Lesson 2.2: Demand Curve Shifts
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on demand curve shifts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
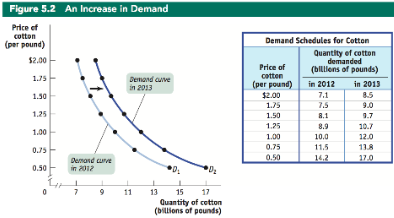
Demand curve shift
A change in the quantity demanded at any given price, represented by the movement of the original demand curve to a new position
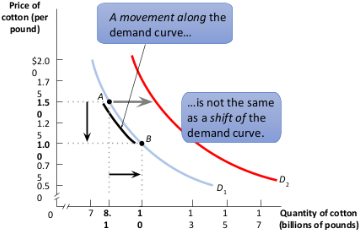
Demand curve movement
A change in the quantity demanded, caused by a change in price
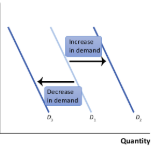
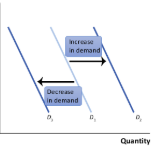
Decrease in demand
A situation where, at any given price, consumers demand a smaller quantity than before
This results in a leftward shift of the demand curve
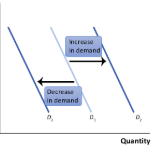
Increase in demand
A situation where, at any given price, consumers demand a larger quantity than before
This results in a rightward shift of the demand curve
Demand curve shift factors
Represented by TRIBE, a mnemonic device:
Taste changes
Related goods and services price changes
Income changes
Buyer number changes
Expectation changes
Taste changes
Changes or beliefs, culture, or current fads that shift the demand curve for a good or service
Men’s hats became less popular after World War 2, causing the demand curve to shift to the left
Hip-hop and alternative rock became more popular in the 1990s, causing the demand curve to shift to the right
Related goods and services price changes
Changes in the prices of a related good or service that shifts the demand curve depending on whether they are:
substitutes (consumers flock to another product based on price) or
complements (consumers buy a product with another product)
Substitutes
A pair of products where the increase in the price of one product causes people to demand more of the other
Higher jeans prices cause people to buy more khakis

Complements
A pair of products where the decrease in the price of one product makes people buy more of the other
Cookies and milk are often consumed together; lower cookie prices may result in more demand for milk
Income changes
Changes which can shift demand for a good differently depending on whether it is a:
normal good (higher incomes result in higher demands), or an
inferior good (higher incomes result in lower demands)
Normal good
A good where an increase in income raises the demand for a good (most goods)
Higher incomes correlate with more real estate purchases
Inferior good
A good where an increase in income lowers the demand for a good (rarer)
Higher incomes correlate with lower bus pass purchases as people opt for more expensive taxis
Buyer number changes
A situation where a change in the number of buyers or consumers shifts the demand curve
A decrease in the number of consumers causes demand to shift left
An increase in the number of consumers causes demand to shift right
Expectation changes
A situation where the expectation of rising prices in the future causes an increase in demand today
Consumers who think computers will be more expensive next year may opt to buy them now, increasing the demand for computers today