AP Psychology Unit 3: Sensation and Perception
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Sensory Adaptation
Decreasing responsiveness to stimuli due to constant stimulation
Sensory Habituation
Perception of sensations partially due to how focused someone is on them
Perception
What sensations activate senses + what a person is focused on
The process of understanding and interpreting sensations
Cocktail-Party Phenomenon
Brain focuses attention on a particular stimuli (usually auditory like having your name called in a crowded room)
Sensation
Process of activation of senses, perception: understanding sensations
Light intensity
The color the eye sees depends on this
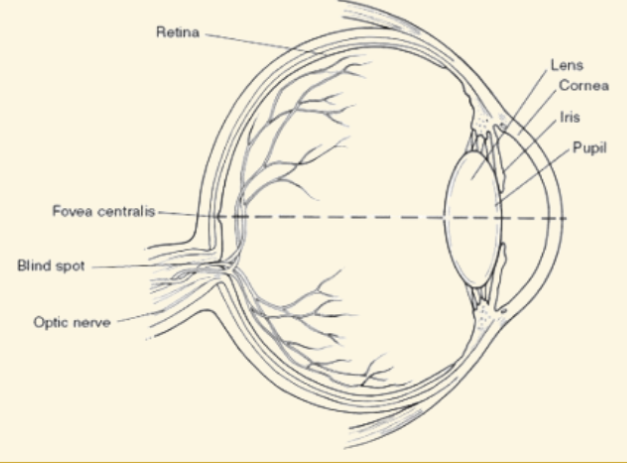
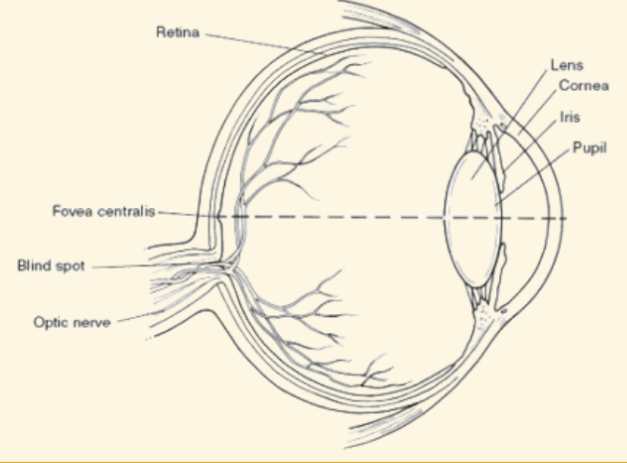
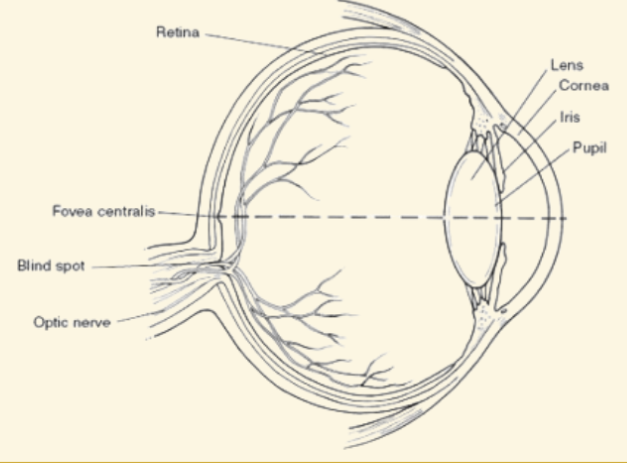
Cornea
This is a protective covering that helps focus light when it enters the eye
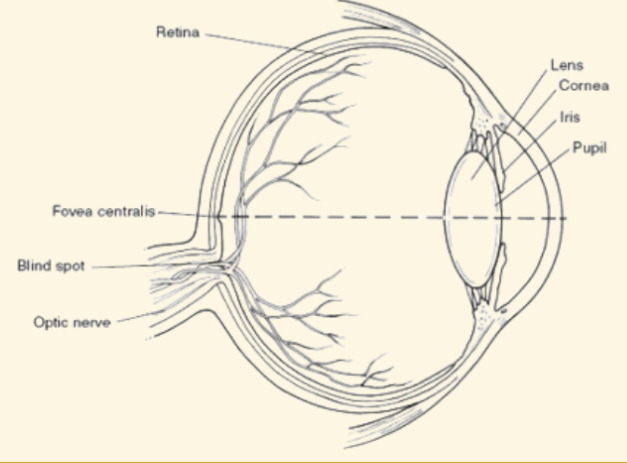
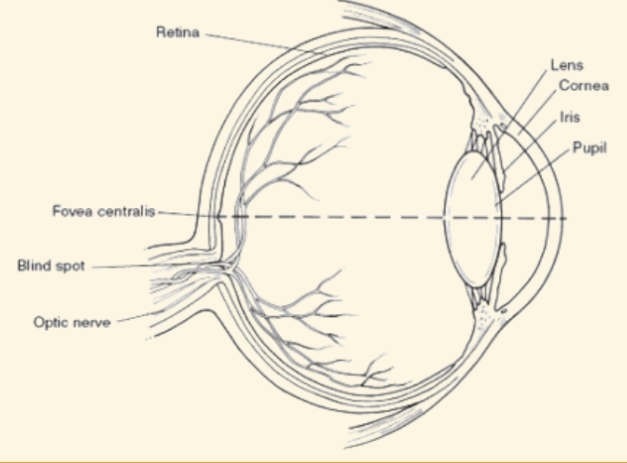
Pupil
This part of the eye is like a camera shutter, and light enters it right after it goes through the cornea
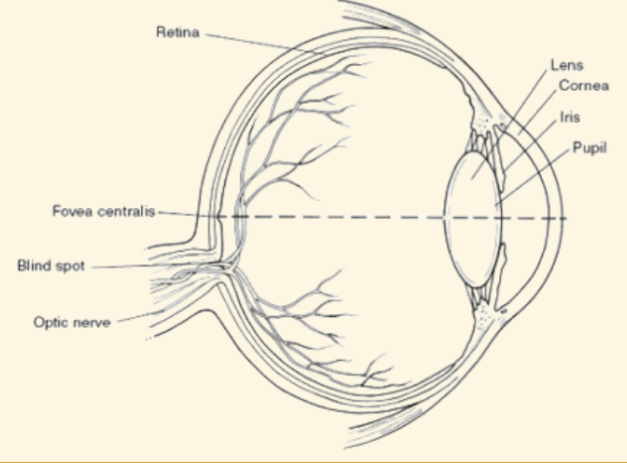
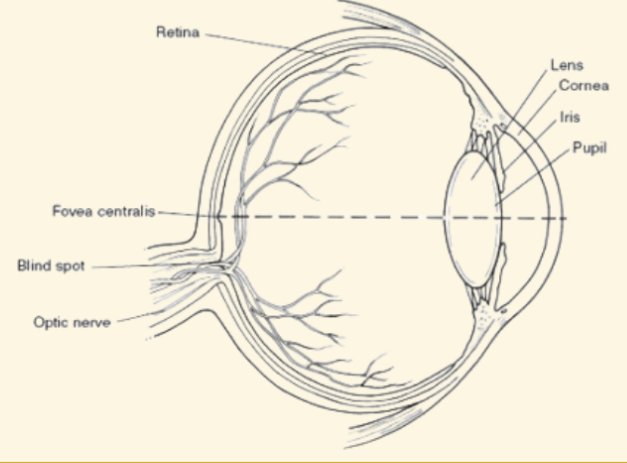
Iris
This part of the eye is muscles that dilate or shrink depending on if there is more or less light
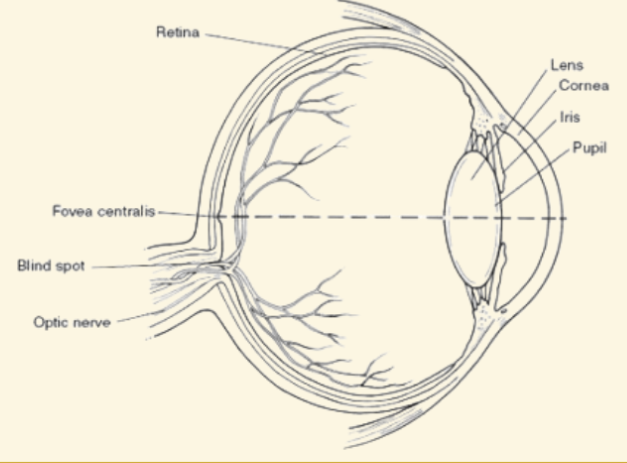
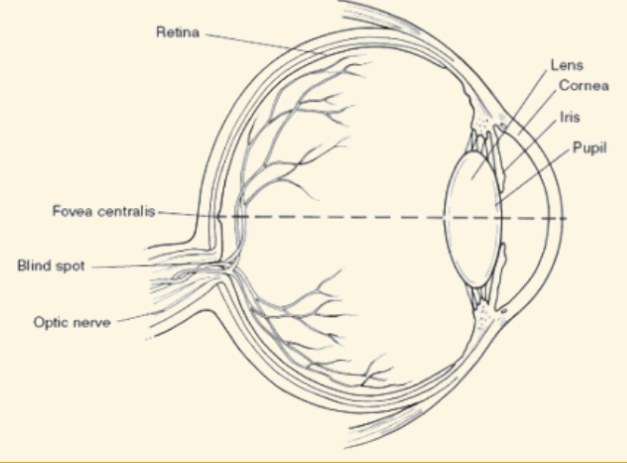
Lens
During the accommodation part of seeing, light is focused by this curved and flexible structure
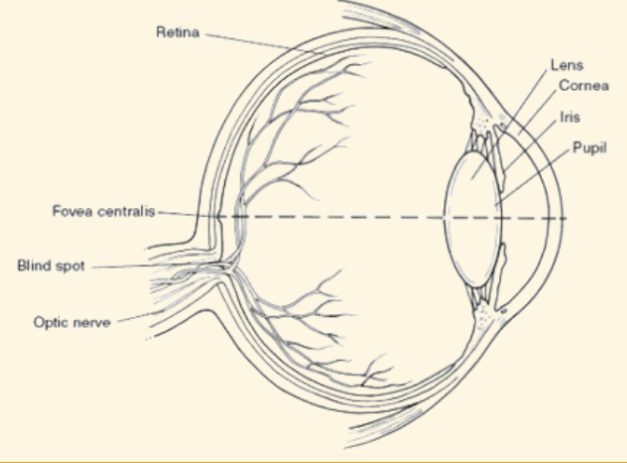
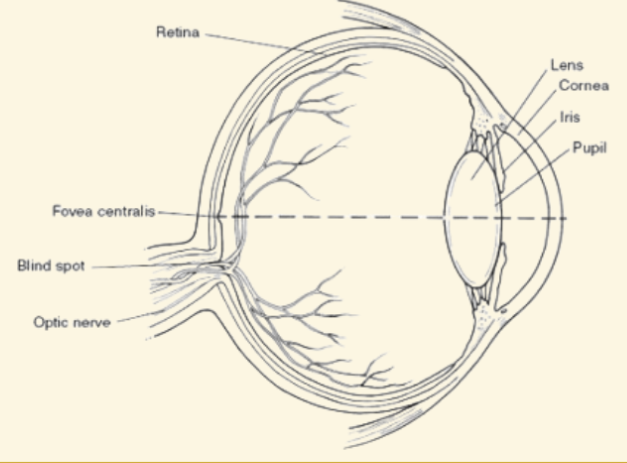
Retina
Images are projected here, onto the back of the eye. It serves like a screen
Cones
In the eye: first cell layer that is activated by color
Rods
In the eye: first cell layer that is activated by black or white
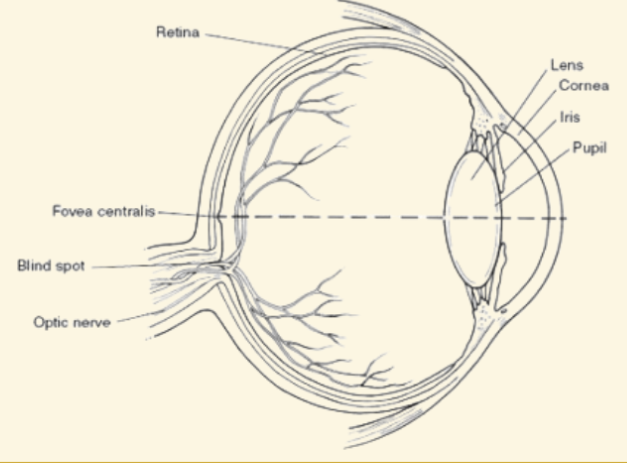
Fovea
The very center of the retina: highest concentration of cones
Peripheral vision relies on rods and is black and white
Ganglion cells
