Module 1 - Planning Phase
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Project Life Cycle
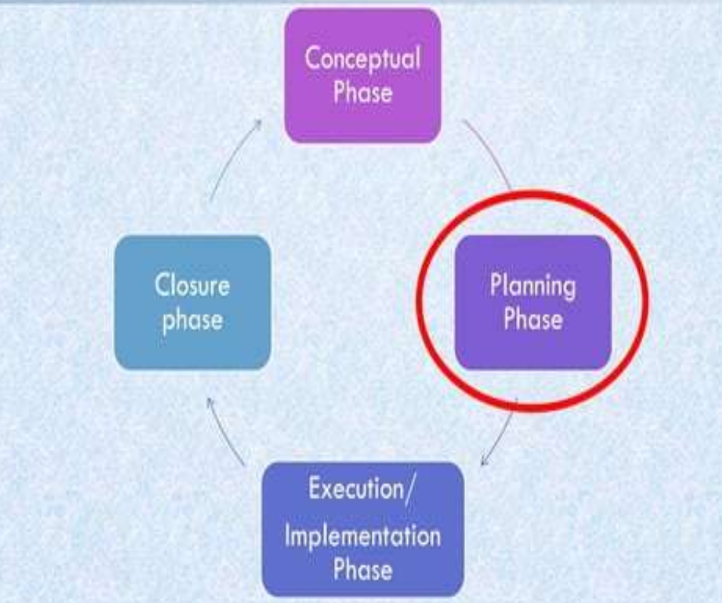
Conceptual Phase → Planning Phase → Execution / Implementation Phase → Closure Phase
Project Planning
is a form of operational planning, whereby the consecutive steps to implement the project activities are carefully mapped out, based on an analysis of relevant information
Project Planning
involves establishing the scope, aims, and objective of a project, the way in which the project will be performed, the roles and responsibilities of those involved and the cost estimates
Planning
normally answers the questions like what, how, who, and when
Planning
is simply how to seek the balance between object constraints to achieve the set goal
Inputs in Project Planning
Project Charter
Concept Proposal
Process of Project Planning
Assessment
Prioritization
Design of plan using various tools and techniques
Output of Project Planning
Project Plan
(Project requirements, Project Plan of Action and Project Management Plan-Implementation plan, Monitoring and Evaluation plan)
Commonly Used Tools for Project Planning
Gantt Chart
Problem Tree Analysis
SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
LFA (Logical Framework Analysis)
Project Managing Softwares
PRECEDE PROCEED
Intervention Mapping (e.g. health promotion projects)
Planning Steps
Assessment of Situation
Identification and Prioritization
Project Design and Development
Plan for Implementation, Monitoring, and Evaluation
Project Development
Assessment of Situation
Stakeholders Analysis (Project Team, Scientific Community, Leaders, Community People, Beneficiaries) → Project Organization Chart
Study of Legal Frameworks
Construct Framework for Situation Analysis
Baseline Information Collection and Analysis (Secondary Data Review, Surveys, and other formal and informal sources)
Two Components of Identification and Prioritization
Problem Identification and Prioritization
Identification and Prioritization of Strategies
Project Design and Development
Defining Scope of Project and set Objectives
Defining Project Duration
Define the Quality Plan
Planning for Communication and Coordination
Planning for Resources
Human Resource Planning
Time and Resource Allocation
Financial Planning (Cost Estimation and Budgeting)
Logistics Planning (Contract suppliers and create procurement plan)
Plan for Implementation
Plan for Piloting/Testing and Scale Up
Plan for Tracking Budget and Work Plan
Plan for Risks and Adaptable Changes
Plan for Monitoring and Evaluation
Done on the basis of Set Targets, Indicators, Quality Standards
PERT/CPM for tracking the projects
LFA for tracking achievements and progress
Evaluation Questions, Evaluation Targets, Evaluation Methods and Timings
Proposal Development
Adjustment in Objectives and Targets and other factors
Proposal Outline
Writing of Proposal
Submission to concerned authority for approval
Planning
is expanding of concepts and refinement of ideas
Relevance of Planning
Selecting the important problem and appropriate strategy
Pre determines appropriate scope and quality
Identification of available resources and ways to mobilize them
Helps in implementation and evaluation process