6. AQA GCSE Physics (9-1) Motion
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is a scalar quantity?
A quantity with only magnitude (size)
What is a vector quantity?
A quantity with both magnitude (size) and direction
Give four examples of scalar quantities
Speed
Distance
Energy
Mass
Give four examples of vector quantities
Velocity
Displacement
Acceleration
Force
What is the unit of speed and velocity?
m/s
Write the word equation that links velocity, time and displacement
displacement = velocity x time
Write the symbol equation that links velocity, time and displacement using symbols
s=vt
What is a typical speed of a person walking?
1.5 m/s
What is a typical speed of a person running?
3 m/s
What is a typical speed of a car?
25 m/s
Write the word equation that links time, acceleration, initial velocity and final velocity
Acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity)/time
Write the symbol equation that links time, acceleration, initial velocity and final velocity using standard symbols
a=(v-u)/t
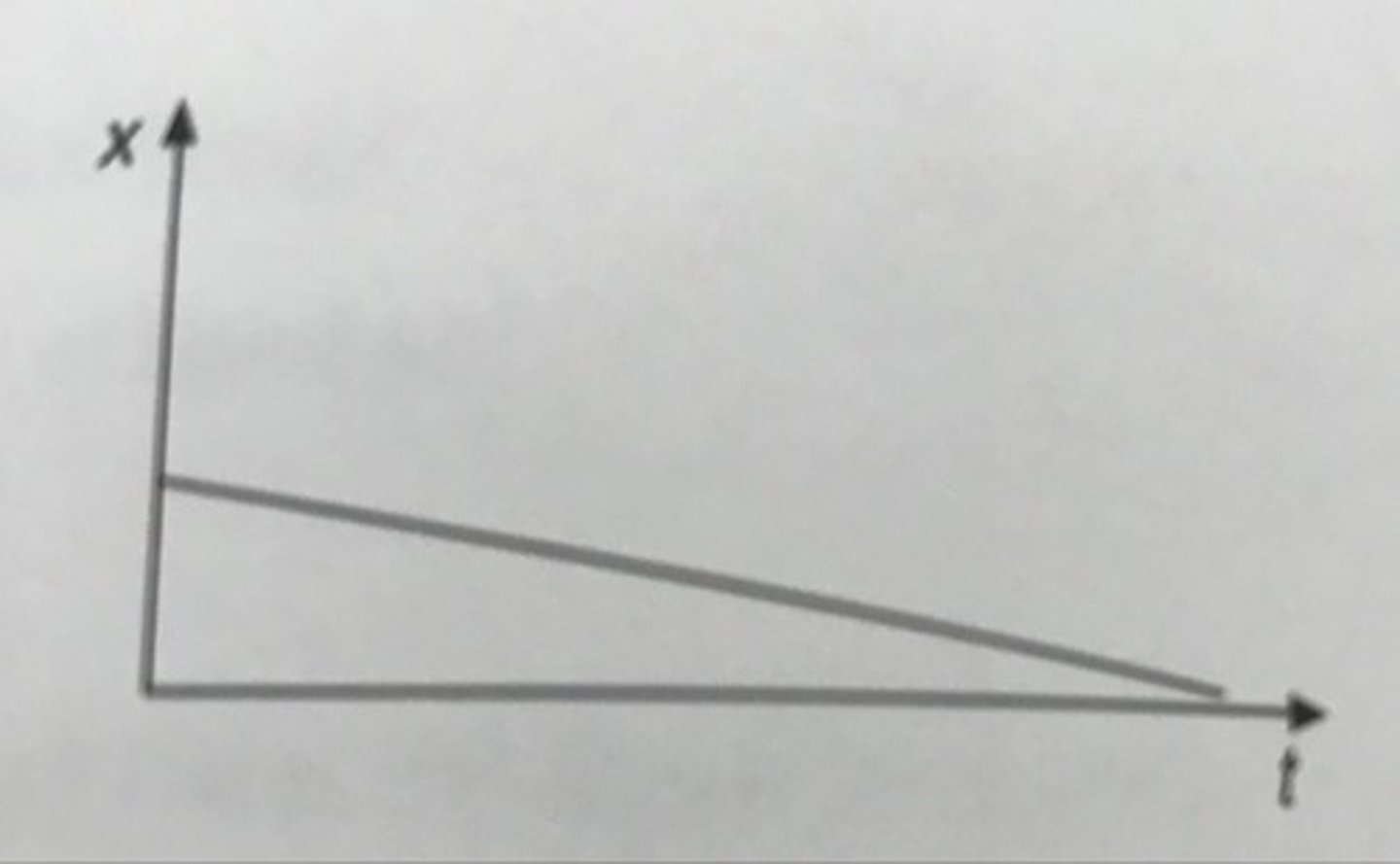
How is a stationary object represented on a distance-time graph?