The next layer of bipolar cells after rods and cones. Activated if enough rods and cones fire
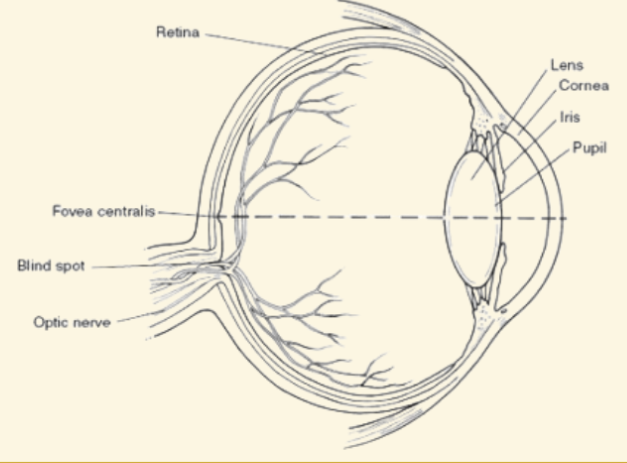
Optic Chiasm
Where the parts of the optic nerve cross
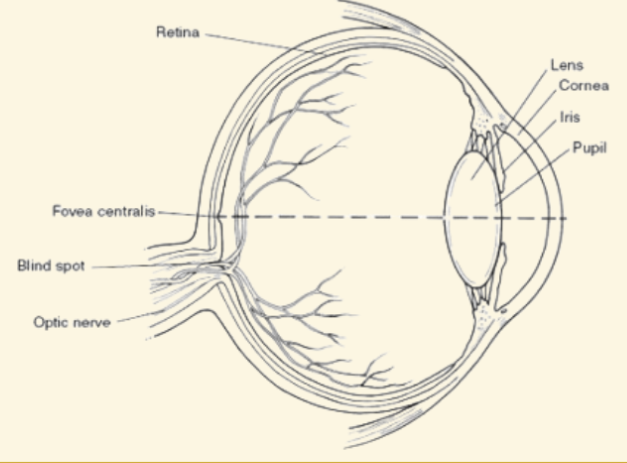
Blind Spot
Where the optic nerve leaves the retina (no rods or cones there)
Trichromatic Theory
A theory of color vision:
(Oldest, simplest): 3 types of cones in the retina (blue, red, green) → activated in different combinations
Cannot explain afterimages (white / blank space shows opposite of previous color), and color blindness
Dichromatic
This type of color blindness can’t see red/green or blue/yellow shades
Monochromatic
This type of color blindness can only see in shades of gray
Opponent-Process Theory
A theory of color vision:
Sensory receptors in retina come in red/green, blue/yellow, black/white (pairs)
If one sensor is stimulated → the other is inhibited from firing
Afterimages: if look at red: fatigue the real sensors → Switch gaze and the opposing ones fire with afterimage
Color blindness: if color sensors do not come in pairs or missing one pair
Amplitude
Height of a sound wave. Th
Frequency
The length of sound waves. Determines pitch of a sound (megahertz
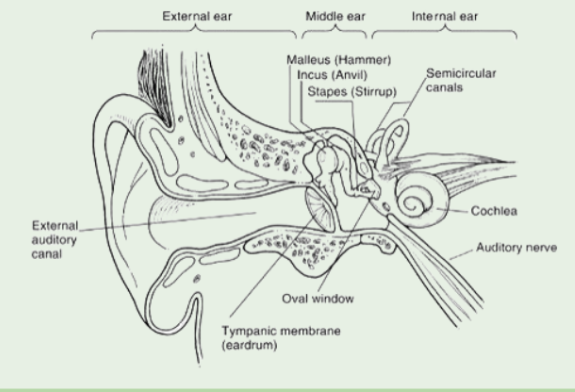
Cochlea
The fluid inside this structure is lined with a basilar membrane, and hair cells inside are connected to the organ of corti
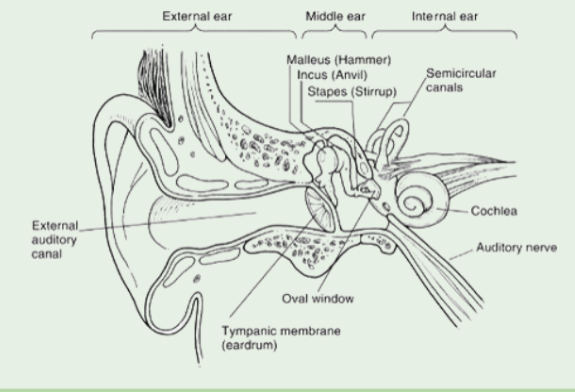
Place theory
A pitch theory:
Hair cells in the cochlea respond to different frequencies based on where they are located (some respond to high, some respond to low) and they move in different places
Accurately describes upper, but not lower pitches
Frequency theory
A type of pitch theory:
Lower tones are sensed by the rate at which cells fire → different firing rates = different frequencies
Conduction Deafness
This type of deafness is when there is something wrong when conducting sound to the cochlea
Nerve / Sensorineural Deafness
