1.2 Obj 2 & 3
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Properties of Water & Biochemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
nonpolar covalent bond
electrons shared equally between two bonded atoms
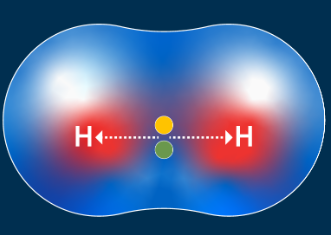
polar covalent bond
electrons shared unequally with the more electronegative atom "pulling" the electrons closer to it
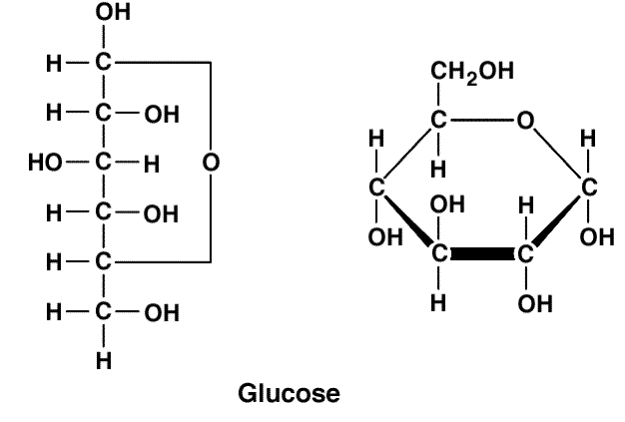
monosaccharide
simple (one) sugar
examples: glucose, galactose, and fructose
disaccharide
two monosaccharides joined together
examples: maltose, lactose, and sucrose
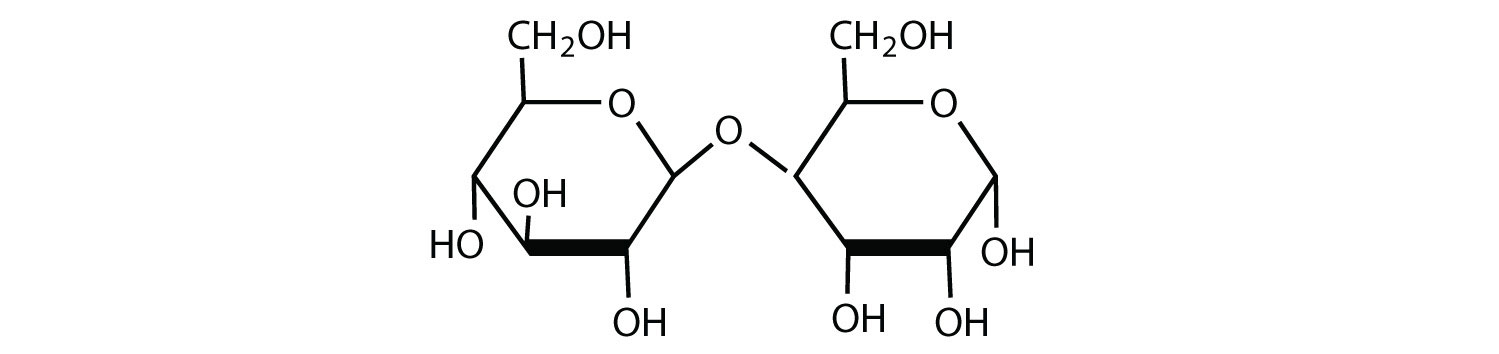
dehydration synthesis
Process that combines two molecules by removing a water molecule, forming a new bond.
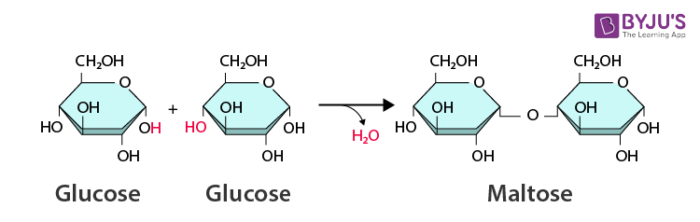
hydrolysis
Chemical breakdown of a compound by adding water.