A horizontal line
What feature of a distance-time graph represents the velocity of an object?
The gradient
How do you calculate the speed from a curved distance-time graph?
Draw a tangent than calculate the gradient of the tangent
What does a horizontal line on a velocity-time graph represent?
Constant velocity
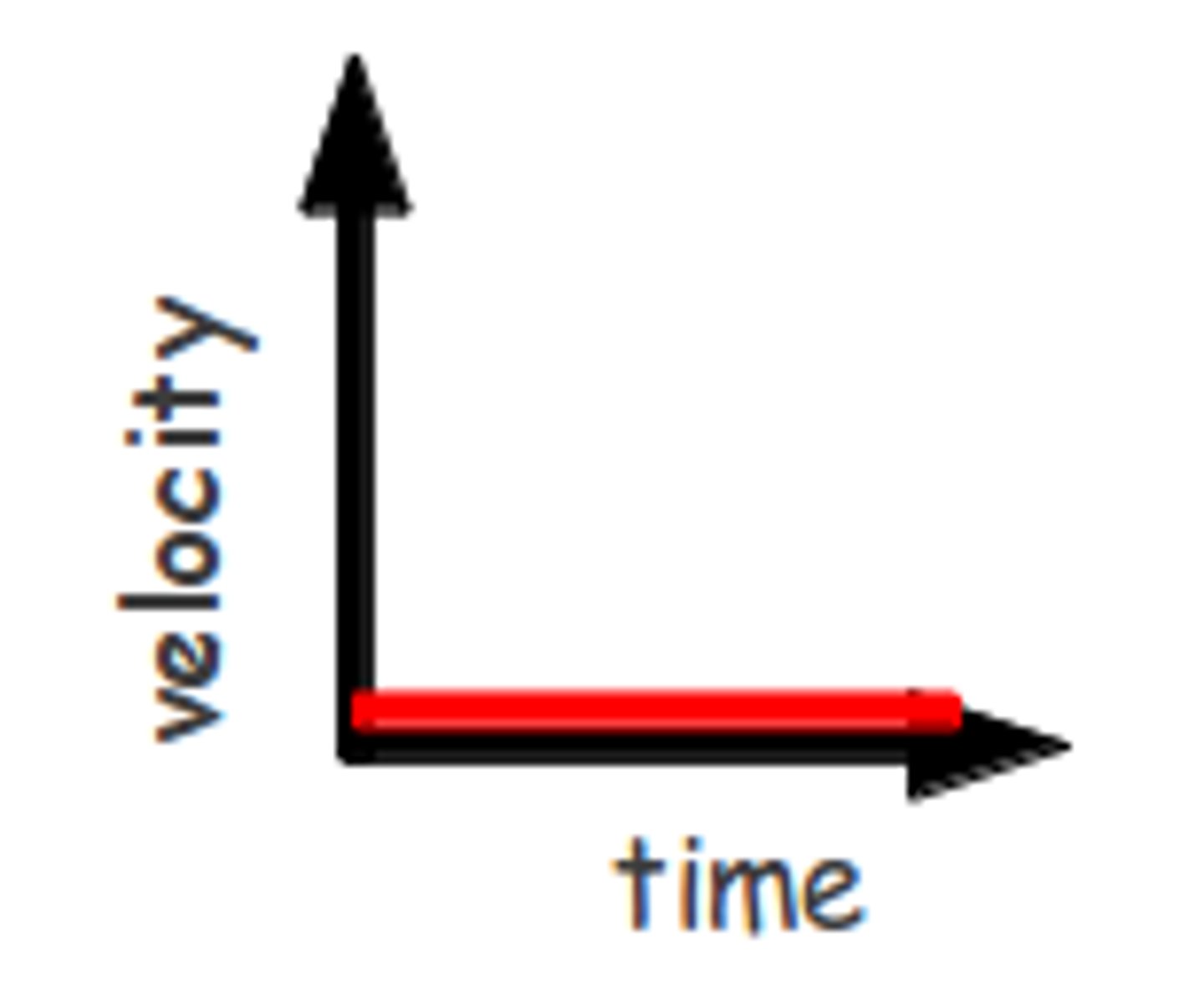
How is a stationary object represented on a velocity-time graph?
