Psych 100 exam 1 review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:11 AM on 9/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
1
New cards
scientific theory
well substantiated explanation of some aspects of the world
2
New cards
terror management theory
when people are reminded of their own deaths they are more readily to enforce their cultural world views often leading to punitive actions/violence
3
New cards
falsifiability of scientific theory
can be proven wrong; failure to falsify a scientific theory makes it a good theory
4
New cards
hypothesis
a testable prediction, often prompted by a theory, to enable us to accept, reject, or reuse the theory
ex: people with high self esteem are less likely to be depressed
ex: people with high self esteem are less likely to be depressed
5
New cards
Case study
closely observe a single person/event/phenomena
ex: psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected mental well-being of those living there
eval: learning about a complex instance
ex: psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected mental well-being of those living there
eval: learning about a complex instance
6
New cards
observational study
naturalistic observation:observe what happens naturally
ex: an opinion survey asking questions about how people liked the most recent documentary
eval: characteristics of a population
ex: an opinion survey asking questions about how people liked the most recent documentary
eval: characteristics of a population
7
New cards
correlational study
survey: collect info about whats out there w/ not manipulation or change
ex: if there are multiple pizza trucks in the area and each one has a different jingle, we would memorize it all and relate it to its pizza truck
eval: correlation does not equal causation
ex: if there are multiple pizza trucks in the area and each one has a different jingle, we would memorize it all and relate it to its pizza truck
eval: correlation does not equal causation
8
New cards
experiment
manipulate or change something to see what happens next
ex:when scientists give rats new medicine and see how they react to learn about the medicine
eval:designed to find out casual relationships
ex:when scientists give rats new medicine and see how they react to learn about the medicine
eval:designed to find out casual relationships
9
New cards
Range of correlation/strength and direction
researcher has control; can collect large quantity of data; social desirability and sampling bias; analysis= when one trait or behavior accompanies another, we say the two correlate
10
New cards
spurious correlation
two or more events of a variable are associated but not casually related
ex: ice cream and drowning
ex: ice cream and drowning
11
New cards
testable hypothesis
a prediction about what should occur if a theory is valid
12
New cards
independent variable
the variable that is being manipulated (control group)
13
New cards
dependent variable
outcome variable
14
New cards
random assignment
randomly assign participants into experimental conditions
15
New cards
social psychology
scientifically studies how we think about influence, and relate to one another
16
New cards
crowds
refers to large gatherings of people who not necessarily know one another
17
New cards
groups
psychological processes involving communication, conflict, and pressure among group members
18
New cards
diffusion of responsibility/bystander effect
as the number of bystanders increases, the personal responsibility that an individual bystander feels decreases
ex: kitty genovese murder
ex: kitty genovese murder
19
New cards
conformity
changing ones behavior to match the responses or actions of others
ex: keeping quiet during a funeral
ex: keeping quiet during a funeral
20
New cards
informational conformity
influenced by group
21
New cards
normative conformity
you know you're correct but don't want criticism from the group
22
New cards
group identification/social validation
the person does not identify strongly with the group/ an interpersonal way to locate and validate the correct choice
23
New cards
compliance
changing ones behavior in response to a direct request
ex: when your neighbor asks you to buy some girl scout cookies from his daughter although you don't really care about sweets you agree to buy a couple of boxes
ex: when your neighbor asks you to buy some girl scout cookies from his daughter although you don't really care about sweets you agree to buy a couple of boxes
24
New cards
reciprocity
a social norm discovered in all cultures of the world
marketing free gifts/free samples
marketing free gifts/free samples
25
New cards
commitment/consistency
people tend to act in ways consistent with past behavior
ex: door to door sales; problem of cancellations technique of having customers complete sales form
ex: door to door sales; problem of cancellations technique of having customers complete sales form
26
New cards
authority
figures that are often used in the marketing world- people with expertise or influence, instead of real authority persons who have substantial power
ex: a construction worker says you can't lean on the bridge vs, a random person saying you can't lean on the bridge
ex: a construction worker says you can't lean on the bridge vs, a random person saying you can't lean on the bridge
27
New cards
scarcity
things that are in short supply seem more valuable- time running out- limited quantities available
28
New cards
liking
people are more likely to say yes to people they know/like
ex: compliments/ multilevel marketing (relies on the principle of liking to broaden their customer base)
ex: compliments/ multilevel marketing (relies on the principle of liking to broaden their customer base)
29
New cards
obedience
changing ones behavior in response to a directive from an authority figure (power status)
ex: soldiers take orders; mom tells kids to wash hands before dinner
ex: soldiers take orders; mom tells kids to wash hands before dinner
30
New cards
milgrams shocking experience
participants were told by an experimenter to administer increasingly powerful electric shocks to another individual
participants obeyed even when the individual was screaming in pain
finding: people obey out of fear or out of desire to appear cooperative
participants obeyed even when the individual was screaming in pain