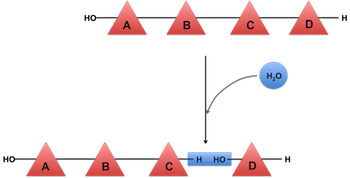
polysaccharide
A complex carbohydrate made up of multiple sugar molecules joined together.
It serves as a long-term energy storage molecule in plants and animals.
Examples include cellulose, starch, and glycogen.
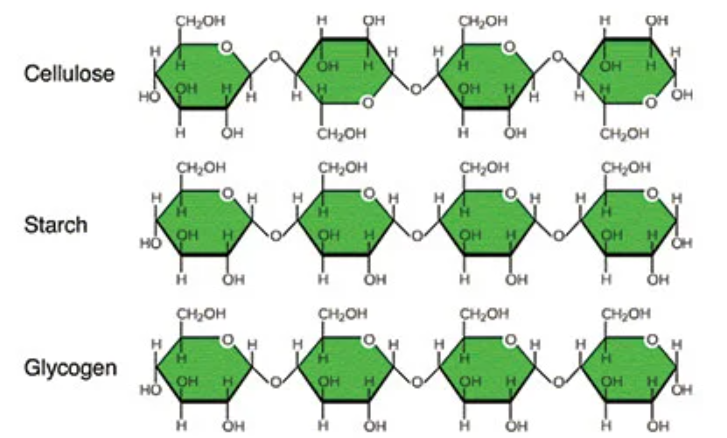