A horizontal line on the x-axis
How do you calculate the distance travelled from a velocity-time graph?
The area underneath the graph
Property of a velocity - time graph that is equal to the acceleration of the object
Gradient
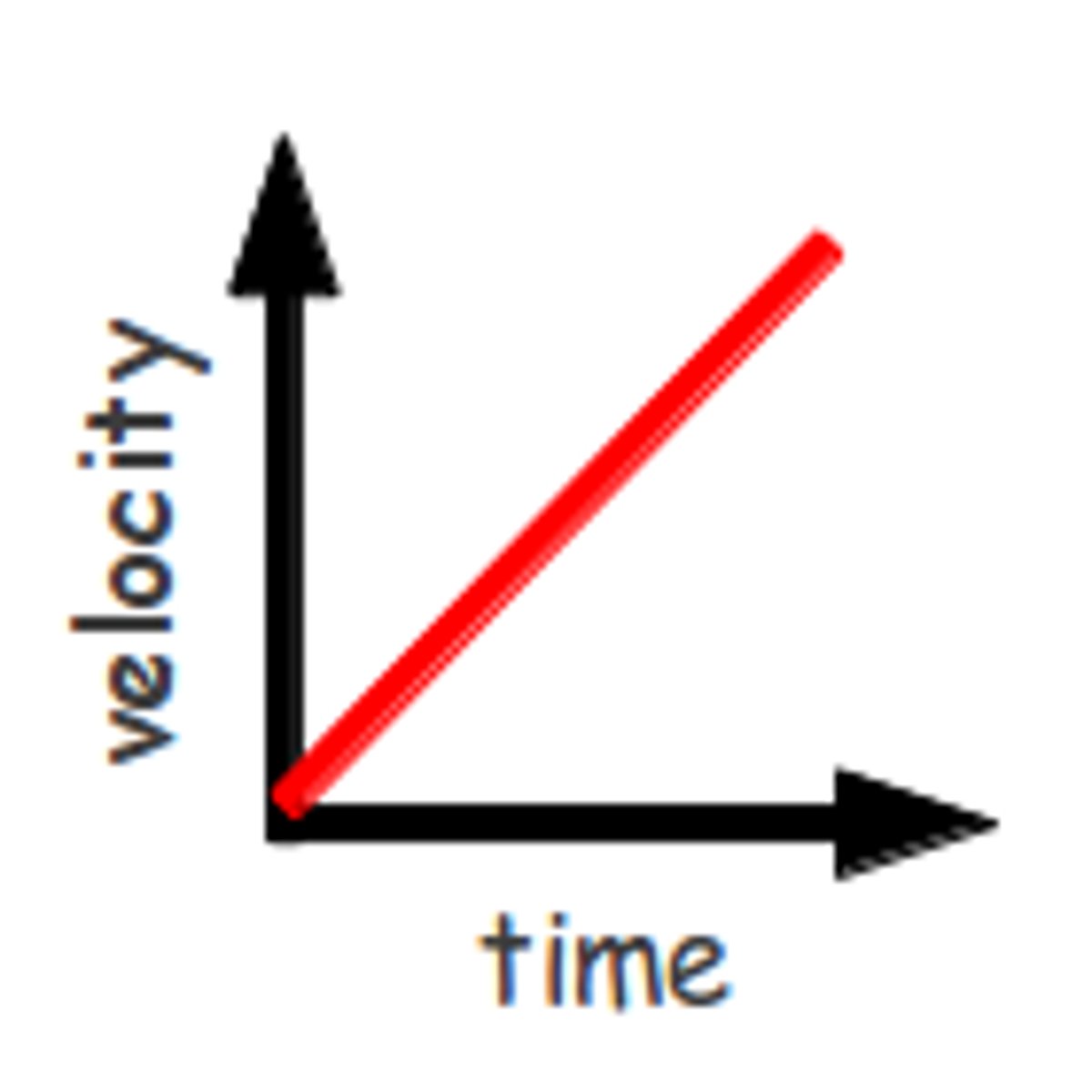
Constant acceleration graph
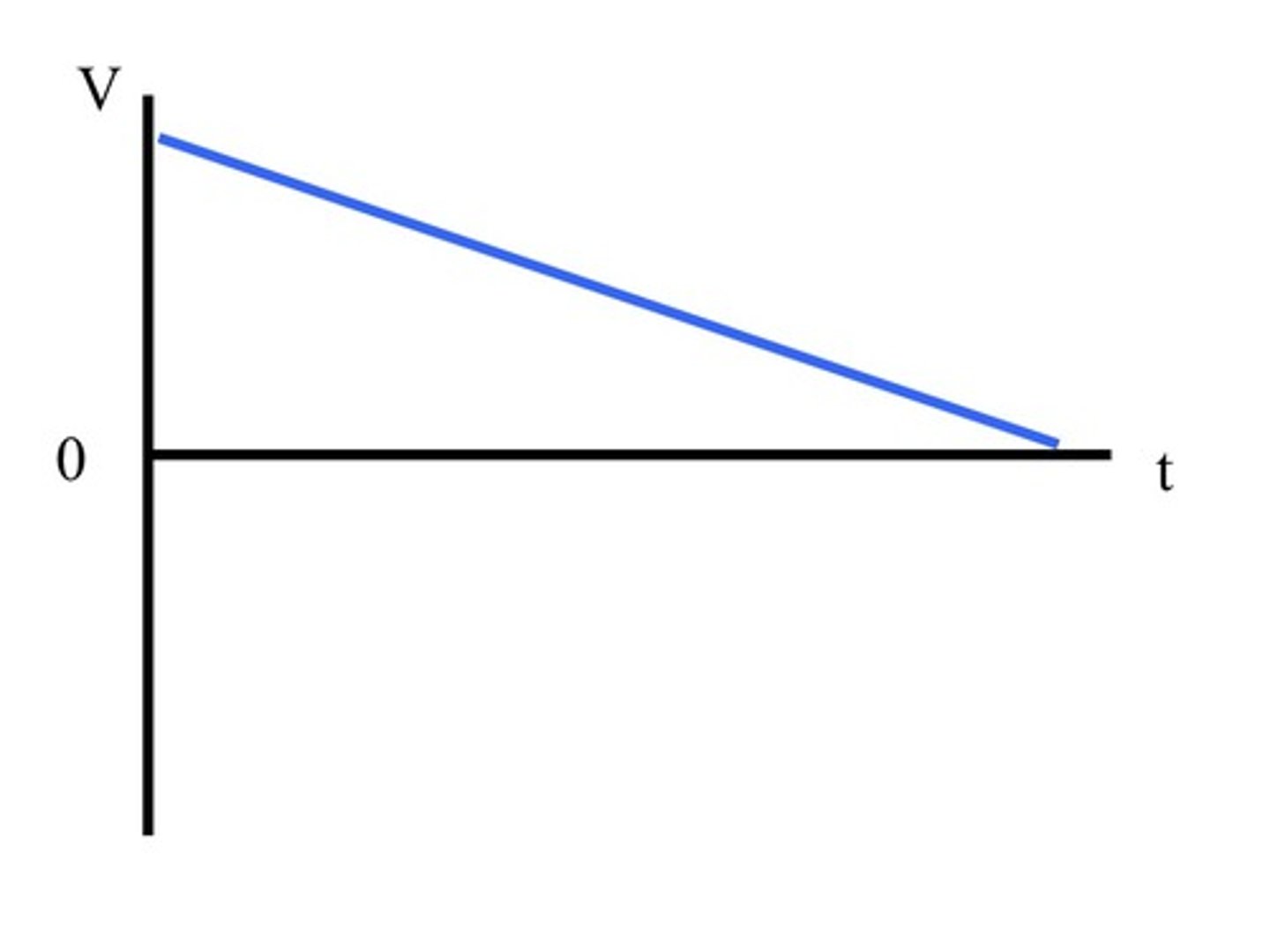
Constant deceleration graph
A runner accelerates from rest to 8m/s in 16s. what is her acceleration?
