CHEM 241 - Organic Chemistry 2
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Why is a benzene ring a functional group?
Because it has 6 pi electrons that work as a single group, not as three individual groups
what process does cyclohexene reaction with bromine (br2)
addition alkene process
why does bromine not react with benzene
because the addition of br2 disrupts the stability of benzene
what are derivatives of benzene called?
substituted benzenes
what is the term used to describe derivatives of benzene
aromatic
what are compounds called when they contain the functional group benzene
arene
what is the parent suffix of an arene compound?
benzene
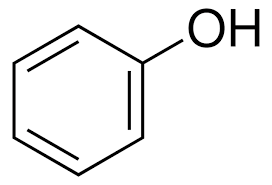
what is this molecule
hydroxybenzene/phenol
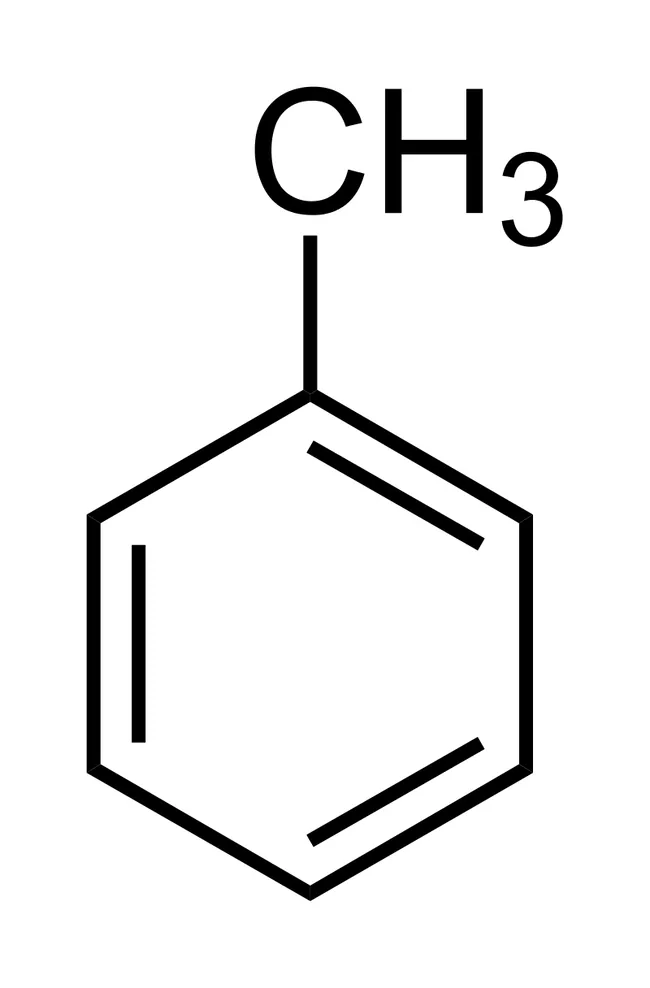
what is this molecule
methylbenzene/toulene
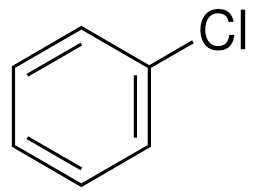
what is this molecule
chlorobenzene
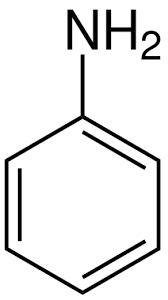
what is this compound?
aminobenzene/aniline
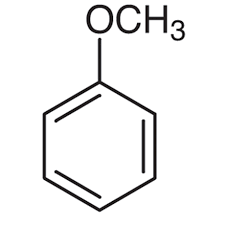
what is this compound?
anisole
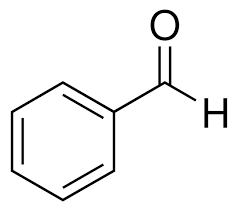
what is this compound?
benzaldehyde
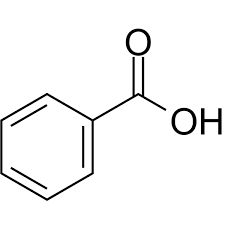
What is this compound?