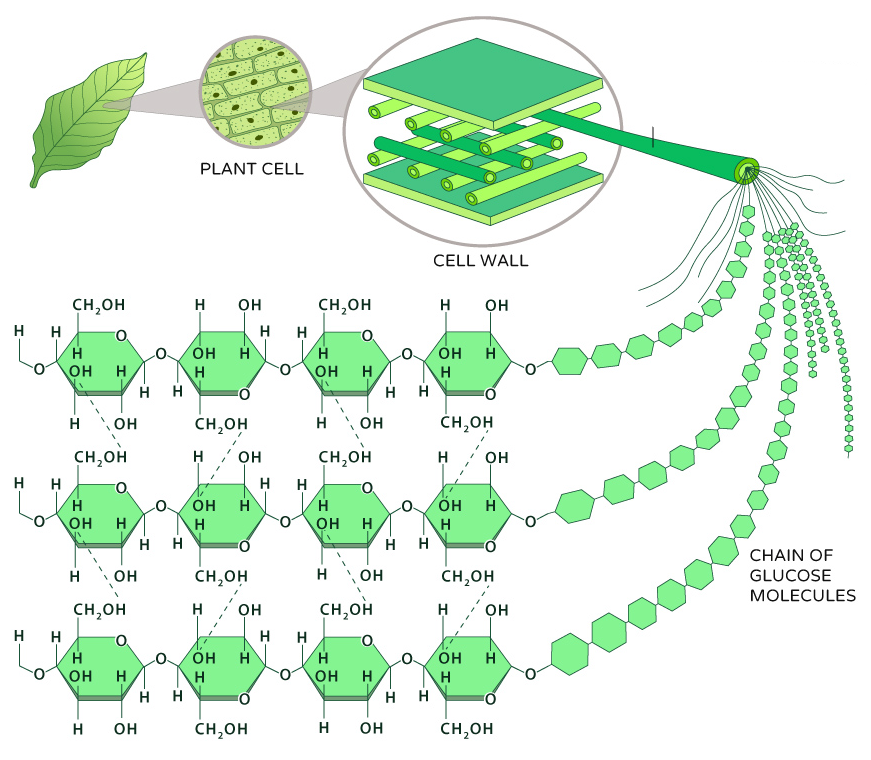
cellulose
structural polysaccharide that makes up plant cell walls
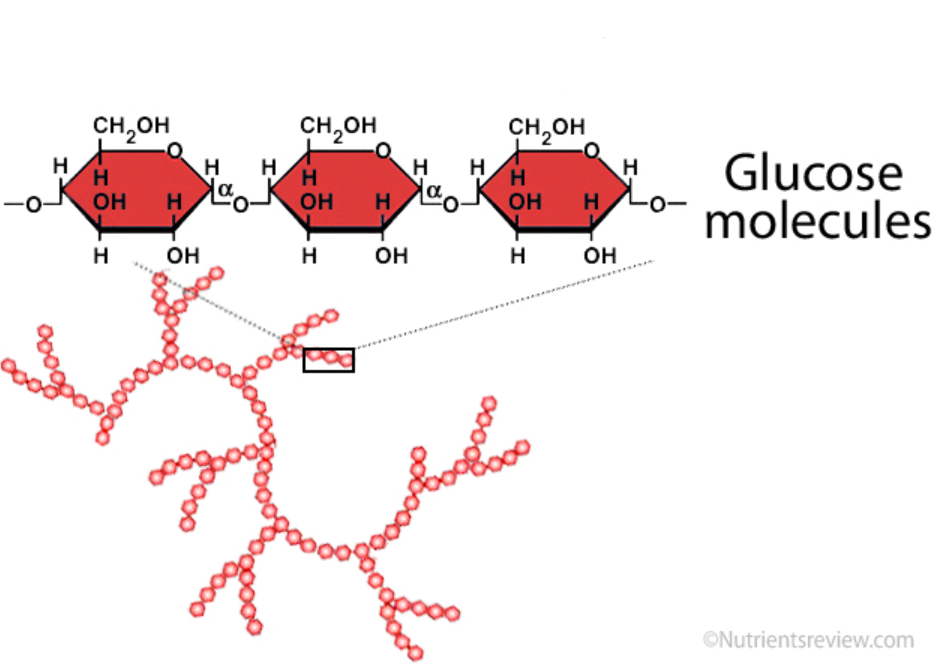
starch
storage polysaccharide found in plants
fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end; majority portion in lipids
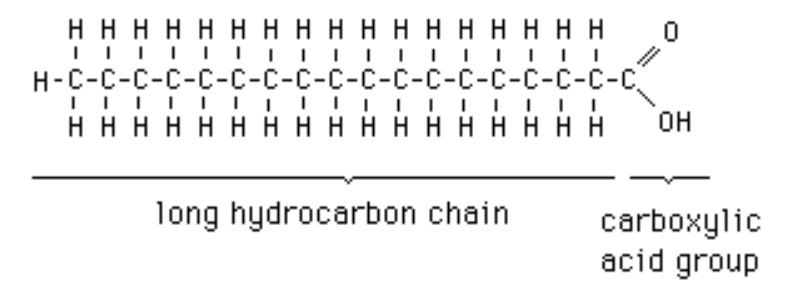
