[BIOLOGY] The Cell Pt 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/73
Last updated 12:32 PM on 4/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
a Dutch scientist known for his works with microscopy and considered one of the pillars of microbiology
2
New cards
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
universally acknowledged as the father of microbiology.
3
New cards
Robert Hooke
who first observed and coined the term cell
4
New cards
honeycomb shape
what shape did Robert Hooke saw when he observed the cell
5
New cards
Cell Theory
the idea that living organisms are composed of basic, structural units called cells.
6
New cards
1. All living organisms are composed of one or many cells.
2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
3. Cells must come from pre-existing cells.
Three main ideas of Cell Theory
7
New cards
1. DNA is passed between cells during cell division.
2. All cells of organisms have the same basic chemical composition.
3. Energy flow occurs within cells.
Three added ideas to the Modern Cell Theory
8
New cards
1. Plasma Membrane
2. Cytosol
3. Chromosomes
4. Ribosomes
All cells share four common components, namely…
9
New cards
plasma membrane
serves as an outer covering that protects the insides of a cell from its surrounding environment
10
New cards
phospholipids bilayer
plasma membrane is commonly composed of ________
11
New cards
**Cytosol**
a fluid region in the cell where other cell components are found
12
New cards
Chromosomes
structures that contain genetic material in the form of DNA
13
New cards
Ribosomes
particles that synthesize proteins
14
New cards
Plasma Membrane
A semi-permeable layer that separates the insides of a cell from the external environment and is the location of chemical exchanges for many life functions.
15
New cards
Cytoplasm
The fluid internal environment of the cell where all internal components of the cell (called “organelles”) are suspended
16
New cards
Nucleus
Stores the genetic material of the cell. In prokaryotes
17
New cards
Nucleoid
where is the genetic material located
18
New cards
Nuclear Membrane
Encloses the nucleus and protects the genetic material.
19
New cards
Nucleoplasm
The environment within the nucleus.
20
New cards
Nucleolus
An area in the nucleoplasm where the genetic material is highly concentrated.
21
New cards
Nuclear Pore
Gateway of materials into or out of the nucleus.
22
New cards
Mitochondrion
Produces energy for the organism, having the moniker “powerhouse of the cell” due to this function.
23
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Sites for lipid and protein synthesis.
24
New cards
Rough ER
Contains ribosomes and is the site for protein synthesis. In addition, it also functions as the cell’s membrane-making machine.
25
New cards
**Smooth ER**
\
\
Contains cell types used in metabolic processes, especially lipid synthesis, as well as storage of calcium ions.
26
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
Site for modifying, sorting, and storing compounds synthesized by the ER.
27
New cards
Lysosome
Contains digestive enzymes that help break down food or damaged organelles.
28
New cards
Peroxisome
Helps break down fatty acids to be used as cellular fuel.
29
New cards
Ribosome
Can be found attached to the rough ER or free in the cytosol
30
New cards
Vacuoles
Storage of food and other chemicals.
31
New cards
Centriole
Organelle for cell division.
32
New cards
chloroplasts
present in plants and used in photosynthesis.
33
New cards
Prokaryotes
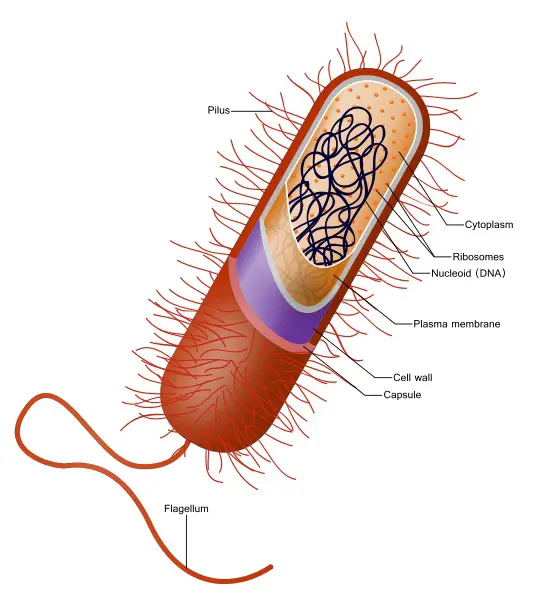
refer to organisms with cells that are simple, often single (unicellular), and **lack a nucleus**, or any other **membrane-bound organelle**.
34
New cards
nucleoid
Prokaryotic DNA is found in the central part of the cell: a darkened region called the
35
New cards
peptidoglycan
a cell wall of bacteria composed of sugars and amino acids, and many have a polysaccharide capsule
36
New cards
peptidoglycan
the cell wall of bacteria that acts as an extra layer of protection, helping the cell maintain its shape, and preventing dehydration.
37
New cards
capsule
another part of procaryote cell that allows the cell to attach to surfaces in its environment
38
New cards
flagella
part of prokaryote cell that is used for locomotion
39
New cards
pili
used to exchange genetic material during a type of reproduction called conjugation.