This type of deafness is when Hair cells in the cochlea are damaged (usually by loud noise)
Hair cells do not regenerate → much more difficult to treat
Touch
This sense is activated when skin is indented or pierced and nerve endings respond to pressure or temperature
Gate control theory
A theory that states that some pain messages have higher priority than others
A “gate” opens for higher priority but stays closed for lower priority pain, meaning that it is into felt
Endorphins swing the gate open/shut and control the amount of pain someone feels
Papillae
Bumps on one’s tongue, inside of cheeks, and the roof of the mouth that hold taste buds, which absorb taste (chemicals)
Olfactory bulb
This part in the smell / olfaction pathway gathers messages from the olfactory receptor cells and sends information to the brain
Vestibular Sense
This body position sense tells one how the body is positioned in space
3 semicircular canals in the inner ear give the brain feedback about body orientation (tubes with fluid)
When the position of the head changes, the fluid moves, causing the sensors to move and the hair cells activate the neurons to the brain
Nausea + Dizziness: When the liquid becomes agitated from too much movement
Kinesthetic Sense
This body position sense gives feedback on the position and orientation of specific body parts
Receptors in muscles and joints send information to the brain about limbs
Visual feedback helps also to keep track of the body
Provides feedback on where your body parts are in relation to other ones
Absolute threshold
Smallest amount of stimulus a person can detect 50% of the time
Stimuli below this are called subliminal
Subliminal
Stimuli below the absolute threshold
Difference threshold
How much a stimulus needs to change before a difference is noticed
Just-Noticeable Difference: Smallest amount of needed change
Just-Noticeable Difference
The smallest amount of needed change to notice a difference
Weber’s Law
change needed is proportional to the original intensity of stimulus