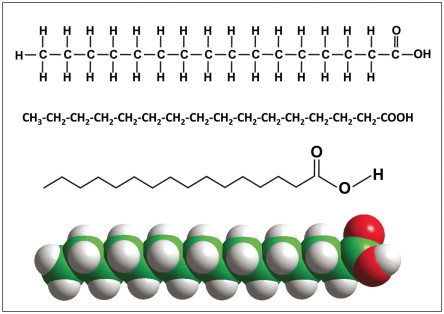
saturated fat
fat without double bonds between carbons
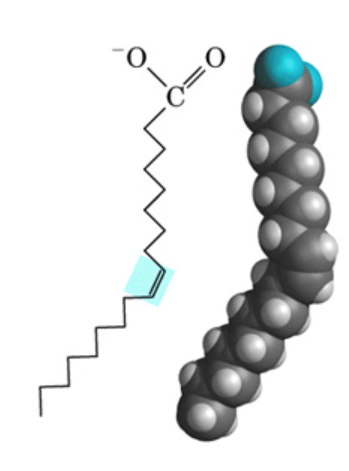
unsaturated fat
fat with double bonds between carbons
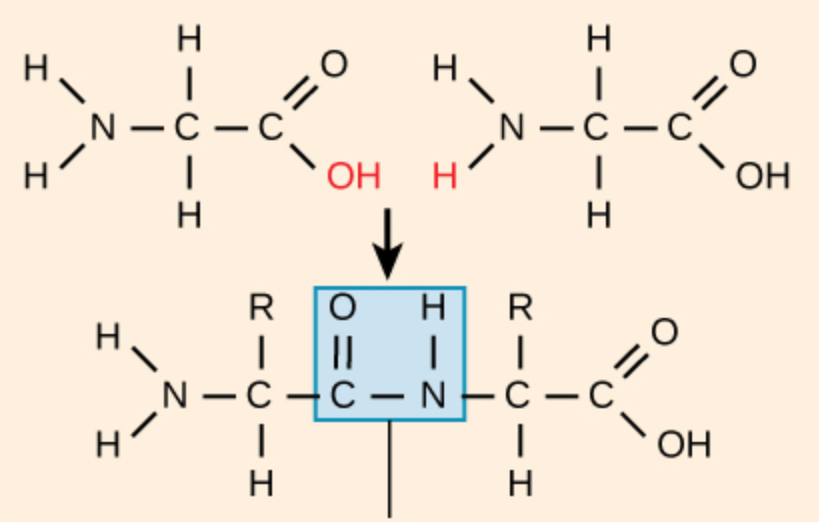
peptide bond
bond creating amino acid chains or polymers
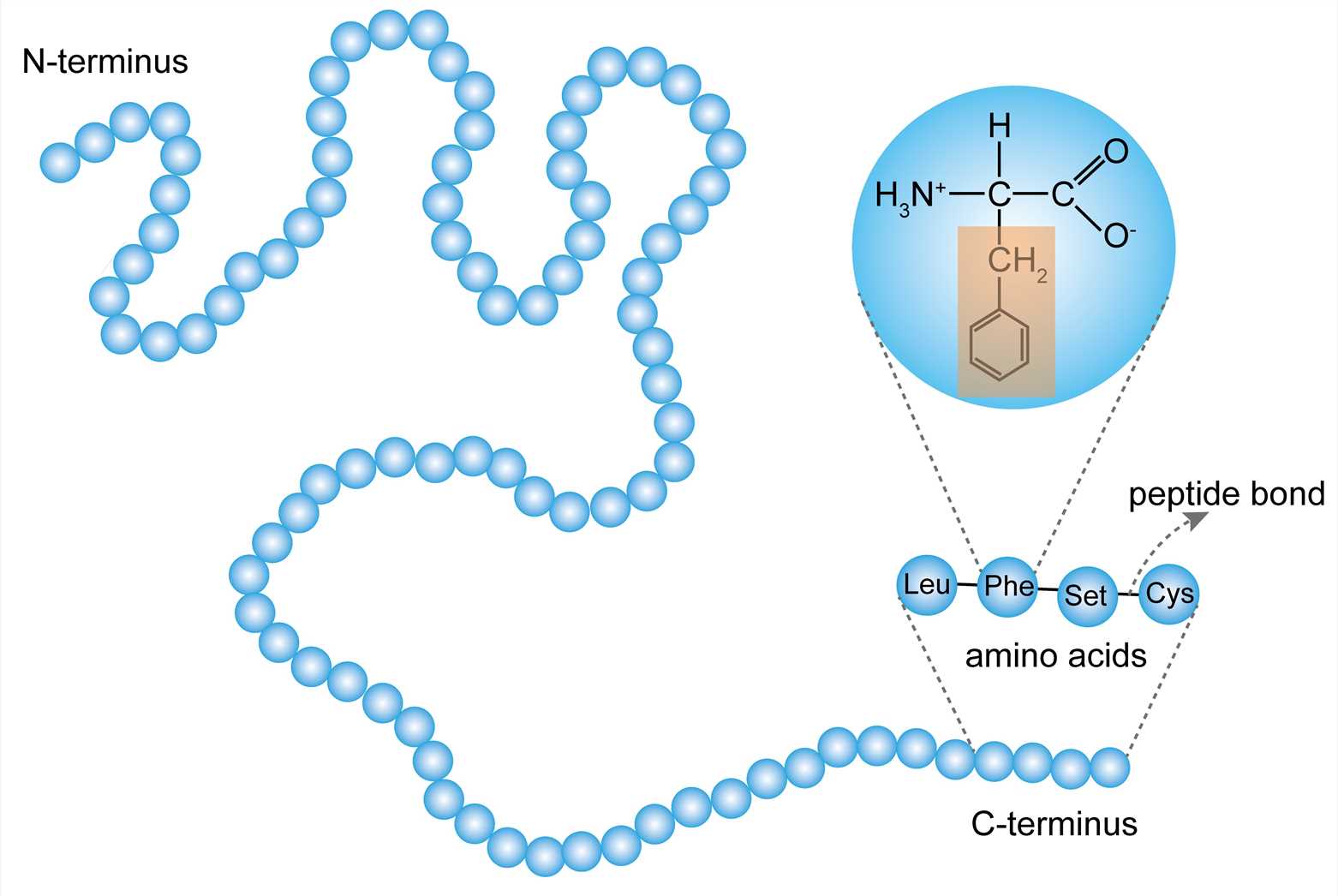