0.5m/s^2
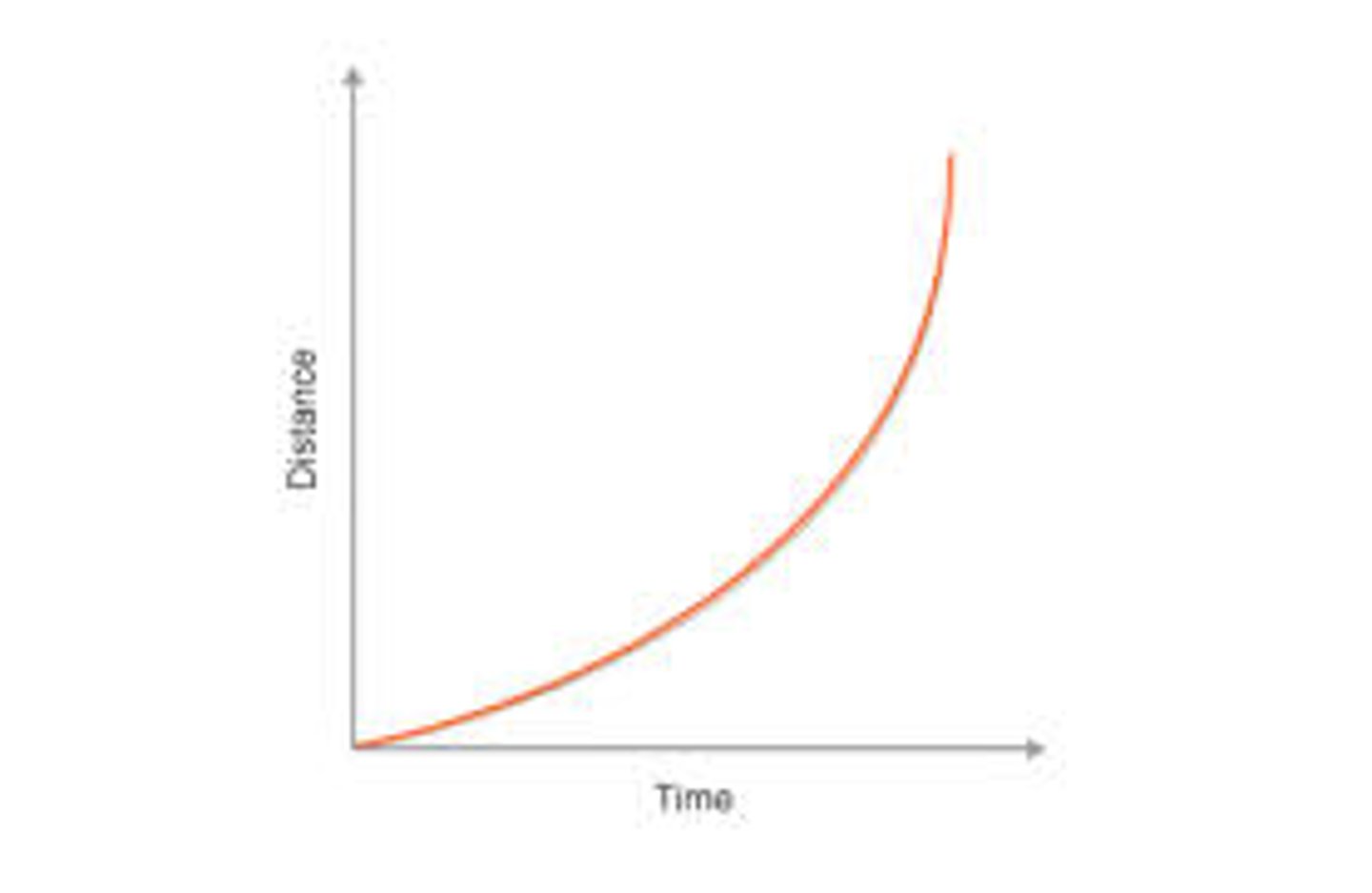
Acceleration graph
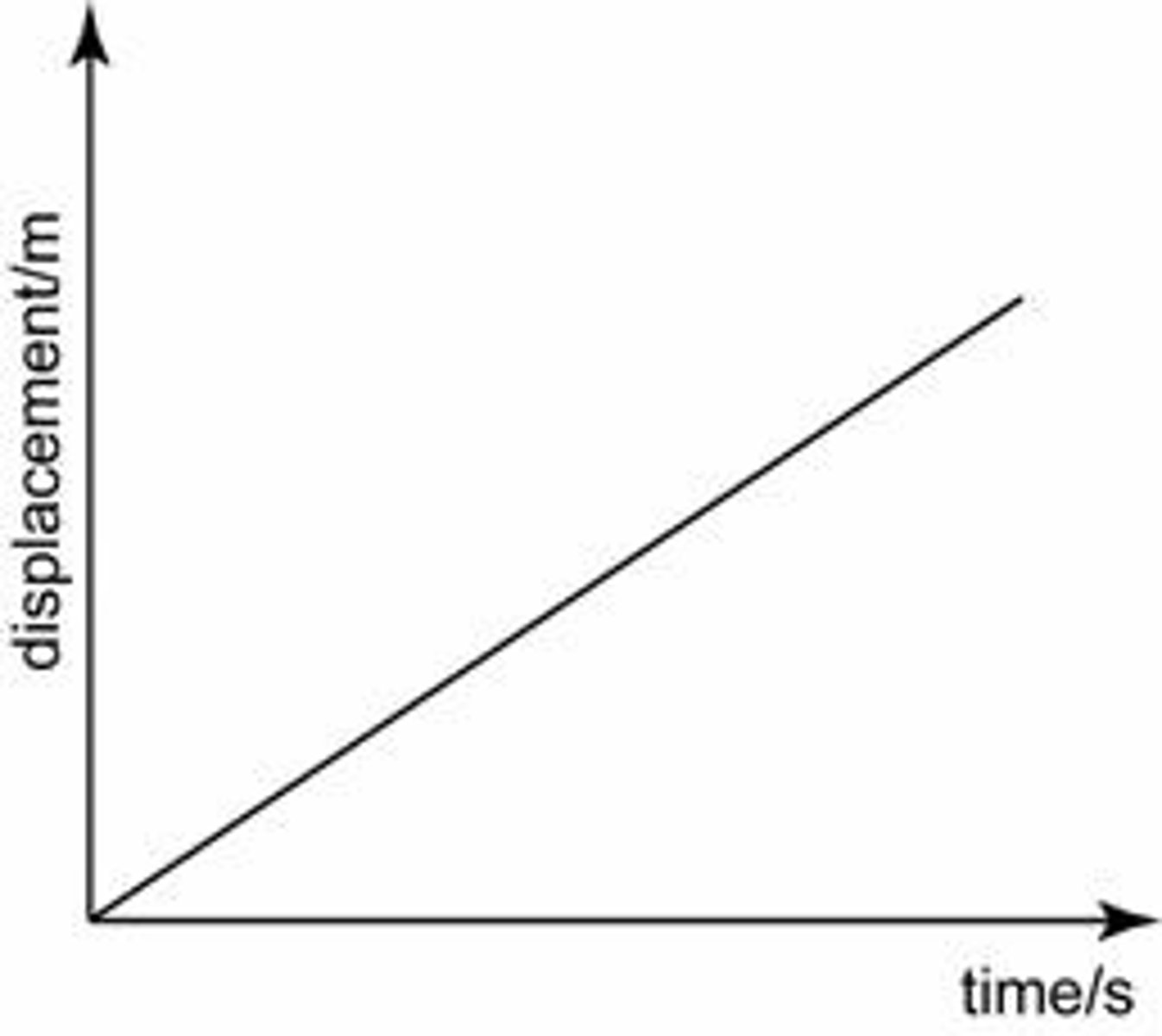
Constant velocity graph
Displacement back to the starting point graph
Stationary object v-t graph
Constant acceleration equation
v^2 - u^2 = 2as
Terminal velocity
the constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity
A more massive object will have a
larger terminal velocity