influences light intensity
canopy shading?
Tomatoes with deeper red color and cucumbers with deeper green color
explain high intensity plant affects plants
High intensity planting means lower exposure to light and therefore lower photosynthetic activity – lower sweetness
explain quality of light and quality of commodity
important in pigmentation
rex: Purple cabbage or eggplant derive their color from exposure to blue & violet light
what color occurs from direct sunlight
Direct exposure to sunlight will result in green color
explain cultural factors influence quality
mineral nutrition
cultural practices: pruning, fruit thinning, planting: high vs low density
chemical sprays/growth regulators
examples of cultural factors?
pesticides
petroleum oil sprays for citrus pests
abscission preventing
control fruit crop
examples of abscission Preventing?
2,4,5 T (2,4,5 trichloro phenoxy acetic acid)
NAA (Naphthalein acetic acid)
CPA (p-chloro phenoxy acetic acid)
Alar (applied 60-70 days prior to harvest apples)
explain cultural factors- postharvest treatments & quality
storage conditions, fungicides and irradiation
when do you know when right stage to harvest?
can ask three questions:
1. Which parameters can be used?
2. How the parameter is related to the maturity?
3. How it can be used to predict maturity?
definition of optimum maturity?
That stage of maturity at which a commodity has reached sufficient stage of development that after harvesting & post-harvest handling (including ripening) the quality will be acceptable to consumers
phyisico-chemical indicators of ripening of tomatoes?
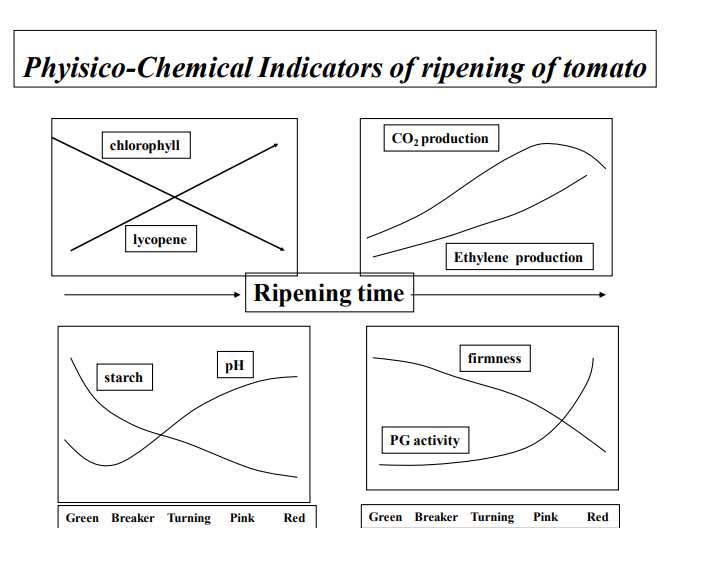
what are some maturity/quality indices?
Elapsed days from full bloom
Meat heat units
Size
Specific gravity
Solidity
Texture properties - firmness, hardness etc Color Chemical tests
chemical tests
what are some chemical tests for maturity/quality indices
Starch,
Sugar
Ascorbic acid,
AIS
Acidity
Enzyme activity
Respiration rate
definition of harvest?
the process of detaching a produce
when harvest should happen?
At proper maturity stage
By proper technique
As rapidly as possible
With minimum damage or loss
Types of harvest?
hand VS mechanical
Hand harvesting ADV. vs DIS
ADV:
Selective pickings
Minimum damage
Minimum capital investment
Output = f (number of people at work)
DIS:
Shortage or labor
Labor srikes costly
Permanent labor force – not feasible
Need efficient labor management
frsh market fruits and veggies are mostly?
hand harvested
when do you mechanized harvesting>
Employed for crops intended for processing
Produce converted to other forms
Physical appearance not an major consideration
Commodity consumed within short time
Commodity is normally needed in bulk lots
ADV for mechanical harvesting
Speed of harvest
Improved conditions for the workers
Reduced labor related problems
what are some incentatives for mechanical harvesting?
Increase cost of manual labor
Decreasing availability of timely labor
Need for high speed-high volume output
DIS of mechanical harvesting
Physical/mechanical damage to the crop
Non selective
Separation of plant debris
Damage to fruit trees during harvesting
Large volume output
Machinery expensive
Social impact
what are the different elements of harvesting
detection
selection
detachment: Mechanical and hand
collection
separation
handling
what are some field considerations for mechanized harvesting
genetic considerations: tree, crop, strength
planting sustem and tree training: high desnity
crop control: pruning, fruit thinning, hand and chemiclas
harvest control: pre harvest sprays
why use growth regulators/ harvest sprays
increase size of teh fruiit: Alar (prebloom application) Ethephon (prebloom a
sprout inhbitor
MH (maleic hydrazide): very common (onions) MENA (methyl ester of NAA)
fruit thinning: NAA, CPA, Ethephon
what are growth regulator for altering the maturity date
lar : both growth inhibitor & growth promotor Retards ripening of pome fruits Accelerates ripening of stone fruits Intensifies the red color of apples Ethephon Advances the maturity date Chemicals in postharvest applications Fungicides, fungistats Desinfectants, fumigants
what are the two types of mechanical harvesters
direct contact devices: cutting, pulling, snapping, twisting, stripping, digging, lifting etc
vibratory devices: Trunk & limb shakers with catch frame & canvas
what are harvest aids
Mechanical device/support which assists in improving the hand harvest operations
what are examples of harvest aids
Picker pole with a knife and a canvas bag
Single/multi station platforms (to position workers)
Conveyor belt (to move harvested heavy produce)
Harvesting cages
Lights for night time harvesting
what happens after mechanization
Fresh market : less than 25%
Processing : more than 75%