More stimulus = more change is required to be noticed
Each sense varies by a constant (ie hearing is 5% (100 decibels need to change to 105 to be noticed. 8% for vision)
Signal Detection Theory
A perceptual theory that states the following:
Effects of distractions and interference experienced when perceiving the world
Tries to predict what will be perceived when stimuli are competing → predict perceptual mistakes
False Positive: Think we perceive a stimulus that isn’t there (ex: think friend is there but it’s actually a stranger)
False Negative: Not perceiving a present stimulus (ex: not reading directions on a test)
False Positive
False perception of an absent stimulus
False negative
Not perceiving a present stimulus
Top-Down Processing
This perceptual theory states the following:
Perceive by filling in gaps in what is sensed (like looking at clouds)
Experiences create schemata: mental representations on how we expect the world to be
Can create a perceptual set: predisposition to perceiving something in a certain way
* Use background knowledge (schemata) to perceive the missing information
Parent groups in the 1970s were concerned about backmasking: hidden messages in music played backwards
Expected to hear threatening message (schemata of evil music) which led them to hear false messages
Schemata
mental representations on how we expect the world to be
Perceptual Set
predisposition to perceiving something in a certain way
Bottom-Up Processing / Feature Analysis
This perceptual theory states the following
Using only features of the object itself to build a complete perception
Start at the bottom with individual characteristics and put together into a final perception
Hard to imagine because it’s an automatic process
Feature detectors in the visual cortex perceive basic features (ines, curves, motion)
Mind builds a picture from bottom → up
Longer but more accurate
Gestalt Rules
Principles that govern how people perceive groups of objects