40
New cards
eukaryote
meanwhile, is composed of cells that have a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound compartments, called organelles, with specialized functions.
41
New cards
true nucleus
The word eukaryotic means
42
New cards
little organ
The word “organelle” means
43
New cards
1. Genetic Control
2. Manufacture, distribution, and breakdown of molecules
3. Energy processing
4. Structural support, movement, and communication
groups of organelles based on function
44
New cards
nucleus and ribosomes
part of the genetic control group
45
New cards
1. Endoplasmic reticulum
2. Golgi apparatus
3. lysosomes
4. vacuoles
5. peroxisomes
tasked for the Manufacture, distribution, and breakdown of molecules
46
New cards
mitochondria and chloroplasts
Energy processing group
47
New cards
1. cytoskeleton
2. plasma membrane
3. plant cell wall
tasked for the Structural support, movement, and communication between cells
48
New cards
plasmodesmata
Unique structures that connect adjacent plant cells
49
New cards
chloroplast
part of plant cell where photosynthesis occures
50
New cards
cytoskeleton
the Networks of protein fibers that provide structural support as well as movement
51
New cards
1. Microtubules
2. Intermediate filaments
3. Microfilaments
Three main kinds of fibers that make up the cytoskeleton
52
New cards
Microtubules
straight and hollow tubes composed of proteins called tubulins.
53
New cards
Microtubules
In animal cells, these grow from the centrosome while plant cells have other means of synthesizing as they lack centrosomes.
54
New cards
**Intermediate filaments**
found in cells of most animals, these reinforce cell shape and anchor some organelles. For example, the outer layer of our skin is made of dead skin cells composed of these
55
New cards
Microfilaments
help support the cell’s shape, particularly in animal cells that lack cell walls. These are also involved in cell movements.
56
New cards
actin filaments
Microfilaments are also called ____
57
New cards
cilia
short and numerous appendages that propel the protist *Paramecium*.
58
New cards
flagellum
is longer than the cilia but present in fewer numbers or as a sole structure per cell.
59
New cards
extracellular matrix (ECM)
Animal cells produce what that helps hold cells together and protects and supports the plasma membrane
60
New cards
glycoproteins
the main components of extracellular matrix (ECM) are
61
New cards
glycoproteins
are proteins bonded with carbohydrates.
62
New cards
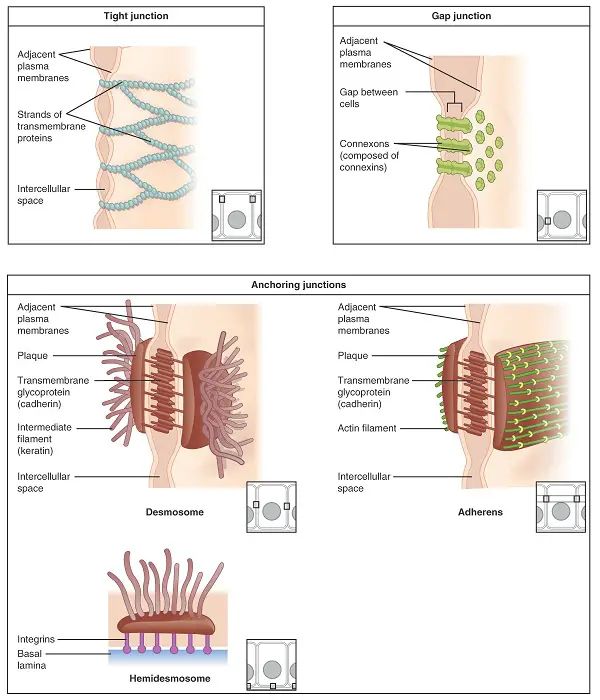
1. Tight Junctions
2. Anchoring Junctions
3. Gap junctions
3 types of junctions
63
New cards
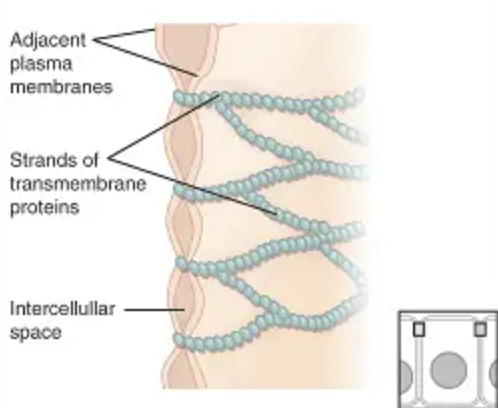
Tight Junction
a type of junction that occurs when the plasma membrane of neighboring cells is knit tightly together by proteins.
64
New cards
Tight Junction
65
New cards
Anchoring junctions
fasten cells into strong sheets. These junctions are connected to the cytoplasm by intermediate filaments.