primary structure
linear sequence of amino acids; peptide bonds
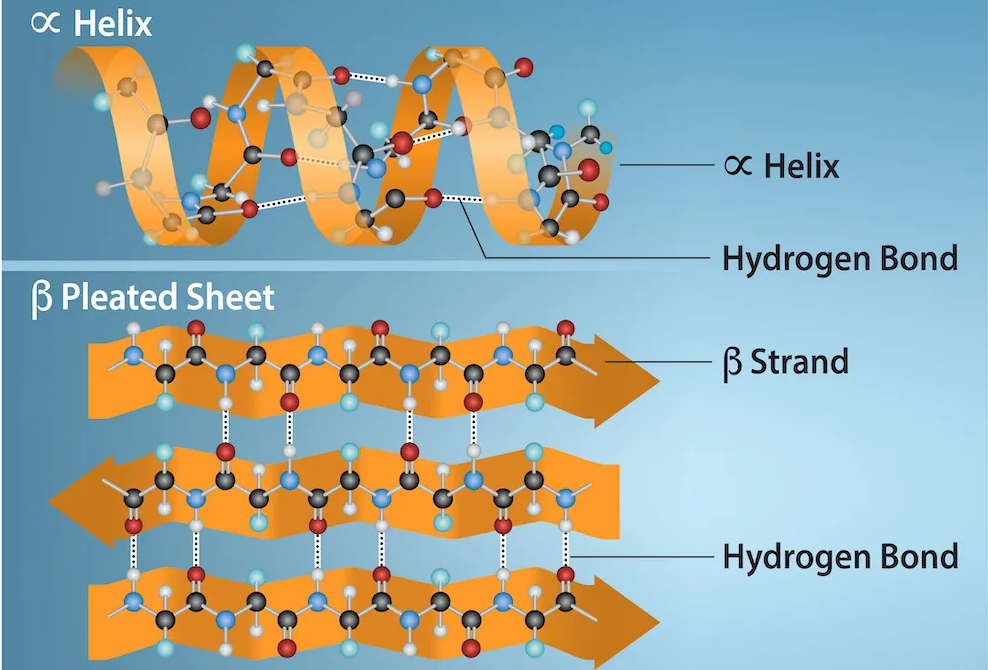
secondary structure
protein formed with hydrogen bonds
tertiary structure
3D conformation formed; determines specificity
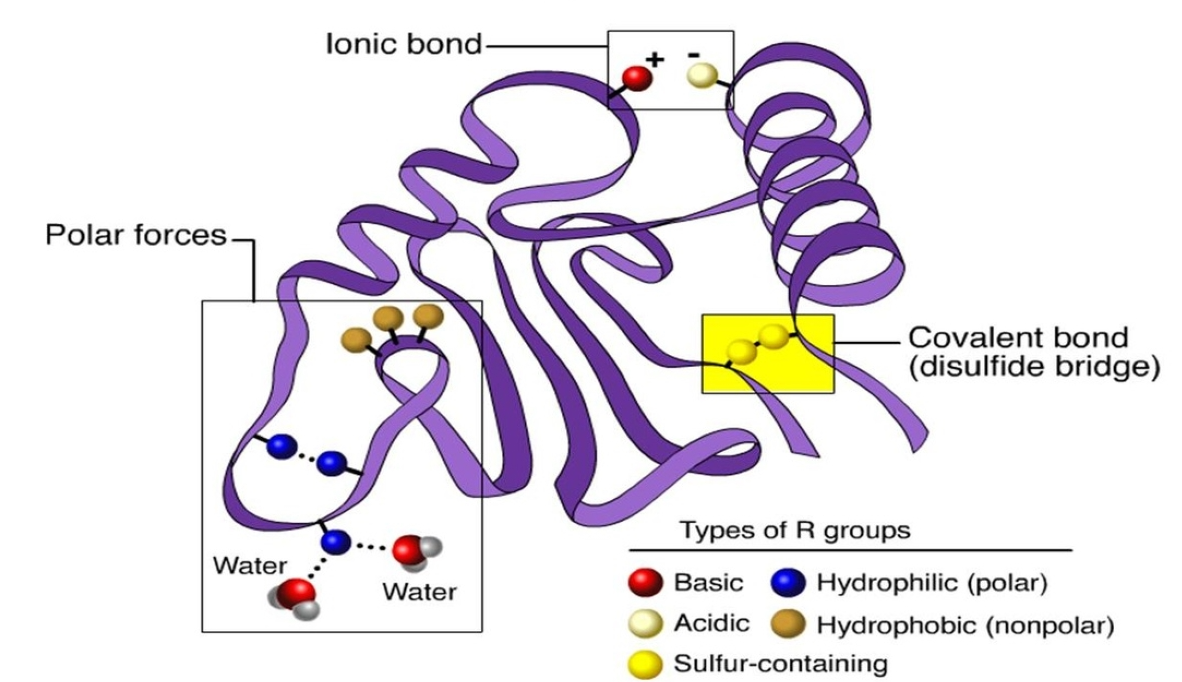
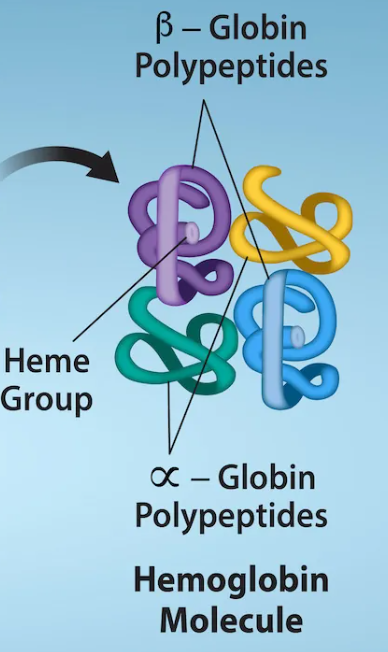
