Adenxal Infections
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
PID
Infectious disease of female reproductive organs
4 stages
Ascending infection
Usually originates from vAgina, starts in UT and extends into tubes/adnexa
First symptom of infection
Vagninitis
PID can lead to
Fitz-Hugh-Syndrome: Inflammation of peritoneum
Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy due to tubal damage, formation of cervical polyps, infertility
Stage 1 PID: Acute endometritis
Endometrial fluid/debris/air
Fluid in posterior cul-de-sac
Increased vascularity on Doppler
Stage 2 PID: Acute salpingitis
Fluid or pus within tubes
Shaggy appearance of tube walls
Thick walled tubes with acute infection (>5mm)
COGWHEEL SIGN - demonstrated in cross-sectional view, longitudinal folds of tube thicken
Stage 3 PID: Acute tubo-ovarian abscess
Multilocular retro-uterine/adnexal masses with debris
May see comet tail artifact due to air produced with bacterial infection
Septations
Irregular thick walls
Commonly bilateral
May see echogenic debris in pelvis
Stage 4 PID: Chronic infection
Hydrosalpinx, pyosalpinx, hematosalpinx
Thin walled fallopian tube (<5mm)
BEADS ON STRING SIGN - remnants of endosalpingeal folds demonstrate multiple 2-3mm nodules
Peritoneal inclusion cyst
PID is associated with
CHLAMYDIA, gonorrhea, TORCH infections, poor hygiene, tuberculosis, non-sterile surgical instruments, childbirth, intrauterine contraception, ruptured appendix
PID symptoms
VAGINITIS, bleeding, discharge, pain, N/V, dysuria, fever, rapid pulse, increased WBC’s, palpable mass
Possible elevated CA-125, C-reactive protein
USA acute PID
Enlarged, swollen uterus, prominent irregular endo
Fluid in cul-de-sac
Edematous adnexa
Hydrosalpinx/pyosalpinx, COGWHEEL
Hypervascularity of tube walls
Abcess
USA chronic PID
Normal UT
Fluid in cul-de-sac
Ascites
Hydrosalpinx/pyosalpinx
Beads on string
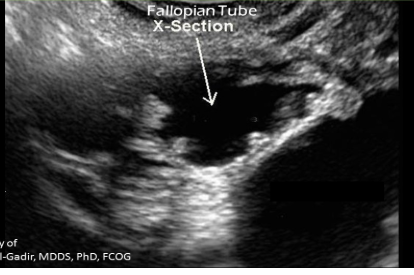
Acute PID (cogwheel)
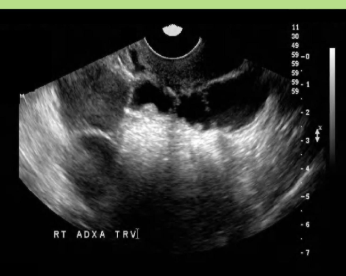
Hydrosalpinx (PID)
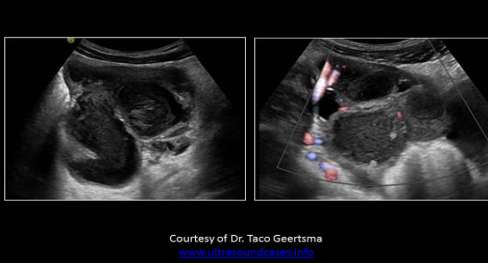
Pyosalpinx (PID)
Tubo-ovarian abscess
Bilateral
Associated with PID and IUDs
Tubo-ovarian abscess is caused by
Ascending infection
Tubo-ovarian abscess symptoms
Pain, fever, nausea, leukocytosis
Tubo-ovarian abscess USA
Abnormally thickened endometrium
Hydrosalpinx/pyosalpinx
Complex adnexal mass
Adnexal borders
Septations and debris
Gassy (DIRTY) SHADOWING may be seen
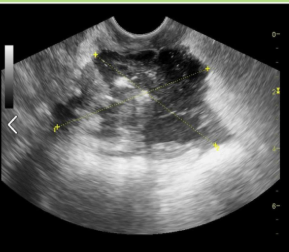
Tubo-ovarian abscess
Most common cause of acute abdomen pain
Acute appendicitis
Acute LLQ pain is commonly associated with
Diverticulitis
Acute RLQ pain is commonly associated with
Acute appendicitis
Appendix is located …
Posterior to terminal ileum and anterior to iliac vessels
In MCBURNEY’s point
Acute appendicitis symptoms/findings
RLD pain, increased WBC, fever, rebound tenderness with transducer compression
Appendicitis can lead to …
Bacterial infection → leads to gangrene and possible perforation
Fecalith
Hard stony mass of feces in intestinal tract that can obstruct the appendix
also known as coprolith and stercolith
USA acute appendicitis
Use graded compression technique
Blind ended structure that will not respond to compression
Aperistalic tube with gut signature that arises from cecum base
TARGET SIGN trans
INCREASED vascularity
Fluid
Gangrenous = lack of blood flow
Diameter of acute appendicitis >__, wall >__
6; 2
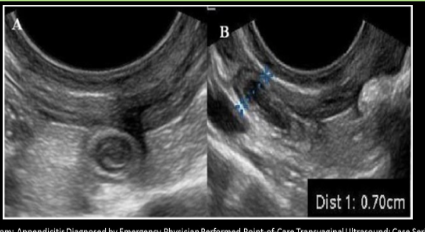
Appendicitis
Diverticulitis
LLQ pain, fever, increased WBC
Segmental, concentric, thickening of wall
MOST COMMON in sigmoid colon
Diverticulitis USA
Inflamed diverticulum (out puching >4mm)
Echogenic areas in wall
Pseudokidney sign - Abnormal bowel thickening
Cogwheel sign indicated what stage of PID
Acute salpingitis