benzoic acid
why do we use common names for functional groups with naming be arene compounds
so we only have to list one substituent - makes the name shorter
what must be done if more than one substituent is present on a benzene
number the substituents
1,2 disubstitution
ortho (o)
1,3 disubstitution
meta (m)
1,4 disubstitution
para (p)
if an amino/functional group is present, what position is it assigned
position 1
ch3
toluene
oh
phenol
och3
anisole
nh2
aniline
no2
nitro
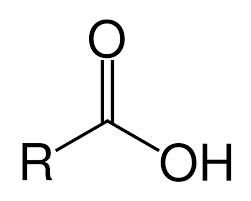
-oic acid
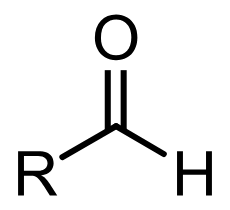
aldehyde
What are the criteria for aromacity
the compound must be a ring
the compound must have continuously overlapping p-orbitals (all atoms must having the same hybridization)
the ring must contain an odd number of pi electrons
What is the formula for huckel numbers
4n+2
n = number of double bonds
what are the characteristics of an antiaromatic compound
it is unstable
it is a ring with continuous system of overlapping p orbitals
it has 4n pi electrons
how can we make a nonaromatic compound aromatic
depronate (subtract a hydrogen ion) from the compound
Mass Spec
provides functional group identification + determines mass of molecule
Nitrogen rule
identifying nitriles, amines, amides
nitriles
2 pi bonds
amines
0 pi bonds
amides
1 pi bond + c=o bond
when mass is odd
nitrogen is present
alkyl halides
bromine and chlorine
Index of Hydrogen Deficiency
number of pi bonds in a molecule that contains nitrogen
isotopes of chlorine
cl-35 and cl-37
isotopes of bromine
br-79 and br-81
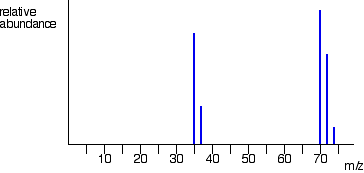
does this contain chlorine or bromine
chlorine
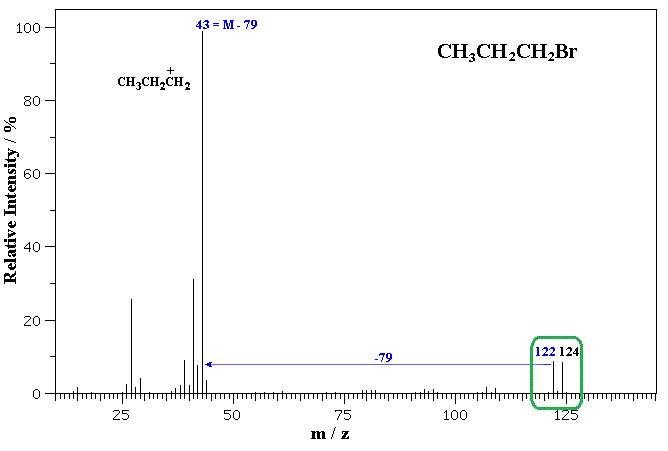
does this molecule contain chlorine or bromine
bromine
what do differing heights in a mass spec mean
distribution of ions
how are simple ethers named
identify organic substituents
add ether to the end
if other functional groups are present, how are ethers considered
alkoxy substituents
what bond angle do ether’s have
120 degrees (tetrahedral)
what is the hybridization of an ether oxygen atom
sp3
why is the boiling point of ethers higher than hydrocarbons
because the oxygen provides a slight dipole moment
what makes peroxides
the combination of ethers and oxygen in the air
are ethers good solvents or solutes
solvents
what type of reaction produces a diethyl ether
sn2
what reagents are used in the williamson ether synthesis
ether + (NaH + THF)/Ag2O
ch3—I
what type of reaction is williamson synthesis
sn2
what reacts well with Ag2O
sugars
Why do you suppose only symmetrical ethers are prepared by the sulfuric-acid-catalyzed dehydration procedure? What product(s) would you expect if ethanol and 1-propanol were allowed to react together? In what ratio would the products be formed if the two alcohols were of equal reactivity?
A mixture of diethyl ether, dipropyl ether, and ethyl propyl ether is formed in a 1 : 1 : 2 ratio.
What has no impact on ethers?
halogens, nucleophiles, dilute acids, bases
what reaction do ethers always go through
acid cleavage
what two leaving groups are best for ether acid cleavage reactions
HBR and HIwha
what acid does not cleave ethers
HCl
ethers with a benzylic, allylic, or tertiary structure go through what type of reactions
Sn1, E1
ethers with primary or secondary alkyl groups go through what type of reaction
Sn1, Sn2
Why are HI and HBr more effective than HCl in cleaving ethers?
Br− and I− are better nucleophiles than Cl−
why is a mixture of products formed when an acid-catalyzed ring is opened?
the ring’s geometrical structure
when the epoxide carbons are secondary and primary, what reaction occurs
sn2
when the epoxide carbons are tertiary and primary, what type of reaction occurs
sn1
what nucleophiles can be used for epoxide opening
amines (RNH2, R2NH) and grigard reagents (RMgX)