66
New cards
Tight junctions
They prevent the leakage of fluid across a layer of cells. For example, the food we eat and are within our digestive tract does not leak because of these cell junctions.
67
New cards
Anchoring junctions
These junctions are common in tissues subjected often to stretching such as our skin and muscle.
68
New cards
Anchoring junctions
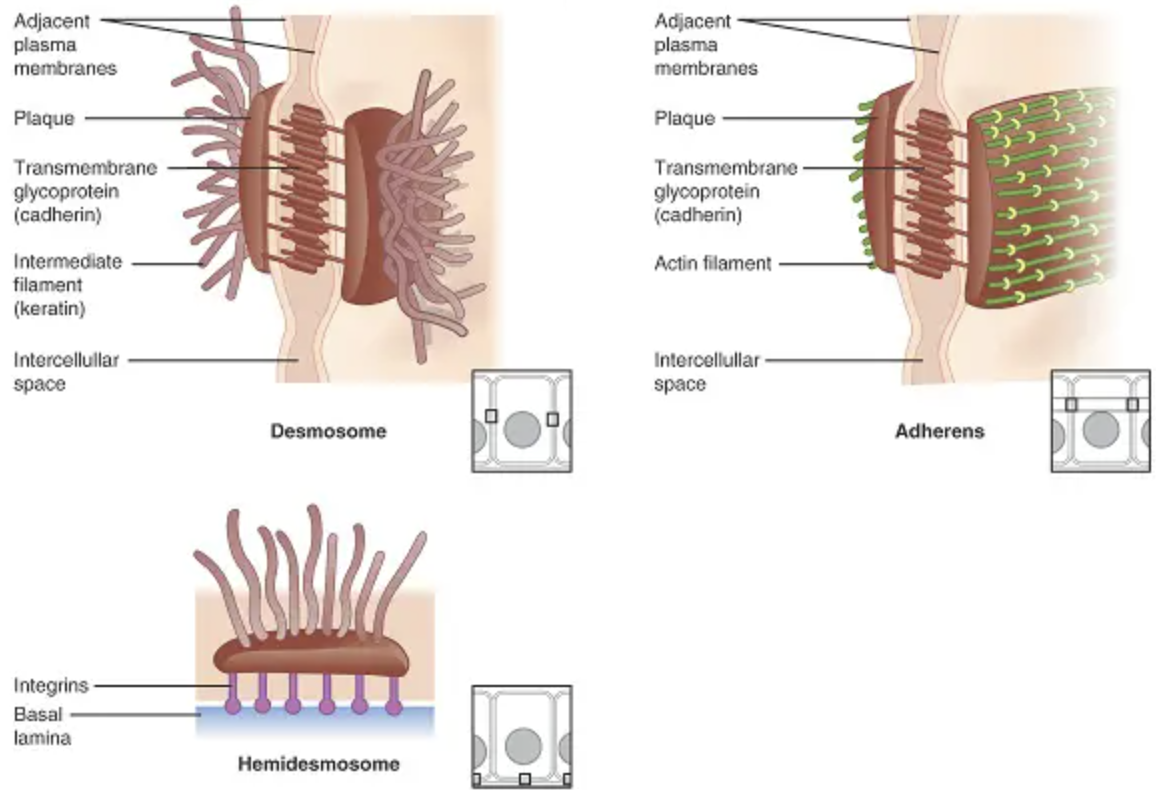
69
New cards
Gap junctions
also called communicating junctions
70
New cards
Gap junctions
this type of junction allows small molecules to flow through protein-lined pores between cells.
71
New cards
Gap junctions
this junction is common in babies in the womb since communication between the mother and the developing baby is necessary for the baby’s development.
72
New cards
Gap junctions
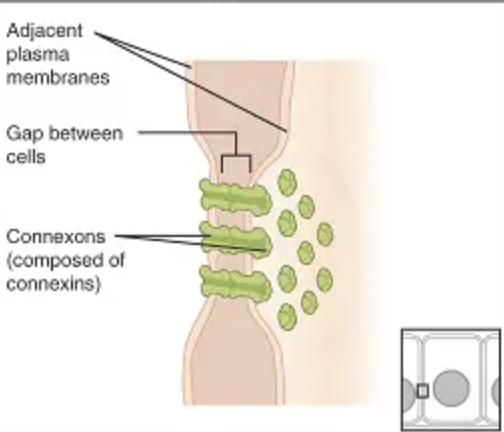
73
New cards
pectin
Plant cells initially lay down a relatively thin and flexible primary wall to allow the cell to continue to enlarge. Between adjacent cells is a sticky substance called _______, gluing cells together. When the plant cell stops growing, it strengthens the wall.
74
New cards
plasmodesmata
it allows water and other small molecules to freely move from cell to cell. These structures allow cells in plant tissues to share water, nourishment, and chemical messages.