quaternary structure
protein with more than one polypeptide chain
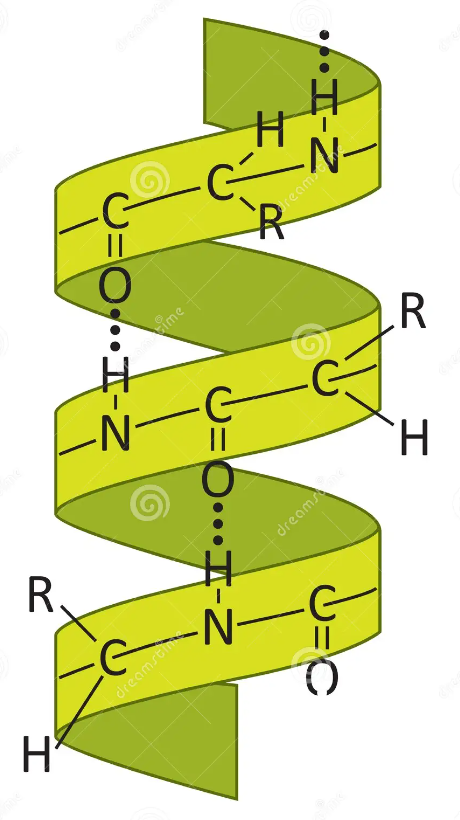
alpha helix
secondary structure form of a protein; human hair (keratin)
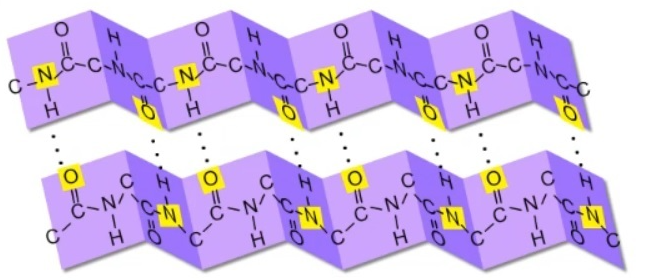
beta pleated sheet
secondary structure form of a protein; spider webs and silk
functional group
