BIO 201 - MODULE 2 | Evolution, Biology and Scientific Inquiry
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Science
A process of inquiry
Inquiry
Seeking information by questioning
Scientific Inquiry
Specifically seeks to understand the natural world based on observations
Hypothesis
Tentative or educated guess
Prediction
Expected outcome based on a testable hypothesis
What’s the difference between a testable hypothesis and a prediction, which is actually being tested?
A testable hypothesis is an idea about how something works that can be tested using experiments or observations. A prediction is a specific outcome expected if the hypothesis is true. The prediction is what is actually being tested to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis.
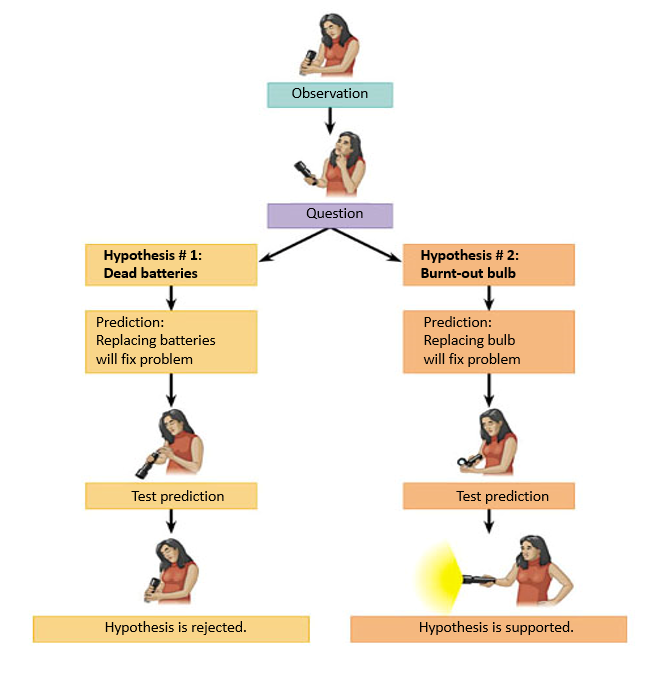
What are the 4 limitations of science?
Science does not define “truth”
Scientific “facts” are only as correct as the measurements and interpretations that obtained them
Science only addresses “how”, not “why”
Science cannot address supernatural phenomena or questions that are not subject to testable hypotheses
Enough experimental evidence supporting a given hypothesis may warrant a _______, substantiated by a large body of evidence.
Theory
All life is characterized by the ability to…
Maintain an organized structure
Metabolize (use energy)
Grow, reproduce, and die
Respond to environment
Evolutionary adaptation
What are the three domains of life?
Eukarya, Archaea, Bacteria
All cells can be categorized as either…
Prokaryotes or Eukaryotes
What are prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes are simple, unicellular organisms without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles (e.g. bacteria and archaea).
What are eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes are complex organisms with cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (e.g. plants, animals, fungi, and protists).
What is evolution?
Evolution is the key to understanding biological diversity and unity
What is common descent?
The concept that all living organisms share a common ancestor.
What is natural selection?
“editing mechanism” The process where traits that improve survival and reproduction become more common in a population.
Who synthesized the idea of evolution by natural selection?
Charles Darwin
What was Darwin’s theory of evolution?
Individuals with traits best suited to the local environment will generally leave more surviving, fertile offspring.
What is heritable variation?
When individuals in a population of any species vary in many heritable traits