Normally, images are perceived as groups instead of individual elements
Proximity: Objects close together -- likely a group
Similarity: : Objects similar in appearance -- likely a group
Continuity: Objects in a particular line or curve (trail or figure) -- group
Closure: Similar to top-down processing (objects making a recognizable image)
Constancy
Ability to maintain a constant perception of an object despite changing angle or light
Size Constancy
objects closer to the eyes create a bigger image in the retina, however the human mind takes instance into account when estimating size
Shape Constancy
Objects from different angles look as if they are different shape. Mind knows that the shape is constant (depending on familiarity)
Brightness Constancy
Perceive objects as constant color even if the light and reflection changes
Depth Cues
These help humans perceive the world in three dimnsions
Stroboscopic Effect
Movies and flipbooks → still images changing at a certain speed appear to be moving
Phi Phenomenon
Holiday lights: series of lights turned on / off at a particular rate make it seem as if they are a moving singular light
Autokinetic Effect
Spot of light projected in dark room → appears to move
Visual Cliff Experiment
An experiment by Eleanor Gibson
Do human infants perceive depth?
Constructed a “cliff” covered with glass
Infant does not go off the visual cliff → meaning it can perceive depth (at 3 months old)
Monocular Cues
These depth cues do not rely on someone having two eyes
Binocular Cues
Depth Cues that rely on someone aving two eyes
Convergence
As an object gets closure to the face, eyes move toward each other to keep focus
The more the eyes converge, the closer the object is
Extrasensory Perception / ESD
Claiming to perceive a sensation “outside” of normal senses
Psychologists are skeptical because no reliable evidence outside our 5 senses
Usually it’s explained by deception, magic tricks, or coincidence