finding: people obey out of fear or out of desire to appear cooperative
31
New cards
social relations
social psychology teaches us how we relate to one another through prejudice, aggression and conflict
32
New cards
prejudice
unjustifiable (usually negative) attitude toward a group and its memories-> directed toward different cultures, ethnicities, and gender groups
ex: after 9/11 many people lashed out on muslim americans
ex: after 9/11 many people lashed out on muslim americans
33
New cards
stereotype threat
negative emotional experience when people recognize a negative stereotype about themselves and conform to such stereotype unknowingly
34
New cards
aggression
behavior intended to injure another -> it is aimed at hurting, its different from assertive behavior- injury can be physical or emotional
35
New cards
direct aggression
behaviors intended to hurt another person to their face
ex: hockey players get into a fight
ex: hockey players get into a fight
36
New cards
indirect aggression
behavioral attempts to hurt another person without confrontation
ex: spreading rumors about another person to hurt their reputation
ex: spreading rumors about another person to hurt their reputation
37
New cards
emotional/instrumental agression
hurtful behavior that stem from angry feelings
ex: someone slaps their partner after finding out they were cheating
hurting another to accomplish another goal
ex: someone uses verbal abuse to hurt their partners
ex: someone slaps their partner after finding out they were cheating
hurting another to accomplish another goal
ex: someone uses verbal abuse to hurt their partners
38
New cards
genetic/situational factors
brain, hormone, weapon effect
39
New cards
psychoanalytic perspective
the self actualizing person: an individuals patters of thinking, feeling, and acting
40
New cards
trait perspective
personality dimensions
41
New cards
conscience
regions of mind containing the mental contents of which you're aware at any given moment
42
New cards
preconscience
regions of mind containing ideas you can easily bring to awareness
43
New cards
unconscience
you're not aware and generally cannot become aware of even if you wanted to
44
New cards
id
motivated people to satisfy basic bodliy (sexual and aggressive) needs (animal self) original energy (drive)
45
New cards
ego
mental system that balances the demands of the id with the opportunities and constraints of the real world- societal self (formed in childhood)
46
New cards
superego
represents societies moral and ethnic tules- moral self (formed older)
47
New cards
psychosexual stages
period during which the child focuses on obtaining sensual gratification through a particular part of the body
48
New cards
oral stage
0-18 months: seek gratification through the mouth
49
New cards
anal stage
18-3 yrs: release of tension resulting from the control and elimination of feces
50
New cards
phallic stage
3-6 yrs: source of gratification is the genitals
51
New cards
latency stage
sexual desires are repressed into the unconscious until puberty
52
New cards
genital stage
starts at puberty; signaling the reawakening of sexual desire
53
New cards
life energies
motivate the preservation of life and reproduction; primarily sexual, pursue sex to desire pleasurable , sensible activities
54
New cards
death energies
oppose the life energies; humans possess an instinctive awareness of their mortality and mental energy that motivates them to attain a final resting place
55
New cards
psychodynamic processes
changes in mental energy that occur as energy flows from one personality structure to another, or is directed to desired objects
56
New cards
anxiety
if energy flow is blocked, it will result in anxiety, which is the ultimate source of mental disorder
57
New cards
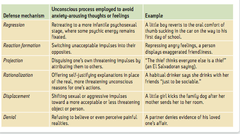
defense mechanism
mental strategy that is devised by the ego to protect against anxiety
ex: projection, denial, displacement, etc.
ex: projection, denial, displacement, etc.
58
New cards
free association
psychologists encourage people to let their thoughts flow freely and say whatever comes to mind
59
New cards
projective tests
interested in the way test takers interpret the ambiguity "projecting" elements of their own personality onto the test
60
New cards
humanistic theory
an approach to personality that focuses on peoples thoughts and feelings about themselves and the ways that interpersonal relationships shape these feelings
61
New cards
self
an organized set of self perceptions of out personal qualities; peoples conceptions of who they are
62
New cards
actual self
peoples perceptions of psychological qualities they possess currently, in the present
63
New cards
ideal self
optimally would possess in the future
64
New cards
self actualization
a motivation to realize ones inner potential
65
New cards
condition of worth
A behavioral requirement imposed by others, such as parents, as a condition for being fully valued, loved, and respected
66
New cards
humanistic therapy
mental health approach emphasizing the importance of being your true self in order to lead the most fulfilling life
67
New cards
Maslow's Heirarchy of Needs Theory
begins with psychological needs, we try to reach the state of self actualization, fulfilling our potential
psychological, safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self actualization
psychological, safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self actualization
68
New cards
trait
a persons typical style of behavior and emotion
69
New cards
lexical approach
all significant individual differences among people will be presented by naturally occurring words in everyday language
70
New cards
factor analysis
a statistical technique that identifies patterns in large sets of correlation
71
New cards
Big 5 factors
openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism
72
New cards
openness
related to motivation, need for variety, need for cognition-> imaginative vs. practical; variety vs. routine
73
New cards
consciousness
organized vs. disorganized; careful vs. careless and disciplined vs. impulsive
74
New cards
Extraversion
sociable vs. retiring, fun-loving vs. sober, affectionate vs. reserved
75
New cards
agreeabless
self hatred vs. ruthless; trusting vs. suspicious' helpful vs. uncooperative
76
New cards
Neuroticism
calm or anxious, secure or insecure, self-satisfied or self-pitying