components of organic molecules most often involved in chemical reactions
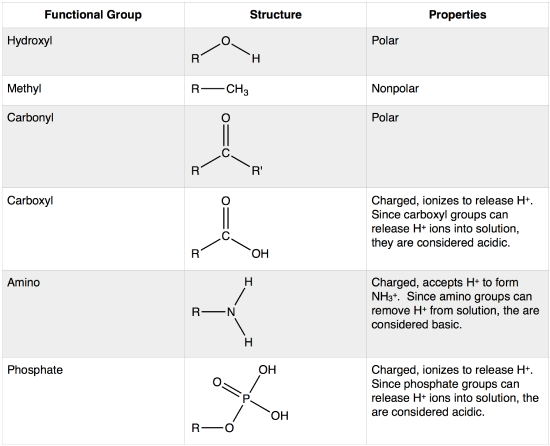
cohesion
The linking together of like molecules, often by hydrogen bonds
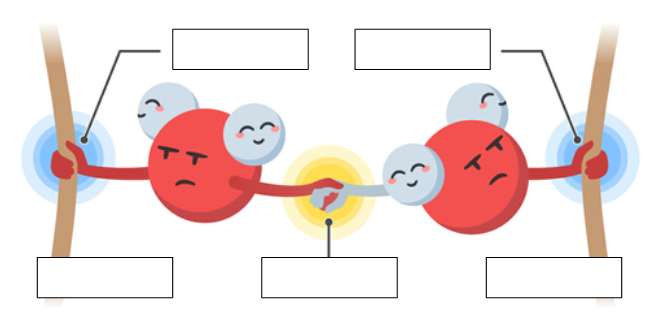
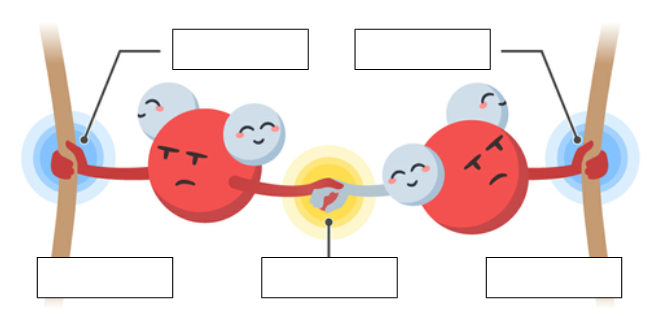
adhesion
attraction between different kinds of molecules
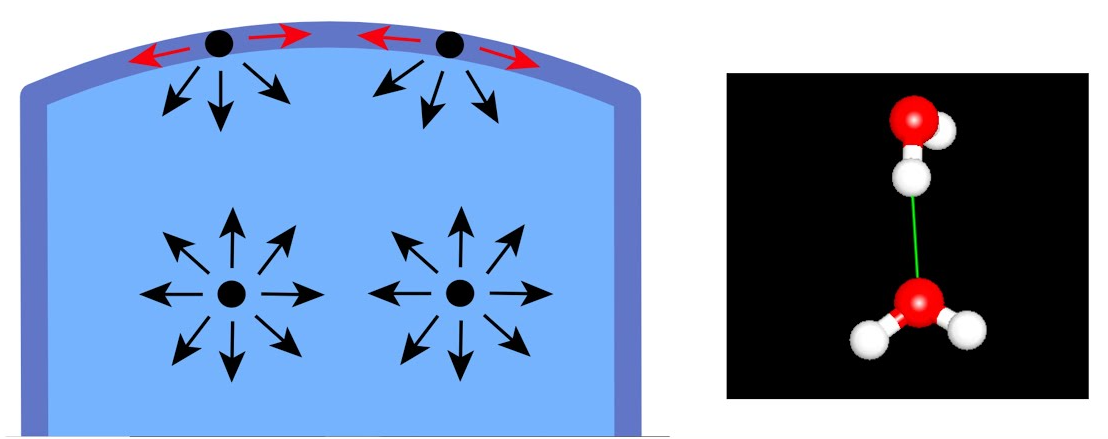
surface tension
measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
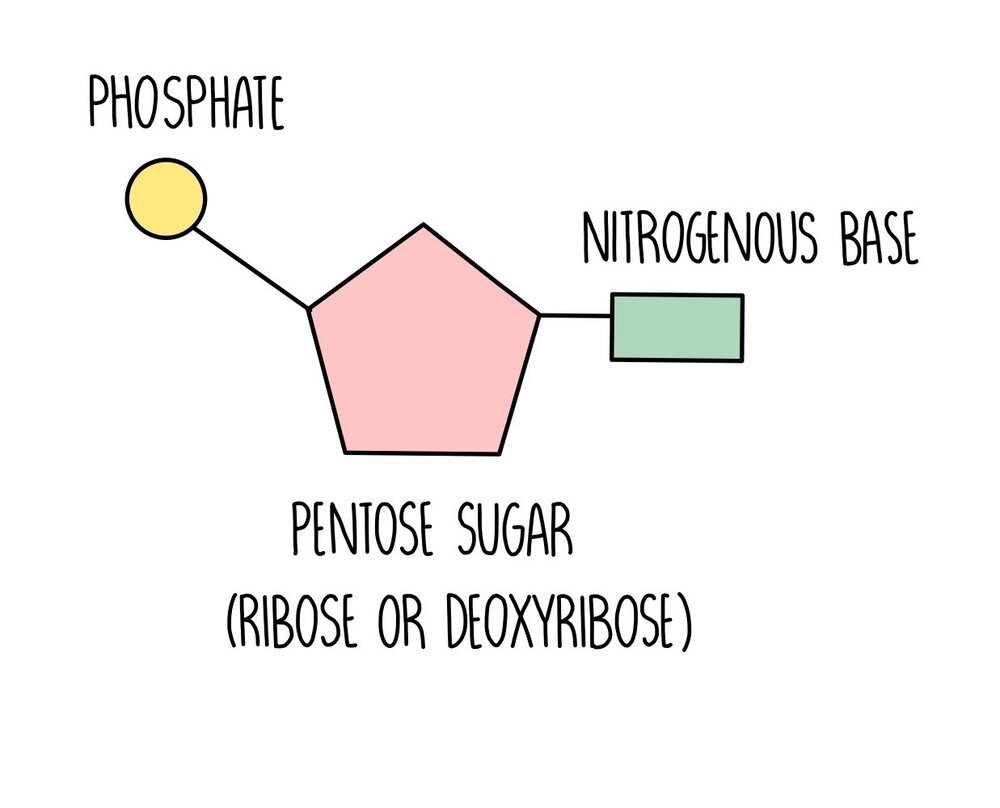
nucleotide
building block of a nucleic acid; five carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogen base and a phosphate group